In Silico and in Vitro-Guided Identification of Inhibitors of Alkylquinolone-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
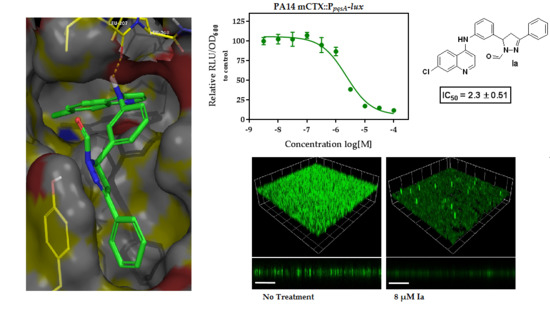
2.1. In Silico Virtual Screening for PqsR Antagonists
2.2. Whole Cell Biosensor Reporter Screening for PqsR Inhibitors
2.3. Impact of PqsR Antagonists on Pyocyanin Production
2.4. Impact of Hit Compounds on Alkylquinolone Production
2.5. Effect of PqsR Antagonists on Biofilms
2.6. Determination of the Plasma and Hepatic Stability of Selected Quinolone Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Molecular Docking
4.1.1. Preparation of Protein and Receptor Grid Generation
4.1.2. Ligand Preparation
4.1.3. Molecular Docking
4.2. Bacterial strains and growth conditions
4.3. Biosensor Reporter Assay
4.4. Pyocyanin Quantification
4.5. LCMS-MS Alkyl Quinoline Quantification
4.6. Biofilms
4.7. Determination of Plasma Stablity
4.8. Determination of Hepatic Stability
4.9. Data Analysis and Figure Preparation
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marston, H.D.; Dixon, D.M.; Knisely, J.M.; Palmore, T.N.; Fauci, A.S. Antimicrobial Resistance. JAMA 2016, 316, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.L.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum-sensing network architectures. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 197–222. [Google Scholar]
- Reuter, K.; Steinbach, A.; Helms, V. Interfering with Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P. Strategies for inhibiting quorum sensing. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2017, 1, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampioni, G.; Leoni, L.; Williams, P. The art of antibacterial warfare: Deception through interference with quorum sensing-mediated communication. Bioorg. Chem. 2014, 55, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellatly, S.L.; Hancock, R.E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New insights into pathogenesis and host defenses. Pathog. Dis. 2013, 67, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potron, A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Emerging broad-spectrum resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and epidemiology. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, M.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Gross, J.; Spring, D.R.; Sams, T. Ligand binding kinetics of the quorum sensing regulator PqsR. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 4433–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, J.T.; Gross, J.; Baker, Y.R.; Spring, D.R.; Welch, M. A new Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) binding partner: MexG. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Krishnan, G.; Goumnerov, B.; Tsongalis, J.; Tompkins, R.; Rahme, L.G. A quorum sensing-associated virulence gene of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a LysR-like transcription regulator with a unique self-regulatory mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14613–14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, D.; Rahme, L.G. Pharmacological Inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa MvfR Quorum Sensing System Interferes with Biofilm Formation and Potentiates Antibiotic-Mediated Biofilm Disruption. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Loughlin, C.T.; Miller, L.C.; Siryaporn, A.; Drescher, K.; Semmelhack, M.; Bassler, B.L. A quorum-sensing inhibitor blocks Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence and biofilm formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17981–17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, N.; Gregor, R.; Rayo, J.; Dandela, R.; Daniel, E.; Liubin, N.; Willems, H.M.E.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Krom, B.P.; Meijler, M.M. Fine-Tuning Covalent Inhibition of Bacterial Quorum Sensing. Chembiochem 2016, 17, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amara, N.; Mashiach, R.; Amar, D.; Krief, P.; Spieser, S.A.H.; Bottomley, M.J.; Aharoni, A.; Meijler, M.M. Covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10610–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Wu, H.; Andersen, J.B.; Riedel, K.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bagge, N.; Kumar, N.; Schembri, M.A.; Song, Z.; Kristoffersen, P. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.D.; Rossi, F.M.; Welsh, M.A.; Nyffeler, K.E.; Blackwell, H.E. A Comparative Analysis of Synthetic Quorum Sensing Modulators in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: New Insights into Mechanism, Active Efflux Susceptibility, Phenotypic Response, and Next-Generation Ligand Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14626–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilangovan, A.; Fletcher, M.; Rampioni, G.; Pustelny, C.; Rumbaugh, K.; Heeb, S.; Camara, M.; Truman, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Emsley, J.; et al. Structural basis for native agonist and synthetic inhibitor recognition by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing regulator PqsR (MvfR). PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkey, M.; Lepine, F.; Maura, D.; Bandyopadhaya, A.; Lesic, B.; He, J.; Kitao, T.; Righi, V.; Milot, S.; Tzika, A. Identification of anti-virulence compounds that disrupt quorum-sensing regulated acute and persistent pathogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Kirsch, B.; Zimmer, C.; de Jong, J.C.; Henn, C.; Maurer, C.K.; Musken, M.; Haussler, S.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W.; et al. Discovery of antagonists of PqsR, a key player in 2-alkyl-4-quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.; Henn, C.; de Jong, J.C.; Zimmer, C.; Kirsch, B.; Maurer, C.K.; Pistorius, D.; Muller, R.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Identification of small-molecule antagonists of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa transcriptional regulator PqsR: Biophysically guided hit discovery and optimization. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zender, M.; Klein, T.; Henn, C.; Kirsch, B.; Maurer, C.K.; Kail, D.; Ritter, C.; Dolazal, O.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Discovery and biophysical characterization of 2-amino-oxadiazoles as novel antagonists of PqsR, an important regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6761–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Prada, J.; Robledo, S.M.; Velez, I.D.; del Pilar Crespo, M.; Quiroga, J.; Abonia, R.; Montoya, A.; Svetaz, L.; Zacchino, S.; Insuasty, B. Synthesis of novel quinoline-based 4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazoles as potential anticancer, antifungal, antibacterial and antiprotozoal agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 131, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.P.; Diggle, S.P.; Crusz, S.A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Williams, P. A dual biosensor for 2-alkyl-4-quinolone quorum-sensing signal molecules. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freschi, L.; Jeukens, J.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; Dupont, M.J.; Laroche, J.; Larose, S.; Maaroufi, H.; Fothergill, J.L.; Moore, M.; et al. Clinical utilization of genomics data produced by the international Pseudomonas aeruginosa consortium. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rampioni, G.; Falcone, M.; Heeb, S.; Frangipani, E.; Fletcher, M.P.; Dubern, J.F.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P. Unravelling the Genome-Wide Contributions of Specific 2-Alkyl-4-Quinolones and PqsE to Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, G.W.; Hasset, D.J.; Ran, H.; Kong, F. The role of pyocyanin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, G.W.; Ran, H.; Kong, F.; Hassett, D.J.; Mavrodi, D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin is critical for lung infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4275–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, P.; Camara, M. Quorum sensing and environmental adaptation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A tale of regulatory networks and multifunctional signal molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orazi, G.; O’Toole, G.A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alters Staphylococcus aureus Sensitivity to Vancomycin in a Biofilm Model of Cystic Fibrosis Infection. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, L.A.; McKnight, S.L.; Kuznetsova, M.S.; Pesci, E.C.; Manoil1, C. Functions required for extracellular quinolone signaling by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 6472–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, D.; Rahme, L.G. Pharmacological Inhibition of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa MvfR Quorum-Sensing System Interferes with Biofilm Formation and Potentiates Antibiotic-Mediated Biofilm Disruption. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmezer, M.C.; Ertem, G.; Erdinc, F.S.; Kaya Kilic, E.; Tulek, N.; Adiloglu, A.; Hatipoglu, C. Evaluation of Risk Factors for Antibiotic Resistance in Patients with Nosocomial Infections Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 1321487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papenfort, K.; Bassler., B.L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlen, S.; Dersch, P. Anti-virulence Strategies to Target Bacterial Infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 398, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Contreras, R.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Resistance to quorum-quenching compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6840–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; García-Contreras, R.; Pu, M.; Sheng, L.; Garcia, L.R.; Tomás, M.; Wood, T.K. Quorum quenching quandary: Resistance to antivirulence compounds. ISME J. 2012, 6, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Anjua, C.P.; Biswasa, L.; Kumarb, V.A.; Mohana, C.G.; Biswasa, R. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alternative therapeutic options. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scutera, S.; Zucca, M.; Savoia, D. Novel approaches for the design and discovery of quorum-sensing inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T. Quorum-Sensing Systems as Targets for Antivirulence Therapy. Trends Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tettmann, B.; Niewerth, C.; Kirschhöfer, F.; Neidig, A.; Dötsch, A.; Brenner-Weiss, G.; Fetzner, S.; Overhage, J. Enzyme-Mediated Quenching of the Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS) Promotes Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Increasing Iron Availability. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Kirsch, B.; Maurer, C.K.; de Jong, J.C.; Braunshausen, A.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Optimization of anti-virulence PqsR antagonists regarding aqueous solubility and biological properties resulting in new insights in structure-activity relationships. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 79, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Maurer, C.K.; Kirsch, B.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Overcoming the unexpected functional inversion of a PqsR antagonist in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An in vivo potent antivirulence agent targeting pqs quorum sensing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, M.; Réfregiers, M.; Pos, K.M.; Pagès, J.M. Mechanisms of envelope permeability and antibiotic influx and efflux in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boopathi, S.; Vashisth, R.; Manoharan, P.; Kandasamy, R.; Sivakumar, N. Stigmatellin Y—An anti-biofilm compound from Bacillus subtilis BR4 possibly interferes in PQS-PqsR mediated quorum sensing system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, K.; Burrows, J.N.; Duncan, K.; Hooft van Huijsduijnen, R.; Kaneko, T.; Kita, K.; Mowbray, C.E.; Schmatz, D.; Warner, P.; Slingsby, B.T. Hit and lead criteria in drug discovery for infectious diseases of the developing world. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahme, L.G.; Stevens, E.J.; Wolfort, S.F.; Shao, J.; Tompkins, R.G.; Ausubel, F.M. Common virulence factors for bacterial pathogenicity in plants and animals. Science 1995, 268, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggle, S.P.; Matthijs, S.; Wright, V.J.; Fletcher, M.P.; Chhabra, S.R.; Lamont, I.L.; Kong, X.; Hider, R.C.; Cornelis, P.; Cámara, M.; et al. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-quinolone signal molecules HHQ and PQS play multifunctional roles in quorum sensing and iron entrapment. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, R.; Crusz, S.A.; Messina, M.; Williams, P.; West, S.A.; Diggle, S.P. Quorum-sensing and cheating in bacterial biofilms. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, M.P.; Diggle, S.P.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P. Biosensor-based assays for PQS, HHQ and related 2-alkyl-4-quinolone quorum sensing signal molecules. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essar, D.W.; Eberly, L.; Hadero, A.; Crawford, I.P. Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program COMSTAT. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






 | ||||||||
| ID | R1 | R2 | R3 | Glide XP Score | PA14 Remaining Activity % * | PAO1-L Remaining Activity % * | IC50 PA14 µM * | IC50 PAO1-L µM * |
| Ia | -H | -Cl | 4-H | −9.856 | 18.7 ± 1.98 | 25.8 ± 1.17 | 2.3 ± 0.51 | 12.4 ± 1.79 |
| Ib | -H | -Cl | 4-Me | −5.179 | 78.4 ± 6.51 | 77.0 ± 2.25 | ||
| Ic | -H | -Cl | 4-OMe | −6.984 | 101.8 ± 11.67 | 100.3 ± 8.46 | ||
| Id | -H | -Cl | 3,4,5-OMe | −7.265 | 109.9 ± 14.98 | 130.3 ± 5.04 | ||
| Ie | -H | -Cl | 4-F | −5.24 | 70.4 ± 6.53 | 40.6 ± 3.71 | ||
