Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Dehalogenases and Different Dehalogenation Processes
1.1.1. Reductive Dehalogenation
1.1.2. Hydrolytic Dehalogenation
1.1.3. The Haloacid Dehalogenase
1.1.4. The Haloalkane Dehalogenase
1.1.5. The Fluoroacetate Dehalogenase
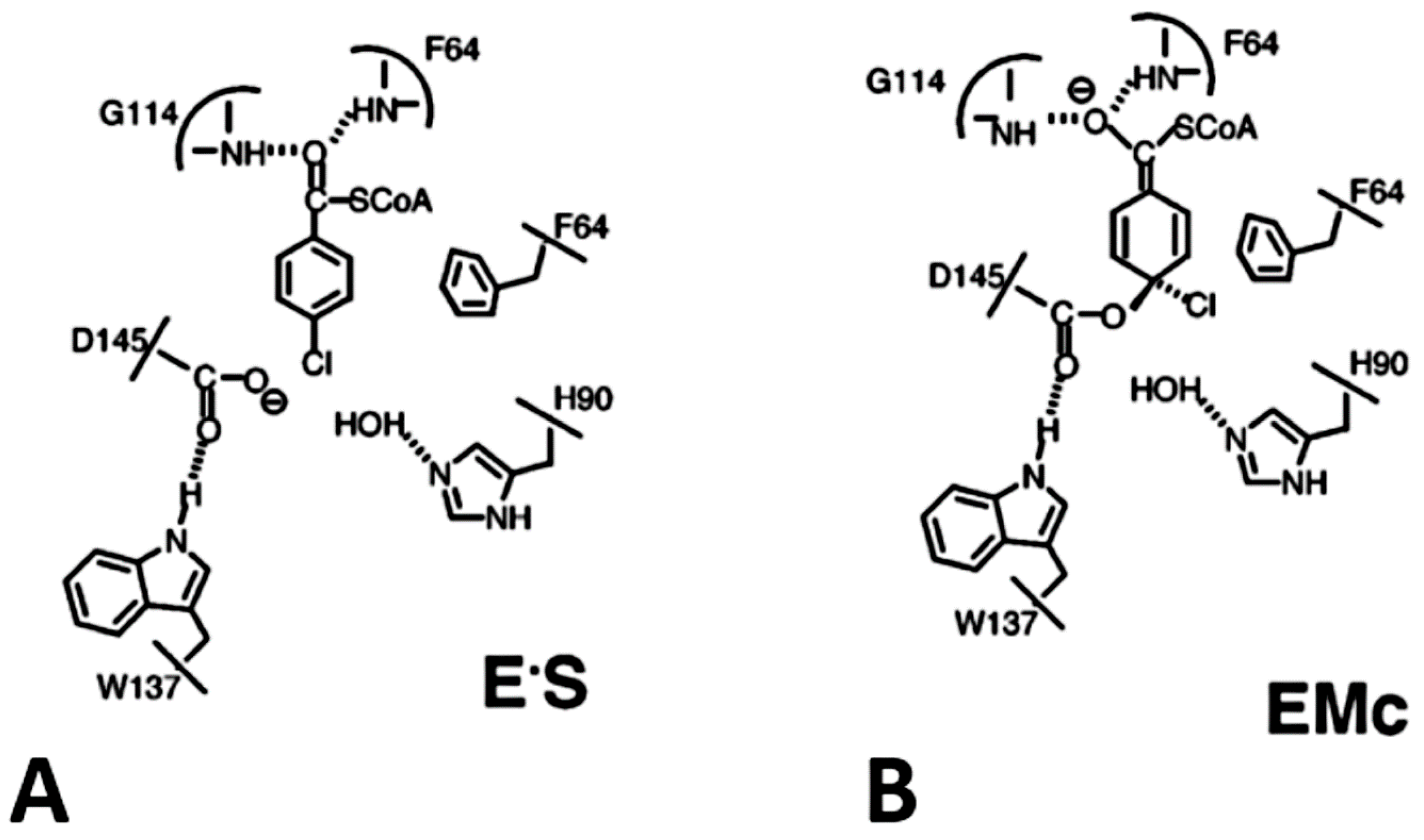
1.1.6. The 4-Chlorobenzoyl CoA Dehalogenase
1.2. Microbial Dehalogenation and Their Significant Properties
1.3. Structural Studies on Dehalogenases and Reaction Mechanisms
1.4. Protein Engineering in Dehalogenases
1.5. Screening and Prospecting of Dehalogenase in Microbes
1.6. Metal Co-Factor-Dependent Dehalogenases
1.7. Creating an Artificial Metal Binding Site
1.8. Potential Applications of Dehalogenases
1.8.1. Application in the Construction of Expression Cassettes
1.8.2. Application in the Production of Useful Compounds
1.8.3. Applications in Bioremediation
1.8.4. Applications in Drinking Water Treatment
1.8.5. Applications in Detoxification
1.8.6. Applications in Decontamination
1.8.7. Applications in Biosensing
1.9. Other Persistent Organic Pollutant (POPS) of PCDD/Fs
2. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negri, A.; Marco, E.; Damborsky, J.; Gago, F. Stepwise dissection and visualization of the catalytic mechanism of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB using molecular dynamics simulations and computer graphics. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2007, 26, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, R.G.; Chapalamadugu, S. Biodegradation of halogenated organic compounds. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkin, S. Biodegradation of haloalkanes. Biodegradation 1992, 3, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePierre, J.W. Mammalian toxicity of organic compounds of bromine and iodine. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Nielson, A.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; Volume 3R, pp. 205–251. ISBN 978-3-540-37055-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bidmanova, S.; Chaloupkova, R.; Damborsky, J.; Prokop, Z. Development of an enzymatic fibre-optic biosensor for detection of halogenated hydrocarbons. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsal, A.A.; Zinjarde, S.S.; RaviKumar, A. Phenol Is the Initial Product Formed during Growth and Degradation of Bromobenzene by Tropical Marine Yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica NCIM 3589 via an Early Dehalogenation Step. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puzyn, T.; Haranczyk, M.; Suzuki, N.; Sakurai, T. Estimating persistence of brominated and chlorinated organic pollutants in the air, water, soil, and sediments with the QSPR-based classsification scheme. Mol. Divers. 2011, 15, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischnak, C.; Loffler, F.E.; Li, J.; Urbance, J.W.; Muller, R. Pseudomonas sp. Strain 273, an Aerobic α,ω-Dichloroalkane-Degrading Bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 3507–3511. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Copley, S.D. Diverse mechanistic approaches to difficult chemical transformations: Microbial dehalogenation of chlorinated aromatic compounds. Chem. Biol. 1997, 4, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, R.M.; Dijkstra, B.W. Structure and mechanism of bacterial dehalogenases: Different ways to cleave a carbon-halogen bond. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N. Bacterial hydrolytic dehalogenases and related enzymes: Occurrences, reaction mechanisms, and applications. Chem. Rec. 2008, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, A.J.; Klvana, M.; Otyepka, M.; Nagata, Y.; Wilce, M.C.J.; Damborský, J. Crystal structure of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 at 0.95 A resolution: Dynamics of catalytic residues. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeb, N.V.; Zindel, D.; Geueke, B.; Kohler, H.P.E.; Lienemann, P. Biotransformation of hexabromocyclododecanes (HBCDs) with LinB-An HCH-converting bacterial enzyme. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6566–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudelakova, T.; Bidmanova, S.; Dvorak, P.; Pavelka, A.; Chaloupkova, R.; Prokop, Z.; Damborský, J. Haloalkane dehalogenases: Biotechnological applications. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, D.B.; Dinkla, I.J.T.; Poelarends, G.J.; Terpstra, P. Bacterial degradation of xenobiotic compounds: Evolution and distribution of novel enzyme activities. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1868–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Toxicological Review of Bromobenzene; EPA/635/R-07/002F; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Nikel, P.I.; Perez-Pantoja, D.; de Lorenzo, V. Why are chlorinated pollutants so difficult to degrade aerobically? Redox stress limits 1,3-dichloprop-1-ene metabolism by Pseudomonas pavonaceae. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franken, S.M.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structure of haloalkane dehalogenase: An enzyme to detoxify halogenated alkanes. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 1297–1302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verschueren, K.H.G.; Seljée, F.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystallographic analysis of the catalytic mechanism of haloalkane dehalogenase. Nature 1993, 363, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop, Z.; Monincová, M.; Chaloupková, R.; Klvana, M.; Nagata, Y.; Janssen, D.B.; Damborský, J. Catalytic mechanism of the maloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 45094–45100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehret, J.J.; Gu, L.; Geders, T.W.; Brown, W.C.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Sherman, D.H.; Smith, J.L. Structure and activity of DmmA, a marine haloalkane dehalogenase. Protein Sci. 2012, 21, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ridder, I.S.; Rozeboom, J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal Structures of Intermediates in the Dehalogenation of Haloalkanoates by L -2-Haloacid Dehalogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30672–30678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisano, T.; Hata, Y.; Fujii, T.; Liu, J.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Crystal Structure of l-2-Haloacid Dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. YL An α/β hydrolase structure that is different from the α/β hydrolase fold. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20322–20330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chovancová, E.; Kosinski, J.; Bujnicki, J.M.; Damborský, J. Phylogenetic analysis of haloalkane dehalogenases. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 67, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennes, C.; Pries, F.; Krooshof, G.H.; Bokma, E.; Kingma, J.; Janssen, D.B. Replacement of tryptophan residues in haloalkane dehalogenase reduces halide binding and catalytic activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 228, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krooshof, G.H.; Floris, R.; Tepper, A.W.; Janssen, D.B. Thermodynamic analysis of halide binding to haloalkane dehalogenase suggests the occurrence of large conformational changes. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Enantioselectivity of haloalkane dehalogenase LinB on the degradation of 1,2-dichloropropane: A QM/MM study. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 73, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetzner, S.; Lingens, F. Bacterial dehalogenases: Biochemistry, genetics, and biotechnological applications. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1994, 58, 641–685. [Google Scholar]
- Fetzner, S. Bacterial dehalogenation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 633–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Anaerobic Microbial Dehalogenation. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leys, D.; Adrian, L.; Smidt, H. Organohalide respiration: Microbes breathing chlorinated molecules. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijenhuis, I.; Kuntze, K. Anaerobic microbial dehalogenation of organohalides-state of the art and remediation strategies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 38, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mészáros, É.; Imfeld, G.; Nikolausz, M.; Nijenhuis, I. Occurrence of dehalococcoides and reductive dehalogenase genes in microcosms, a constructed wetland and groundwater from a chlorinated ethene contaminated field site as indicators for in situ reductive dehalogenation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzorati, M.; Balloi, A.; De Ferra, F.; Corallo, L.; Carpani, G.; Wittebolle, L.; Verstraete, W.; Daffonchio, D. Bacterial diversity and reductive dehalogenase redundancy in a 1,2-dichloroethane-degrading bacterial consortium enriched from a contaminated aquifer. Microb. Cell Fact. 2010, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neumann, A.; Wohlfarth, G.; Diekert, G. Purification and Characterization of Tetrachloroethene Reductive Dehalogenase from Dehalospirillum multivorans. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 16515–16519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, A.; Wohlfarth, G.; Diekert, G. Properties of tetrachloroethene and trichloroethene dehalogenase of Dehalospirillum multivorans. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasotkina, J.; Walters, T.; Maruya, K.A.; Ragsdale, S.W. Characterization of the B12- and Iron-Sulfur-containing Reductive Dehalogenase from Desulfitobacterium chlororespirans. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40991–40997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Pas, B.A.; Smidt, H.; Hagen, W.R.; van der Oost, J.; Schraa, G.; Stams, A.J.M.; de Vos, W.M. Purification and Molecular Characterization of ortho -Chlorophenol Reductive Dehalogenase, a Key Enzyme of Halorespiration in Desulfitobacterium dehalogenans. Biochemistry 1999, 274, 20287–20292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.; Schumacher, W.; Vazquez, F.; Regeard, C.; Hagen, W.R.; Holliger, C. Characterization of the corrinoid iron-sulfur protein tetrachloroethene reductive dehalogenase of Dehalobacter restrictus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4628–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffler, F.E.; Sanford, R.A.; Tiedje, J.M. Initial characterization of a reductive dehalogenase from Desulfitobacterium chlororespirans Co23. