Chemical Profiling of Lobelia chinensis with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF MS) Reveals Absence of Lobeline in the Herb
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chemicals and Solvents
2.3. Sample Extraction
2.4. HPLC/Q-TOF MS Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
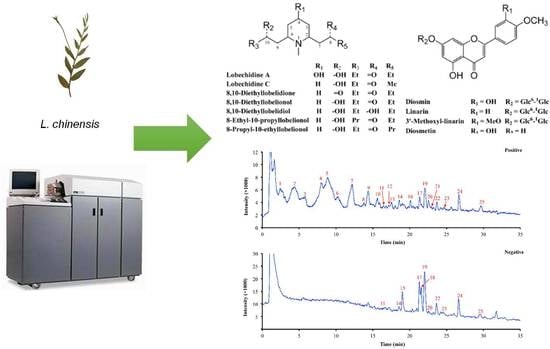
3.1. HPLC/Q-TOF MS Analysis of the Chemical Constituents of L. Chinensis
3.2. Investigation of Lobeline in L. Chinensis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Z.Z.; Xiao, P.G. Lobelia chinensis Lour. In Encylopedia of Medicinal Plants; World Publishing Corporation: Beijing, China, 2007; Volime 2, pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pharmacopoeia Commission. Lobeliae chinensis Herbal. In Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010; Volime 1, p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Bao, W.R.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L.; Ge, Z.; Lu, A.P.; Wang, S.C.; Han, Q.B. Chemical structure and immunomodulating activities of an α-glucan purified from Lobelia chinensis Lour. Molecules 2016, 21, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.W.; Chen, W.R.; Zhang, J.M.; Long, X.Y.; Wang, Y.T. Lobelia chinensis: Chemical constituents and anticancer activity perspective. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.F.; Guo, F.; Yan, C. Two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry for the analysis of Lobelia chinensis Lour. using an ESI/APCI multimode ion source. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 2388–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, H.; Shimoumura, K.; Ishimaru, K. Polyacetylenes in hairy root cultures of Lobelia chinensis Lour. Plant Physiol. 1995, 146, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibano, M.; Tsukamoto, D.; Masuda, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Kusano, G. Two new pyrrolidine alkaloids, radicamines A and B, as inhibitors of glucosidase from Lobelia chinensis LOUR. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1362–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Shen, T.; Zhao, L.J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, H.X.; Ren, D.M. Chemical constituents of Lobelia chinensis. Fitoterapia 2014, 93, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felpin, F.X.; Lebreton, J. History, chemistry and biology of alkaloids from Lobelia Inflata. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 10127–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinszki, L.; Ludányi, K.; Szöke, E. LC-DAD and LC-MS-MS analysis of piperidine alkaloids of Lobelia inflata L. (in vitro and in vivo). Chromatographia 2008, 68, S27–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Mass spectrometry-driven drug discovery for development of herbal medicine. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, J.; Yang, M. Simultaneous analysis of iridoid glycosides and anthraquinones in morinda officinalis using UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS and UPLC-Q/TOF-MSE. Molecules 2018, 23, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammat, A.; Yili, A.; Aisa, H.A. Rapid quantification and quantitation of alkaloids in Xinjiang Fritillaria by ultra performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Molecules 2017, 22, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donovan, D.G.; Long, D.J.; Forde, E.; Geary, P. The biosynthesis of Lobelia alkaloids. Part III. Intermediates in the biosynthesis of lobeline; biosynthesis of 8,10-diethyl-lobelidione. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1975, 5, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschesche, R.; Kometani, K.; Kowitz, F.; Snatzke, G. Über die Alkaloide aus Lobelia syphilitica L. I. Chem. Ber. 1961, 94, 3327–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardin, T.; Piasentier, E.; Barnaba, C.; Larcher, R. Targeted and untargeted profiling of alkaloids in herbal extracts using online solid-phase extraction and high-resolution mass spectrometry (Q-Orbitrap). J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Q.; Leung, A.K.M.; Chan, C.L.; Su, T.; Li, W.D.; Li, S.M.; Fong, D.W.F.; Yu, Z.L. UHPLC UHD Q-TOF MS/MS analysis of the impact of sulfur fumigation on the chemical profile of Codonopsis Radix (Dangshen). Analyst 2014, 139, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Hou, Z.; Lou, H.; Ren, D. Chiral separation of two diastereomeric pairs of enantiomers of novel alkaloid-lignan hybrids from Lobelia chinensis and determination of the tentative absolute configuration. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1311, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Jain, L.; Pandey, V.B. Flavonoids of Abies pindrow leaves. Fitoterapia 1996, 67, 477. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Shi, R.B.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dai, Y. Studies on chemical constituents of flavones from Lobelia chinensis Lour. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2009, 32, 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Philipov, S.; Istatkova, R.; Ivanovska, N.; Denkova, P.; Tosheva, K.; Navas, H.; Villegas, J. Phytochemical study and antiinflammatory properties of Lobelia Iaxiflora L. Z. Naturforsch. C 1998, 53, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinszki, L.; Szöke, E. HPLC-ESI-MS/MS of brain neurotransmitter modulator lobeline and related piperidine alkaloids in Lobelia inflata L. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tan, X.; Li, J.T.; Yang, J. Extraction of alkaloids from Lobelia chinensis Lour. and their inhibitory effects on growth of stomach cancer cells. J. China West Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 28, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, P.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Kuo, Y.C.; Leu, Y.L. Chemical constituents from Lobelia chinensis and their anti-virus and anti-inflammatory bioactivities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciolino, H.P.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Yeh, G.C. Diosmin and diosmetin are agonists of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor that differentially affect cytochrome P450 1A1 activity. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Ramírez, T.A.; Lastra, A.; Bye, R. A comparative study of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of pectolinarin isolated from Cirsium subcoriaceum and linarin isolated from Buddleia cordata. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnaj, M.I.; Patrick, G.S.; Creasy, K.R.; Martin, B.R. Pharmacology of lobeline, a nicotinic Receptor ligand. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 282, 410–419. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Lobelia chinensis herb are available from the authors. |





| Sample Number | Origin |
|---|---|
| LC-01 | Zhuzhou, Huan |
| LC-02 | Zhuzhou, Huan |
| LC-03 | Jiujiang, Jiangxi |
| LC-04 | Qingyuan, Guangdong |
| LC-05 | Yizhou, Guangxi |
| LC-06 | Yizhou, Guangxi |
| LC-07 | Chengdu, Sichuan |
| LC-08 | Chengdu, Sichuan |
| LC-09 | Lianqiao, Hunan |
| LC-10 | Chengdu, Sichuan |
| Peak No. | tR (min) | Identification | Chemical Formula | Positive Ionization Mode | Negative Ionization Mode | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | MS/MS Fragments | Error (ppm) | m/z | MS/MS Fragments | Error (ppm) | |||||
| 1 | 2.5 | lobechidine A | C14H27NO3 | [M + H]+ 258.2052 | 58.1, 94.1, 96.1, 150.1, 168.1, 184.1, 240.2 | −4.6 | − | − | − | [8] |
| 2 | 4.3 | lobechidine C | C13H25NO2 | [M + H]+ 228.1965 | 96.1, 98.1, 138.1, 152.1, 156.1, 170.2, 210.2 | 0.8 | − | − | − | [8] |
| 3 | 5.4 | lobechidine C | C13H25NO2 | [M + H]+ 228.1962 | 96.1, 98.1, 152.1, 154.1, 156.1, 170.2, 210.2 | 1.6 | − | − | − | [8] |
| 4 | 8.1 | 8,10−diethyllobelidione | C14H25NO2 | [M + H]+ 240.1951 | 58.1, 96.1, 116.1, 168.1 | −3.0 | − | − | − | [14] |
| 5 | 8.8 | 8,10−dietheyllobelionol | C14H27NO2 | [M + H]+ 242.2132 | 96.1, 98.1, 152.1, 170.2, 224.2 | 7.1 | − | − | − | [15] |
| 6 | 10.2 | 8,10−diethyllobelidiol | C14H29NO2 | [M + H]+ 244.2261 | 81.1, 98.1, 152.1, 154.1, 170.1, 226.2 | −4.2 | − | − | − | [16] |
| 7 | 12.1 | 8,10−dietheyllobelionol | C14H27NO2 | [M + H]+ 242.2106 | 96.1, 98.1, 152.1, 168.1, 170.2, 224.2 | −3.7 | − | − | − | [15] |
