Phloroglucinols with Antioxidant Activities Isolated from Lysidice rhodostegia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of Compounds 1–4
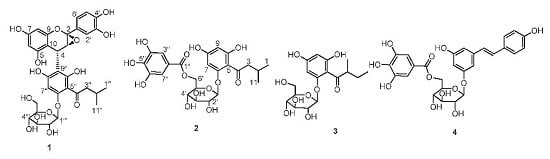
2.2. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–4
2.3. Antioxidative Activity of Compounds 1 and 2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Computational Details
3.3. Plant Materials
3.4. Isolation and Purification of Compounds 1–4
3.5. Characterization of Compounds 1–4
3.6. Hydrolysis and Determination of Absolute Configuration of Sugars
3.7. Biological Activity Assessment of Compounds 1 and 2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Chen, D.Z. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988; Volume 39, pp. 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Feng, N.; Yu, S.S.; Yu, D.Q.; Wang, X. Vasodilator constituents from the roots of Lysidice rhodostega. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Fu, G.M.; Fan, L.H.; Yu, S.S.; Yu, D.Q. Flavonoids from Lysidice rhodostegia Hance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2005, 47, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fu, G.M.; Fan, L.H.; Yu, S.S. Studies on the chemical constituents from roots of Lysidice rhodostegia Hance. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2005, 3, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.C.; Wu, X.F.; Gao, S.; Yu, S.S.; Liu, Y.; Qu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.B. Novel phloroglucinol derivatives from the roots of Lysidice rhodostegia. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2269–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Fu, G.M.; Hu, Y.C.; Yu, S.S.; Fan, L.H.; Yu, D.Q.; Qu, J. Resveratrol/phloroglucinol glycosides from the roots of Lysidice rhodostegia. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Hu, Y.C.; Gao, S.; Yu, S.S.; Pei, Y.H.; Tang, W.Z.; Huang, X.Z. Two new compounds from the roots of Lysidice rhodostegia. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res 2007, 9, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Hu, Y.C.; Yu, S.S.; Jiang, N.; Ma, J.; Tan, R.X.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.N.; Liu, J.; Ma, S.G. Lysidicins F-H, three new phloroglucinols from Lysidice rhodostegia. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2390–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.F.; Wang, Y.D.; Yu, S.S.; Jiang, N.; Ma, J.; Tan, R.X.; Hu, Y.C.; Qu, J. Antioxidative acylphloroglucinols from the roots of Lysidice rhodostegia. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 8155–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohr, G.; Gerhauser, C.; Knauft, J.; Zapp, J.; Becker, H. Anti-inflammatory acylphloroglucinol derivatives from Hops (Humulus lupulus). J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okasaka, M.; Takaishi, Y.; Kogure, K.; Fukuzawa, K.; Shibata, H.; Higuti, T.; Honda, G.; Ito, M.; Kodzhimatov, O.K.; Ashurmetov, O. New stilbene derivatives from Calligonum leucocladum. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziej, H. The first naturally occurring 4-aryl flavan-3-ol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 1825–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jayaprakasam, B.; Seeram, N.P.; Olson, L.K.; DeWitt, D.; Nair, M.G. Insulin secretion and cyclooxygenase enzyme inhibition by Cabernet Sauvignon grape skin compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, K.B.; Jayasuriya, H.; Bills, G.F.; Polishook, J.D.; Dombrowski, A.W.; Guan, Z.; Felock, P.J.; Hazuda, D.J.; Singh, S.B. Isolation, structure, absolute stereochemistry, and HIV-1 integrase inhibitory activity of integrasone, a novel fungal polyketide. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reategui, R.F.; Wicklow, D.T.; Gloer, J.B. Phaeofurans and sorbicillin analogues from a fungicolous Phaeoacremonium species (NRRL 32148). J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, F.; Takahashi, Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Tanaka, R.; Ohtaki, S.; Yoshida, M.; Nakanishi, S.; Ikeda, S.I. Structure elucidation of EI-1941-1 and -2, novel interleukin-1β converting enzyme inhibitors produced by Farrowia sp. E-1941. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7419–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, J.; Gaucher, G.M. Isoepoxydon, a new metabolite of the patulin pathway in Penicillium urticae. Biochem. J. 1979, 182, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, A.E.; Morita, H. Circular dichroism calculation for natural products. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Kurtan, T.; Mandi, A.; Yan, X.H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.W. Biscembranoids formed from an α, β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring as a dienophile: Structure revision and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, P.J.; McCann, D.M.; Devlin, F.J.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Frisch, M.J. Determination of the absolute configuration of [32](1,4)barrelenophanedicarbonitrile using concerted time-dependent density functional theory calculations of optical rotation and electronic circular dichroism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7514–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, X.C.; Ferreira, D. Theoretical calculation of electronic circular dichroism of the rotationally restricted 3,8″-biflavonoid morelloflavone. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 9010–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Bruhn, T.; Maksimenka, K.; Hemberger, Y. The assignment of absolute stereostructures through quantum chemical circular dichroism calculations. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2009, 2717–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disadee, W.; Mahidol, C.; Sahakitpichan, P.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kanchanapoom, T. Flavonol 3-O-robinobiosides and 3-O-(2″-O-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-robinobiosides from Sesuvium portulacastrum. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 4221–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinjo, J.; Araki, K.; Fukui, K.; Higuchi, H.; Ikeda, T.; Nohara, T.; Ida, Y.; Takemoto, N.; Miyakoshi, M.; Shoji, J. Six new triterpenoidal glycosides including two new sapogenols from Albizziae Cortex V. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOE2009.10. Chemical Computing Group Inc.