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3809–3813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, S.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Acteriol, J.B. Purification and characterization of a novel 3-chlorobenzoate- reductive dehalogenase from the cytoplasmic membrane of Desulfomonile tiedjei DCB-1. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 5135–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWeerd, K.A.; Suflita, J.M. Anaerobic aryl reductive dehalogenation of halobenzoates by cell extracts of “Desulfomonile tiedjei”. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 2999–3005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohn, W.W.; Tiedje, J.M. Microbial reductive dehalogenation. Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 56, 482–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, K.A.P.; Quezada, C.P.; Fisher, K.; Dunstan, M.S.; Collins, F.A.; Sjuts, H.; Levy, C.; Hay, S.; Rigby, S.E.J.; Leys, D. Reductive dehalogenase structure suggests a mechanism for B12-dependent dehalogenation. Nature 2014, 517, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.; Ragsdale, S.W. The Many Faces of Vitamin B12: Catalysis by Cobalamin-Dependent Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 209–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelarends, G.J.; Veetil, V.P.; Whitman, C.P. The chemical versatility of the β–α–β fold: Catalytic promiscuity and divergent evolution in the tautomerase superfamily. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 3606–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, J.S.H.; Sallis, P.J.; Bull, A.T.; Hardman, D.J. A monobromoacetate dehalogenase from Pseudomonas cepacia MBA4. Arch. Microbiol. 1988, 150, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarze, R.; Brokamp, A.; Schmidt, F. Isolation and Characterization of Dehalogenases from 2,2-Dichloropropionate-Degrading Soil Bacteria. Curr. Microbiol. 1997, 34, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Q.; Kurihara, T.; Miyagi, M.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Reaction mechanism of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase of Pseudomonas sp. YL: Identification of Asp10 as the active site nucleophile by 18O incorporation experiments. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 18309–18312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omi, R.; Jitsumori, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Ichiyama, S.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N.; Kamiya, N.; Hirotsu, K.; Miyahara, I. Expression, purification and preliminary X-ray characterization of DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Methylobacterium sp. CPA1. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2007, 63, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi-Dei, V.; Kurihara, T.; Park, C.; Miyagi, M.; Tsunasawa, S.; Soda, K.; Esaki, N. dl-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. 113 is a new class of dehalogenase catalyzing hydrolytic dehalogenation not involving enzyme- substrate ester intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20977–20981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, R.; Kukimoto-niino, M.; Kuroishi, C.; Bessho, Y.; Shirouzu, M. Crystal structure of the probable haloacid dehalogenase PH0459 from Pyrococcus horikoshii OT3. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridder, I.S.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Janssen, D.B.; Dijkstra, B.W. Three-dimensional structure of l-2-haloacid dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 complexed with the substrate-analogue formate. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 33015–33022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidberger, J.W.; Wilce, J.A.; Tsang, J.S.H.; Wilce, M.C.J. Crystal Structures of the Substrate Free-enzyme, and Reaction Intermediate of the HAD Superfamily Member, Haloacid Dehalogenase DehIVa from Burkholderia cepacia MBA4. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmara, W.; Murdiyatmo, U.; Baines, A.J.; Bull, A.T.; Hardman, D.J. Protein engineering of the 2-haloacid halidohydrolase IVa from Pseudomonas cepacia MBA4. Biochem. J. 1993, 292 Pt 1, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.C.M.; Tsang, J.S.H. Mutagenic analysis of the conserved residues in dehalogenase IVa of Burkholderia cepacia MBA4. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 204, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.; Müller, R.; Frank, R.; Lingens, F. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of the 2-Haloalkanoic Acid Dehalogenase I Gene from Pseudomonas sp. Strain CBS3 and its Effect on Catalytic Activity. Biol. Chem. Hoppe Seyler 1993, 374, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, J.S.H.; Pang, B.C.M. Identification of the Dimerization Domain of Dehalogenase IVa of Burkholderia cepacia MBA4. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3180–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, E.; Nocek, B.; Brown, G.; Makarova, K.S.; Flick, R.; Wolf, Y.I.; Khusnutdinova, A.; Evdokimova, E.; Jin, K.; Tan, K.; et al. Functional Diversity of Haloacid Dehalogenase Superfamily Phosphatases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Biochemical, Structural, and Evolutionary Insights. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18678–18698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, K. Biochemical and genetic bases of microbial degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, D.B. Evolving haloalkane dehalogenases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudelakova, T.; Chovancova, E.; Brezovsky, J.; Monincova, M.; Fortova, A.; Jarkovsky, J.; Damborsky, J. Substrate specificity of haloalkane dehalogenases. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palau, J.; Cretnik, S.; Shouakar-Stash, O.; Höche, M.; Elsner, M.; Hunkeler, D. C and Cl Isotope Fractionation of 1,2-Dichloroethane Displays Unique δ13C/δ37Cl Patterns for Pathway Identification and Reveals Surprising C–Cl Bond Involvement in Microbial Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9430–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikkemaat, M.G.; Linssen, A.B.M.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Janssen, D.B. Molecular dynamics simulations as a tool for improving protein stability. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2002, 15, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.; Peat, T.S.; Richard, R.; Kan, L.; Swanson, P.E.; Affholter, J.A.; Holmes, I.H.; Schindler, J.F.; Unkefer, C.J.; Terwilliger, T.C. Haloalkane Dehalogenases: Structure of a Rhodococcus Enzyme. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 16105–16114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, J.; Vevodova, J.; Smatanova, I.K.; Nagata, Y.; Svensson, L.A.; Newman, J.; Takagi, M.; Damborsky, J. Crystal structure of the haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14082–14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutý, M.; Damborský, J.; Prokop, M.; Koča, J. A Molecular Modeling Study of the Catalytic Mechanism of Haloalkane Dehalogenase. 2. Quantum Chemical Study of Complete Reaction Mechanism. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1998, 38, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladilkova, J.; Prokop, Z.; Chaloupkova, R.; Damborsky, J.; Jungwirth, P. Release of halide ions from the buried active site of the haloalkane dehalogenase LinB revealed by stopped-flow fluorescence analysis and free energy calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 14329–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlová, M.; Klvaňa, M.; Jesenská, A.; Prokop, Z.; Konečná, H.; Sato, T.; Tsuda, M.; Nagata, Y.; Damborský, J. The identification of catalytic pentad in the haloalkane dehalogenase DhmA from Mycobacterium avium N85: Reaction mechanism and molecular evolution. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 157, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buryska, T.; Daniel, L.; Kunka, A.; Brezovsky, J.; Damborsky, J.; Prokop, Z. Discovery of Novel Haloalkane Dehalogenase Inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaloupková, R.; Sýkorová, J.; Prokop, Z.; Jesenská, A.; Monincová, M.; Pavlová, M.; Tsuda, M.; Nagata, Y.; Damborský, J. Modification of Activity and Specificity of Haloalkane Dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 by Engineering of Its Entrance Tunnel. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52622–52628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.W.Y.; Yakunin, A.F.; Edwards, E.A.; Pai, E.F. Mapping the Reaction Coordinates of Enzymatic Defluorination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7461–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, K.G.; Walsh, C.T. Stereochemical studies on a plasmid-coded fluoroacetate halidohydrolase. Bioorg. Chem. 1984, 12, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Ichiyama, S.; Takahata, H.; Esaki, N. Purification, characterization, and gene cloning of a novel fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Burkholderia sp. FA1. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 23, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, P. The carbon-fluorine bond in compounds of biological interest. Science 1969, 164, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmquist, M. Alpha Beta-Hydrolase Fold Enzymes Structures, Functions and Mechanisms. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2000, 1, 209–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamachi, T.; Nakayama, T.; Shitamichi, O.; Jitsumori, K.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N.; Yoshizawa, K. The catalytic mechanism of fluoroacetate dehalogenase: A computational exploration of biological dehalogenation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 7394–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Du, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Catalytic mechanism of C–F bond cleavage: Insights from QM/MM analysis of fluoroacetate dehalogenase. