A Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, with Anti-Melanogenesis Properties in α-MSH and IBMX-Induced B16F10 Melanoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
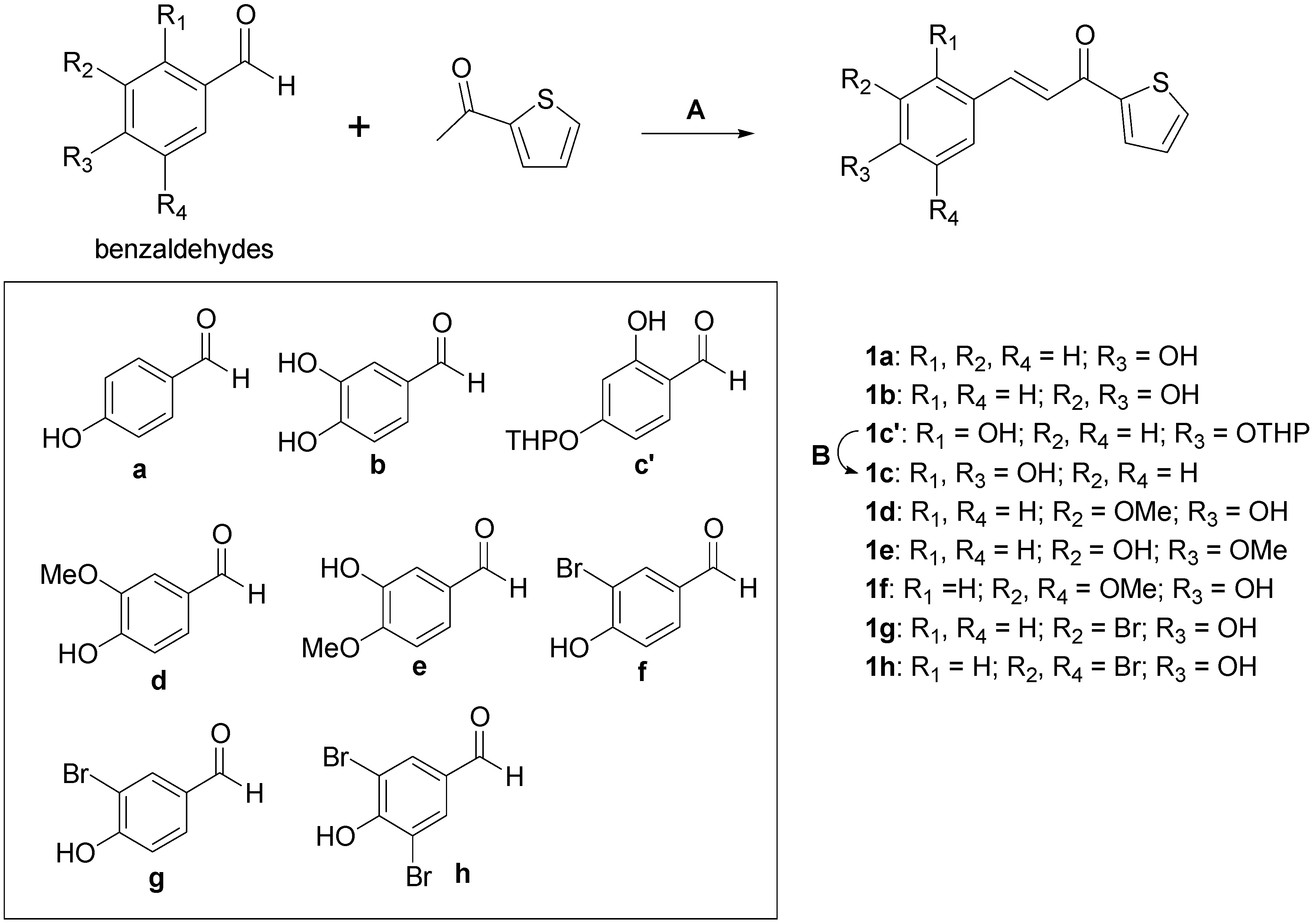
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Inhibitory Effect of Compound 1c on Mushroom Tyrosinase
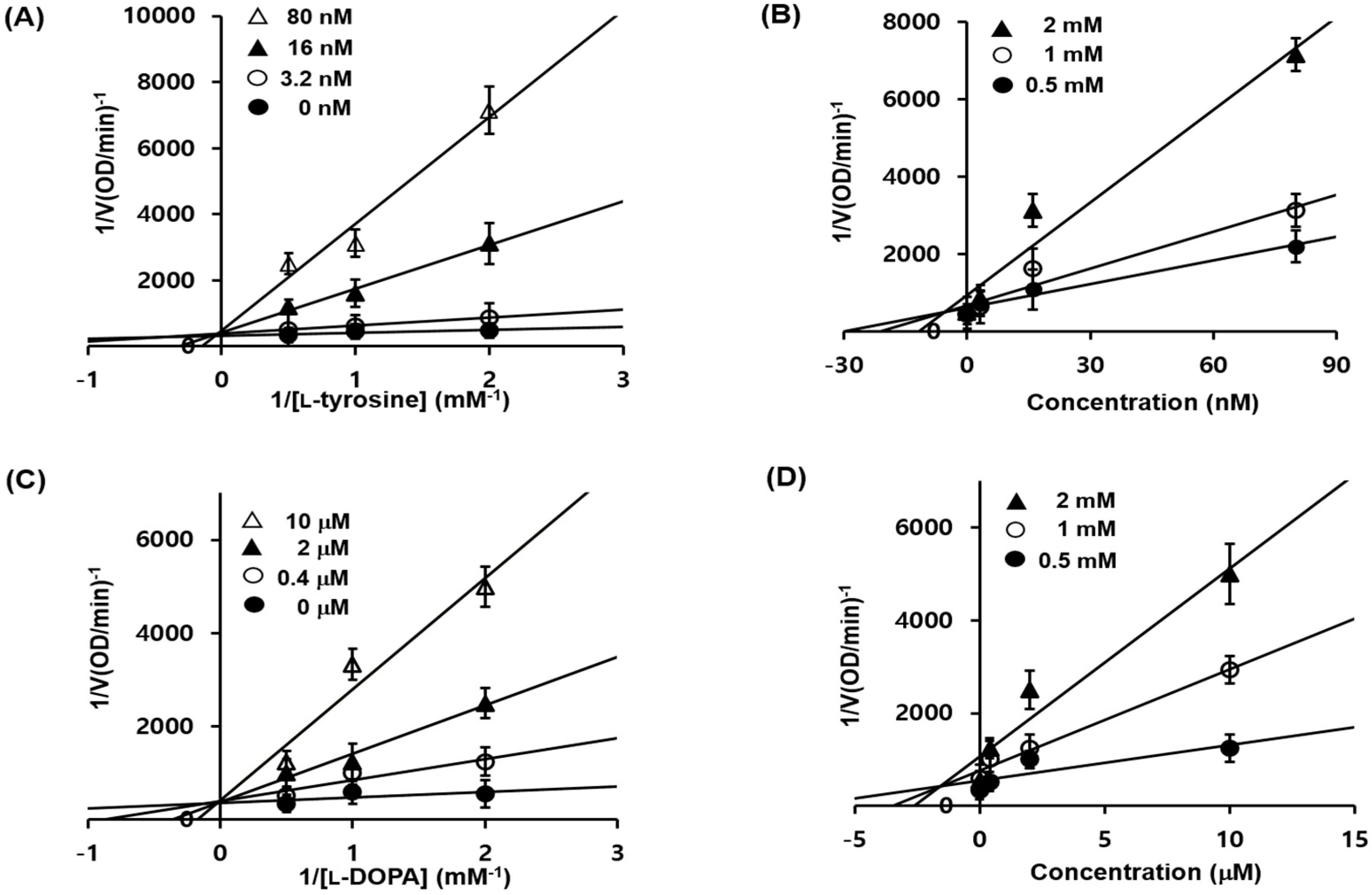
2.3. 1c Inhibition of Tyrosinase and Kinetic Analysis
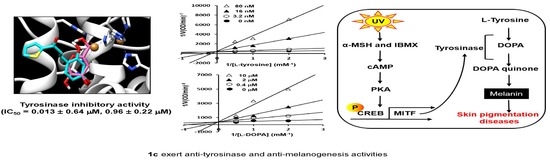
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulation of Tyrosinase and Binding Residues Interacting with 1c
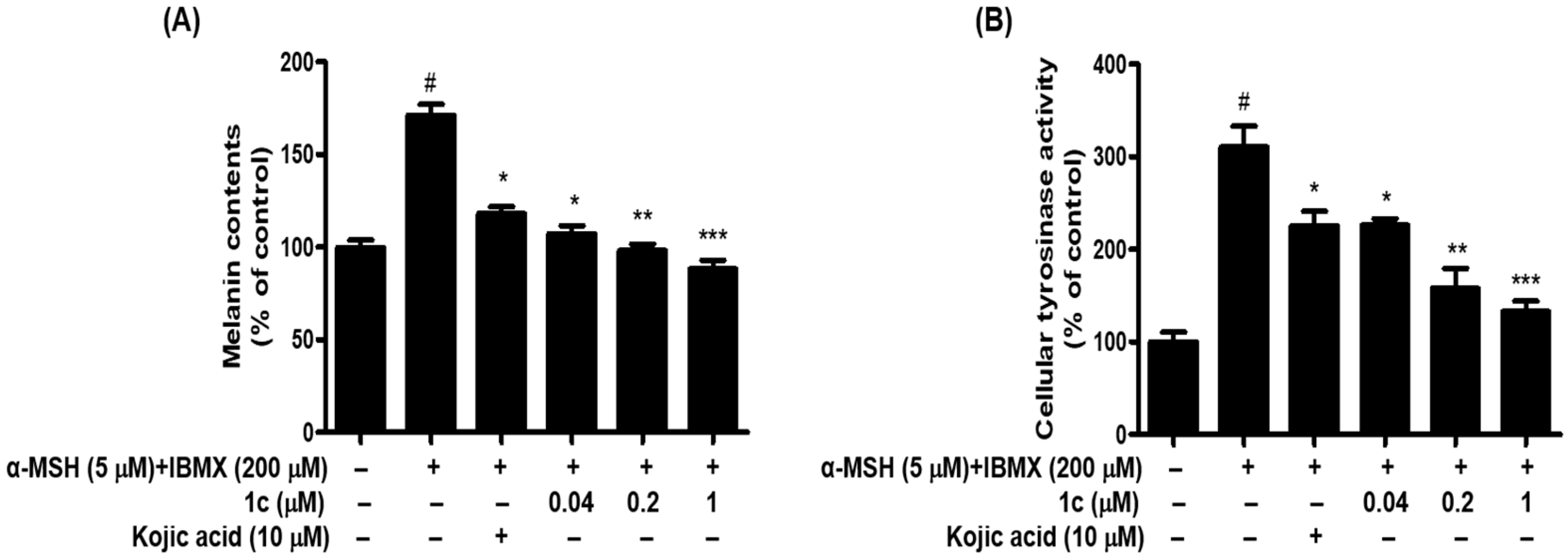
2.5. 1c Inhibited the Melanin Content and Intracellular Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. Synthetic Procedure for Compounds 1a, 1b, and 1d
3.2.2. Synthetic Procedure for Compounds 1e–h
3.2.3. Synthetic Procedure for (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one (1c)
3.3. Biological Assessment
3.3.1. Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibitory Assay
3.3.2. Enzyme Kinetic Analysis in Mushroom Tyrosinase Inhibition
3.3.3. In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation of Tyrosinase Inhibition
3.3.4. Cell Culture
3.3.5. Assay for Cell Viability
3.3.6. Inhibitory Activity of Melanin Contents in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
3.3.7. Inhibitory Activity of Cellular Tyrosinase Activity Assay in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
3.3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nerya, O.; Musa, R.; Khatib, S.; Tamir, S.; Vaya, J. Chalcones as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: The effect of hydroxyl positions and numbers. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.S.; Han, M.; Yao, C.; Chung, J.H. Chaetocin inhibits IBMX-induced melanogenesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells through activation of ERK. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 245, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, H.; Kondoh, H.; Ichihashi, M.; Hearing, V.J. Hearing approaches to identify inhibitors of melanin biosynthesis via the quality control of tyrosinase. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J. Determination of melanin synthetic pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, E8–E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiino, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Umezawa, K. Synthesis and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of novel N-hydroxybenzyl-N-nitrosohydroxylamines. Bioorg. Chem. 2003, 31, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Ho, M.L.; Chou, Y.T.; Chang, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, C.Z.; Chum, I.M. (−)-N-Formylanonaine from Michelia alba as a human tyrosinase inhibitor and antioxidant. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5241–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Sakeh, N.M.; Zareen, S.; Gul, S.; LoKM Ul-Haq, Z.; Shah, S.A.A.; Ahmad, S. Design and synthesis of chalcone derivatives as potent tyrosinase inhibitors and their structural activity relationship. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1085, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, H.P.; Smânia Ede, F.; Monache, F.D.; Smânia, A.J. Structure-activity relationship of antibacterial chalcones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 9790–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashita, K.; Kobori, M.; Yamaki, K.; Tsushida, T. Flavonoids inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in B16 melanoma 4A5 cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.R.; Sharma, S.; Mandal, S.; Goswami, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Majumder, H.K. Luteolin, an emerging anti-cancer flavonoid, poisons eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kadayat, T.; Kim, D.E.; Lee, E.S.; Park, P.H. TI-I-174, a synthetic chalcone derivative, suppresses nitric oxide production in murine macrophages via heme oxygenase-1 induction and inhibition of AP-1. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.H.; Wang, R.F.; Guo, S.Z.; Liu, B. An update on antitumor activity of naturally occurring chalcones. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 815621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Massiah, M.A.; Bozak, R.E.; Hicks, R.J.; Talalay, P. Potency of Michael reaction acceptors as inducers of enzymes that protect against carcinogenesis depends on their reactivity with sulfhydryl groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3404–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Son, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, H.P. Tyrosinase inhibitory prenylated flavonoids form Sophora flabescens. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1348–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.K.; Lee, W.H.; Jeong, D.M.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.S. Inhibitory effects of kurarinol, kuraridinol, and trifolirhizin from Sophora flavescens on tyrosinase and melanin synthesis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Takara, K.; Toyozato, T.; Wada, K. A novel bioactive chalcone of Morus australis inhibits tyrosinase activity and melanin biosynthesis in B16 melanoma cells. J. Oleo Sci. 2012, 61, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Ha, Y.M.