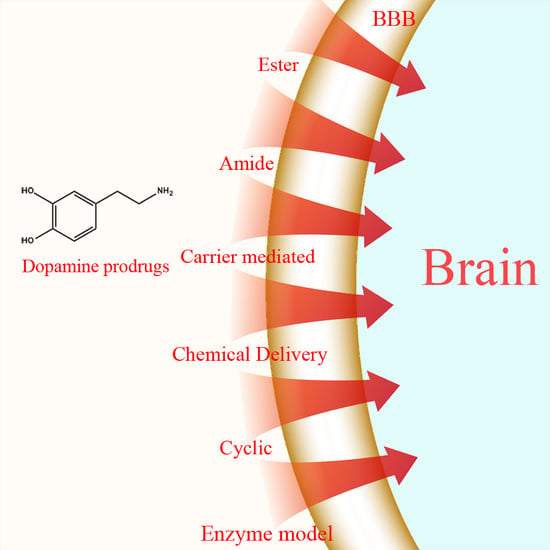
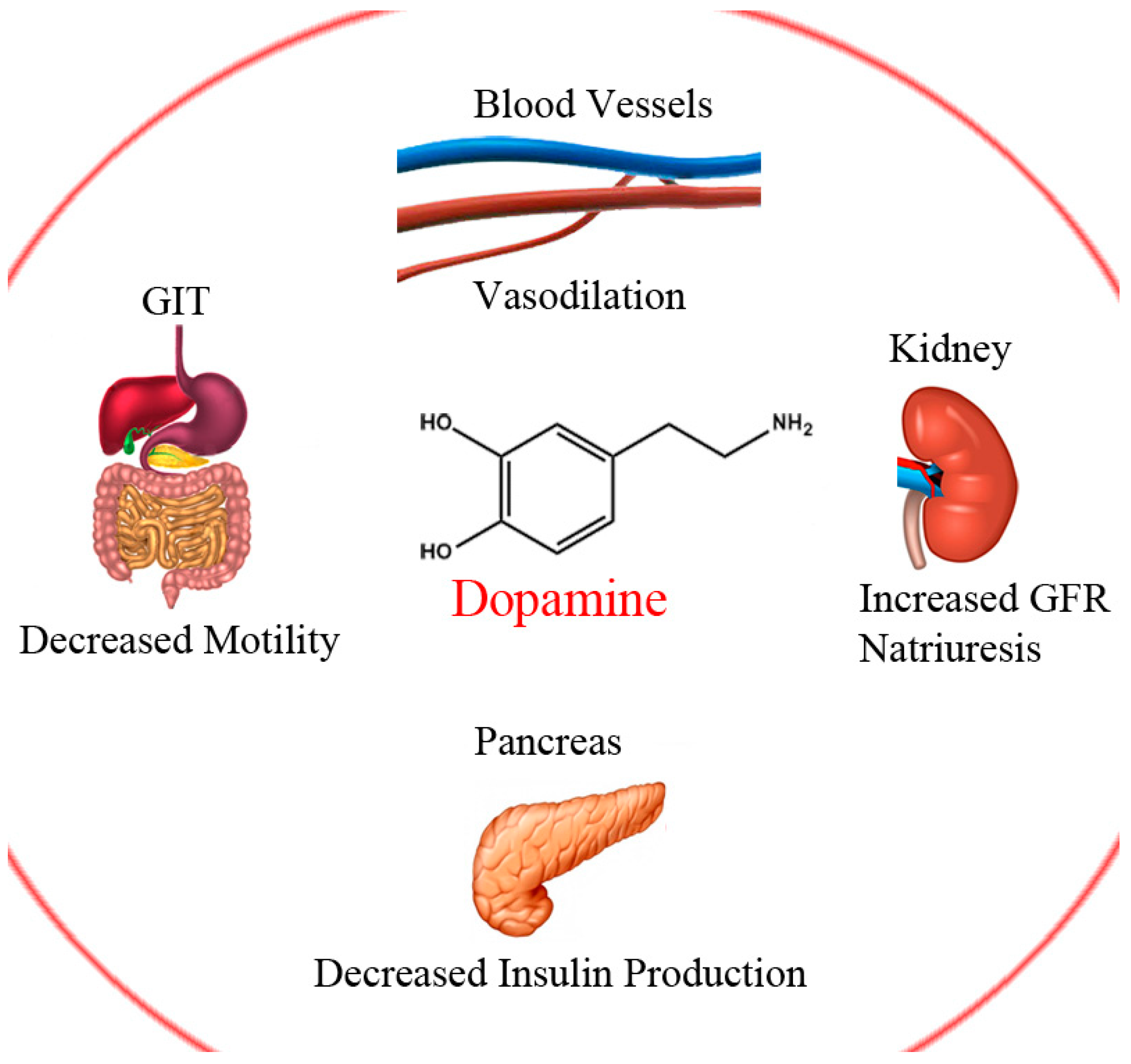
Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Ester Prodrugs
1.2. Amide Prodrugs
1.3. Dimeric Amide Prodrugs
1.4. Carrier-Mediated Prodrugs
1.5. Peptide Transport-Mediated Prodrugs
1.6. Chemical Delivery Systems
1.7. Cyclic Prodrugs
1.8. Enzyme Model (Intramolecular Processes)
2. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| DA | Dopamine |
| LD | LevoDopa |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| 6-OHDA | 6-hydroxydopamine |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneal |
| COMT | Catechol-O-methyltransferase |
| DDC | Dopa-decarboxylase |
| MAO | Mono amino oxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| DA-PHEN | 2-Amino-N-[2-(3,4-dihydroxy-phenyl)-ethyl]-3-phenyl-propionamide |
| PAMPA | parallel artificial permeability assay |
| GLUT1 | glucose transporter |
| MCT | monocarboxylic acid transporter |
| PDDP | dopamine-3-(dimethylamino) propanamide |
| LAT1 | large neutral amino acid transporter |
References
- Iversen, L.L. Dopamine Handbook; Oxford University Press: Cary, NC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Daubner, S.C.; Le, T.; Wang, S. Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shastry, B.S. Parkinson disease: Etiology, pathogenesis and future of gene therapy. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 41, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Sleiman, P.M.; Muqit, M.M.; Wood, N.W. Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. A-synuclein in lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L.J.; Pan, Y.; Price, A.C.; Sterling, W.; Copeland, N.G.; Jenkins, N.A.; Price, D.L.; Lee, M.K. Parkinson’s disease α-synuclein transgenic mice develop neuronal mitochondrial degeneration and cell death. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senek, M.; Nyholm, D. Continuous drug delivery in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 2014, 28, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Iannitelli, A.; Cerasa, L.S. New drug delivery strategies for improved Parkinson’s disease therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, E.; Hefti, F.; Wurtman, R.J. Nonaminergic striatal neurons convert exogenous l-dopa to dopamine in Parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 1980, 8, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, J.; Kumpulainen, H.; Heimbach, T.; Oliyai, R.; Oh, D.; Järvinen, T.; Savolainen, J. Prodrugs: Design and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.; Feeney, P. Toward minimalistic modeling of oral drug absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, D.J.; Brightman, M.W. Structural and functional aspects of the blood-brain barrier. In Peptide Transport and Delivery into the Central Nervous System; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 39–78. [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge, W.M. Blood-brain barrier drug targeting: The future of brain drug development. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakoutikhah, M.; Teixidó, M.; Giralt, E. Shuttle-mediated drug delivery to the brain. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7998–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandini, F.; Greenamyre, J.T. Protective and symptomatic strategies for therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Drugs Today 1999, 35, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Group, P.S. Levodopa and the progression of Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 2004, 2498–2508. [Google Scholar]
- Olanow, C.W.; Stern, M.B.; Sethi, K. The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease (2009). Neurology 2009, 72, S1–S136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlskog, J.E.; Muenter, M.D. Frequency of levodopa-related dyskinesias and motor fluctuations as estimated from the cumulative literature. Mov. Disord. 