| Ig | -H | -Cl | 4-Br | −6.34 | 94.8 ± 8.91 | 88.1 ± 6.05 | ||
| Ih | -H | -Cl | 3,4-Methy-lenedioxy | −4.056 | 85.8 ± 9.42 | 49.9 ± 12.01 | ||
| Ii | -H | -CF3 | 4-H | −8.087 | 16.6 ± 1.3 | 15.6 ± 2.53 | 5.0 ± 0.82 | 5.1 ± 0.32 |
| Ij | -H | -CF3 | 4-Me | −6.868 | 84.9 ± 8.17 | 93.7 ± 6.15 | ||
| Ik | -H | -CF3 | 4-OMe | −4.867 | 99.7 ± 9.37 | 78.6 ± 5.75 | ||
| Il | -H | -CF3 | 3,4,5-OMe | −2.219 | 106 ± 15.27 | 85.8 ± 2.39 | ||
| Im | -H | -CF3 | 4-F | −7.118 | 74.9 ± 8.28 | 65.1 ± 4.89 | - | |
| In | -H | -CF3 | 4-Cl | −6.044 | 93.6 ± 4.45 | 61.8 ± 3.97 | ||
| Io | -H | -CF3 | 4-Br | −6.390 | 80.6 ± 6.26 | 68.5 ± 3.43 | ||
| Ip | -H | -CF3 | 3,4-Methy-lenedioxy | −6.099 | 81.4 ± 9.36 | 84.3 ± 5.48 | ||
| IIa | -Me | -Cl | 4-H | −8.918 | 19.7 ± 1.9 | 31.6 ± 6.60 | 4.0 ± 1.62 | 1.6 ± 0.29 |
| IIb | -Me | -Cl | 4-Me | −5.0855 | 96.2 ± 4.34 | 59.5 ± 1.86 | ||
| IIc | -Me | -Cl | 4-OMe | −6.58033 | 114.9 ± 2.13 | 120.3 ± 8.28 | ||
| IId | -Me | -Cl | 3,4,5-OMe | −6.5015 | 110.4 ± 1.6 | 127.3 ± 9.69 | ||
| IIe | -Me | -Cl | 4-F | −7.1105 | 120.4 ± 1.59 | 82.6 ± 22.73 | ||
| IIf | -Me | -Cl | 4-Cl | −7.732 | 102.6 ± 4.91 | 90.2 ± 3.84 | ||
| IIg | -Me | -Cl | 4-Br | −4.9555 | 108.6 ± 2.79 | 63.7 ± 5.01 | ||
| IIh | -Me | -Cl | 3,4-Methy-lenedioxy | −4.13 | 115.4 ± 6.02 | 65.8 ± 5.63 | ||
| IIi | -Me | -CF3 | 4-H | −8.5165 | 16.8 ± 1.01 | 26.1 ± 0.99 | 4.9 ± 0.30 | 5.14 ± 0.60 |
| IIj | -Me | -CF3 | 4-Me | −5.371 | 108.2 ± 6.05 | 97.3 ± 6.46 | ||
| IIk | -Me | -CF3 | 4-OMe | −6.799 | 118.1 ± 5.97 | 66.7 ± 0.42 | ||
| IIl | -Me | -CF3 | 3,4,5-OMe | −7.006 | 102.9 ± 4.84 | 86.1 ± 2.39 | ||
| IIm | -Me | -CF3 | 4-F | −3.578 | 99.9 ± 3.17 | 90.2 ± 4.40 | ||
| IIn | -Me | -CF3 | 4-Cl | −5.533 | 98.1 ± 11.38 | 97.8 ± 5.52 | ||
| IIo | -Me | -CF3 | 4-Br | −7.5535 | 95.6 ± 9.58 | 80.8 ± 5.06 | ||
| IIp | -Me | -CF3 | 3,4-Methylenedioxy | −6.8975 | 99.6 ± 4.09 | 71.6 ± 5.07 | ||
| Plasma Stability | Microsomal Stability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat | Human | Rat | Human | |||
| Compound ID | t1/2 (min) | t 1/2 (min) | Clint * (µL/min/mg) | t1/2 (min) | Clint (µL/min/mg) | t1/2 (min) |
| Ia | >240 | 132.2 | 122.5 | 11.5 | 60.3 | 23.3 |
| Ii | >240 | 69.1 | 54.1 | 25.7 | 80.7 | 17.2 |
| IIa | >240 | 73.8 | 87.8 | 15.8 | 73.0 | 19.0 |
| IIi | >240 | 157.1 | 65.7 | 21.1 | 72.9 | 19.0 |
| Strain or Plasmid | Relevant Characteristics | Reference or Origin |
|---|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa | ||
| PAO1-L | Wild type PAO1, Lausanne subline. | B. Holloway, via D. Haas |
| PAO1-L mCTX::PpqsA-lux | PAO1-L with chromosomal mini-CTX::PpqsA-lux insertion; TcR | This study |
| PA14 | Wild type UCBPP-PA14 | [49] |
| PA14 mCTX::PpqsA-lux | PA14 with chromosomal mini-CTX::PpqsA-lux insertion; TcR | This study |
| Plasmids | ||
| mini-CTX::PpqsA-lux | R6K-based mini-CTX suicide plasmid for the chromosomal insertion of a PpqsA-lux transcriptional reporter fusion; TcR | [50] |
| pMMG | pME6032∆lacI constitutively expressing GFP from the Ptac promoter | [51] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soukarieh, F.; Vico Oton, E.; Dubern, J.-F.; Gomes, J.; Halliday, N.; De Pilar Crespo, M.; Ramírez-Prada, J.; Insuasty, B.; Abonia, R.; Quiroga, J.; et al. In Silico and in Vitro-Guided Identification of Inhibitors of Alkylquinolone-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2018, 23, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020257
Soukarieh F, Vico Oton E, Dubern J-F, Gomes J, Halliday N, De Pilar Crespo M, Ramírez-Prada J, Insuasty B, Abonia R, Quiroga J, et al. In Silico and in Vitro-Guided Identification of Inhibitors of Alkylquinolone-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules. 2018; 23(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoukarieh, Fadi, Eduard Vico Oton, Jean-Frédéric Dubern, Janice Gomes, Nigel Halliday, Maria De Pilar Crespo, Jonathan Ramírez-Prada, Braulio Insuasty, Rodrigo Abonia, Jairo Quiroga, and et al. 2018. "In Silico and in Vitro-Guided Identification of Inhibitors of Alkylquinolone-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" Molecules 23, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020257
APA StyleSoukarieh, F., Vico Oton, E., Dubern, J.-F., Gomes, J., Halliday, N., De Pilar Crespo, M., Ramírez-Prada, J., Insuasty, B., Abonia, R., Quiroga, J., Heeb, S., Williams, P., Stocks, M. J., & Cámara, M. (2018). In Silico and in Vitro-Guided Identification of Inhibitors of Alkylquinolone-Dependent Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules, 23(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020257