Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Neurotransmitters in the Brain Tissue of Alzheimer’s Disease Rats before and after Oral Administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HPLC-MS/MS Method Development and Optimization
2.1.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.1.2. Optimization of Mass Spectrometric Conditions
2.2. Morris Water Maze Testing
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Linearity and Lower Limit of Quantitation
2.3.2. Precision and Accuracy
2.3.3. Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.3.4. Stability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Standards
4.2. Animals
4.3. Instrumentation and chromatographic conditions
4.4. Preparation of the Xanthoceras Sorbifolia Bunge. Extract and Huperzine Administration Solution
4.5. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Calibration Curve Standards
4.6. Sample Preparation
4.7. Method Validation
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morinaga, A.; Ono, K.; Takasaki, J.; Ikeda, T.; Hirohata, M.; Yamada, M. Effects of sex hormones on Alzheimer’s disease-associated β-amyloid oligomer formation in vitro. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 228, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazin, T.; Ball, K.A.; Lu, H.; Park, H.; Ataeijannati, Y.; Gordon, T.H.; Poo, M.; Schaffer, V.D. Axonal and synaptic failure suppress the transfer of firing rate oscillations, synchrony and information during high frequency deep brain stimulation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 62, 86–99. [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chu, H.; Zhang, A.; Han, Y.; Lu, S.; Kong, L.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Metabolomics approach to explore the effects of Kai-Xin-San on Alzheimer’s disease using UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 50, 1015–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Kushwah, A.S.; Singh, R.; Farswan, M.; Kaur, R. Current therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1651–1654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Fu, Q.; Leung, K.W.; Wong, Z.C.F.; Choi, R.C.Y.; Tsim, K.W.K. The establishment of a sensitive method in determining different neurotransmitters simultaneously in rat brains by using liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppila, T.J.; Nikkola, T.; Ketola, R.A.; Kostiainen, R. Atmospheric pressure photoionization-mass spectrometry and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry of neurotransmitters. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 41, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J.; Lv, C.; Liu, R.; Zhao, L.; Xu, H.; Chena, X.; Li, Q. Rapid analysis of neurotransmitters in rat brain using ultra-fast liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry: Application to a comparative study in normal and insomnic rats. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raúl, G.-D.; Tamara, G.-B.; José, L.G.-A. Metabolite profiling for the identification of altered metabolic pathways in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharma. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; He, B.; Sui, Z.; Xu, H.; Yin, Y.; Liu, R.; Bi, K. Determination of catecholamines and their metabolites in rat urine by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the study of identifying potential markers for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Hou, S.L.; Su, M.; Yang, M.F.; Shen, S.H.; Jiang, G.M.; Qi, D.M.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, G.S. Major energy plant and their potential for bioenergy development in China. Environ. Manage 2010, 46, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.M.; Ma, K.; Du, X.H.; Li, F.L. Advances in Research on Xanthoceras sorbifolia. