Discrimination of Chrysanthemum Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
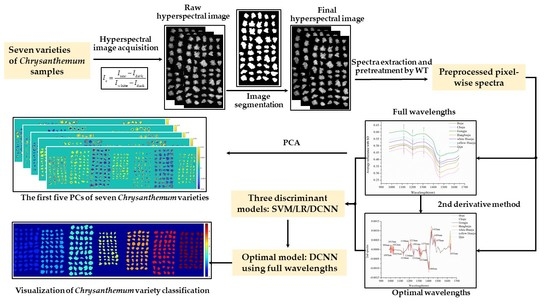
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overview of Spectra
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
2.3. Selection of Optimal Wavelengths
2.4. Discrimination Results of Different Models
2.5. Visualization of Chrysanthemum Variety Classification
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Hyperspectral Image Acquisition and Correction
4.3. Spectra Extraction and Pretreatment
4.4. Chemometrics Analysis
4.5. Discriminant Methods
4.5.1. Support Vector Machine
4.5.2. Logistic Regression
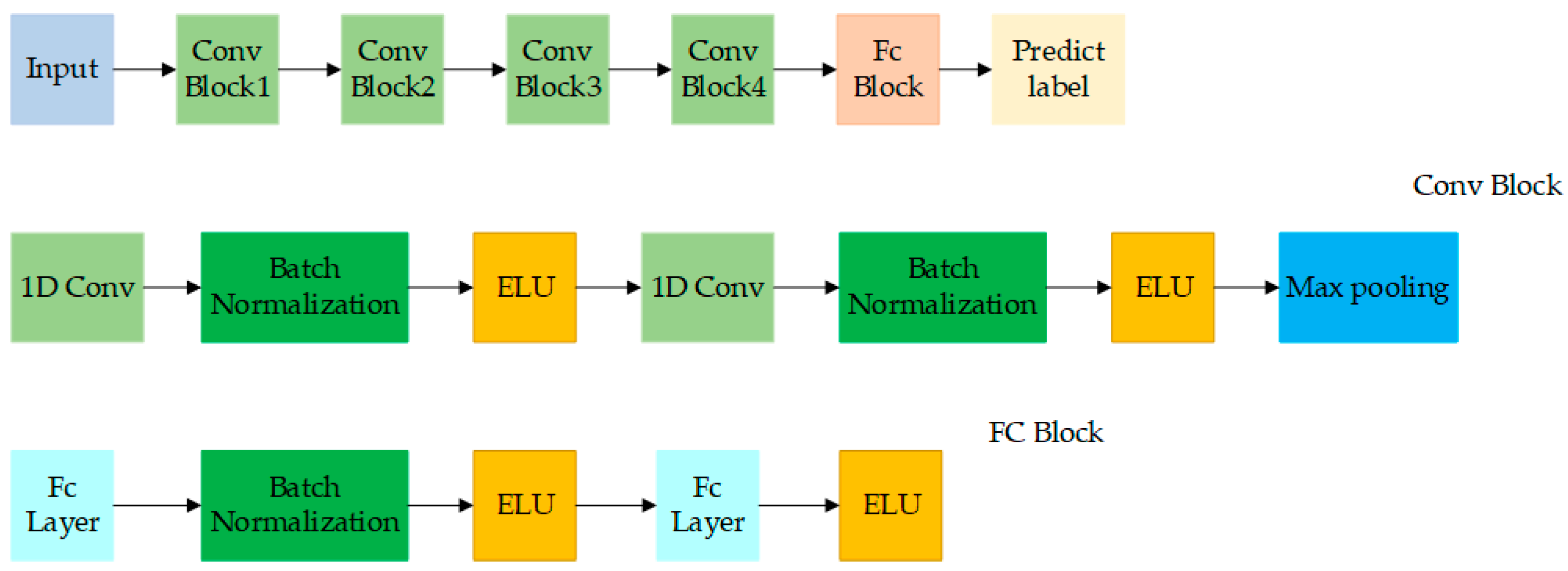
4.5.3. Deep Convolutional Neural Network
4.6. Chrysanthemum Varieties Visualization
4.7. Software
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, C.; Dong, Q.; Chen, H.; Cong, Q.; Ding, K. Structural characterization of a polysaccharide from Chrysanthemum morifolium flowers and its antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Chen, H. Enzymatic-assisted microwave extraction of total flavonoids from dud of Chrysanthemum indicum L. and evaluation of biological activities. Int. J. Food Eng. 2016, 12, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Kang, L.; Chen, S.; Ma, B.; Guo, B. Quantitative and qualitative analysis of flavonoids and phenolic acids in snow chrysanthemum (Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt.) by HPLC-DAD and UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS. Molecules 2016, 21, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zou, X.; Shen, T.; Shi, J.; Zhao, J.; Holmes, M. Determination of geographical origin and anthocyanin content of black goji berry (Lycium ruthenicum Murr.) using near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, S.; Knapič, M.; Žibrat, U.; Deleuran, L.; Gislum, R. Single seed near-infrared hyperspectral imaging in determining tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seed quality in association with multivariate data analysis. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 237, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yan, H.; Chen, C.; Yao, H.; Dai, J.; Chen, N. A rapid identification of four medicinal chrysanthemum varieties with near infrared spectroscopy. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley, M. Near-infrared spectroscopy and hyperspectral imaging: Non-destructive analysis of biological materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8200–8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Sun, D.; Zeng, X. Recent advances in wavelength selection techniques for hyperspectral image processing in the food industry. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 7, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, J.; Fernandes, A.; Barrenechea, E.; Silva, S.; Santos, V.; Gonçalves, N.; Paternain, D.; Jurio, A.; Melo-Pinto, P. Lamb muscle discrimination using hyperspectral imaging: Comparison of various machine learning algorithms. J. Food Eng. 2016, 174, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhu, Q. Classification of maize seeds of different years based on hyperspectral imaging and model updating. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 122, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Medeiros, E.; Pasquini, C.; Morello, C.; Galvão, R.; Araújo, M. Classification of individual cotton seeds with respect to variety using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 8498–8505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, P.; Geladi, P.; Fox, G.; Manley, M. Maize kernel hardness classification by near infrared (NIR) hyperspectral imaging and multivariate data analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 653, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pulido, F.; Barbin, D.; Sun, D.; Gordillo, B.; González-Miret, M.; Heredia, F. Grape seed characterization by NIR hyperspectral imaging. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 76, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Kucheryavskiy, S. Classification of maize kernels using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Plaza, A.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Wei, Z. Real-time implementation of the sparse multinomial logistic regression for hyperspectral image classification on GPUs. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1456–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Nie, P.; He, Y. Rice seed cultivar identification using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging and multivariate data analysis. Sensors 2013, 13, 8916–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Identification of coffee bean varieties using hyperspectral imaging: Influence of preprocessing methods and pixel-wise spectra analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, C. Extreme learning machine with composite kernels for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wei, L.; Zhang, F.; Li, H. Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification. J. Sens. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, C. Variety identification of single rice seed using hyperspectral imaging combined with convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jie, L.; Wang, S.; Qi, H.; Li, S. Classifying wheat hyperspectral pixels of healthy heads and Fusarium head blight disease using a deep neural network in the wild field. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, A.; Shi, Y.; Duan, Y. 3D convolutional neural networks for crop classification with multi-temporal remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, L.; Chu, B.; Zhang, C. Determination of total polysaccharides and total flavonoids in Chrysanthemum morifolium using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging and multivariate analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Peng, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Feng, X.; He, Y. Discrimination of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutants of rice seeds using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serranti, S.; Cesare, D.; Marini, F.; Bonifazi, G. Classification of oat and groat kernels using NIR hyperspectral imaging. Talanta 2013, 103, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, H.; Liu, F.; He, Y. Application of near-infrared hyperspectral imaging with variable selection methods to determine and visualize caffeine content of coffee beans. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.; Ferreira, M.; Salva, T. Chemometric models for the quantitative descriptive sensory analysis of Arabica coffee beverages using near infrared spectroscopy. Talanta 2011, 83, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restaino, E.; Fassio, A.; Cozzolino, D. Discrimination of meat patés according to the animal species by means of near infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics Discriminación de muestras de paté de carne según tipo de especie mediante el uso de la espectroscopia en el infrarrojo cercano y la quimiometria. J. Food 2011, 9, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chung, H.; Choi, H.; Ku, M. Rapid identification of petroleum products by near-infrared spectroscopy. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 1999, 20, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. Analysis of different Flos Chrysanthemum tea samples with the use of two-dimensional chromatographic fingerprints, which were interpreted by different multivariate methods. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Yan, L.; Hao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L. Discrimination of cultivars and determination of luteolin content of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. using multispectral imaging system. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yan, H.; Han, B. Rapid identification of three varieties of Chrysanthemum with near infrared spectroscopy. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014, 24, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; He, Y.; Zhou, W. Mid-infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics to detect Sclerotinia stem rot on oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) leaves. Plant Methods 2017, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroforakis, M.; Theodoridis, S. A geometric approach to support vector machine (SVM) classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2006, 17, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevert, D.; Unterthiner, T.; Hochreiter, S. Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (ELUs). arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07289. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |




| Models | Full Wavelengths | Optimal Wavelengths | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters 1 | Training | Testing | Parameters | Training | Testing | |
| SVM | (106, 10−5) | 99.83% | 94.02% | (107, 10−4) | 98.26% | 90.03% |
| LR | (L2, 100, liblinear) | 99.34% | 96.59% | (L2, 100, liblinear) | 94.35% | 85.75% |
| DCNN | (4, 32, 93) | 99.98% | 99.98% | (3, 32, 125) | 98.45% | 94.27% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, N.; Zhang, C.; Bai, X.; Du, X.; He, Y. Discrimination of Chrysanthemum Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Molecules 2018, 23, 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112831
Wu N, Zhang C, Bai X, Du X, He Y. Discrimination of Chrysanthemum Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Molecules. 2018; 23(11):2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112831
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Na, Chu Zhang, Xiulin Bai, Xiaoyue Du, and Yong He. 2018. "Discrimination of Chrysanthemum Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network" Molecules 23, no. 11: 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112831
APA StyleWu, N., Zhang, C., Bai, X., Du, X., & He, Y. (2018). Discrimination of Chrysanthemum Varieties Using Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Molecules, 23(11), 2831. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112831