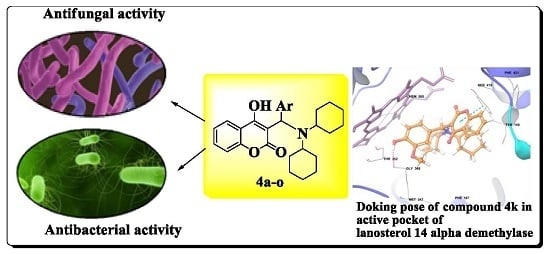
Facile Synthesis of Novel Coumarin Derivatives, Antimicrobial Analysis, Enzyme Assay, Docking Study, ADMET Prediction and Toxicity Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Result and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. In Vitro Antifungal Activity
2.2.2. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
2.2.3. Ergosterol Extraction and Quantitation Assay
2.3. Computational Studies
2.3.1. Molecular Docking
2.3.2. In Silico ADMET Investigation Results
2.4. Toxicity Study
2.4.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
2.4.2. In vivo Acute Oral Toxicity Study and Behavioral Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis of 3-((Dicyclohexylamino)(substituted phenyl/heteryl)methyl)-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one Derivatives 4a–o
3.3. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity
3.3.1. In Vitro Antifungal Activity
3.3.2. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity
3.3.3. Ergosterol Extraction and Quantitation Assay
3.4. Computational Studies
3.4.1. Molecular Docking
3.4.2. In Silico ADMET Prediction
3.5. Toxicity Study
3.5.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Study
3.5.2. In Vivo Acute Oral Toxicity Study and Behavioral Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zomorodian, K.; Moein, N.R.; Rahimi, M.J.; Pakshir, K.; Ghasemi, Y.; Abdi, S.; Sharbatfar, S. Possible Application and Chemical Compositions of Carumcopticum Essential Oils Against Food borne and Nosocomial Pathogens. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2011, 9, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Mamishi, S.; Zomorodian, K.; Saadat, F.; Gerami-Shoar, M.; Tarazooie, B.; Siadati, S.A. A case of invasive aspergillosis in CGD patient successfully treated with Amphotericin B and INF-gamma. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2005, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoar, M.G.; Zomorodian, K.; Saadat, F.; Hashemi, M.J.; Tarazoei, B. Fatal endocarditis due to Aspergillus flavus in Iran. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2004, 54, 485–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drakensjo, I.T.; Chryssanthou, E. Epidemiology of dermatophyte infections in Stockholm, Sweden: A retrospective study from 2005–2009. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badiee, P.; Alborzi, A. Invasive fungal infections in renal transplant recipients. Exp. Clin. Transpl. 2011, 9, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Q.; Ge, Z.; Chen, K.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yang, X.; Liao, F. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel phosphoramidate derivatives of coumarin as chitin synthase inhibitors and antifungal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostova, I. Synthetic and natural coumarins as cytotoxic agents. Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 2005, 5, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.V.S.; Divya, B.; Swain, M.; Rao, T.P.; Yadav, J.S.; Vishnuvardhan, M.V.P.S. A domino Knoevenagel hetero-Diels–Alder reaction for the synthesis of polycyclic chromene derivatives and evaluation of their cytotoxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, N.; Raghunathan, R.; Almansour, A.I.; Karama, U. An efficient synthesis of highly functionalized novel chromeno [4,3-b]pyrroles and indolizino[6,7-b]indoles as potent antimicrobial and antioxidant agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devakaram, R.; Black, D.S.; Choomuenwai, V.; Davis, R.A.; Kumar, N. Synthesis and anti-plasmodial evaluation of novel chromeno[2,3-b]chromene derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devakaram, R.; Black, D.S.; Andrews, K.T.; Fisher, G.M.; Davis, R.A.; Kumar, N. Synthesis and antimalarial evaluation of novel benzopyrano[4,3-b]benzopyran derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5199–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, C.; Proietti Monaco, L.; Desideri, N. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of novel chroman-4-one, chroman, and 2H-chromene derivatives as human rhinovirus capsid-binding inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7357–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Yin, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, W. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis and Antifungal Activities of Poly substituted Furo[3,2-c]chromen-4-ones and 7,8,9,10-Tetrahydro-6H-benzofuro[3,2-c]chromen-6-ones. Synth. Commun. 2014, 44, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinnia, R.; Mamaghani, M.; Tabatabaeian, K.; Shirini, F.; Rassa, M. An expeditious regioselective synthesis of novel bioactive indole-substituted chromene derivatives via one-pot three-component reaction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5956–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdi, N.; Puerta, M.C.; Valerga, P. Synthesis, structure, antimicrobial and antioxidant investigations of dicoumarol and related compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, R.; Goesmann, H.; Waldmann, H. N,N-Phthaloyl amino acids as chiral auxiliaries in asymmetric Mannich-type reactions. Angew. Chem. Ed. Engl. 1999, 38, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbeater, N.E.; Torenius, H.M.; Tye, H. Microwave-assisted Mannich-type three-component reactions. Mol. Divers. 2003, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.V.; Seijas, J.; Vazquez-Tato, M.P.; Sarkate, A.P.; Lokwani, D.K.; Nikalje, A.G. Ultrasound Mediated One-Pot, Three Component Synthesis, Docking and ADME prediction of Novel 5-amino-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-substitutedphenyl-8,8a-dihydro-7H-[1,3,4]thiadiazolo[3,2-α]pyrimidine-6-carbonitrile Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimbalkar, U.D.; Tupe, S.G.; Seijas Vazquez, J.A.; Khan, F.A.K.; Sangshetti, J.N.; Nikalje, A.P.G. Ultrasound- and Molecular Sieves-Assisted Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Antifungal Evaluation of 5-(4-(Benzyloxy)-substituted phenyl)-3-((phenylamino)methyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole-2(3H)-thiones. Molecules 2016, 21, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruickshank, R.; Duguid, J.P.; Marmion, B.P.; Swain, R.H.A. Medicinal Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 1975; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, A.H. Microbiological Methods, 2nd ed.; Butterworth: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.K. In vitro and in vivo screening techniques for bioactivity screening and evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Workshop UNIDO-CDRI, Lucknow, India, 2–5 December 1997; pp. 210–211. [Google Scholar]
