Warfarin and Flavonoids Do Not Share the Same Binding Region in Binding to the IIA Subdomain of Human Serum Albumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
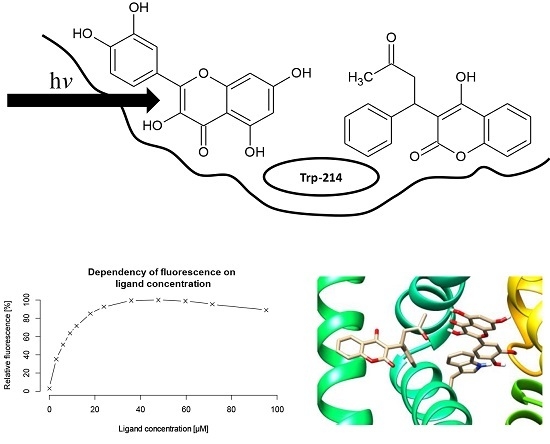
2.1. Ligand Binding Constants
2.2. Warfarin Displacement Studies
2.2.1. Simultaneous Binding of Warfarin and Flavonoid Aglycons
2.2.2. Simultaneous Binding of Warfarin and Flavonoid Glycosides
2.3. Molecular Modeling of the Quercetin-HSA and Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide-HSA Complexes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Fluorescence Measurements
3.3. Determination of Binding Constants
3.4. Fluorescence Measurements
3.5. Docking Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, T. Ligand Binding by Albumin. In All about Albumin; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 76–132. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, T. Metabolism: Albumin in the Body. In All about Albumin; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 188–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. Characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.; McLachlan, A.J.; Pegg, M.; MacKay, A.D.; Cole, R.B.; Rowland, M. Disposition of warfarin enantiomers and metabolites in patients during multiple dosing with rac-warfarin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 37, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Woo, H.I.; Bang, O.Y.; On, Y.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.Y. How to use warfarin assays in patient management: Analysis of 437 warfarin measurements in a clinical setting. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 54, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, B.P.; Chin, P.K.L.; Roberts, R.L.; Begg, E.J. Influence of adult age on the total and free clearance and protein binding of (R)- and (S)-warfarin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacobi, A.; Udall, J.A.; Levy, G. Serum protein binding as a determinant of warfarin body clearance and anticoagulant effect. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1976, 19, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, F.J.; Veronich, K.; Kapoor, A.L. Binding of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents and their effect on binding of racemic warfarin and its enantiomers to human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. Molecular aspects of ligand binding to serum albumin. Pharmacol. Rev. 1981, 33, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DeVane, C.L. Clinical significance of drug binding, protein binding, and binding displacement drug interactions. Psychopharmacol. Bull. 2002, 36, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hochman, J.; Tang, C.; Prueksaritanont, T. Drug-drug interactions related to altered absorption and plasma protein binding: Theoretical and regulatory considerations, and an industry perspective. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanali, G.; Di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benet, L.Z.; Hoener, B.-A. Changes in plasma protein binding have little clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 71, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Fezeu, L.; Touvier, M.; Arnault, N.; Manach, C.; Hercberg, S.; Galan, P.; Scalbert, A. Dietary intake of 337 polyphenols in French adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1220–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bors, W.; Michel, C.; Stettmaier, K. Antioxidant effects of flavonoids. BioFactors 1997, 6, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauchet, L.; Amouyel, P.; Hercberg, S.; Dallongeville, J. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2588–2593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bojić, M.; Debeljak, Ž.; Medić-Šarić, M.; Tomičić, M. Interference of selected flavonoid aglycons in platelet aggregation assays. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brglez Mojzer, E.; Knez Hrnčić, M.; Škerget, M.; Knez, Ž.; Bren, U. Polyphenols: Extraction methods, antioxidative action, bioavailability and anticarcinogenic effects. Molecules 2016, 21, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, J.H.M.; Hollman, P.C.H.; Meyboom, S.; Buysman, M.N.C.P.; Zock, P.L.; van Staveren, W.A.; Katan, M.B. Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of the antioxidant flavonols quercetin and kaempferol as biomarkers for dietary intake. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campanero, M.A.; Escolar, M.; Perez, G.; Garcia-Quetglas, E.; Sadaba, B.; Azanza, J.R. Simultaneous determination of diosmin and diosmetin in human plasma by ion trap liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour, C.; Dangles, O. Flavonoid-serum albumin complexation: Determination of binding constants and binding sites by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2005, 1721, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Ding, L.; Tian, Y.; Song, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Investigation of the interaction between flavonoids and human serum albumin. J. Mol. Struct. 