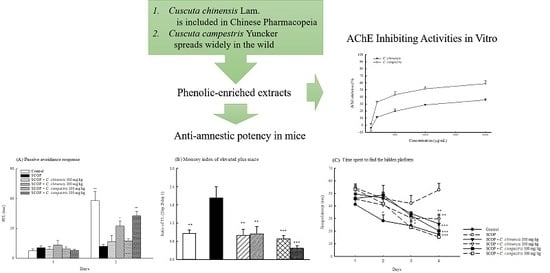
Cuscuta chinensis and C. campestris Attenuate Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit and Oxidative Damage in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of C. chinensis and C. campestris Extracts on Locomotor and Exploratory Activities in SCOP-Treated Mice
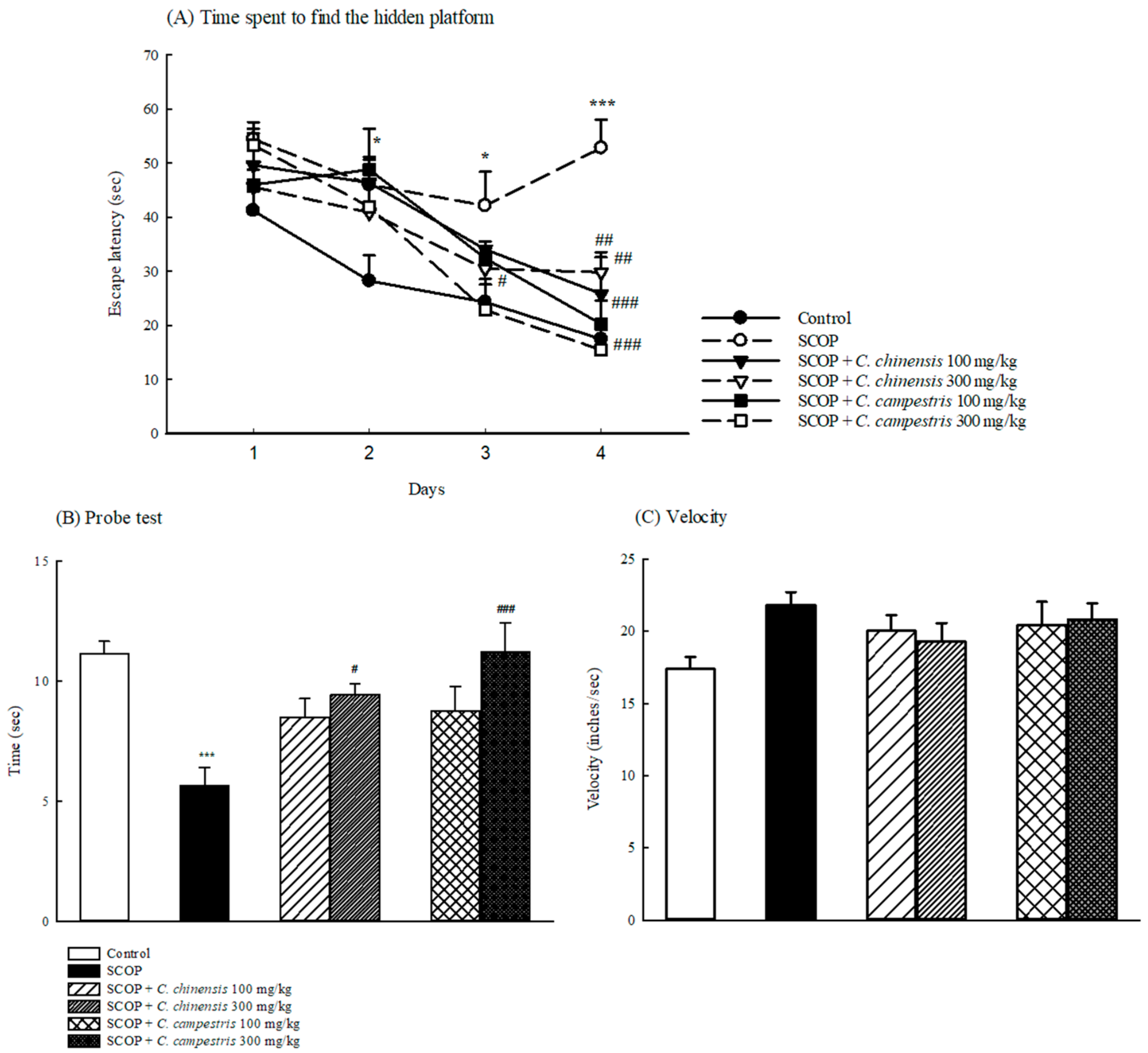
2.2. Effects of C. chinensis and C. campestris Extracts on Memory Deficits in SCOP-Treated Mice
2.3. Effects of C. chinensis and C. campestris Extracts on Brain Acetylcholinesterase Activities in SCOP-Treated Mice
2.4. Effects of C. chinensis and C. campestris Extracts on Brain Oxidative Damage in SCOP-Treated Mice
2.5. Effects of C. chinensis and C. campestris Extracts on Brain Cytokine Levels in SCOP-Treated Mice
2.6. AChE-Inhibiting Activities of C. chinensis and C. campestris In Vitro
2.7. Antioxidant Compounds and Activity of C. chinensis and C. campestris In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Plant Extract
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. HPLC Analysis
4.4. Animals
4.5. Drug Treatment and Group Division
4.6. Locomotor and Exploratory Tests
4.7. Passive Avoidance Response
4.8. Elevated Plus-Maze
4.9. MWM
4.10. Brain Tissue Preparation
4.11. Measurement of Brain AChE Activities
4.12. Measurement of Brain Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.13. Measurement of Brain IL-1β and TNF-α Levels
4.14. In Vitro AChE-Inhibiting Activity Assay
4.15. Measurement of Antioxidant Phytoconstituent Contents and Activity In Vitro
4.16. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| AChE | acetylcholinesterase |
| ACtCh | acetylthiocholine iodide |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| BF | basal forebrain |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DPPH | diphenyl picrylhydrazyl |
| DTNB | 5,5′-dithio-bis(2-nitrobenzoic) acid |
| GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| GR | glutathione reductase |
| GSH | glutathione |
| iso-OMPA | tetraisopropyl pyrophosphoramide |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| MWM | Morris water maze |
| NBT | nitroblue tetrazolium chloride |
| SCOP | scopolamine |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| TBA | thiobarbituric acid |
| TCA | trichloroacetic acid |
References
- Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid cascade hypothesis: Are we poised for success or failure? J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. 2), 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Alzheimer s disease and oxidative stress: A review. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, R.A.; Chyan, Y.J.; Andorn, A.C.; Poeggeler, B.; Robakis, N.K.; Pappolla, M.A. Increased expression but reduced activity of antioxidant enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 1999, 1, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querfurth, H.W.; LaFerla, F.M. Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodar, L.; Kaneto, H. Synaptic plasticity: Stairway to memory. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 68, 359–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhrer, T. Neurotransmitter systems involved in learning and memory in the rat: A meta-analysis based on studies of four behavioral tasks. Brain Res. Rev. 2003, 41, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaichi, H.; Oshima, Y.; Jarrard, L.E. Scopolamine impairs both working and reference memory in rats: A replication and extension. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1989, 34, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrod, K.; Buccafusco, J.J. An evaluation of the mechanism of scopolamine-induced impairment in two passive avoidance protocols. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1988, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.W.; Sung, S.H.; Han, J.S.; Jeon, W.K. Terminalia chebula extract prevents scopolamine-induced amnesia via cholinergic modulation and anti-oxidative effects in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, K.; Naziroglu, M.; Ovey, I.S.; Balaban, H. Selenium attenuates apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in the blood and brain of aged rats with scopolamine-induced dementia. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Tandon, S.; Xuan, T.D.; Nooreen, Z. A Review on phytoconstituents and biological activities of Cuscuta species. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 92, 772–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lee, M.S.; Chiu, Y.J.; Chao, W.K.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, M.K.; Peng, W.H. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Cuscuta chinensis seeds in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnapee, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Ge, A.H.; Donkor, P.O.; Gao, X.M.; Chang, Y.X. Cuscuta chinensis Lam.: A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 157, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Y.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Chae, S.W.; Park, Y.K. Effect of the semen extract of Cuscuta chinensis on inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Chen, C.J.; Wan, L.; Koizumi, A.; Chang, W.T.; Yang, M.J.; Lin, W.H.; Tsai, F.J.; Lin, M.K. Quercetin is increased in heat-processed Cuscuta campestris seeds, which enhances the seed’s anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities. Process. Biochem. 2001, 46, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Ye, H.; Wang, T. The protective mechanism of total flavonoids from Semen Cuscutae (TFSC) on learning-memory function in Alzheimer’s disease mice with hypoendocrinism. Acta Laser Biol. Sinica 2014, 23, 218–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Wang, G.M.; Zhai, H.Y. Effects of Cuscuta chinensis flavonoids on inflammatory response of brain tissue in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Zhongguo Yaofang 2013, 24, 979–982. [Google Scholar]
- Jakovljević, D.V.; Vrvić, M.M.; Vrbničanin, S.; Sarić‐Krsmanović, M. Phytochemical, free radical scavenging and antifungal profile of Cuscuta campestris Yunck. Chem. biodiversity 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, M.S.; Chang, W.T.; Tsai, J.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, M.K. Hepatoprotective effect of Cuscuta campestris Yunck. whole plant on carbon tetrachloride induced chronic liver injury in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Yan, Y.N.; Qiao, L.; Ni, X.M. Studies on chemical constituents of Cuscuta chinensis. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2002, 27, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, G.G.; Shi, W.; Liu, H.Y. The anti-aging effects of the extracts of Cuscuta chinensis in D-galactose-induced aging mice. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2015, 35, 5444–5446. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, H.; Du, S.M. Study on the anti-aging action of the extrects of Cuscuta chinensis in natural aging mice. Chin. Pharm. 2010, 21, 3667–3669. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Dong, L.F. Effect of the water extract of Cuscuta chinensis Lam. on memory impairment in cerebral ischemic rats. Chin. J. Behav. Med. Sci. 2006, 15, 681–682. [Google Scholar]