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Tsuda, K.; Matsushita, I.; Tonomura, K. Lack of homology between two haloacetate dehalogenase genes encoded on a plasmid from Moraxella sp. strain B. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, L.E.X.; Khan, S.; Davis, C.K.; Denman, S.E.; McSweeney, C.S. Fluoroacetate in plants—A review of its distribution, toxicity to livestock and microbial detoxification. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Q.; Kurihara, T.; Ichiyama, S.; Miyagi, M.; Tsunasawa, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Soda, K.; Esaki, N. Reaction mechanism of fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Moraxella sp. B. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30897–30902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, W.Y.; Wong, M.; Guthrie, J.; Savchenko, A.V.; Yakunin, A.F.; Pai, E.F.; Edwards, E.A. Sequence- and activity-based screening of microbial genomes for novel dehalogenases. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Taylor, K.L.; Xiang, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dunaway-Mariano, D. Role of active site binding interactions in 4-chlorobenzoyl-coenzyme A dehalogenase catalysis. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 15684–15692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Liang, P.-H.; Dunaway-Mariano, D. Evidence for Nucleophilic Catalysis in the Aromatic Substitution Reaction Catalyzed by (4-Chlorobenzoyl) coenzyme A Dehalogenase. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 8527–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.P.; Xu, L.; Barkley, R.M.; Copley, S.D. Exploration of Possible Mechanisms for 4-Chlorobenzoyl CoA Dehalogenase: Evidence for an Aryl—Enzyme Intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krooshof, G.H.; Kwant, E.M.; Damborský, J.; Koča, J.; Janssen, D.B. Repositioning the Catalytic Triad Aspartic Acid of Haloalkane Dehalogenase: Effects on Stability, Kinetics, and Structure. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 9571–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smilda, T.; Kamminga, A.H.; Reinders, P.; Baron, W.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; Beintema, J.J. Enzymic and Structural Studies on Drosophila Alcohol Dehydrogenase and Other Short-Chain Dehydrogenases/Reductases. J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 52, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulakov, L.A.; Poelarends, G.J.; Janssen, D.B.; Larkin, M.J. Characterization of IS2112, a new insertion sequence from Rhodococcus, and its relationship with mobile elements belonging to the IS110 family. Microbiology 1999, 145, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtz, R.; Messi, F.; Leisinger, T.; Cook, A.M. Three dehalogenases and physiological restraints in the biodegradation of haloalkanes by Arthrobacter sp. strain HA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 3034–3038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casellas, M.; Grifoll, M.; Bayona, J.M.; Solanas, A.M. New metabolites in the degradation of fluorene by Arthrobacter sp. strain F101. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van den Wijngaard, A.J.; Reuvekamp, P.T.; Janssen, D.B. Purification and Characterization of Haloalcohol Dehalogenase. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Tang, H.; Su, F.; Xu, P. Comparative genome analysis reveals the molecular basis of nicotine degradation and survival capacities of Arthrobacter. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husserl, J.; Hughes, J.B.; Spain, J.C. Key enzymes enabling the growth of Arthrobacter sp. Strain JBH1 with nitroglycerin as the sole source of carbon and nitrogen. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3649–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K.; Dreisbach, J.H.; Spain, J.C. Biodegradation of p-Nitrophenol via 1,2,4-Benzenetriol by an Arthrobacter sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 3030–3032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Yahara, H.; Tonomura, K. Isolation and Characterization of Plasmid pUOl Mediating Dehalogenation of Haloacetate and Mercury Resistance in Moraxella sp. B. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1981, 45, 1477–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Toyama, T.; Maeda, T.; Nishino, H.; Tonomura, K. Cloning and sequence analysis of a plasmid-encoded 2-haloacid dehalogenase gene from Pseudomonas putida no. 109. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Ploeg, J.; Van Hall, G.; Janssen, D.B. Characterization of the haloacid dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 and sequencing of the dhlB gene. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 7925–7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.H.; Barth, P.T.; Byrom, D.; Thomas, C.M. Nucleotide sequence of the structural gene encoding a 2-haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase of Pseudomonas putida strain AJ1 and purification of the encoded protein. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidberger, J.W.; Wilce, J.A.; Weightman, A.J.; Wilce, M.C.J. Purification, crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of DehI, a group I α-haloacid dehalogenase from Pseudomonas putida strain PP3. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2008, 64, 596–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, P.; Knoke, K.L.; Trevors, J.T.; Lee, H. Alteration of the substrate range of haloalkane dehalogenase by site-directed mutagenesis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 59, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, R.; Brokamp, A.; Schwarze, R.; Reiting, R.H.; Schmidt, F.R.J. Characteristics and DNA-sequence of a cryptic haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens RS5. Curr. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, R.M.; Brugman, W.; Poelarends, G.J.; Whitman, C.P.; Dijkstra, B.W. The X-ray Structure of trans-3-Chloroacrylic Acid Dehalogenase Reveals a Novel Hydration Mechanism in the Tautomerase Superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11546–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, A.; Kurihara, T.; Kamachi, H.; Esaki, N. Asymmetric reduction of 2-chloroacrylic acid to (S)-2-chloropropionic acid by a novel reductase from Burkholderia sp. WS. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2004, 15, 2837–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Hata, Y.; Fujii, T.; Hisano, T.; Nishihara, M.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N. Crystal structures of reaction intermediates of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase and implications for the reaction mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15035–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, R.; Thiele, J.; Klages, U.; Lingens, F. Incorporation of [18O]water into 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the reaction of 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. CBS 3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1984, 124, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Reconsideration Acid of the Essential Dehalogenase Role of a Histidine Residue of L-2-Halo Acid Dehalogenase Role. J. Biochem. 1994, 249, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rye, C.A.; Isupov, M.N.; Lebedev, A.A.; Littlechild, J.A. Biochemical and structural studies of a l-haloacid dehalogenase from the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus tokodaii. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, H.R.; Sayer, C.; Isupov, M.N.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Gotz, D.; Mearns Spragg, A.; Littlechild, J.A. Marine Rhodobacteraceae l-haloacid dehalogenase contains a novel His/Glu dyad that could activate the catalytic water. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1664–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egland, P.G.; Gibson, J.; Harwood, C.S. Reductive, Coenzyme A-Mediated Pathway for 3-Chlorobenzoate Degradation in the Phototrophic Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1396–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tratsiak, K.; Degtjarik, O.; Drienovska, I.; Chrast, L.; Rezacova, P.; Kuty, M.; Chaloupkova, R.; Damborsky, J.; Kuta Smatanova, I. Crystallographic analysis of new psychrophilic haloalkane dehalogenases: DpcA from Psychrobacter cryohalolentis K5 and DmxA from Marinobacter sp. ELB17. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drienovska, I.; Chovancova, E.; Koudelakova, T.; Damborsky, J.; Chaloupkova, R. Biochemical characterization of a novel haloalkane dehalogenase from a cold-adapted bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4995–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Shao, Z. Biochemical characterization of a haloalkane dehalogenase DadB from Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senoo, K.; Wada, H. Isolation and identification of an aerobic γ-HCH-decomposing bacterium from soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1989, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Senoo, K.; Takai, Y. Rapid degradation of γ-HCH in upland soil after multiple applications. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1989, 35, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Marks, T.S.; Poh, R.P.C.; Smith, R.J.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Smith, A.R.W. The purification and characterisation of 4-chlorobenzoate:CoA ligase and 4-chlorobenzoyl CoA dehalogenase from Arthrobacter sp. strain TM-1. Biodegradation 2004, 15, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherbaigi, S.; Gicana, R.G.; Lamis, R.J.; Nemati, M.; Huyop, F. Characterisation of Arthrobacter sp. S1 that can degrade α and β-haloalkanoic acids isolated from contaminated soil. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, P.A.; Hulecki, J.C.; Cherney, M.M.; Garen, C.R.; James, M.N.G. X-ray crystal structure of Mycobacterium tuberculosis haloalkane dehalogenase Rv2579. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2008, 1784, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiyama, S.; Kurihara, T.; Miyagi, M.; Galkin, A.; Tsunasawa, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Esaki, N. Catalysis-linked inactivation of fluoroacetate dehalogenase by ammonia: A novel approach to probe the active-site environment. J. Biochem. 