- Gaussian, Inc. Gaussian09.
- Dai, S.J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; He, W.Y.; Chen, R.Y.; Yu, D.Q. New Diels-Alder type adducts from Morus macroura and their anti-oxidant activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–4 are unavailable from the authors. |



| No. | Lysidiside X (1) | Lysidiside Y (2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH mult. (J in Hz) a | δC b | HMBC | δH mult. (J in Hz) c | δC d | HMBC | |
| 1 | 0.84 d (6.5) | 23.3 | 2, 3, 4 | |||
| 2 | 109.1 | 2.15 m | 26.3 | 1, 3, 4, 11 | ||
| 3 | 4.13 d (3.6) | 67.1 | 10 | 3.07 dd (15.5, 6.5) | 54.1 | 1, 2, 4, 5, 11 |
| 2.81 dd (15.5, 7.5) | ||||||
| 4 | 4.36 d (3.6) | 28.9 | 2, 3, 5, 9, 10, 8″, 9″, 10″ | 207.3 | ||
| 5 | 156.8 | 107.3 | ||||
| 6 | 5.94 d (2.0) | 98.4 | 5, 7, 8, 10 | 162.1 | ||
| 7 | 158.4 | 6.11 d (2.0) | 95.8 | 4, 5, 6, 8, 9 | ||
| 8 | 6.03 d (2.0) | 96.6 | 6, 7, 9, 10 | 165.7 | ||
| 9 | 154.1 | 5.91 d (2.0) | 98.6 | 5, 7, 8, 10 | ||
| 10 | 103.7 | 167.5 | ||||
| 11 | 0.83 d (6.5) | 22.8 | 2, 3, 4 | |||
| 1′ | 128.8 | 5.03 d (7.5) | 102.2 | 6, 2′, 3′, 5′ | ||
| 2′ | 6.88 d (2.0) | 108.3 | 2, 1′, 3′, 4′, 6′ | 3.67 | 74.8 | |
| 3′ | 152.9 | 3.49 | 78.3 | |||
| 4′ | 154.1 | 3.52 | 71.2 | |||
| 5′ | 6.56 d (8.0) | 108.2 | 1′, 3′ | 3.49 | 75.8 | |
| 6′ | 6.91 dd (8.0, 2.0) | 118.1 | 2, 2′, 4′, 5′ | 4.56 dd (12.0, 1.0) | 64.2 | 4′, 5′, 1″ |
| 4.35 dd (12.0, 5.0) | ||||||
| 1″ | 0.89 d (6.8) | 22.9 | 2″, 3″ | 168.3 | ||
| 2″ | 2.21 m | 26.1 | 3″ | 121.3 | ||
| 3″ | 3.14 (16.0, 6.4) | 54.3 | 1″, 2″, 4″, 11″ | 7.03 s | 110.3 | 1″, 2″, 4″(6″), 5″ |
| 2.88 dd (16.0, 7.2) | ||||||
| 4″ | 208.2 | 146.5 | ||||
| 5″ | 108.2 | 139.9 | ||||
| 6″ | 160.2 | 146.5 | ||||
| 7″ | 6.33 s | 96.2 | 5″, 6″, 8″, 9″ | 7.03 s | 110.3 | 1″, 2″, 4″(6″), 5″ |
| 8″ | 159.6 | |||||
| 9″ | 110.4 | |||||
| 10″ | 161.2 | |||||
| 11″ | 0.92 d (6.8) | 23.3 | 1″, 2″, 3″ | |||
| 1′′′ | 4.96 d (7.6) | 102.1 | 6″, 2′′′, 3′′′, 5′′′ | |||
| 2′′′ | 3.45 | 74.9 | ||||
| 3′′′ | 3.39 | 78.3 | ||||
| 4′′′ | 3.35 | 71.2 | ||||
| 5′′′ | 3.39 | 78.4 | ||||
| 6′′′ | 3.84 br d (12.0) | 62.3 | ||||
| 3.65 dd (12.0, 5.0) | ||||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.-F.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Lv, H.-N.; Liu, Y.-B.; Hu, Y.-C. Phloroglucinols with Antioxidant Activities Isolated from Lysidice rhodostegia. Molecules 2017, 22, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060855
Wu X-F, Li L, Li Y, Lv H-N, Liu Y-B, Hu Y-C. Phloroglucinols with Antioxidant Activities Isolated from Lysidice rhodostegia. Molecules. 2017; 22(6):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060855
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xian-Fu, Li Li, Yong Li, Hai-Ning Lv, Yun-Bao Liu, and You-Cai Hu. 2017. "Phloroglucinols with Antioxidant Activities Isolated from Lysidice rhodostegia" Molecules 22, no. 6: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060855
APA StyleWu, X.-F., Li, L., Li, Y., Lv, H.-N., Liu, Y.-B., & Hu, Y.-C. (2017). Phloroglucinols with Antioxidant Activities Isolated from Lysidice rhodostegia. Molecules, 22(6), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22060855