2001, 16, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porras, G.; De Deurwaerdere, P.; Li, Q.; Marti, M.; Morgenstern, R.; Sohr, R.; Bezard, E.; Morari, M.; Meissner, W.G. l-Dopa-induced dyskinesia: Beyond an excessive dopamine tone in the striatum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, J.J.; Middlemiss, D.N.; Sharpe, P.C.; Poste, G.H. Parkinson’s disease: Prospects for improved drug therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1997, 18, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, J.G.; Woodward, W.R.; Anderson, J.L. The effect of carbidopa on the pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered levodopa: The mechanism of action in the treatment of Parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 1985, 18, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standaert, D.G.; Young, A.B. Treatment of central nervous system degenerative disorders. In The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, IXth ed.; Hardman, J.G., Limbrid, L.E., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 503–519. [Google Scholar]
- LeWitt, P.A. Levodopa for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2468–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, J.; Woodward, W.; Beckner, R.; Stone, C.; Berggren, K.; Carter, J.; Gancher, S.; Hammerstad, J.; Gordin, A. Effect of peripheral catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibition on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levodopa in Parkinsonian patients. Neurology 1994, 44, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutt, J.G. Effect of COMT inhibition on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levodopa in Parkinsonian patients. Neurology 1999, 55, S33–S37, discussion S38–S41. [Google Scholar]
- Kurlan, R.; Rothfield, K.; Woodward, W.; Nutt, J.; Miller, C.; Lichter, D.; Shoulson, I. Erratic gastric emptying of levodopa may cause “random” fluctuations of Parkinsonian mobility. Neurology 1988, 38, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaldetti, R.; Baron, J.; Ziv, I.; Melamed, E. Gastric emptying in Parkinson’s disease patients with and without response fluctuations. Neurology 1996, 46, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W. The scientific basis for the current treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2004, 55, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olanow, C.W.; Obeso, J.A.; Stocchi, F. Continuous dopamine-receptor treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Scientific rationale and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.J. Optimizing levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease with levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone: Implications from a clinical and patient perspective. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2008, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denora, N.; Trapani, A.; Laquintana, V.; Lopedota, A.; Trapani, G. Recent advances in medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical technology-strategies for drug delivery to the brain. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Serafina Cerasa, L.; Iannitelli, A. l-Dopa prodrugs: An overview of trends for improving Parkinson’s disease treatment. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 3482–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, J.; Laine, K.; Gynther, M.; Savolainen, J. Prodrug approaches for CNS delivery. AAPS J. 2008, 10, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.-W.; Hung, C.-F.; Fang, J.-Y. Current prodrug design for drug discovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2236–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Abbadessa, A.; Di Stefano, A. Designing prodrugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.E.; Ruiz-Lopez, M.; Fox, S.H. Novel levodopa formulations for Parkinson’s disease. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinokrot, H.; Smerat, T.; Najjar, A.; Karaman, R. Advanced prodrug strategies in nucleoside and non-nucleoside antiviral agents: A review of the recent five years. Molecules 2017, 22, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz de Montellano, P.R. Cytochrome p450-activated prodrugs. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krecmerova, M. Amino acid ester prodrugs of nucleoside and nucleotide antivirals. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, H.D.; Traboulsi, A.; Itoh, S.; Dittert, L.; Hussain, A. Enhancement of the systemic and CNS specific delivery of l-dopa by the nasal administration of its water soluble prodrugs. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodor, N.; Sloan, K.B.; Higuchi, T.; Sasahara, K. Improved delivery through biological membranes. 