- Shiao, Y.J.; Su, M.H.; Lin, H.C.; Wu, C.R. Acteoside and isoacteoside protect amyloid beta peptide induced cytotoxicity, cognitive deficit and neurochemical disturbances in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.R.; Chang, C.L.; Hsieh, P.Y.; Lin, L.W.; Ching, H. Psoralen and isopsoralen, two coumarins of Psoraleae Fructus, can alleviate scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Budzynska, B.; Biala, G.; Boguszewska-Czubara, A. Scopolamine-Induced memory impairment is alleviated by xanthotoxin: Role of acetylcholinesterase and oxidative stress processes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Ramasamy, K.; Jaafar, S.M.; Majeed, A.B.; Mani, V. Total isoflavones from soybean and tempeh reversed scopolamine-induced amnesia, improved cholinergic activities and reduced neuroinflammation in brain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.L.; Wu, T.H.; Lin, L.T.; Lin, C.C. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of Cuscuta chinensis against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.H.; Jiang, B.; Bao, Y.M.; Li, D.X.; An, L.J. The protect effect of flavonoids from Cuscuta chinensis in PC12 cells from damage induced by H2O2. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2006, 29, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Kashchenko, N.I.; Chirikova, N.K.; Akobirshoeva, A.; Zilfikarov, I.N.; Vennos, C. Isorhamnetin and Quercetin Derivatives as Anti-Acetylcholinesterase Principles of Marigold (Calendula officinalis) Flowers and Preparations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedara, I.A.; Ego, V.C.; Subair, T.I.; Oyediran, O.; Farombi, E.O. Quercetin Improves Neurobehavioral Performance Through Restoration of Brain Antioxidant Status and Acetylcholinesterase Activity in Manganese-Treated Rats. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ademosun, A.O.; Oboh, G.; Bello, F.; Ayeni, P.O. Antioxidative Properties and Effect of Quercetin and Its Glycosylated Form (Rutin) on Acetylcholinesterase and Butyrylcholinesterase Activities. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha, I.C.; Jose, R.F.; Orlandi Pereira, L.; Pimenta, J.A.; Oliveira de Souza, I.A.; Reiser, R.; Moreno, H., Jr.; Marino Neto, J.; Paschoalini, M.A.; Faria, M.S. The role of nitric oxide in the emotional learning of rats in the plus-maze. Physiol. Behav. 2005, 84, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.R.; Chang, H.C.; Cheng, Y.D.; Lan, W.C.; Yang, S.E.; Ching, H. Aqueous Extract of Davallia mariesii Attenuates 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Oxidative Damage and Apoptosis in B35 Cells Through Inhibition of Caspase Cascade and Activation of PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β Pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |









| Contents of Antioxidant Compounds | Radical Scavenging Ability l-Ascorbic Acid Equivalent (μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids (mg quercetin equivalent/g) | Total phenolics (mg gallic acid equivalent/g) | ABTS | DPPH | |
| C. chinensis | 20.07 ± 0.22 | 76.78 ± 1.58 | 27.87 ± 3.46 | 11.18 ± 0.46 |
| C. campestris | 28.34 ± 0.95 | 65.11 ± 0.21 | 26.48 ± 3.26 | 10.80 ± 0.48 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, M.-K.; Lee, M.-S.; Huang, H.-C.; Cheng, T.-J.; Cheng, Y.-D.; Wu, C.-R. Cuscuta chinensis and C. campestris Attenuate Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit and Oxidative Damage in Mice. Molecules 2018, 23, 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123060
Lin M-K, Lee M-S, Huang H-C, Cheng T-J, Cheng Y-D, Wu C-R. Cuscuta chinensis and C. campestris Attenuate Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit and Oxidative Damage in Mice. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123060
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ming-Kuem, Meng-Shiou Lee, Hui-Chi Huang, Tun-Jen Cheng, Yih-Dih Cheng, and Chi-Rei Wu. 2018. "Cuscuta chinensis and C. campestris Attenuate Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit and Oxidative Damage in Mice" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123060
APA StyleLin, M. -K., Lee, M. -S., Huang, H. -C., Cheng, T. -J., Cheng, Y. -D., & Wu, C. -R. (2018). Cuscuta chinensis and C. campestris Attenuate Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficit and Oxidative Damage in Mice. Molecules, 23(12), 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123060