2004, 703, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, L.; Ripoli, S.; Pradhan, S.; Salvadori, P. Interactions between quercetin and warfarin for albumin binding: A new eye on food/drug interference. Chirality 2010, 22, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poór, M.; Li, Y.; Kunsági-Máté, S.; Petrik, J.; Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Koszegi, T. Molecular displacement of warfarin from human serum albumin by flavonoid aglycones. J. Lumin. 2013, 142, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graefe, E.U.; Wittig, J.; Mueller, S.; Riethling, A.-K.; Uehleke, B.; Drewelow, B.; Pforte, H.; Jacobasch, G.; Derendorf, H.; Veit, M. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of quercetin glycosides in humans. Herb. Med. 2001, 41, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangles, O.; Dufour, C.; Manach, C.; Mornad, C.; Remesy, C. Binding of flavonoids to plasma proteins. Method Enzymol. 2001, 335, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Boulton, D.W.; Walle, U.K.; Walle, T. Extensive binding of the bioflavonoid quercetin to human plasma proteins. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 1998, 50, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsila, F.; Bikádi, Z.; Simonyi, M.; Bika, Z. Probing the binding of the flavonoid, quercetin to human serum albumin by circular dichroism, electronic absorption spectroscopy and molecular modelling methods. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epps, D.E.; Raub, T.J.; Caiolfa, V.; Chiari, A.; Zamai, M. Determination of the affinity of drugs toward serum albumin by measurement of the quenching of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of the protein. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1999, 51, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftink, M.R.; Ghiron, C.A. Fluorescence quenching studies with proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 114, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Carter, D.C. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 1992, 358, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfbeis, O.S.; Begum, M.; Geiger, H. Fluorescence properties of hydroxy- and methoxyflavones and the effect of shift reagents. Z. Für Naturforsch. 1984, 39b, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T. The Albumin molecule: Its structure and chemical properites. In All about Albumin; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1996; pp. 9–75. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcy, P.F.; McElnay, J.C. Drug interactions involving the displacement of drugs from plasma protein and tissue binding sites. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982, 17, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöholm, I.; Ekman, B.; Kober, A.; Ljungstedt-Påhlman, I.; Seiving, B.; Sjödin, T. Binding of drugs to human serum albumin: XI. The specificity of three binding sites as studied with albumin immobilized in microparticles. Mol. Pharmacol. 1979, 16, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Gonzales, D.; Derendorf, H. Significance of protein binding in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 1107–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagercrantz, C.; Larsson, T.; Denfors, I. Stereoselective binding of the enantiomers of warfarin and trytophan to serum albumin from some different species studied by affinity chromatography on columns of immobilized serum albumin. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1981, 69, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Twine, S.; East, M.; Curry, S. Crystal structure analysis of warfarin binding to human serum albumin. Anatomy of drug site I. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22804–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kokot, S. Spectrometric and voltammetric studies of the interaction between quercetin and bovine serum albumin using warfarin as site marker with the aid of chemometrics. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 71, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bren, U.; Oostenbrink, C. Cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition by ketoconazole: Tackling the problem of ligand cooperativity using molecular dynamics simulations and free-energy calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guharay, J.; Sengupta, B.; Sengupta, P.K. Protein-flavonol interaction: Fluorescence spectroscopic study. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2001, 43, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, Z.; Parivar, K.; Sanee, H.; Amiri-Tehranizadeh, Z.; Baratian, A.; Saberi, M.R.; Asoodeh, A.; Chamani, J. Investigations with spectroscopy, zeta potential and molecular modeling of the non-cooperative behaviour between cyclophosphamide hydrochloride and aspirin upon interaction with human serum albumin: Binary and ternary systems from multi-drug therapy. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2011, 29, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Maruyama, T.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Characterization of site I on human serum albumin: Concept about the structure of a drug binding site. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1996, 1295, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Maruyama, T.; Takadate, A.; Suenaga, A.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Characterization of site I of human serum albumin using spectroscopic analyses: Locational relations between regions Ib and Ic of site I. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poór, M.; Boda, G.; Needs, P.W.; Kroon, P.A.; Lemli, B.; Bencsik, T. Interaction of quercetin and its metabolites with warfarin: Displacement of warfarin from serum albumin and inhibition of CYP2C9 enzyme. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimac, H.; Debeljak, Ž.; Šakić, D.; Weitner, T.; Gabričević, M.; Vrček, V.; Zorc, B.; Bojić, M. Structural and electronic determinants of flavonoid binding to human serum albumin: An extensive ligand-based study. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75014–75022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangles, O.; Dufour, C.; Bret, S. Flavonol-serum albumin complexation. Two-electron oxidation of flavonols and their complexes with serum albumin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1999, 2, 737–744. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.-M.; Sehnal, D.; Falginella, F.L.; Pant, P.; Pravda, L.; Bouchal, T. AtomicChargeCalculator: Interactive web-based calculation of atomic charges in large biomolecular complexes and drug-like molecules. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors as well as commercially. |







| Name | R1 | R2 | R3 | K ± S.D. (× 104 M−1) | Corr 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warfarin | N/A | N/A | N/A | 10.56 ± 0.68 | 0.998 |
| Luteolin | -H | -H | -OH | 12.20 ± 0.53 | 0.999 |
| Isoorientin | -H | -Glc | -OH | 4.57 ± 0.30 | 0.999 |
| Cynaroside | -H | -H | -O-Glc | 4.20 ± 0.25 | 0.999 |
| Quercetin | -OH | -H | -OH | 14.40 ± 0.52 | 1.000 |
| Isoquercitrin | -O-Glc | -H | -OH | 4.47 ± 0.21 | 1.000 |
| Hyperoside | -O-Gal | -H | -OH | 3.24 ± 0.19 | 0.999 |
| Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide | -O-Gluc | -H | -OH | 5.36 ± 0.13 | 1.000 |
| Rutin | -Glc-Rha | -H | -OH | 2.92 ± 0.13 | 1.000 |
| Quercetin Anion at Position 7 | Quercetin Anion at Position 4’ | ||||
| Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| 1. | 3 | −4.79 | 1. | 1 | −4.68 |
| 2. | 1 | −4.42 | 2. | 19 | −4.38 |
| 3. | 2 | −4.22 | 3. | 1 | −4.30 |
| 4. | 4 | −4.20 | 4. | 2 | −4.16 |
| 5. | 12 | −4.12 | 5. | 9 | −4.11 |
| 6. | 23 | −4.07 | 6. | 9 | −4.08 |
| 7. | 3 | −3.94 | 7. | 2 | −3.69 |
| 8. | 14 | −3.94 | 8. | 8 | −3.68 |
| Fluorescent quercetin anion at positions 3 and 7 | Fluorescent quercetin anion at positions 3 and 4’ | ||||
| Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| 1. | 43 | −4.66 | 1. | 5 | −4.42 |
| 2. | 1 | −4.61 | 2. | 18 | −4.04 |
| 3. | 4 | −4.60 | 3. | 13 | −3.87 |
| 4. | 7 | −4.24 | 4. | 3 | −3.82 |
| 5. | 4 | −4.20 | 5. | 1 | −3.81 |
| Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide Anion at Position 7 | Quercetin-3-O-glucuronide Anion at Position 4’ | ||||
| Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| 1. | 4 | −5.02 | 1. | 5 | −6.09 |
| 2. | 5 | −4.76 | 2. | 3 | −4.89 |
| 3. | 1 | −4.62 | 3. | 2 | −4.78 |
| 4. | 4 | −4.49 | 4. | 4 | −4.74 |
| 5. | 2 | −4.49 | 5. | 6 | −4.52 |
| 6. | 9 | −4.45 | 6. | 1 | −4.16 |
| 7. | 5 | −4.45 | 7. | 4 | −4.02 |
| 8. | 1 | −4.35 | 8. | 4 | −3.99 |
| Fluorescent quercetin-3-O-glucuronide anion at position 7 | Fluorescent quercetin-3-O-glucuronide anion at position 4’ | ||||
| Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| 1. | 13 | −4.21 | 1. | 5 | −4.42 |
| 2. | 2 | −4.07 | 2. | 18 | −4.04 |
| 3. | 11 | −4.06 | 3. | 13 | −3.87 |
| 4. | 1 | −4.05 | 4. | 3 | −3.82 |
| 5. | 3 | −3.95 | 5. | 1 | −3.81 |
| (R)-Warfarin | (S)-Warfarin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Cluster Rank | Number of Runs | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
| 1. | 9 | −6.70 | 1. | 27 | −6.70 |
| 2. | 6 | −6.52 | 2. | 6 | −6.56 |
| 3. | 4 | −6.49 | 3. | 5 | −6.51 |
| 4. | 35 | −6.28 | 4. | 15 | −6.42 |
| 5. | 4 | −6.27 | 5. | 2 | −6.31 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rimac, H.; Dufour, C.; Debeljak, Ž.; Zorc, B.; Bojić, M. Warfarin and Flavonoids Do Not Share the Same Binding Region in Binding to the IIA Subdomain of Human Serum Albumin. Molecules 2017, 22, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071153
Rimac H, Dufour C, Debeljak Ž, Zorc B, Bojić M. Warfarin and Flavonoids Do Not Share the Same Binding Region in Binding to the IIA Subdomain of Human Serum Albumin. Molecules. 2017; 22(7):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071153
Chicago/Turabian StyleRimac, Hrvoje, Claire Dufour, Željko Debeljak, Branka Zorc, and Mirza Bojić. 2017. "Warfarin and Flavonoids Do Not Share the Same Binding Region in Binding to the IIA Subdomain of Human Serum Albumin" Molecules 22, no. 7: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071153
APA StyleRimac, H., Dufour, C., Debeljak, Ž., Zorc, B., & Bojić, M. (2017). Warfarin and Flavonoids Do Not Share the Same Binding Region in Binding to the IIA Subdomain of Human Serum Albumin. Molecules, 22(7), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071153