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, S.R.; Jeong, H.O.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Song, Y.M.; Chun, P.; et al. De novo tyrosinase inhibitor: 4-(6,7-dihydro-5H-indeno[5,6-d]thiazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-diol (MHY1556). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4172–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kang, D.; Akter, J.; Uliah, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.Y. The tyrosinase inhibitory effects of isoxazolone derivatives with a (Z)-β-phenyl-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3882–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, M.J.; Park, Y.J.; Noh, S.G.; Lee, A.K.; Moon, K.M.; Lee, E.K.; Bang, E.J.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, S.J.; et al. A novel synthetic compound, (Z)-5-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene)-2-iminothiazolidin-4-one (MHY773) inhibits mushroom tyrosinase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, A.K.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Kang, D.; Jung, Y.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Moon, H.R. (2E,5E)-2,5-Bis(3-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzylidene) cyclopentanone exerts anti-melanogenesis and anti-wrinkle activities in B16F10 melanoma and Hs27 fibroblast cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Ha, Y.M.; Moon, K.M.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Jeong, H.O.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R.; et al. Anti-melanogenic effect of (Z)-5-(2,4-dihydroxybenzylidene) thiazolidine-2,4-dione, a novel tyrosinase inhibitor. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Moon, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Woo, Y.; Chung, K.W.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.; Chun, P.; Byun, Y.; et al. The inhibitory effect of a synthetic compound, (Z)-5-(2,4-dihydroxybenzylidene) thiazolidine-2,4-dione (MHY498), on nitric oxide-induced melanogenesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4332–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; An, H.J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, Y.R.; Son, S.; Kim, M.J.; et al. (Z)-5-(2,4-dihydroxybenzylidene)thiazolidine-2,4-dione prevents UVB-induced melanogenesis and wrinkle formation through suppressing oxidative stress in HRM-2 hairless mice. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2761463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.W.; Park, Y.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, M.H.; Ha, Y.M.; Uehara, Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Chun, P.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo anti-melanogenic activity of a newly synthesized strong tyrosinase inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-dihydroxybenzylidene)pyrrolidine-2,5-dione (3-DBP). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.K.; Park, Y.J.; Ha, Y.M.; Park, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, N.; Yoon, J.H.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. Characterization of a novel tyrosinase inhibitor, (2RS,4R)-2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (MHY384). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.H.; Kim, H.S. Synthesis of heterocyclic chalcone derivatives and their radical scavenging ability toward. Bull Korea Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2585–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.H.; Karki, R.; Lee, E.S.; Na, Y.; Kwon, Y. Synthesis and investigation of dihydroxychalcones as calpain and cathepsin inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2013, 51, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, Y.J.; Woo, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, M.H.; Lee, H.W.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. Benzylidene-linked thiohydantoin derivatives as inhibitors of tyrosinase and melanogenesis: Importance of the β-phenyl-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl functionality. Med. Chem. Comm. 2014, 9, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, B.T. Curcumin suppresses α-melanocyte stimulating hormone-stimulated melanogenesis in B16F10 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 26, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dixon, M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constant. Biochem. J. 1953, 55, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish-Bowden, A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem. J. 1974, 137, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, W.W.; Su, C.C.; Peng, H.Y.; Chou, S.T. Melaleuca quinquenervia essential oil inhibits-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanin production and oxidative stress in B16 melanoma cells. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koirala, P.; Seong, S.H.; Zhou, Y.; Shrestha, S.