- Duraiswamy, B.; Mishra, S.K.; Subhashini, V.; Dhanraj, S.A.; Suresh, B. Studies on the antimicrobial potential of Mahonialeschenaultii Takeda root and root bark. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 68, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengauer, T.; Rarey, M. Computational methods for bio-molecular docking. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1996, 6, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, D.J.; Hitchcock, C.A.; Sibley, C.M. Current and Emerging Azole Antifungal Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 12, 40–79. [Google Scholar]
- Sangshetti, J.N.; Lokwani, D.K.; Sarkate, A.P.; Shinde, D.B. Synthesis, Antifungal Activity, and Docking Study of Some New 1,2,4-triazole Analogs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 2, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington-Skaggs, B.A.; Warnock, D.W.; Morrison, C.J. Quantitation of Candida albicans ergosterol content improves the correlation between in vitro antifungal susceptibility test results and in vivo outcome after fluconazole treatment in murine model of invasive candidiasis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, I.O.; de Medeiros Nobrega, F.; de Oliveira, W.A.; Lima, E.O.; Menezes, E.A.; Cunha, F.; MeloDiniz, A.M.F.F. Anti-Candida albicans effectiveness of citral and investigation of mode of action. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayine-Tora, D.M.; Kingsford-Adaboh, R.; Asomaning, W.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Mills-Robertson, F.C.; Bukari, Y.; Sakyi, P.O.; Kaminta, S.; Reynisson, J. Coumarin Antifungal Lead Compounds from Millettiathonningii and Their Predicted Mechanism of Action. Molecules 2016, 21, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granados, T.V.; Garcia, S.; Vazquez, M.A.; Robles, J. Molecular docking-based screening of newly designed coumarin derivatives with potential antifungal activity against lanosterol 14α-demethylase. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2016, 135, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, J.I.; Walker, B.D.; Campbell, T.J. HERG K+ channels: Friend and foe. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronov, A.M. Predictive in silico modeling for HERG channel blockers. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 4a–o are available with the authors A.P.G.N. and S.V.T. |





| Compound | MIC a μg/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Candida albicans | Candida glabrata | Fusarium oxysporum | Aspergillus fumigates | Aspergillus flavus | Aspergillus niger | Cryptococcus neoformans | |
| 4a | 66 | 58 | 55 | 84 | 38 | 43 | 54 |
| 4b | 30 | 32 | 34 | 30 | 14 | 15 | 15 |
| 4c | 30 | 28 | 35 | 28 | 15 | 18 | 14 |
| 4d | 28 | 30 | 30 | 28 | 15 | 20 | 18 |
| 4e | 28 | 26 | 30 | 28 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| 4f | 43 | 57 | 39 | 44 | 20 | 22 | 20 |
| 4g | 50 | 57 | 35 | 52 | 24 | 20 | 26 |
| 4h | 48 | 64 | 45 | 50 | 38 | 34 | 34 |
| 4i | 32 | 35 | 35 | 42 | 25 | 28 | 24 |
| 4j | 46 | 47 | 38 | 55 | 32 | 30 | 35 |
| 4k | 25 | 30 | 28 | 38 | 12 | 15 | 15 |
| 4l | 25 | 28 | 28 | 36 | 15 | 12 | 12 |
| 4m | 48 | 46 | 40 | 45 | 25 | 22 | 28 |
| 4n | 55 | 53 | 58 | 67 | 32 | 38 | 33 |
| 4o | 56 | 55 | 55 | 65 | 46 | 49 | 48 |
| Miconazole | 25 | 25 | 25 | 35 | 12 | 12 | 12 |
| Compound | MIC a μg/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Bacillus subtilis | Staphylococcus aureus | |
| 4a | 70 | 68 | 65 |
| 4b | 52 | 50 | 54 |
| 4c | 50 | 48 | 50 |
| 4d | 50 | 49 | 50 |
| 4e | 48 | 50 | 52 |
| 4f | 64 | 58 | 55 |
| 4g | 62 | 60 | 62 |
| 4h | 68 | 68 | 66 |
| 4i | 64 | 66 | 67 |
| 4j | 68 | 72 | 72 |
| 4k | 55 | 55 | 54 |
| 4l | 56 | 54 | 54 |
| 4m | 68 | 74 | 78 |
| 4n | 65 | 74 | 72 |
| 4o | 66 | 74 | 70 |