4. Prodrugs of l-dopa. J. Med. Chem. 1977, 20, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.; Marrel, C.; Waterbeemd, H.; Testa, B.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C. l-Dopa esters as potential prodrugs: Behavioural activity in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon-Aburbeh, A.; Poupaert, J.H.; Claesen, M.; Dumont, P. A lymphotropic prodrug of l-dopa: Synthesis, pharmacological properties and pharmacokinetic behavior of 1, 3-dihexadecanoyl-2-[(S)-2-amino-3-(3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl) propanoyl] propane-1, 2, 3-triol. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, D.; Marrel, C.; Waterbeemd, H.; Testa, B.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C. l-Dopa esters as potential prodrugs: Effect on brain concentration of dopamine metabolites in reserpinized mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1987, 39, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Sawasaki, Y.; Hisaka, A.; Takehana, H.; Tomimoto, K.; Yano, M. A new potential prodrug to improve the duration of l-dopa: l-3-(3-hydroxy-4-pivaloyloxyphenyl)alanine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1989, 78, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Nakajima, S.; Hisaka, A.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Sakuma, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Kitani, K.; Yano, M. Hydrolysis and acyl migration of a catechol monoester of l-dopa: l-3-(3-hydroxy-4-pivaloyloxyphenyl) alanine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1990, 79, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Huff, F.J.; Hauser, R.A.; Chen, D.; Lissin, D.; Zomorodi, K.; Cundy, K.C. Double-blind study of the actively transported levodopa prodrug xp21279 in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaldetti, R.; Giladi, N.; Hassin-Baer, S.; Shabtai, H.; Melamed, E. Pharmacokinetics of etilevodopa compared to levodopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease: An open-label, randomized, crossover study. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2003, 26, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, C.; Ferrari, G. 3, 4–0-diacyl derivatives of dopamine. Farmaco Sci. 1973, 28, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borgman, R.J.; McPhillips, J.J.; Stitzel, R.E.; Goodman, I.J. Synthesis and pharmacology of centrally acting dopamine derivatives and analogs in relation to Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 1973, 16, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, I.K.; Lee, K.E.; Chun, I.K.; Rhie, J.Y.; Gwak, H.S. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of formulated levodopa methyl ester nasal delivery systems. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokineti. 2014, 39, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaturro, A.L.; De Caro, V.; Campisi, G.; Giannola, L.I. Potential transbuccal delivery of l-dopa methylester prodrug: Stability in the environment of the oral cavity and ability to cross the mucosal tissue. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2355–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaldetti, R.; Melamed, E. Levodopa ethylester: A novel rescue therapy for response fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, D. l-Dopa Amide Derivatives and Uses Thereof. U.S. Patent WO2004069146 A2, 19 Aug 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Lv, L.; Zhou, S.; Huang, X.; Shi, X.; Lv, C.; Wu, L.; Xu, C. Simultaneous determination of l-dopa and its prodrug (S)-4-(2-acetamido-3-ethoxy-3-oxopropyl)-1, 2-phenylene diacetate in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and its application in a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Hider, R.C.; Jenner, P.; Campbell, B.; Hobbs, C.J.; Rose, S.; Jairaj, M.; Tayarani-Binazir, K.A.; Syme, A. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of l-dopa amide derivatives as potential prodrugs for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 4035–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denora, N.; Laquintana, V.; Lopedota, A.; Serra, M.; Dazzi, L.; Biggio, G.; Pal, D.; Mitra, A.K.; Latrofa, A.; Trapani, G.; et al. Novel l-dopa and dopamine prodrugs containing a 2-phenyl-imidazopyridine moiety. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1309–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltayb, A.; Wadenberg, M.-L.G.; Svensson, T.H. Enhanced cortical dopamine output and antipsychotic-like effect of raclopride with adjunctive low-dose l-dopa. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 58, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, M.; Quintard, D.; Abalain, C. Synthesis of symmetrical Pseudopeptides as potential inhibitors of the human immunodeficiency virus-1 protease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 29, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaans, J.; Timmerman, H. Cardiovascular hybrid drugs: Combination of more than one pharmacological property in one single molecule. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, N.M.; Aboul-Fadl, T.; Diab, A.K. Metronidazole twin ester prodrugs: Synthesis, physicochemical properties, hydrolysis kinetics and Antigiardial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 33, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannola, L.; Giammona, G.; Alotta, R. Pro-drugs of isoniazid: Synthesis and diffusion characteristics of acyl derivatives. Die Pharm. 1992, 47, 423–425. [Google Scholar]
- Ducho, C.; Görbig, U.; Jessel, S.; Gisch, N.; Balzarini, J.; Meier, C. Bis-cyclosal-d4t-monophosphates: Drugs that deliver two molecules of bioactive nucleotides. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, A.M.; Winter, D.P.; Wang, S.-S.; Kulesha, I.D.; Pool, W.R.; Hane, D.L.; Sheppard, H. Synthesis and antireserpine activity of peptides of l-dopa. J. Med. Chem. 1974, 17, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Mosciatti, B.; Cingolani, G.M.; Giorgioni, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Cacciatore, I.; Sozio, P.; Claudi, F. Dimeric l-dopa derivatives as potential prodrugs. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannazza, G.; Di Stefano, A.; Mosciatti, B.; Braghiroli, D.; Baraldi, M.; Pinnen, F.; Sozio, P.; Benatti, C.; Parenti, C. Detection of levodopa, dopamine and its metabolites in rat striatum dialysates following peripheral administration of l-dopa prodrugs by mean of HPLC–EC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 36, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Carafa, M.; Sozio, P.; Pinnen, F.; Braghiroli, D.; Orlando, G.; Cannazza, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Marianecci, C.; Santucci, E. Evaluation of rat striatal l-dopa and da concentration after intraperitoneal administration of l-dopa prodrugs in liposomal formulations. J. Controll. Release 2004, 99, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Iannitelli, A.; Marianecci, C.; Santucci, E.; Carafa, M. Maleic-and fumaric-diamides of (O,O-diacetyl)-l-dopa-methylester as anti-Parkinson prodrugs in liposomal formulation. J. Drug Target. 2006, 14, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.D. Prodrugs for improved CNS delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 19, 171–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. Contribution of carrier-mediated transport systems to the blood–brain barrier as a supporting and protecting interface for the brain; importance for CNS drug discovery and development. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, I.; Tsuji, A. Transporter-mediated permeation of drugs across the blood–brain barrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1371–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautio, J.; Gynther, M.; Laine, K. Lat1-mediated prodrug uptake: A way to breach the blood-brain barrier? Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peura, L.; Malmioja, K.; Huttunen, K.; Leppänen, J.; Hämäläinen, M.; Forsberg, M.M.; Rautio, J.; Laine, K. Design, synthesis and brain uptake of Lat1-targeted amino acid prodrugs of dopamine. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2523–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, C.; Nieto, O.; Rivas, E.; Montenegro, G.; Fontenla, J.A.; Fernández-Mayoralas, A. Synthesis and biological studies of glycosyl dopamine derivatives as potential antiparkinsonian agents. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 327, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Nieto, O.; Fontenla, J.A.; Rivas, E.; de Ceballos, M.L.; Fernández-Mayoralas, A. Synthesis of glycosyl derivatives as dopamine prodrugs: Interaction with glucose carrier glut-1. Organ. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonina, F.; Puglia, C.; Rimoli, M.G.; Melisi, D.; Boatto, G.; Nieddu, M.; Calignano, A.; Rana, G.L.; Caprariis, P.D. Glycosyl derivatives of dopamine and l-dopa as anti-Parkinson prodrugs: Synthesis, pharmacological activity and in vitro stability studies. J. Drug Target. 2003, 11, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruocco, L.; Viggiano, D.; Viggiano, A.; Abignente, E.; Rimoli, M.G.; Melisi, D.; Curcio, A.; Nieddu, M.; Boatto, G.; Carboni, E.; et al. Galactosylated dopamine enters into the brain, blocks the mesocorticolimbic system and modulates activity and scanning time in Naples high excitability rats. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannola, L.I.; De Caro, V.; Giandalia, G.; Siragusa, M.G.; Lamartina, L. Synthesis and in vitro studies on a potential dopamine prodrug. Die Pharm. 2008, 63, 704–710. [Google Scholar]
- De Caro, V.; Sutera, F.M.; Gentile, C.; Tutone, M.; Livrea, M.A.; Almerico, A.M.; Cannizzaro, C.; Giannola, L.I. Studies on a new potential dopaminergic agent: In vitro BBB permeability, in vivo behavioural effects and molecular docking evaluation. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangas-Sanjuan, V.; González-Alvarez, M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Bermejo, M. Drug penetration across the blood-brain barrier: An overview. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, S.S.; Vince, R. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of glutathione Peptidomimetics as components of anti-Parkinson prodrugs. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4581–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikura, T.; Senou, T.; Ishihara, H.; Kato, T.; Ito, T. Drug delivery to the brain. Dopa prodrugs based on a ring-closure reaction to quaternary Thiazolium compounds. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 116, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, G.M.; Di Stefano, A.; Mosciatti, B.; Napolitani, F.; Giorgioni, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Claudi, F. Synthesis of l-(+)-3-(3-hydroxy-4-pivaloyloxybenzyl)-2, 5-diketomorpholine as potential prodrug of l-dopa. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgioni, G.; Claudi, F.; Ruggieri, S.; Ricciutelli, M.; Palmieri, G.F.; Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Chiavaroli, A.; Ferrante, C.; et al. Design, synthesis, and preliminary pharmacological evaluation of new imidazolinones as l-dopa prodrugs. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1834–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, G.J.; Bundgaard, H. Prodrugs of peptides. 15. 4-Imidazolidinone prodrug derivatives of enkephalins to prevent aminopeptidase-catalyzed metabolism in plasma and absorptive mucosae. Int. J. Pharm. 1991, 76, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, R. Prodrugs Design Based on Inter-and Intramolecular Processes; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, C.A. Drug-like properties and the causes of poor solubility and poor permeability. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2000, 44, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brime, B.; Ballesteros, M.; Frutos, P. Preparation and in vitro characterization of gelatin microspheres containing levodopa for nasal administration. J. Microencapsul. 2000, 17, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
















© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haddad, F.; Sawalha, M.; Khawaja, Y.; Najjar, A.; Karaman, R. Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2018, 23, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010040
Haddad F, Sawalha M, Khawaja Y, Najjar A, Karaman R. Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules. 2018; 23(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaddad, Fatma, Maryam Sawalha, Yahya Khawaja, Anas Najjar, and Rafik Karaman. 2018. "Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease" Molecules 23, no. 1: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010040
APA StyleHaddad, F., Sawalha, M., Khawaja, Y., Najjar, A., & Karaman, R. (2018). Dopamine and Levodopa Prodrugs for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules, 23(1), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23010040