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Structure-activity relationship of the tyrosinase inhibitors kuwanon G, mulberrofuran G, and albanol B from Morus Species: A kinetics and molecular docking Study. Molecules 2018, 23, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.H.; Chiang, Y.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Liang, C.J.; Hsu, L.F.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, M.C.; Yen, F.L.; Lee, C.W. Eupafolin, a skin whitening flavonoid isolated from Phyla nodiflora, downregulated melanogenesis: Role of MAPK and Akt pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, N.; Vicanova, J.; Pavel, S. The hunt for natural skin whitening agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 5326–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.Y.; You, Y.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Hou, C.W.; Wu, C.S.; Wen, K.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Chiang, H.M. Sesamol inhibited melanogenesis by regulating melanin-related signal transduction in B16F10 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Pawelek, J. l-Tyrosine and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busca, R.; Ballotti, R. Cyclic AMP a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation. Pigment Cell Res. 2000, 13, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.M.; Son, Y.O.; Lee, S.A.; Jeon, Y.M.; Lee, J.C. Quercetin inhibits α-MSH-stimulated melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, D.; Han, I.O.; Oh, E.S. Melanocortin 1 receptor regulates melanoma cell migration by controlling syndecan-2 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19326–19335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaya, W.T.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Weijn, A.; Mes, J.J.; Fusetti, F.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structure of Agaricus bisporus mushroom tyrosinase: Identity of the tetramer subunits and interaction with tropolone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, M.L.; Greulich, J.D.; Hullinger, R.L.; Bertolotto, C.; Ballotti, R.; Andrisani, O.M. BMP-2 stimulates tyrosinase gene expression and melanogenesis in differentiated melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.J.; Ha, Y.M.; Kim, J.A.; Park, J.Y.; Ha, T.K.; Park, D.; Chun, P.; Park, N.H.; Moon, H.R.; Chung, H.Y. A novel synthesized tyrosinase inhibitor: (E)-2-((2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)diazenyl)phenyl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate as an azo-resveratrol analog. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (1a–h) are available from the authors. |