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2002, 19, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Nakamura, N.; Hattori, M.; Kakuda, H.; Qiao, J.; Yu, H. Inhibitory effects on HIV-1 protease of constituents from the wood of Xanthoceras sorbifolia. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.l.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Research progress in the chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. J. Shenyang Pharma. Univ. 2004, 21, 472–475. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.J.; Takeda, T.; Ogihara, Y.; Iitaka, Y. Studies on the constituents of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. II. Major sapogenol and a prosapogenin from the fruits of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1984, 32, 3378–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Zou, L.B.; Jiao, Q.; Chi, T.Y.; Ji, X.F.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.H. Xanthoceraside attenuates learning and memory deficits via improving insulin signaling in STZ-induced AD rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 543, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Wang, L.H.; Ji, X.F.; Chi, T.Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, Q.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zou, L.B. Xanthoceraside rescues learning and memory deficits through attenuating beta-amyloid deposition and tau hyperphosphorylation in APP mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 573, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y. Simultaneous determination of catecholamines and polyamines in PC-12 cell extracts by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography with ultraviolet absorbance detection. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 805, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenbrand, R.; Garg, U. Quantitation of homovanillic acid (HVA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) in urine using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 603, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Walaszczyk, E.J.; Li, K.; Chung-Davidson, Y.W.; Li, W. High-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and ultra-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of indoleamine neurotransmitters and their metabolites in sea lamprey plasma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 721, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kano, H.; Niranjan, A.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, L.D. Stereotactic radiosurgery for pituitary metastases. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Vegt, B.J.; Lieuwes, N.; Cremers, T.I.; de Boer, S.F.; Koolhaas, J.M. Cerebrospinal fluid monoamine and metabolite concentrations and aggression in rats. Horm. Behav. 2003, 44, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa, T.; Al-Dirbashi, O.Y.; Fukushima, T. Derivatization reageneurotransmitters in liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for biomedical analysis. Drug Discov. Ther. 2007, 1, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Graham, K.S.; de Vries, E.G.; Kema, I.P. Urinary 5-HIAA measurement using automated on-line solid-phase extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 868, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deibel, S.H.; Weishaupt, N.; Regis, A.M.; Honga, N.S.; Keeley, R.J.; Baloga, R.J.; Byea, C.M.; Himmler, S.M.; Whitehead, S.N.; McDonald, R.J. Subtle learning and memory impairment in an idiopathic rat model of Alzheimer’s disease utilizing cholinergic depletions and β-amyloid. Brain Res. 2016, 1646, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Di, X.; Li, W.; Li, Q.; Bi, K. A UHPLC–TOF/MS method based metabonomic study of total ginsenosides effects on Alzheimer disease mouse model. J. Pharma. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 115, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.J.; Guillemin, G.J.; Teipel, S.J.; Buerger, K.; Hampel, H. Increased 3-Hydroxykynurenine serum concentrations differentiate Alzheimer’s disease patieneurotransmitters from controls. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 263, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekkes, D.; Van Der Cammen, T.J.M.; Van Loon, C.P.M.; Verschoor, C.; Van Harskamp, F.; De Koning, I.; Schudel, W.J.; Pepplinkhuizen, L. Abnormal amino acid metabolism in patieneurotransmitters with early stage Alzheimer dementia. J. Neural Transm. 1998, 105, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eduardo, L.K.; Carolina dos, S.P.; Luiz Carlos, K.-J.; Henriques, A.T. Alkaloids as a source of potential anticholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharma. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1701–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Q.; Tan, C.H.; Zhu, D.Y.; Gang, D.R. A survey of potential huperzine a natural resources in China: The huperziaceae. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraoanu, L.E.; Steinert, G.; Klaczinski, J.; Becker-Röck, M.; Bytyqi, A.; Layer, P.G. On functions of cholinesterases during embryonic development. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 30, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duysen, E.G.; Lockridge, O. Phenotype comparison of three acetylcholinesterase knockout strains. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 30, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, M.X.; García-Ayllón, M.S.; Calero, M.; Sáez-Valero, J. Altered glycosylation of acetylcholinesterase in the creutzfeldt-jakob cerebrospinal fluid. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2006, 30, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation (updated). Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/UCM070107.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2018).
- Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en GB/document library/Scientific guideline/2011/08/WC500109686.pdf (accessed on 29 October 2018).
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are all available from the authors. |

| Analyte | Q1 Mass (m/z) | Q3 Mass (m/z) | DP (V) | EP (V) | CE (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | 154.1 | 137.2 | 37 | 10 | 13 | 8 |
| Norepinephrine | 170.1 | 152.2 | 33 | 5 | 11 | 9 |
| Acetylcholine | 146.2 | 87.2 | 52 | 3 | 20 | 4 |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine | 177.1 | 160.2 | 43 | 10 | 14 | 10 |
| Glutamic acid | 148.2 | 84.1 | 41 | 10 | 24 | 15 |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 104.2 | 87.1 | 26 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| l-Tryptophan | 205.2 | 188.0 | 40 | 4 | 14 | 12 |
| Aspartic acid | 134.0 | 74.0 | 38 | 9 | 20 | 13 |
| Analyte | Concentration Range (ng mg−1) | Regression Equation (r) (10−4) | LLOQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (RE%) | Precision (RSD%) | |||
| Dopamine | 30.00–3000 | y = 6.247x − 170.1 (0.9949) | 8.4 | 5.0 |
| Norepinephrine | 40.00–4000 | y = 1.231x − 6.498(0.9950) | −6.2 | 3.3 |
| Acetylcholine | 30.00–3000 | y = 6.363x − 1.825(0.9926) | 3.9 | 1.8 |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine | 20.00–2000 | y = 12.42x − 94.77 (0.9949) | −11.3 | 13.5 |
| Glutamic acid | 0.5000–50.00 | y = 259.3x − 18.57 (0.9914) | 4.9 | 7.2 |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 30.00–3000 | y = 136.9x − 1177 (0.9920) | 7.8 | 4.8 |
| l-Tryptophan | 0.5000–50.00 | y = 983.3x − 106.3 (0.9912) | −2.2 | 6.6 |