2002, 131, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringfellow, J.M.; Cairns, S.S.; Cornish, A.; Cooper, R.A. Haloalkanoate dehalogenase II (DehE) of a Rhizobium sp. molecular analysis of the gene and formation of carbon monoxide from trihaloacetate by the enzyme. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 250, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop, Z.; Sato, Y.; Brezovsky, J.; Mozga, T.; Chaloupkova, R.; Koudelakova, T.; Jerabek, P.; Stepankova, V.; Natsume, R.; Van Leeuwen, J.G.E.; et al. Enantioselectivity of haloalkane dehalogenases and its modulation by surface loop engineering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6111–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okai, M.; Ohtsuka, J.; Imai, L.F.; Mase, T.; Moriuchi, R.; Tsuda, M.; Nagata, K.; Nagata, Y.; Tanokura, M. Crystal structure and site-directed mutagenesis analyses of haloalkane dehalogenase linB from Sphingobium sp. Strain MI1205. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 2642–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, J.K.; Romine, M.F.; Burris, D.R.; Kingsley, M.T. Trichloroethene reductive dehalogenase from Dehalococcoides ethenogenes: Sequence of tceA and substrate range characterization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 5141–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajmalnik-Brown, R.; Holscher, T.; Thomson, I.N.; Saunders, F.M.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Loffler, F.E. Genetic Identification of a Putative Vinyl Chloride Reductase in strain BAV1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6347–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Yabuki, H.; Okai, M.; Ohtsuka, J.; Tanokura, M. Crystal structure of the novel haloalkane dehalogenase DatA from Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 reveals a special halide-stabilizing pair and enantioselectivity mechanism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 8573–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prudnikova, T.; Mozga, T.; Rezacova, P.; Chaloupkova, R.; Sato, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Brynda, J.; Kuty, M.; Damborsky, J.; Kuta Smatanova, I. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of a novel haloalkane dehalogenase DbeA from Bradyrhizobium elkani USDA94. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2009, 65, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohner, S.T.; Spormann, A.M. Identification of a reductive tetrachloroethene dehalogenase in Shewanella sediminis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, R.M. Structure and mechanism of a bacterial haloalcohol dehalogenase: A new variation of the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase fold without an NAD(P)H binding site. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4933–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedetti, I.; de Lorenzo, V.; Nikel, P.I. Genetic programming of catalytic Pseudomonas putida biofilms for boosting biodegradation of haloalkanes. Metab. Eng. 2016, 33, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Fuse, H.; Omori, T.; Minoda, Y. Microbial Dehalogenation of Haloalkanes Mediated by Oxygenase or Halidohydrolase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Jesenská, A.; Sedláček, I.; Damborský, J. Dehalogenation of haloalkanes by Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and other mycobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelarends, G.J.; Van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dos Santos, L.M.F.; Janssen, D.B. Degradation of 1,2-dibromoethane by Mycobacterium sp. strain GP1. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulakova, A.N.; Larkin, M.J.; Kulakov, L.A. The plasmid-located haloalkane dehalogenase gene from Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 13064. Microbiology 1997, 143, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kmunicek, J.; Hynkova, K.; Jedlicka, T.; Nagata, Y.; Negri, A.; Gago, F.; Wade, R.C.; Damborsky, J. Quantitative Analysis of Substrate Specificity of Haloalkane Dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, V.; Hauser, A.; Buser, H.R.; Rentsch, D.; Sharma, P.; Lal, R.; Holliger, C.; Poiger, T.; Muller, M.D.; Kohler, H.P.E. Hydroxylated metabolites of β- and δ-hexachlorocyclohexane: Bacterial formation, stereochemical configuration, and occurrence in groundwater at a former production site. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4291–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, K.; Geueke, B.; Miska, M.E.; Rentsch, D.; Poiger, T.; Dadhwal, M.; Lal, R.; Holliger, C.; Kohler, H.P.E. Enzymatic conversion of ε-hexachlorocyclohexane and a heptachlorocyclohexane isomer, two neglected components of technical hexachlorocyclohexane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4051–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Miyauchi, K.; Damborsky, J.; Manova, K.; Ansorgova, A.; Takagi, M. Purification and characterization of a haloalkane dehalogenase of a new substrate class from a γ-hexachlorocyclohexane—Degrading bacterium, Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3707–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowafy, A.M.; Kurihara, T.; Kurata, A.; Uemura, T.; Esaki, N. 2-Haloacrylate Hydratase, a New Class of Flavoenzyme That Catalyzes the Addition of Water To the Substrate for Dehalogenation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6032–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horvat, C.M.; Wolfenden, R.V. A persistent pesticide residue and the unusual catalytic proficiency of a dehalogenating enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16199–16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurata, A.; Kurihara, T.; Kamachi, H.; Esaki, N. 2-Haloacrylate reductase, a novel enzyme of the medium chain dehydrogenase/reductase superfamily that catalyzes the reduction of a carbon-carbon double bond of unsaturated organohalogen compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20286–20291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quamrul Hasan, A.K.M.; Takada, H.; Koshikawa, H.; Liu, J.Q.; Kurihara, T.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Two Kinds of 2-Halo Acid Dehalogenases from Pseudomonas sp. YL Induced by 2-Chloroacrylate and 2-Chloropropionate. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, J.S.H.; Sam, L. Cloning and characterization of a cryptic haloacid dehalogenase from Burkholderia cepacia MBA4. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6003–6009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Kurihara, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Soda, K.; Esaki, N. A new DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase acting on 2-haloacid amides: Purification, characterization, and mechanism. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motosugi, K.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Purification and properties of a new enzyme, DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase, from Pseudomonas sp. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 150, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huyop, F.; Sudi, I.Y. D-specific dehalogenases, a review. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2012, 26, 2817–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weightman, A.J.; Weightman, A.L.; Slater, J.H. Stereospecificity of 2-Monochloropropionate Dehalogenation by the Two Dehalogenases of Pseudomonas putida PP3: Evidence for Two Different Dehalogenation Mechanisms. Microbiology 1982, 128, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hagan, D.; Schaffrath, C.; Cobb, S.L.; Hamilton, J.T.G.; Murphy, C.D. Biochemistry: Biosynthesis of an organofluorine molecule. Nature 2002, 416, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, M.A.; Steensma, H.Y. Expression cassettes for formaldehyde and fluoroacetate resistance, two dominant markers in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 1997, 13, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Wada, M.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Synthesis of fluoroacetate from fluoride, glycerol, and beta- hydroxypyruvate by Streptomyces cattleya. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 2265–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Huang, S.; Zang, X.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Identification of the metal center of chlorothalonil hydrolytic dehalogenase and enhancement of catalytic efficiency by directed evolution. Appl. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, N.; Van Eekert, M.H.A.; De Vos, W.M.; Smidt, H. The little bacteria that can - Diversity, genomics and ecophysiology of “Dehalococcoides” spp. in contaminated environments. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.L.; Jiang, J.; Zinder, S.H. Dehalogenation of chlorobenzenes, dichlorotoluenes, and tetrachloroethene by three Dehalobacter spp. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3776–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchester, M.J.; Hug, L.A.; Zarek, M.; Zila, A.; Edwards, E.A. Discovery of a trans-dichloroethene-respiring Dehalogenimonas species in the 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane-dechlorinating WBC-2 consortium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 5280–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Ding, C.; He, J. Detoxification of 1,1,2-trichloroethane to ethene by desulfitobacterium and identification of its functional reductase gene. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, A.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, D.; Rogers, M.J.; Lee, P.K.H.; He, J. A comparative genomics and reductive dehalogenase gene transcription study of two chloroethene-respiring bacteria, Dehalococcoides mccartyi strains MB and 11a. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, D.B.; Oppentocht, J.E.; Poelarends, G.J. Microbial dehalogenation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beil, S.; Timmis, K.N.; Pieper, D.H. Genetic and biochemical analyses of the tec operon suggest a route for evolution of chlorobenzene degradation genes. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anandarajah, K.; Kiefer, P.M.; Donohoe, B.S.; Copley, S.D. Recruitment of a double bond isomerase to serve as a reductive dehalogenase during biodegradation of pentachlorophenol. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 5303–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, R.N. Structure, Catalytic Mechanism, and Evolution of the Glutathione Transferases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1997, 10, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.; Rhee, S.; Fennell, D.E.; Kerkhof, J.; Hentschel, U.; Häggblom, M.M.; Kerkhof, L.J.; Ha, M.M. Reductive Dehalogenation of Brominated Phenolic Compounds by Microorganisms Associated with the Marine Sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigold, P.; El-Hadidi, M.; Ruecker, A.; Huson, D.H.; Scholten, T.; Jochmann, M.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. A metagenomic-based survey of microbial (de)halogenation potential in a German forest soil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.; Sandy, M. Mechanistic considerations of halogenating enzymes. Nature 2009, 460, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofrichter, M.; Ullrich, R.; Pecyna, M.J.; Liers, C.; Lundell, T. New and classic families of secreted fungal heme peroxidases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 871–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, P.; Morris, D.R.; Brown, S.; Eberwein, H. Chloroperoxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Wuosmaa, A.M.; Hager, L.P. Methyl Chloride Transferase: A Carbocation Route for Biosynthesis of Halometabolites. Science 1982, 249, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollis, D.L.; Cheah, E.; Cygler, M.; Dijkstra, B.; Frolow, F.; Franken, S.M.; Harel, M.; Remington, S.J.; Silman, I.; Schrag, J. The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benning, M.M.; Taylor, K.L.; Liu, R.-Q.; Yang, G.; Xiang, H.; Wesenberg, G.; Dunaway-Mariano, D.; Holden, H.M. Structure of 4-Chlorobenzoyl Coenzyme A Dehalogenase Determined to 1.8 Å Resolution: An Enzyme Catalyst Generated via Adaptive Mutation. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 8103–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T.; Vlieg, H.; Tang, L.; Spelberg, J.H.L.; Smilda, T.I.M.; Poelarends, G.J.; Bosma, T.; van Merode, A.E.J.; Fraaije, M.W.; Janssen, D.B. Halohydrin Dehalogenases Are Structurally and Mechanistically Related to Short-Chain Dehydrogenases/Reductases. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5058–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.B.; Sternberg, M.J.E. Two new examples of protein structural similarities within the structure—Function twilight zone. Protein Eng. 1997, 10, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stammers, D.K.; Ren, J.; Leslie, K.; Nichols, C.E.; Lamb, H.K.; Cocklin, S.; Dodds, A.; Hawkins, A.R. The structure of the negative transcriptional regulator NmrA reveals a structural superfamily which includes the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6619–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppermann, U.; Filling, C.; Hult, M.; Shafqat, N.; Wu, X.; Lindh, M.; Shafqat, J.; Nordling, E.; Kallberg, Y.; Persson, B.; et al. Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (SDR): The 2002 update. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2003, 143–144, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filling, C.; Berndt, K.D.; Benach, J.; Knapp, S.; Prozorovski, T.; Nordling, E.; Ladenstein, R.; Jörnvall, H.; Oppermann, U. Critical residues for structure and catalysis in short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25677–25684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomvall, H.; Persson, B.; Jörnvall, H.; Persson, B.; Krook, M.; Atrian, S.; Gonzàlez-Duarte, R.; Jeffery, J.; Ghosh, D. Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases(SDR). Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6003–60013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, I.S.; Dijkstra, B.W. Identification of the Mg2+-binding site in the P-type ATPase and phosphatase members of the HAD (haloacid dehalogenase) superfamily by structural similarity to the response regulator protein CheY. Biochem. J. 1999, 339 Pt 2, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.L.; Liu, R.Q.; Liang, P.H.; Price, J.; Dunaway-Mariano, D.; Tonge, P.J.; Clarkson, J.; Carey, P.R. Evidence for Electrophilic Catalysis in the 4-Chlorobenzoyl-CoA Dehalogenase Reaction: UV, Raman, and 13C-NMR Spectral Studies of Dehalogenase Complexes of Benzoyl-CoA Adducts. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 13881–13888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peat, T.S.; Newman, J.; Balotra, S.; Lucent, D.; Warden, A.C.; Scott, C. The structure of the hexameric atrazine chlorohydrolase AtzA. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffernick, J.L.; Reynolds, E.; Fedorov, A.A.; Fedorov, E.; Almo, S.C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Wackett, L.P. X-ray structure and mutational analysis of the atrazine chlorohydrolase TrzN. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30606–30614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streltsov, V.A.; Prokop, Z.; Damborský, J.; Nagata, Y.; Oakley, A.; Wilce, M.C.J. Haloalkane dehalogenase LinB from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26: X-ray crystallographic studies of dehalogenation of brominated substrates. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 10104–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, R.M.; Bazzacco, P.; Poelarends, G.J.; Johnson, W.H.; Yoon, J.K.; Burks, E.A.; Serrano, H.; Thunnissen, A.M.W.H.; Whitman, C.P.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structures of native and inactivated cis-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase: Structural basis for substrate specificity and inactivation by (R)-oxirane-2-carboxylate. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwek, A.; Omi, R.; Hirotsu, K.; Jitsumori, K.; Esaki, N.; Kurihara, T.; Paneth, P. Binding modes of DL-2-haloacid dehalogenase revealed by crystallography, modeling and isotope effects studies. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 540, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widersten, M. Heterologous Expression in Escherichia coli of Soluble Active-Site Random Mutants of Haloalkane Dehalogenase from Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 by Coexpression of Molecular Chaperonins GroEL/ES 1. Protein Exp. Purif. 1998, 395, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kurihara, T.; Miyagi, M.; Tsunasawa, S.; Nishihara, M.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K. Paracatalytic Inactivation of L-2-Haloacid Dehalogenase from Pseudomonas sp. YL by Hydroxylamine. Biochemistry 1997, 272, 3363–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, F.; Van Den Wijngaard, A.J.; Bos, R.; Pentenga, M.; Janssen, D.B. The role of spontaneous cap domain mutations in haloalkane dehalogenase specificity and evolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17490–17494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pries, F.; Kingma, J.; Krooshof, G.H.; Jeronimus-Stratingh, C.M.; Bruins, A.P.; Janssen, D.B. Histidine 289 is essential for hydrolysis of the alkyl-enzyme intermediate of haloalkane dehalogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10405–10411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otyepka, M.; Banáš, P.; Magistrato, A.; Carloni, P.; Damborský, J. Second step of hydrolytic dehalogenation in haloalkane dehalogenase investigated by QM/MM methods. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 70, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, D.W.; Müller, C.; Reardon, K.F. Development of a fibre-optic enzymatic biosensor for 1,2-dichloroethane. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, T.; Liu, J.-Q.; Nardi-Dei, V.; Koshikawa, H.; Nobuyoshi, E.; Soda, K. Comprehensive Site-Directed Mutagenesis of L-2-Halo Acid Dehalogenase to to Probe Catalytic Amino Residues. J. Biochem 1995, 117, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdiyatmo, U.; Asmara, W.; Tsang, J.S.; Baines, A.J.; Bull, A.T.; Hardman, D.J. Protein engineering of the 2-haloacid halidohydrolase IVa from Pseudomonas cepacia MBA4. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohana, R.F.; Encell, L.P.; Zhao, K.; Simpson, D.; Slater, M.R.; Urh, M.; Wood, K.V. HaloTag7: A genetically engineered tag that enhances bacterial expression of soluble proteins and improves protein purification. Protein Exp. Purif. 2009, 68, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, A.J.; Prokop, Z.; Boháč, M.; Kmuníček, J.; Jedlička, T.; Monincová, M.; Kutá-Smatanová, I.; Nagata, Y.; Damborský, J.; Wilce, M.C.J. Exploring the structure and activity of haloalkane dehalogenase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26: Evidence for product- and water-mediated inhibition. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Guo, H. Electrostatic influence of active-site waters on the nucleophilic aromatic substitution catalyzed by 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA dehalogenase. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4249–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jitsumori, K.; Omi, R.; Kurihara, T.; Kurata, A.; Mihara, H.; Miyahara, I.; Hirotsu, K.; Esaki, N. X-Ray crystallographic and mutational studies of fluoroacetate dehalogenase from Burkholderia sp. strain FA1. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, R.; Konkimalla, V.B.; Ratha, J. In-silico Rational Protein Engineering and Design Approach to Improve Thermostability of a Haloalkane Dehalogenase Enzyme. Am. J. Bioinform. 2015, 4, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, S.; Changey, F.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Scott, C.; Martin-Laurent, F. Ongoing functional evolution of the bacterial atrazine chlorohydrolase AtzA. Biodegradation 2014, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, S.; Taylor, M.C.; Russell, R.J.; Jermiin, L.S.; Jackson, C.J.; Oakeshott, J.G.; Scott, C. Intramolecular Epistasis and the Evolution of a New Enzymatic Function. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banta, S. Protein Engineering for Bioelectrocatalysis: We can do more than Vmax. In Proceedings of the 217th ECS Meeting, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 25–30 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, D. Directed evolution and characterization of atrazine chlorohydrolase variants with enhanced activity. Biochemistry 2013, 78, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seffernick, J.L.; McTavish, H.; Osborne, J.P.; De Souza, M.L.