| Ampicillin | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Entry | M.W a | Log Po/w b (−2.0 to 6.5) | n-ON c (<10) | n-OHNH d (<5) | PSA e (7–200.0) | Log Khsa f (−1.5–1.2) | Log S g (−6–0.5) | % ABS h | # Meta i (1–8) | Log HERG j (below −5) | Lipinski Rule of 5 (≤1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4a | 431.5 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 1 | 51.7 | 0.9 | −4.7 | 100 | 4 | −6.1 | 0 |
| 4b | 466.0 | 5.5 | 5.2 | 1 | 48.5 | 1.1 | −5.5 | 100 | 3 | −6.1 | 0 |
| 4c | 498.1 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 1 | 48.9 | 1.0 | −5.0 | 100 | 3 | −6.0 | 0 |
| 4d | 449.5 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 1 | 48.6 | 1.0 | −5.1 | 100 | 3 | −6.1 | 0 |
| 4e | 467.5 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 1 | 50.7 | 1.0 | −4.9 | 96.9 | 4 | −6.0 | 0 |
| 4f | 461.6 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 1 | 58.9 | 0.9 | −4.7 | 95.9 | 4 | −6.1 | 0 |
| 4g | 491.6 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 1 | 64.5 | 1.0 | −5.2 | 100 | 4 | −6.2 | 0 |
| 4h | 521.0 | 5.3 | 7.5 | 1 | 69.6 | 1.0 | −5.3 | 84.9 | 6 | −6.1 | 0 |
| 4i | 447.5 | 4.2 | 6 | 1 | 71.8 | 0.8 | −4.6 | 95.0 | 4 | −6.2 | 0 |
| 4j | 447.5 | 4.1 | 6 | 1 | 70.9 | 0.8 | −4.6 | 95.0 | 4 | −6.2 | 0 |
| 4k | 478.2 | 4.2 | 6 | 1 | 71.8 | 0.9 | −4.7 | 95.0 | 4 | −6.0 | 0 |
| 4l | 490.2 | 4.1 | 6 | 1 | 50.7 | 1.0 | −5.1 | 96.9 | 4 | −6.0 | 0 |
| 4m | 432.5 | 4.4 | 6.2 | 1 | 62.0 | 0.7 | −4.4 | 100 | 5 | −6.2 | 0 |
| 4n | 437.5 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 1 | 47.7 | 0.8 | −4.6 | 100 | 4 | −6.0 | 0 |
| 4o | 421.5 | 4.4 | 5.7 | 1 | 53.5 | 0.7 | −4.3 | 100 | 4 | −6.1 | 0 |
| Compound | GI50 (µg/mL) a |
|---|---|
| HeLa | |
| 4e | >50 |
| 4k | >50 |
| Adriamycin | 0.5 |
| Observation | Compound | |
|---|---|---|
| 4e | 4k | |
| Toxicity | N | N |
| Deaths | N | N |
| Eye Lacrimation | N | N |
| Salivation | N | N |
| Diarrhea | N | N |
| Respiration Problems | N | N |
| Straub Tail | N | N |
| Pilo Erection | N | N |
| Convulsions | N | N |
| Normal Motor Activity | Y | Y |
| Stereotypy | N | N |
| Tremors | N | N |
| Sedation | N | N |
| Hypnosis | N | N |
| Muscle Spasms | N | N |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiwari, S.V.; Seijas, J.A.; Vazquez-Tato, M.P.; Sarkate, A.P.; Karnik, K.S.; Nikalje, A.P.G. Facile Synthesis of Novel Coumarin Derivatives, Antimicrobial Analysis, Enzyme Assay, Docking Study, ADMET Prediction and Toxicity Study. Molecules 2017, 22, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071172
Tiwari SV, Seijas JA, Vazquez-Tato MP, Sarkate AP, Karnik KS, Nikalje APG. Facile Synthesis of Novel Coumarin Derivatives, Antimicrobial Analysis, Enzyme Assay, Docking Study, ADMET Prediction and Toxicity Study. Molecules. 2017; 22(7):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071172
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiwari, Shailee V., Julio A. Seijas, Maria Pilar Vazquez-Tato, Aniket P. Sarkate, Kshipra S. Karnik, and Anna Pratima G. Nikalje. 2017. "Facile Synthesis of Novel Coumarin Derivatives, Antimicrobial Analysis, Enzyme Assay, Docking Study, ADMET Prediction and Toxicity Study" Molecules 22, no. 7: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071172
APA StyleTiwari, S. V., Seijas, J. A., Vazquez-Tato, M. P., Sarkate, A. P., Karnik, K. S., & Nikalje, A. P. G. (2017). Facile Synthesis of Novel Coumarin Derivatives, Antimicrobial Analysis, Enzyme Assay, Docking Study, ADMET Prediction and Toxicity Study. Molecules, 22(7), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071172