Compounds Identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLCs) Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of UPLC-MS Conditions
2.2. Optimization for Sample Extraction
2.3. Structural Characterization by UPLC-MS
2.4. Chlorogenic Acids
2.4.1. Characterization of p-Coumaroylquinic Acids (pCoQA, Mr = 338.1002)
2.4.2. Characterization of Caffeoylquinic Acids (CQA, Mr = 354.0951)
2.4.3. Characterization of Feruloylquinic Acids (FQA, Mr = 368.1107)
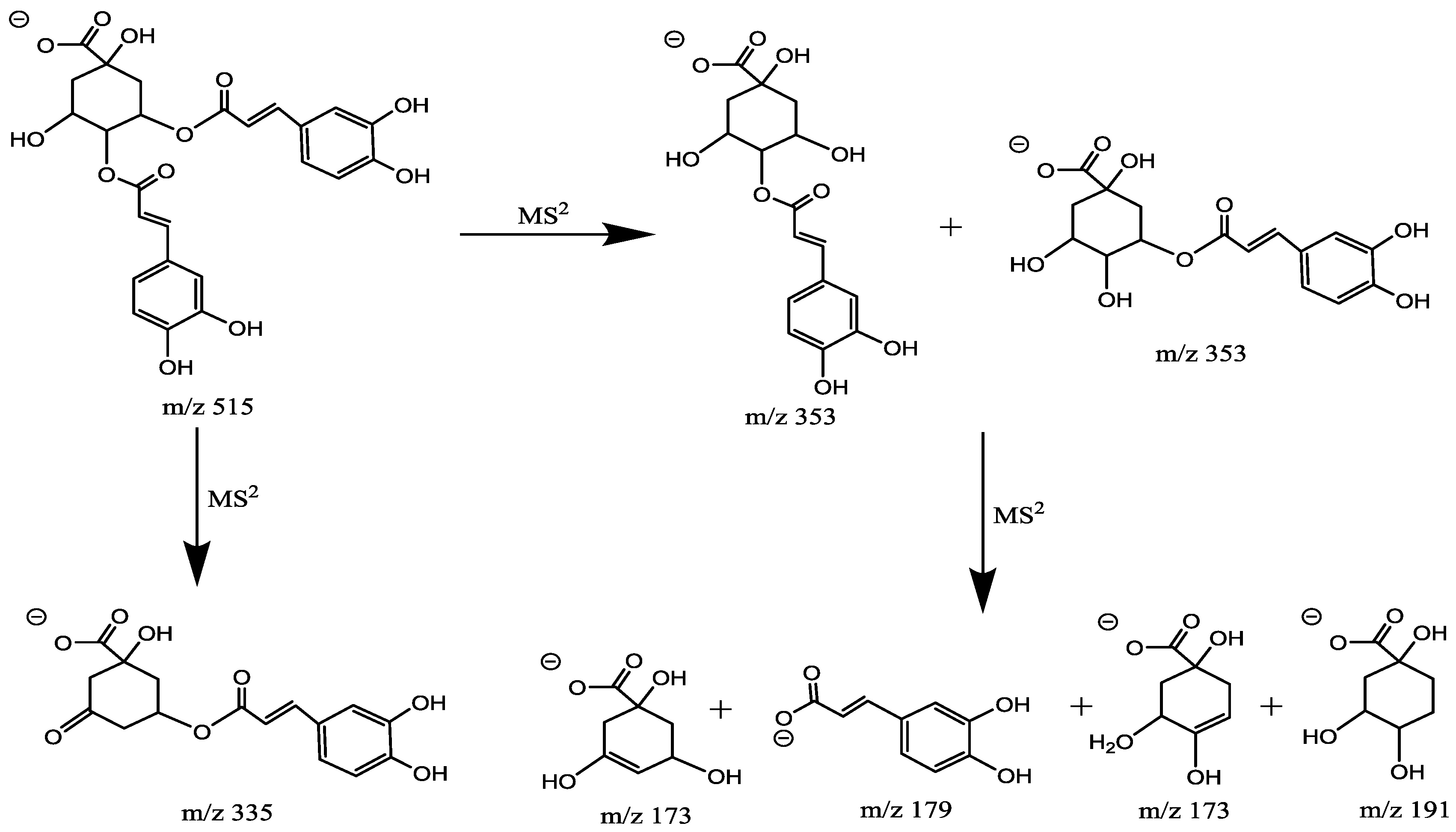
2.4.4. Characterization of Di-Caffeoylquinic Acid (di-CQA, Mr = 516.1268)
2.4.5. Characterization of Caffeoylglycoside (Mr = 342.0951)
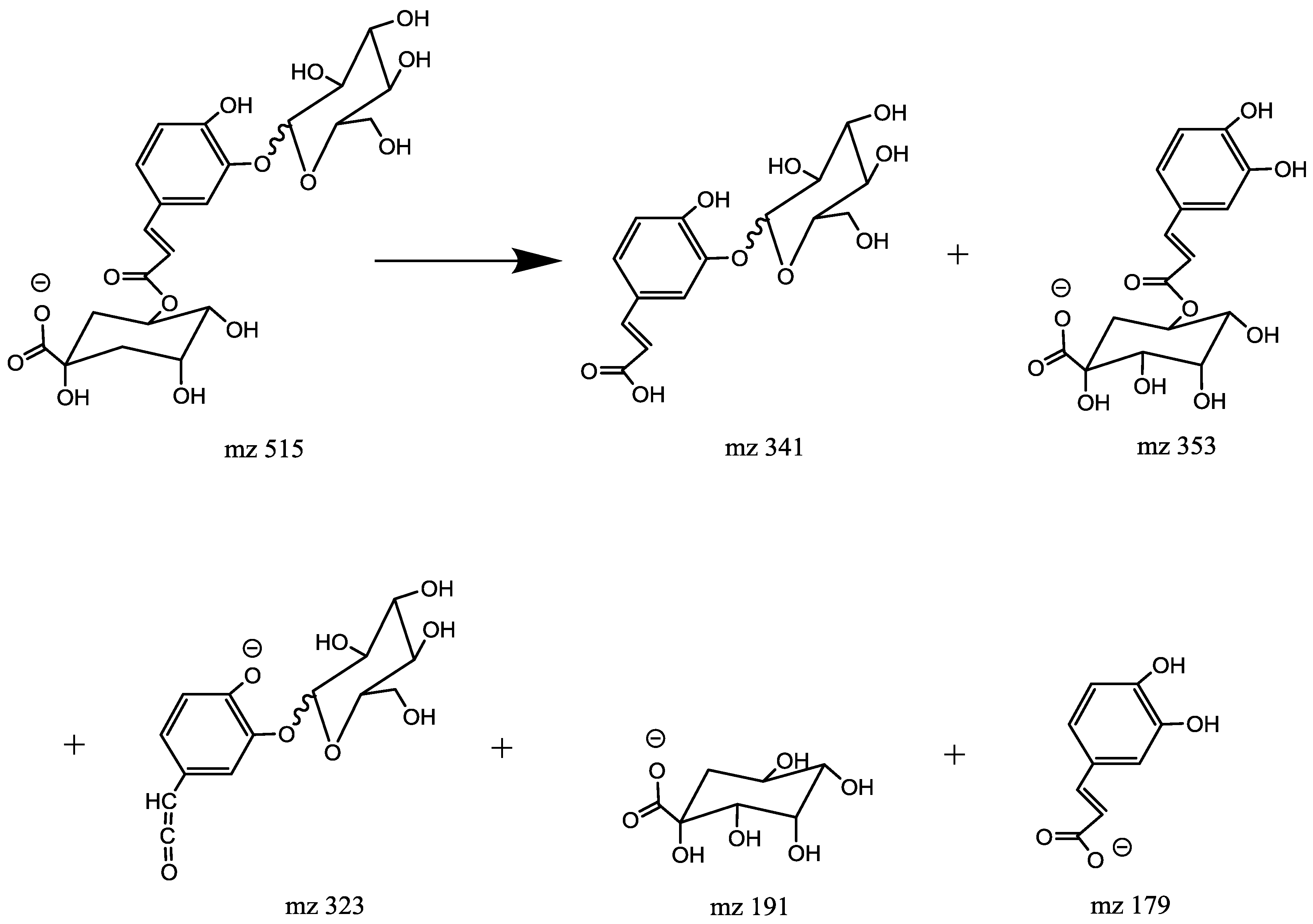
2.4.6. Characterization of Caffeoylquinic Acid Glucoside (CQA-Glycoside, Mr = 516.1434)
2.4.7. Characterization of Coumaroyl-Tricaffeoylquinic Acid (Mr = 824)
2.5. Flavonoids Derivatives
2.5.1. Characterization of Apigenin (Mr = 270.0528)
2.5.2. Characterization of Isorhamnetin (Mr = 316.0583)
2.5.3. Characterization of Kaempferol-Hexoside (Mr = 448.1006)
2.5.4. Characterization of Kaempferol-O-Dihexoside, Isorhamnetin-3-Apiosyl-(1→2)-Hexoside and Quercetin-3-O-Coumaroylgalactoside (Mr = 610.1323)
2.5.5. Characterization of Isorhamnetin-Hexoside (Mr = 478.1111)
2.5.6. Characterization of Kaempferol-Glucoside (Mr = 568.1217)
2.5.7. Characterization of Kaempferol-O-Glucoside-7-Rhamnoside and Kaempferol-3-O-Coumaroylglucoside (Mr = 594.1373)
2.5.8. Characterization of Quercetin-3-O-Apiosyl-(1→2)-Galactoside (Mr = 596.1377)
2.5.9. Characterization of Kaempferol-3-O-Galactoside and Quercetin-Hexoside (Mr = 464.0955)
2.5.10. Characterization of Quercetin-3-(2′′-Acetylgalactoside) (Mr = 506.1060)
2.5.11. Characterization of Quercetin-Dihexoside (Mr = 626.1483)
2.5.12. Characterization of Kaempferol 3-Apiosyl-(1→2)-Glucoside (Mr = 580.1428)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Extraction Method
3.4. UPLC−MS Analysis