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Wackett, L.P. Atrazine chlorohydrolase from Pseudomonas sp. strain ADP is a metalloenzyme. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 14430–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yeung, N.; Sieracki, N.; Marshall, N.M. Design of Functional Metalloproteins. Nature 2009, 460, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schanstra, J.P.; Janssen, D.B. Kinetics of halide release of haloalkane dehalogenase: Evidence for a slow conformational change. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 5624–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdul Hamid, A.A.; Tengku Abdul Hamid, T.H.; Abdul Wahab, R.; Omar, M.S.S.; Huyop, F. An S188V Mutation Alters Substrate Specificity of Non-Stereospecific α-Haloalkanoic Acid Dehalogenase E (DehE). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, A.A.A.; Wong, E.L.; Joyce-Tan, K.H.; Shamsir, M.S.; Hamid, T.H.T.A.; Huyop, F. Molecular modelling and functional studies of the non-stereospecific α -haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase (DehE) from Rhizobium sp. RC1 and its association with 3-chloropropionic acid (β-Chlorinated Aliphatic acid). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2013, 27, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.A.A.; Hamid, T.H.T.A.; Wahab, R.A.; Huyop, F. Identification of functional residues essential for dehalogenation by the non-stereospecific α-Haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase from Rhizobium sp. RC1. J. Basic Microbiol. 2015, 55, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banáš, P.; Otyepka, M.; Jeřábek, P.; Petřek, M.; Damborsky, J. Mechanism of enhanced conversion of 1,2,3-Trichloropropane by mutant Haloalkane dehalogenase revealed by molecular modeling. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosma, T.; Damborsk, J.; Stucki, G.; Janssen, D.B. Biodegradation of 1,2,3-Trichloropropane through Directed Evolution and Heterologous Expression of a Haloalkane Dehalogenase Gene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3582–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, M.; Klvana, M.; Prokop, Z.; Chaloupkova, R.; Banas, P.; Otyepka, M.; Wade, R.C.; Tsuda, M.; Nagata, Y.; Damborsky, J. Redesigning dehalogenase access tunnels as a strategy for degrading an anthropogenic substrate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepankova, V.; Damborsky, J.; Chaloupkova, R. Organic co-solvents affect activity, stability and enantioselectivity of haloalkane dehalogenases. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 8, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepankova, V.; Khabiri, M.; Brezovsky, J.; Pavelka, A.; Sykora, J.; Amaro, M.; Minofar, B.; Prokop, Z.; Hof, M.; Ettrich, R.; et al. Expansion of access tunnels and active-site cavities influence activity of haloalkane dehalogenases in organic cosolvents. Chembiochem 2013, 14, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manickam, N.; Mau, M.; Schlömann, M. Characterization of the novel HCH-degrading strain, Microbacterium sp. ITRC1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 69, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnuson, J.K.; Stern, R.V.; Gossett, J.M.; Zinder, S.H.; Burris, D.R. Reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene to ethene by a two-component enzyme pathway. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maymó-Gatell, X.; Chien, Y.; Gossett, J.M.; Zinder, S.H. Isolation of a bacterium that reductively dechlorinates tetrachloroethene to ethene. Science 1997, 276, 1568–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.K.; Webb, R.I.; Sly, L.I.; Denman, S.E.; Mcsweeney, C.S. Isolation and survey of novel fluoroacetate-degrading bacteria belonging to the phylum Synergistetes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, J.A.; Skinner, A.J.; Cooper, R.A. Partial purification, stereospecificity and stoichiometry of three dehalogenases from a Rhizobium species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1988, 49, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.H.; Lovatt, D.; Weightman, A.J.; Senior, E.; Bull, A.T. The growth of Pseudomonas putida on chlorinated aliphatic acids and its dehalogenase activity. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1979, 114, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brokamp, A.; Schmidt, F.R.J. Survival of Alcaligenes xylosoxidans degrading 2,2-dichloropropionate and horizontal transfer of its halidohydrolase gene in a soil microcosm. Curr. Microbiol. 1991, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, E.; Bull, A.T.; Slater, J.H. Enzyme evolution in a microbial community growing on the herbicide Dalapon. Nature 1976, 263, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, W. Isolation, characterization and identification of a Paracoccus sp. 2-haloacid-degrading bacterium from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perlevis. J. Basic Microbiol. 2011, 51, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, L.M.; Marchesi, J.R. Isolation of novel bacteria able to degrade α-halocarboxylic acids by enrichment from environmental samples. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Ritalahti, K.M.; Aiello, M.R.; Löffler, F.E. Complete detoxification of vinyl chloride by an anaerobic enrichment culture and identification of the reductively dechlorinating population as a Dehalococcoides species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, E.R.; Payne, J.A.; Young, R.M.; Starr, M.G.; Perry, M.P.; Fahnestock, S.; Ebersole, R.C.; Ellis, D.E. Molecular Analysis of Dehalococcoides 16S Ribosomal DNA from throughout North America and Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doesburg, W.; Van Eekert, M.H.A.; Middeldorp, P.J.M.; Balk, M.; Schraa, G.; Stams, A.J.M. Reductive dechlorination of β-hexachlorocyclohexane (β-HCH) by a Dehalobacter species in coculture with a Sedimentibacter sp. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 54, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrian, L.; Manz, W.; Szewzyk, U.; Görisch, H. Physiological characterization of a bacterial consortium reductively dechlorinating 1,2,3- and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Cangelosi, V.M.; Zastrow, M.L.; Tegoni, M.; Plegaria, J.S.; Tebo, A.G.; Mocny, C.S.; Ruckthong, L.; Qayyum, H.; Pecoraro, V.L. Protein Design: Toward Functional Metalloenzymes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 3495–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degtyarenko, K. Bioinorganic motifs: Towards functional classification of metalloproteins. Bioinform. Rev. 2000, 16, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, J. Metalloproteins. Nature 2009, 460, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, K.J.; Rutherford, J.C.; Ford, D.; Robinson, N.J. Metalloproteins and metal sensing. Nature 2009, 460, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, R.H.; Kennepohl, P.; Solomon, E.I. Structural and Functional Aspects of Metal Sites in Biology. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 2239–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palm-Espling, M.E.; Niemiec, M.S.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Role of metal in folding and stability of copper proteins in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.J.; Sontz, P.A.; Ambroggio, X.I.; Tezcan, F.A. Metals in Protein–Protein Interfaces. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2014, 43, 409–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.S.; Majumdar, I.; Grishin, N.V. Structural classification of zinc fingers: Survey and summary. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 532–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auld, D.S. Structural Zinc Sites. In Handbook of Metalloproteins; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; ISBN 9780470028636. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, L.C.; McTavish, H.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Wackett, L.P. Field-scale remediation of atrazine-contaminated soil using recombinant Escherichia coli expressing atrazine chlorohydrolase. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Peacock, A.F.A.; Stuckey, J.A.; Pecoraro, V.L. Hydrolytic catalysis and structural stabilization in a designed metalloprotein. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berks, B.C. A common export pathway for proteins binding complex redox cofactors? Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 22, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, A.S.; Pike, D.; Nanda, V. Computational Design of Metalloproteins. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Clifton, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 1216, pp. 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hellinga, H.W.; Richards, F.M. Construction of new ligand binding sites in proteins of known structure: I. Computer-aided modeling of sites with pre-defined geometry. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 763–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, N.D.; Yuan, S. Metal search: A computer program that helps design tetrahedral metal-binding sites. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 1995, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stucki, G.; Thüer, M. Experiences of a Large-Scale Application of 1,2-Dichloroethane Degrading Microorganisms for Groundwater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamo-Bethencourt, V.; Aldridge, S.; Coombs, A.; Defrancesco, L.; Huggett, B.; Osborne, R. Mustard gas enzyme (News in brief). Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokop, Z.; Opluštil, F.; DeFrank, J.; Damborský, J. Enzymes fight chemical weapons. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieters, R.J.; Lutje Spelberg, J.H.; Kellogg, R.M.; Janssen, D.B. The enantioselectivity of haloalkane dehalogenases. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerbeek, A.; Szymański, W.; Feringa, B.L.; Janssen, D.B. Dynamic kinetic resolution process employing haloalkane dehalogenase. ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, G.V.; Encell, L.P.; McDougall, M.G.; Hartzell, D.D.; Karassina, N.; Zimprich, C.; Wood, M.G.; Learish, R.; Ohana, R.F.; Urh, M.; et al. HaloTag: A novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weimer, E.P.; Rao, E.; Brendel, M. Molecular structure and genetic regulation of SFA, a gene responsible for resistance to formaldehyde in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and characterization of its protein product. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1993, 237, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusn, T.Y.; Huyop, F. Degradation of 3-Chloropropionic Acid by Escherichia coli JM109 Expressing Dehalogenase (deh) Gene used as Selection Marker. Biotechnology 2009, 8, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, P.E. Dehalogenases applied to industrial-scale biocatalysis. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegel, J.; Wu, Q. Microbial reductive dehalogenation of polychrorinated biphenyls. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2000, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena-Benitez, G.L.; Gandia-Herrero, F.; Graham, S.; Larson, T.R.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; French, C.E.; Rylott, E.L.; Bruce, N.C. Engineering a Catabolic Pathway in Plants for the Degradation of 1,2-Dichloroethane. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LeBel, G.L.; Benoit, F.M.; Williams, D.T. A one-year survey of halogenated disinfection by-products in the distribution system of treatment plants using three different disinfection processes. Chemosphere 1997, 34, 2301–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.T.; LeBel, G.L.; Benoit, F.M. Disinfection by-products in Canadian drinking water. Chemosphere 1997, 34, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hozalski, R.M.; Leach, L.H.; Camper, A.K.; Goslan, E.H.; Parsons, S.A.; Xie, Y.F.; Lapara, T.M. Isolation and characterization of haloacetic acid-degrading Afipia spp. from drinking water. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 297, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauble, H.; Kennedy, M.C.; Emptage, M.H.; Beinert, H.; Stout, C.D. The reaction of fluorocitrate with aconitase and the crystal structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13699–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunge, M.; Lechner, U. Anaerobic reductive dehalogenation of polychlorinated dioxins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Park, J.W.; Häggblom, M.M. Enriching for microbial reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, D.E.; Nijenhuis, I.; Wilson, S.F.; Zinder, S.H.; Häggblom, M.M. Dehalococcoides ethenogenes Strain 195 Reductively Dechlorinates Diverse Chlorinated Aromatic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Fennell, D.E. Dechlorination and Detoxification of 1,2,3,4,7,8-Hexachlorodibenzofuran by a Mixed Culture Containing Dehalococcoides ethenogenes Strain 195. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodenburg, L.A.; Du, S.; Lui, H.; Guo, J.; Oseagulu, N.; Fennell, D.E. Evidence for dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and -furans in wastewater collection systems in the New York Metropolitan Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6612–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.B.; Häggblom, M.M.; Kerkhof, L.J. Comparison of anaerobic microbial communities from Estuarine sediments amended with halogenated compounds to enhance dechlorination of 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 61, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, C.; Fennell, D.; Häggblom, M. Anaerobic reductive dechlorination of chlorinated dioxins in estuarine sediments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 57, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.B.; Liu, F.; Fennell, D.E.; Häggblom, M.M. Biostimulation and bioaugmentation to enhance dechlorination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins in contaminated sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunge, M.; Adrian, L.; Kraus, A.; Opel, M.; Lorenz, W.G.; Andreesen, J.R.; Görisch, H.; Lechner, U. Reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated dioxins by an anaerobic bacterium. Nature 2003, 421, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cichocka, D.; Nijenhuis, I.; Richnow, H.H.; Fennell, D.E. Carbon isotope fractionation during dechlorination of 1,2,3,4-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by a Dehalococcoides-containing culture. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunge, M.; Wagner, A.; Fischer, M.; Andreesen, J.R.; Lechner, U. Enrichment of a dioxin-dehalogenating Dehalococcoides species in two-liquid phase cultures. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2670–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäntynen, S.; Rantalainen, A.L.; Häggblom, M.M. Dechlorinating bacteria are abundant but anaerobic dechlorination of weathered polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in contaminated sediments is limited. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesseler, M.; Bogdanović, X.; Hidalgo, A.; Berenguer, J.; Palm, G.J.; Hinrichs, W.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Cloning, functional expression, biochemical characterization, and structural analysis of a haloalkane dehalogenase from Plesiocystis pacifica SIR-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortova, A.; Sebestova, E.; Stepankova, V.; Koudelakova, T.; Palkova, L.; Damborsky, J.; Chaloupkova, R. DspA from Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: The first biochemically characterized haloalkane dehalogenase of non-microbial origin. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffar, A.; Tabata, M. Enhanced dechlorination of chlorobenzene compounds on fly ash: Effects of metals, solvents, and temperature. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2010, 3, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidberger, J.W.; Wilce, J.A.; Weightman, A.J.; Whisstock, J.C.; Wilce, M.C.J. The Crystal Structure of DehI Reveals a New α-Haloacid Dehalogenase Fold and Active-Site Mechanism. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 378, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, D.L. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Aquatic Sediments: Environmental Fate and Outlook for Biological Treatment. In Dehalogenation; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 443–465. [Google Scholar]
- Pepino, M.; Tiemann, C.; Patterson, B.; Wice, B.; Klein, S. Sucralose affects glycemic and hormonal responses to an oral glucose load. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2530–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Liu, G.; Hu, J.; Zheng, M. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans formed from sucralose at high temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wielgosiński, G. The Possibilities of Reduction of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-P-Dioxins and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans Emission. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 2010, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Huang, H. Chemical dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene with polyethylene glycol and hydroxide: Dominant effect of temperature and ionic potential. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addink, R.; Olie, K. Mechanisms of Formation and Destruction of Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans in Heterogeneous Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Cieplik, M.K.; Budarin, V.L.; Gronnow, M.; Jansson, S. Mechanistic evaluation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin, dibenzofuran and naphthalene isomer fingerprints in microwave pyrolysis of biomass. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |



| Organism | Dehalogenase Designate | Habitats | Substrate of Halogenation | Corresponding Product | Property of Reaction Mechanism | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moraxella Sp. strain B | haloacetate dehalogenase H-1 and H-2 | soil | l-2-haloacid | d-2-hydroxy acids | stereospecific | [95] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. YL, Pseudomonas putida No. l09, Pseudomonas Sp. CBS3 | l-2-haloacid dehalogenase, 2-haloacid dehalogenase | soil | l-2- chloropropionate, 2-monochloropropionate | lactate, glyoxylate, and pyruvate | stereospecific | [49,57,96] |
| Pseudomonas cepacia MBA4 | l-2-haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase IVa | soil | monobromoacetic acid | N.S | stereospecific | [47] |
| Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 | haloacid dehalogenase (dhlB) | soil | 2-halogenated carboxylic acids | d-Lactate | stereospecific | [53,97] |
| Pseudomonas. putida AJ1 (hadL) | l-2-haloakanoic acid halidohydrolase | soil | 2-monochloropropionic acid | lactate with the release of chloride | stereospecific | [98] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. 113 | d,l-2-haloacid dehalogenase | d- and l-2-haloalkanoic acids, producing | l- and d-2-hydroxyalkanoic acids | non-stereospecific | [51] | |
| Pseudomonas putida strain PP3 | α-haloacid dehalogenase DehI and DehII | soil | d- and l-2-haloalkanoic acids | l- and d-2-hydroxyalkanoic | stereospecific | [99] |
| Microbacterium Sp. strain, ITRC1 | hydrolytic dehalogenase (linB) and dehydrogenase (linC) | soil | γ-pentachlorocyclohexen and a 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-diol | 2,5-dichlorophenol (2,5-DCP) | non-stereospecific | [100] |
| Agrobacterium tumefaciens RS5 | hydrolytic haloalkanoic acid dehalogenase (DhlS5II) and cryptic l-isomer-specific dehalogenase (DhlS5I) | soil | 2,2-dichloropropionate (DCPA), chloroacetic acid (MCA), dichloroacetic acid (DCA), and 2-chloropropionic acid (CPA) | N.S | non-stereospecific and stereospecific | [101] |
| Burkholderia cepacia MBA4 | dehalogenase IVa (hdlIVa) | soil | l-2-haloacid | d-2-hydroxyacids | stereospecific | [47,56] |
| Pseudomonas pavonaceae | cis- and trans-3-chloroacrylic acid dehalogenase (CaaD and cis-CaaD) | soil | cis- and trans-3-chloroacrylate | malonate semialdehyde | specific hydrolysis | [102] |