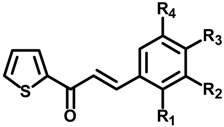
| Compounds | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | IC50 (μM) a | IC50 (μM) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | H | H | OH | H | 46.16 ± 0.55 | 60.05 ± 7.85 |
| 1b | H | OH | OH | H | 75.72 ± 2.46 | 103.44 ± 8.47 |
| 1c | OH | H | OH | H | 0.013 ± 0.64 | 0.93 ± 0.22 |
| 1d | H | OMe | OH | H | 98.78 ± 2.11 | >200 |
| 1e | H | OH | OMe | H | 17.44 ± 1.81 | 28.72 ± 1.98 |
| 1f | H | OMe | OH | OMe | 77.91 ± 8.74 | >200 |
| 1g | H | Br | OH | H | >200 | 112.09 ± 14.27 |
| 1h | H | Br | OH | Br | >200 | >200 |
| Kojic acid c | 22.84 ± 0.09 | 24.57 ± 0.23 |
| Inhibition Type a (Ki) b | ||
|---|---|---|
| l-Tyrosine | l-DOPA | |
| 1c | Competitive (5.01 nM) | Competitive (1.76 μM) |
| Kojic acid c | NT d | NT d |
| Binding Energy a (kcal/mol) | No. of H-Bond b | H-Bond Interacting b Residues | Van der Waals Bond Interaction Residues b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1c | −5.9 | 2 | ASN260, MET280 | MET257, VAL248, PHE264, VAL283, ALA286 |
| Kojic acid c | −4.2 | 2 | MET280 | HIS263 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.S.; Noh, S.G.; Park, Y.; Kang, D.; Chun, P.; Chung, H.Y.; Jung, H.J.; Moon, H.R. A Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, with Anti-Melanogenesis Properties in α-MSH and IBMX-Induced B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102725
Kim CS, Noh SG, Park Y, Kang D, Chun P, Chung HY, Jung HJ, Moon HR. A Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, with Anti-Melanogenesis Properties in α-MSH and IBMX-Induced B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules. 2018; 23(10):2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102725
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chang Seok, Sang Gyun Noh, Yujin Park, Dongwan Kang, Pusoon Chun, Hae Young Chung, Hee Jin Jung, and Hyung Ryong Moon. 2018. "A Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, with Anti-Melanogenesis Properties in α-MSH and IBMX-Induced B16F10 Melanoma Cells" Molecules 23, no. 10: 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102725
APA StyleKim, C. S., Noh, S. G., Park, Y., Kang, D., Chun, P., Chung, H. Y., Jung, H. J., & Moon, H. R. (2018). A Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitor, (E)-3-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-1-(thiophen-2-yl)prop-2-en-1-one, with Anti-Melanogenesis Properties in α-MSH and IBMX-Induced B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules, 23(10), 2725. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23102725