| Aspartic acid | 30.00–3000 | y = 8.054x − 149.6 (0.9951) | 4.8 | 10.2 |
| Analytes | Conc (ng mg−1) | Intra-Day RSD% | Inter-Day RSD% | Accuracy RE% | Recovery (Mean ± SD%) | IS-Normalized MF (RSD%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | 60 | 5.9 | 3.4 | 5.1 | 87.6 ± 4.7 | 5.4 |
| 375 | 5.7 | 9.2 | 0.3 | 82.0 ± 4.9 | 7.6 | |
| 2400 | 10.1 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 79.45 ± 1.24 | 1.0 | |
| Norepinephrine | 80 | 11.5 | 8.4 | 11.7 | 82.3 ± 6.8 | 8.7 |
| 500 | 9.2 | 3.8 | −4.3 | 66.94 ± 7.40 | 9.2 | |
| 3200 | 2.2 | 7.2 | −2.8 | 71.97 ± 0.78 | 7.2 | |
| Acetyl choline | 60 | 8.7 | 11.1 | −10.1 | 70.62 ± 2.61 | 3.3 |
| 375 | 11.4 | 5.9 | 9.7 | 73.06 ± 4.92 | 3.7 | |
| 2400 | 10.0 | 0.9 | 11.6 | 65.25±4.09 | 6.5 | |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine | 40 | 10.4 | 8.8 | −10.4 | 83.3 ± 5.3 | 9.7 |
| 250 | 9.6 | 1.7 | 7.1 | 85.2 ± 7.2 | 0.4 | |
| 1600 | 4.6 | 8.4 | −5.1 | 77.12 ± 2.27 | 10.1 | |
| Glutamic acid | 1 | 11.4 | 5.6 | 8.4 | 82.8 ± 7.6 | 5.9 |
| 6.25 | 2.9 | 11.0 | 6.5 | 67.00 ± 4.87 | 6.9 | |
| 40 | 5.5 | 7.1 | 3.7 | 79.92 ± 0.77 | 4.5 | |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 60 | 4.5 | 3.2 | −11.5 | 84.1 ± 0.9 | 7.9 |
| 375 | 1.6 | 6.6 | −10.3 | 69.53 ± 5.5 | 6.3 | |
| 2400 | 3.7 | 9.3 | 5.7 | 73.44 ± 8.83 | 10.7 | |
| l-Tryptophan | 1 | 3.8 | 5.4 | −5.1 | 81.2 ± 6.7 | 3.6 |
| 6.25 | 6.0 | 7.9 | 9.6 | 81.1 ± 6.4 | 10.5 | |
| 40 | 4.4 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 67.70 ± 2.64 | 5.0 | |
| Aspartic acid | 60 | 9.0 | 11.1 | 4.8 | 77.97 ± 1.40 | 9.9 |
| 375 | 6.1 | 7.7 | −11.9 | 85.8 ± 7.3 | 1.4 | |
| 2400 | 7.1 | 6.7 | 0.9 | 72.90 ± 7.62 | 0.8 |
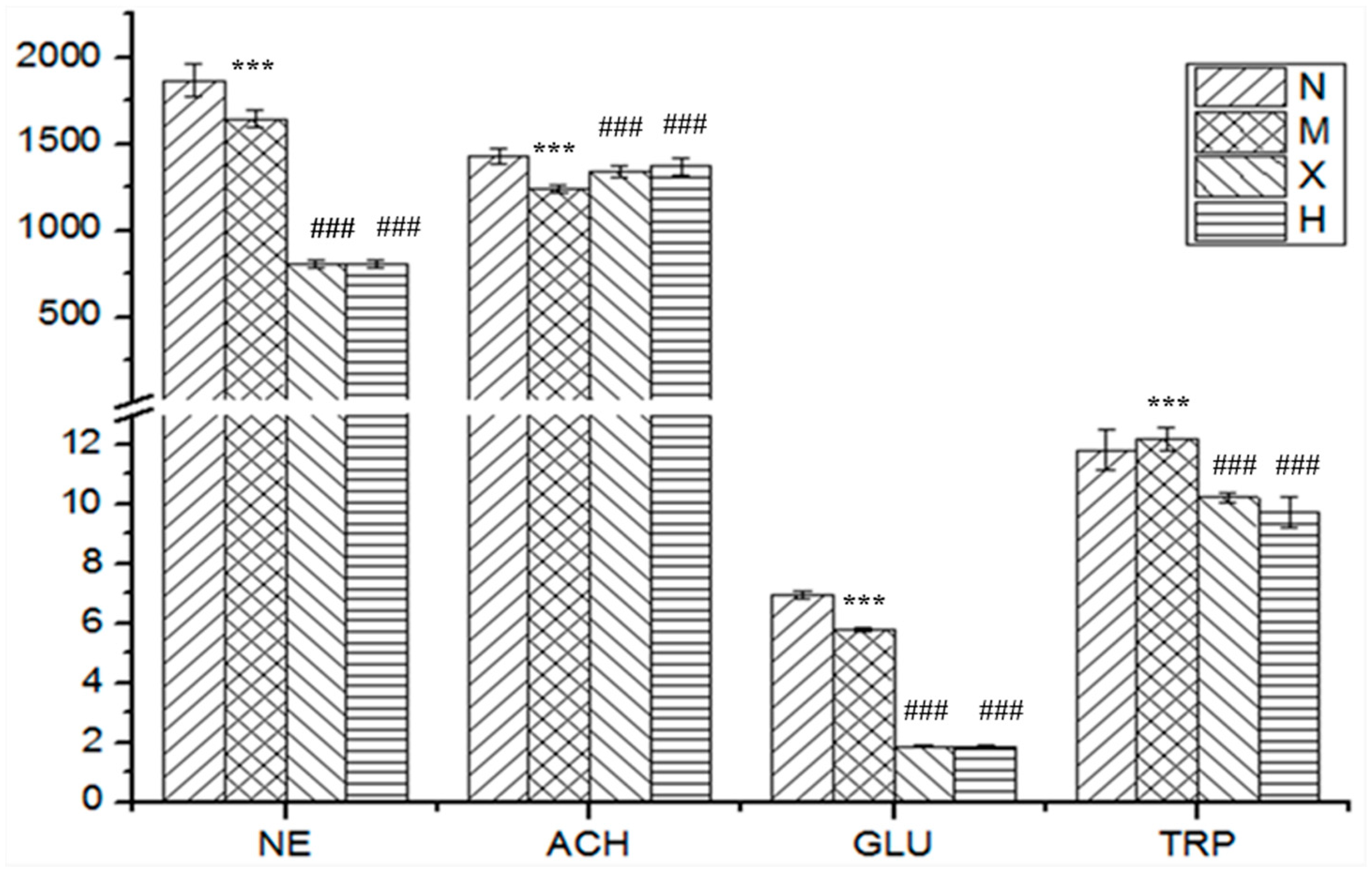
| Analytes | Group N | Group M | Group X | Group H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | 1132 ± 57 | 1157 ± 60 | 1111 ± 67 | 1084 ± 69 |
| Norepinephrine | 1868 ± 95 | 1601 ± 51 *** | 808 ± 20 ### | 807 ± 21 ### |
| Acetylcholine | 1431 ± 47 | 1195 ± 21 *** | 1340 ± 31 ### | 1371 ± 49 ### |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine | 305.0 ± 61.1 | 268.5 ± 54.9 | 283.8 ± 78.7 | 248.3 ± 42.3 |
| Glutamic acid | 6.977 ± 0.137 | 5.370 ± 0.068 *** | 1.866 ± 0.045 ### | 1.829 ± 0.060 ### |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid | 618.2 ± 163.6 | 644.6 ± 128.5 | 494.4 ± 54.2 | 514.7 ± 70.1 |
| l-Tryptophan | 11.83 ± 0.67 | 13.56 ± 0.38 *** | 10.23 ± 0.18 ### | 9.73 ± 0.50 ### |
| Aspartic acid | 533.2 ± 47.7 | 577.6 ± 65.7 | 635.3 ± 84.2 | 677.5 ± 83.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Li, Q.; Bi, K. Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Neurotransmitters in the Brain Tissue of Alzheimer’s Disease Rats before and after Oral Administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Molecules 2018, 23, 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123111
Sun Z, Li Q, Bi K. Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Neurotransmitters in the Brain Tissue of Alzheimer’s Disease Rats before and after Oral Administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123111
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zheng, Qing Li, and Kaishun Bi. 2018. "Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Neurotransmitters in the Brain Tissue of Alzheimer’s Disease Rats before and after Oral Administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123111
APA StyleSun, Z., Li, Q., & Bi, K. (2018). Rapid HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Analysis of Neurotransmitters in the Brain Tissue of Alzheimer’s Disease Rats before and after Oral Administration of Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge. Molecules, 23(12), 3111. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123111