| Burkholderia Sp. WS | (S)-2-haloacid dehalogenase, 2-haloacrylate r | soil | (S)-2-haloalkanoic acids, 2-chloroacrylate | (S)-2-chloropropionate, (R)-lactate, (S)-2-chloropropionic | NADPH-dependent reduction | [103,104] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. Strain CBS3 | 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase | soil | 4-chlorobenzoate | 4-hydroxybenzoate | non-stereospecific | [105] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. strain YL | 2-haloacrylate hydratase l-2-haloacid dehalogenase (l-DEX) (d,l-DEX) | soil | l-2-chloropropionate –chloroacrylate (2-CAA) of l and d isomers of 2-CPA of l-2-haloalkanoic acid, monochloroacetate and monoiodoacetate, as 2-bromohexadecanoate | 2-chloro-2-hydroxypropionate, d- and l-lactates, d-2-hydroxyalkanoic acids | Stereo and non-stereospecific | [106] |
| Methylobacterium Sp. CPA1 (dl-DEX Mb) | d,l-2-Haloacid dehalogenase | soil | d- and l-2-haloalkanoic acids, d- and L-2-chloropropionates | l- and d-2-hydroxyalkanoic acids | non-stereospecific | [50] |
| Sulfolobus tokodaii | l-2-haloacid dehalogenase | soil | chloropropionic acid | stereospecific | [107] | |
| Marine Rhodobacteraceae | l-haloacid dehalogenase | soil | monobromoacetic acid (100%) followed by monochloroacetic acid (MCAA) (71%), S-bromopropionic acid (71%), S-chloropropionic acid (MCPA) (10%) and dichloroacetic acid | N.S | stereospecific | [108] |
| Burkholderia Sp. FA1 | fluroacetate dehalogenase | soil | fluoroacetate to glycolate | glycolate | non-stereospecific | [74] |
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009 | reductive dehalogenase | soil | 3-chlorobenzoate | 3-chlorobenzoyl coenzyme A (3-chlorobenzoyl–CoA) to benzoyl-CoA and further to | non-stereospecific | [109] |
| Rhodococcus Sp. m15-3 (DhaA) and Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10 (DhlA) | haloalkane dehalogenase | soil | 1,2-dichloroethane andtrihalopropanes to 2,3-dihalogenated propanols | 2-chloroethanol, chloroacetaldehyde, chloroacetate, and glycolate | non-stereospecific | [110,111] |
| Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5 | haloalkane Dehalogenase (DadB) | arctic Ocean | haloalkanes | alkanols | non-stereospecific | [112,113,114] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. strain 113 | d,l-2-haloacid Dehalogenase, | soil | d - and l-2-chloropropionates, trichloroacetate | l- and d-lactates, oxalate | non-stereospecific dehalogenation | [59] |
| Arthrobacter Sp. strain TM-1 | 4-chlorobenzoyl-coenzyme A dehalogenase | soil | 4-chlorobenzoyl coenzyme A (4-CBA-CoA), 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA | 4-hydroxybenzoyl coenzyme A (4-HBA-CoA), 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA | hydrolytic substitution | [115] |
| Paracoccus Sp. DEH99 | 2-haloacid dehalogenase | Marine sponge H. perlevis | 2-CPA, 2-bromopropionic acid (2-BPA), and iodoacetic acid | chiral reagents | stereospecific dehalogenation | [116] |
| Alcaligenes xylosoxidans Sp. denitrificans ABIV | d,l-2-haloalkanoic acid halidohydrolase (DhlIV) | Soil | mono- and dichloroacetic acid and mono- and dichloropropionic acid | glycolate and pyruvate | specific hydrolysis | [117] |
| Rhizobium Sp. | haloalkanoate dehalogenases (DehL, (DehD, (DehE))) | soil | 2,2-dichloropropionic acid, 2-chloropropionic acid, monochloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, 2-chlorobutyric acid and 2,3-dichloropropionic acid | d(−) and l(+) lactate, pyruvate | stereo/non-stereospecific | [118,119,120] |
| Methylobacterium Sp. HJ1 | 2-haloalkanoic acid hydrolytic dehalogenase (DehE) | soil | 2,2-dichloropropionic acid and d,l-2-chloro-propionic acid | to produce pyruvate and lactate | non-stereospecific | [121] |
| Arthrobacter Sp. strain S1 | ||||||
| Dehalococcoides ethenogenes | TCE reductive dehalogenase (TCE-RDase) | tetrachloroethene or trichloroethene (TCE) | ethene | non-stereospecific | [122] | |
| Dehalococcoides Sp. Strain BAV1 | reductive dehalogenase (RDase) | aquifer | chloroethene | ethene | non-stereospecific | [33,34,123,124] |
| Sphingomonas chlorophenolica | tetrachlorohydroquinone dehalogenase | soil | pentacholophenol | tetrachlorohydroquinone (TCHQ), trichlorohydroquinone, and 2,6-dichlorohydroquinone | non-stereospecific | [125] |
| Shewanella sediminis | reductive tetrachloroethene dehalogenase | soil | tetrachloroethene (PCE) | trichloroethene (TCE) | non-stereospecific | [126] |
| Psychrobacter cryohalolentis K5 | haloalkane dehalogenase (DpcA) | Saline-water (Siberian permafrost | 1b and other halogenated subtrates | non-stereospecific | [117,120] | |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 | haloalkane dehalogenase LinB | soil | 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-1,4-cyclo- hexadiene to 2,5-dichloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-diol via 2,4,5-trichloro-2,5-cyclohexane-1-ol during γ-HCH dechlorination | chlorophenols | non-stereospecific | [66,121,124] |
| Agrobacterium radiobacter strain AD1 | haloalcohol dehalogenase (HheC) | soil | 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol | eposide (chloride, halide and proton) | non-specific | [127] |
| Organisms | Dehalogenase Complex | Gene | PDB Entry | Catalytically Active Residue | Halide-Stabilizing Residues | Refinement Resolution (Å) | Family | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudomonas Sp. YL | l-2-haloacid dehalogenase | l-DEX YL | 1JUD | Asp-10, Asn-177 and Lys-151 | Tyr-12, Asn-119, Lys-151, Asn-177 and Trp-179 | 2.5 | homodimeric | [23] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. ADP | atrazine chlorohydrolase | AtzA | 4v1x, 4v1y | Asp-327, Glu-246, His-243 | N.S | 2.2, 2.8 | hexameric | [175] |
| Xanthobacter autotrophicus | haloalkane dehalogenase | dhlA | 2DHC | Asp-124, His-289, Asp-260 | Trp-125, Trp-175 | 1.9 | α/β fold | [19] |
| Rhodococcus Sp. | haloalkane dehalogenase | dhaA | 1BN6 | Asp-117, His-283, Glu-141 | Asn-52, Trp-118 | 1.5 | monomer | [65] |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv | haloalkane dehalogenase | Rv2579 | 2QVB | Asp-109, His-273, Glu-133 | Asn-39, Trp-110 | 1.19 | monomer | [117] |
| Bradyrhizobium japonicum | haloalkane dehalogenase | dhaA | 3A2M | Asp-103, His-280, Glu-127 | Asn-38, Trp-104 | 1.84 | homodimer | [120] |
| Marine microbial consortium | haloalkane dehalogenase | dmmA | 3U1T | Asp-144, His-315, Glu-168 | Asn-78, Trp-145 | 2.2 | monomer | [21] |
| Sphingobium Sp. MI1205 | haloalkane dehalogenase | linB | 4H77 | Asp-108, His-272, Glu-132 | Asn-38, Trp-109 | 1.6 | monomer | [121] |
| Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 | haloalkane dehalogenase | datA | 3WI7 | Asp-108, His-274, Glu-132 | Asn-43, Tyr-109 | 1.7 | monomer | [124] |
| Bradyrhizobium elkani USDA94 | haloalkane dehalogenase | dbeA | 4K2A | Asp-103, His-271, Glu-127 | Asn-38, Trp-104 | 2.2 | homodimer | [125] |
| Bradyhizobium japonicum USDA110 | haloalkane dehalogenase | dbjA | 3A2N | Asp-103, His-280, Glu-127 | Asn-38, Trp-104 | 1.89 | homodimer | [120] |
| Plesiocystis pacifica SIR-1 | dppA | 2XT0 | Asp-123, His-178, Asp-249 | Trp-124, Trp-163 | [264] | |||
| Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | dspA | NA | Asp-120, His-285, Glu-144 | Asn-53, Trp-121 | N.S | N.S | [265] | |
| Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5 | dadB | NA | Asp-108, His-271, Glu-132 | Asn-37, Trp-109 | N.S | N.S | [112] | |
| Pseudomonas Sp. YL | l-2-haloacid dehalogenase complexed with monochloroacetate, l-2-chlorobutyrate, l-2-chloro-3-methylbutyrate, or l-2-chloro-4-methylvalerate | l-DEX | 1ZRN, 1ZRM | Asp-10 | Arg-41 | 1.83, 2.0, 2.2, 2.2, | homodimer | [104] |
| Burkholderia cepacia | haloacid dehalogenase, l-2-monochloropropanoate intermediate | DehIVa | 2NO4, 2NO5 | Asp11 (Asp108), Ser119 and Asp181 | Arg42 (Arg41, 39), Asn120 (Asn119, 115), Trp180 (Trp 179, Phe175) | 1.93, 2.7 | homodimer | [54] |
| Rhodopseudomonas palustris | fluoroacetate dehalogenases | RPA1163 | 3R3U, 3R3V, 3R3W, 3R3X, 3R3Y, 3R3Z, 3R40, 3R41 | Asp110, His280, Asp134 | His155, Trp156 and Tyr219 | 1.6, 1.5, 1.6, 1.8, 1.15, 1.7, 1.05, 1.05, 1.05 | homodimeric | [266] |
| Methylobacterium Sp. CPA1 | D,l-2-haloacid dehalogenase | 4N2X | N.S | N.S | 1.7 | hexamer | [179] | |
| Pseudomonas putida strain PP3 | group I α-haloacid dehalogenase | Dehl | 3BJX | (Thr-62, Glu-66), and Asp189 | N.S | 2.3 | homodimer | [267] |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 | haloalkane dehalogenase | LinB | 1MJ5 | Asp-108, His-272, and Glu-132 | Asn-38 and Trp-109 | 0.95 | monomer | [12] |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 | haloalkane dehalogenase and complexes of linb with 1,2-propanediol/l-bromopropane-2-ol and 2-bromo-2-propene-l-ol | LinB | 1K6E, 1K63 | Asp-108, Glu-132, and His-272 | Primary (Asn-38 and Trp-109), Secondary (Trp-207, Pro-208, and Ile-211) | 1.85 | monomer | [177] |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 | haloalkane dehalogenase LinB/LinB with 1,3-propanediol | LinB | 1CV2, 1D07 | Asp-108, His-272, and Glu-132 | Asn-38 and Trp-109 | 1.58 Å, 2.0 Å | monomer | [66] |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26 | 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-1,4-cyclohexadiene hydrolase linB complexed with 1,2-dichloropropane | LinB | 1G42 | Asp-108, Glu-132, and His-272 | Asn-38 and Trp-109 | 1.8 | monomer | [189] |
| Burkholderia Sp. Strain FA1 | fluoroacetate dehalogenase | FAcD | 1Y37 | Asp-104, His-271, Asp-128 | Trp-150 and His-149 | 1.5 | homodimer | [191] |
| Pseudomonas Sp. Strain CBS-3 | 4-chlorobenzoyl-coenzyme A dehalogenase | CoA | 1NZY | Asp-145 and His-90, Gly-114/Ala-121 | Asp-145 | 1.8 | hexamer | [166] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ang, T.-F.; Maiangwa, J.; Salleh, A.B.; Normi, Y.M.; Leow, T.C. Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051100
Ang T-F, Maiangwa J, Salleh AB, Normi YM, Leow TC. Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications. Molecules. 2018; 23(5):1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051100
Chicago/Turabian StyleAng, Thiau-Fu, Jonathan Maiangwa, Abu Bakar Salleh, Yahaya M. Normi, and Thean Chor Leow. 2018. "Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications" Molecules 23, no. 5: 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051100
APA StyleAng, T. -F., Maiangwa, J., Salleh, A. B., Normi, Y. M., & Leow, T. C. (2018). Dehalogenases: From Improved Performance to Potential Microbial Dehalogenation Applications. Molecules, 23(5), 1100. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051100





