Nine Different Chemical Species and Action Mechanisms of Pancreatic Lipase Ligands Screened Out from Forsythia suspensa Leaves All at One Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Inhibition of the Subfractions of F. suspensa Leaves on PL
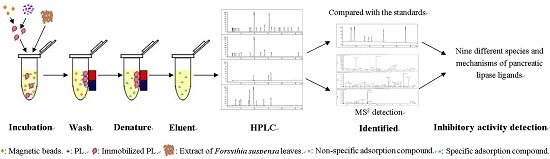
2.2. Screening of PL Inhibitors in the Remaining Precipitation
2.3. The Detection of Enzyme Inhibitory Activity and Competition Types of All Inhibitors
2.4. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of the Subfractions of F. suspensa Leaves
3.3. Determination of Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of All Subfractions
3.4. Screening of Inhibitors in the Subfraction with the Highest Inhibitory Activity
3.5. Identification of Screened-Out Compounds
3.6. Determination of Enzyme Inhibitory Activity and Competition Types of Screened-Out Compounds
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Report of a WHO Consultation. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P.T. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html (accessed on June 2016).
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Murray, C.J. Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/ (accessed on June 2016).
- Baretic, M. Targets for medical therapy in obesity. Digest. Dis. Sci. 2012, 30, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. Anti-obesity drugs: A review about their effects and their safety. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2012, 11, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.W. Possible anti-obesity therapeutics from nature—A review. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1625–1641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roh, C.; Jung, U. Screening of crude plant extracts with anti-obesity activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 1710–1719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birari, R.B.; Bhutani, K.K. Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: Unexplored potential. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De la Garza, A.L.; Milagro, F.I.; Boque, N.; Campion, J.; Martinez, J.A. Natural inhibitors of pancreatic lipase as new players in obesity treatment. Planta. Medica. 2011, 77, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Castillo-Santaella, T.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Cabrerizo-Vilchez, M.A.; Rivadeneira-Ruiz, C.; Rondon-Rodriguez, D.; Galvez-Ruiz, M.J. Natural inhibitors of lipase: Examining lipolysis in a single droplet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10333–10340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wang, Y. Rapid screening and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from mulberry leaves using enzyme-immobilized magnetic beads coupled with HPLC/MS and NMR. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-G.; Wei, Y.-R.; Zhang, L.-W. Screening and Identification of pancreatic lipase inhibitors in polygonum cuspidatum with enzyme-immobilized magnetic nanoparticles and LC-MS/MS. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2017, 29, 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, H.H.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wang, Y. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of two compounds (forsythiaside and forsythin) isolated from Forsythia suspensa. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.G.; Song, S.J.; Ren, J.; Xu, S.X. A new compound from Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl with antiviral effect on RSV. J. Herb. Pharmacol. 2002, 2, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, S.J.; Ren, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhang, D.W. New alkaloids from Forsythia suspensa and their anti-inflammatory activities. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.Y.; Wang, J.M. In vitro antioxidant properties and in vivo lowering blood lipid of Forsythia suspense leaves. Med. Chem. Res. 2010, 19, 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Yuda, N.; Tanaka, M.; Suzuki, M.; Asano, Y.; Ochi, H.; Iwatsuki, K. Polyphenols extracted from black tea (Camellia sinensis) residue by hot-compressed water and their inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase in vitro. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, H254–H261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Fukui, Y.; Asami, S.; Toyoda-Ono, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Shibata, H.; Mitsunaga, T.; Hashimoto, F.; Kiso, Y. Inhibitory effects of oolong tea polyphenols on pancreatic lipase in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; He, W.; Yao, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.; Ye, Y.; Cao, J. Characterization of binding interactions of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate from green tea and lipase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8829–8835. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, S. Antihyperlipidemic components of cassia auriculata aerial parts: Identification through in vitro studies. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, Y.; Iwai, K.; Fukunaga, T.; Nakagiri, O. Inhibitory activity of Chlorogenic acids in decaffeinated green coffee beans against porcine pancreas lipase and effect of a decaffeinated green coffee bean extract on an emulsion of olive oil. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 2329–2331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.B.; Wang, O.; Wang, M.Q.; He, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B.P. In vitro inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase activity of subfractions from ethanol extracts of fermented Oats (Avena sativa L.) and synergistic effect of three phenolic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7245–7251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Mizuno, T.; Aida, K.; Uchino, K. Hesperidin as an inhibitor of lipases from porcine pancreas and pseudomonas. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds rutin, phillyrin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, forsythiaside A, hesperidin, phillygenin are available from the authors. |









| Subfractions (1500 μg/mL) | Inhibitory Ratio |
|---|---|
| Crude extract | 39.28% |
| Acetic ether extract | 44.17% |
| Ethanol extract | 15.91% |
| Water extract | 50.21% |
| Remaining precipitate | 81.48% |
| Peak No. | tR (min) | UV (nm) | MS (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | Tentative Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 9.986 | 216,247,290,330 | 624 | 479, 471, 325, 309, 181, 163 | Isomer of forsythiaside A |
| 7 | 15.682 | 208,230,280 | 372 | 355, 337, 325, 284, 201, 189, 137 | Arctigenin |
| 10 | 26.716 | 265,337 | 594 | 285, 255, 229, 227, | Kaempferol-3-O-rutinose |
| No. | Compounds | Species | IC50 (μg/mL) | IC50 (μmol/L) | Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rutin [22] | Flavonoids | 91 ± 3.66 * | 149 ± 6.0 * | competitive inhibition |
| 2 | Phillyrin | Lignanoids | Promotion | Promotion | promotor |
| 3 | Isomer of forsythiaside A | Phenethylols | No tested | No tested | possible competitive inhibition |
| 4 | Chlorogenic acid [23] | Polyphenols | 1120 ± 40 * | 3150 ± 120 * | uncompetitive inhibition |
| 5 | Caffeic acid [24] | Polyphenols | 251.2 ± 9.3 * | 1394 ± 52 * | uncompetitive inhibition |
| 7 | Arctigenin | Lignanoids | 793.4 ± 3.9 | 2129 ± 10.5 | uncompetitive inhibition |
| 8 | Forsythiaside A | Phenethylols | 1346 ± 5.3 | 2155 ± 8.5 | competitive inhibition |
| 9 | Hesperidin [25] | Flavonoids | 32 * | 52.4 * | competitive inhibition |
| 10 | Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside [22] | Flavonoids | 1.7 ± 0.3 * | 2.9 ± 0.5 * | noncompetitive inhibition |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Nine Different Chemical Species and Action Mechanisms of Pancreatic Lipase Ligands Screened Out from Forsythia suspensa Leaves All at One Time. Molecules 2017, 22, 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050795
Chen T, Li Y, Zhang L. Nine Different Chemical Species and Action Mechanisms of Pancreatic Lipase Ligands Screened Out from Forsythia suspensa Leaves All at One Time. Molecules. 2017; 22(5):795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050795
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tinggui, Yayun Li, and Liwei Zhang. 2017. "Nine Different Chemical Species and Action Mechanisms of Pancreatic Lipase Ligands Screened Out from Forsythia suspensa Leaves All at One Time" Molecules 22, no. 5: 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050795
APA StyleChen, T., Li, Y., & Zhang, L. (2017). Nine Different Chemical Species and Action Mechanisms of Pancreatic Lipase Ligands Screened Out from Forsythia suspensa Leaves All at One Time. Molecules, 22(5), 795. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050795