| 8 | 13.8 | 8,10−diethyllobelidiol | C14H29NO2 | [M + H]+ 244.2265 | 98.1, 152.1, 154.2, 170.2, 226.2 | −2.5 | − | − | − | [16] |
| 9 | 14.3 | 8,10−dietheyllobelionol | C14H27NO2 | [M + H]+ 242.2098 | 58.1, 116.1 | −6.7 | − | − | − | [15] |
| 10 | 15.6 | 8−ethyl−10−propyllobelionol | C15H29NO2 | [M + H]+ 256.2269 | 96.1, 98.1, 166.2, 184.2, 238.2 | −0.7 | − | − | − | − |
| 11 | 16.4 | demethyllobechinenoid glucoside | C34H41NO12 | [M + H]+ 656.2699 | 137.1, 166.1, 175.1, 265.1, 285.1, 297.1, 311.1, 315.1, 323.1, 341.1, 464.2 | −0.4 | [M − H]− 654.2552 | − | 1.1 | − |
| 12 | 17.1 | 8−propyl−10−ethyllobelionol | C15H29NO2 | [M + H]+ 256.2265 | 96.1, 98.1, 152.1, 170.2, 182.2, 238.2 | −2.2 | − | − | − | − |
| 13 | 17.5 | 8−ethyl−10−propyllobelionol | C15H29NO2 | [M + H]+ 256.2272 | 96.1, 98.1, 166.2, 168.1, 184.2, 238.2 | 0.4 | − | − | − | − |
| 14 | 18.5 | lobechinenoid glucoside | C35H43NO12 | [M + H]+ 670.2863 | 137.1, 175.1, 180.1, 265.1, 285.1, 297.1, 311.1, 315.1, 323.1, 341.1, 478.2 | 0.7 | [M − H]− 668.2691 | − | −1.6 | − |
| 15 | 19.0 | unknown | − | − | − | − | 401.1744 | 59.0, 71.0, 89.0, 101.0, 113.0, 119.0, 123.1, 159.0, 177.1, 221.1 | − | − |
| 16 | 20.0 | demethyllobechinenoid | C28H31NO7 | [M + H]+ 494.2177 | 137.1, 166.1, 175.1, 265.1, 285.1, 297.1, 311.1, 315.1, 323.1, 341.1, 464.2 | 0.8 | [M − H]− 492.2040 | − | 4.8 | − |
| 17 | 21.3 | lobetyolinin | C26H38O13 | [M + H]+ 559.2396 * [M + NH4]+ 576.2637 * | 155.1, 199.1, 217.1, 397.2 | 1.9 | [M − H]− 557.2223 [M + Cl]− 593.1975 [M + HCOO]− 603.2279 * | 59.0, 71.0, 89.0, 101.0, 113.0, 119.0, 143.0, 161.1, 179.1, 221.1 | −1.0 | [4,5,6] |
| 18 | 21.5 | nonanedioic acid | C9H16O4 | − | − | − | [M − H]− 187.0957 | 97.1, 125.1, 126.1, 169.1 | −4.4 | [17] |
| 19 | 22.0 | diosmin | C28H32O15 | [M + H]+ 609.1812 | 301.1, 463.1 | −0.3 | [M − H]− 607.1662 | 284.0, 299.1 | 0.7 | [4,5] |
| 20 | 22.5 | lobechinenoid | C29H33NO7 | [M + H]+ 508.2336 | 137.1, 151.1, 180.1, 265.1, 285.1, 297.1, 311.1, 315.1, 323.1, 341.2, 478.2 | 1.2 | [M − H]− 506.2180 | − | 1.3 | [18] |
| 21 | 22.9 | unknown | − | 679.5180 | 100.1, 182.2, 209.2, 226.2, 326.3, 336.2, 435.3, 452.4, 661.5 | − | − | − | − | − |
| 22 | 23.6 | lobetyolin | C20H28O8 | [M + H]+ 397.1852 [M + NH4]+ 414.2062 * [M + Na]+ 419.1627 | 129.1, 155.1, 199.1, 217.1 | −1.2 | [M − H]− 395.1725 [M + Cl]− 431.1602 [M + HCOO]− 441.1884 * | 59.0, 71.0, 89.0, 113.0, 119.0, 143.1, 159.1, 185.1 | 6.2 | [4,5,6] |
| 23 | 24.6 | 3’-methoxyl-linarin | C29H34O15 | [M + H]+ 623.1986 | 315.1, 477.2 | 2.5 | [M − H]− 621.1826 [M + Cl]− 657.1519 [M + HCOO]− 667.1775 | − | 1.9 | [19] |
| 24 | 26.6 | linarin | C28H32O14 | [M + H]+ 593.1868 | 285.1, 447.1 | 0.5 | [M − H]− 591.1722 [M + Cl]− 627.1536 * [M + HCOO]− 637.1788 | 268.1, 283.1 | 2.3 | [4,5] |
| 25 | 29.6 | diosmetin | C16H12O6 | [M + H]+ 301.0708 | 153.0, 229.1, 258.1, 286.1 | 0.4 | [M − H]− 299.0560 | 284.0 | 3.3 | [20] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Cheung, H.-Y. Chemical Profiling of Lobelia chinensis with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF MS) Reveals Absence of Lobeline in the Herb. Molecules 2018, 23, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123258
Wang H, Li Y, Huang Y, Zhao C, Cheung H-Y. Chemical Profiling of Lobelia chinensis with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF MS) Reveals Absence of Lobeline in the Herb. Molecules. 2018; 23(12):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123258
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haixing, Yuanyuan Li, Yeqing Huang, Chunyan Zhao, and Hon-Yeung Cheung. 2018. "Chemical Profiling of Lobelia chinensis with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF MS) Reveals Absence of Lobeline in the Herb" Molecules 23, no. 12: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123258
APA StyleWang, H., Li, Y., Huang, Y., Zhao, C., & Cheung, H.-Y. (2018). Chemical Profiling of Lobelia chinensis with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/Q-TOF MS) Reveals Absence of Lobeline in the Herb. Molecules, 23(12), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23123258