3.5. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, J.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lee, M.S.; Chiu, Y.J.; Chao, W.K.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, M.K.; Peng, W.H. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Cuscuta chinensis Seeds in Mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Xu, S.; Lin, Q.; Jia, Z.; Han, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X. Purification, characterization and biological effect of reversing the kidney-yang deficiency of polysaccharides from semen cuscutae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhao, B.; Li, S.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, T.; Lin, R.; Li, J.; Li, X. The Difference of Chemical Components and Biological Activities of the Crude Products and the Salt-Processed Product from Semen Cuscutae. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 8656740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tan, D.; Wei, G.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhu, H.; Xue, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y. Studies on the Chemical Constituents of Cuscuta chinensis. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kuai, D.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Li, X. The Study on Total Flavonoids Content Comparison of Cuscuta chinensis and Three Differently Processed Products. World Sci. Technol.-Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Medica 2015, 17, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Pan, L.; Yuan, S.; Hao, B.; Lv, J.; Li, X. Study on simultaneous determination of five kinds of flavonoids in seeds of semen cuscutae by HPLC. World Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lv, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Li, X. HPLC Simultaneous Determination of 7 Components in Shuanghuangqudu Tablets. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2012, 18, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras-Claveria, L.; Jauregui, O.; Codina, C.; Tiburcio, A.F.; Bastida, J.; Viladomat, F. Analysis of phenolic compounds by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry in senescent and water-stressed tobacco. Plant Sci. 2012, 182, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbo-Neto, L.; Lopes, N.P. Online Identification of Chlorogenic Acids, Sesquiterpene Lactones, and Flavonoids in the Brazilian Arnica Lychnophora ericoides Mart. (Asteraceae) Leaves by HPLC-DAD-MS and HPLC-DAD-MS/MS and a Validated HPLC-DAD Method for Their Simultaneous Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regos, I.; Urbanella, A.; Treutter, D. Identification and Quantification of Phenolic Compounds from the Forage Legume Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5843–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.N.; Knight, S.; Kuhnert, N. Discriminating between the Six Isomers of Dicaffeoylquinic Acid by LC-MSn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.N.; Johnston, K.L.; Knight, S.; Kuhnert, N. Hierarchical scheme for LC-MSn identification of chlorogenic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2900–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Li, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; He, M.; Feng, Y. A robust platform based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography Quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry with a two-step data mining strategy in the investigation, classification, and identification of chlorogenic acids in Ainsliaea fragrans Champ. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1502, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ncube, E.N.; Mhlongo, M.I.; Piater, L.A.; Steenkamp, P.A.; Dubery, I.A.; Madala, N.E. Analyses of chlorogenic acids and related cinnamic acid derivatives from Nicotiana tabacumtissues with the aid of UPLC-QTOF-MS_MS based on the in-source collision-induced dissociation method. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, I.; Threadgill, M.D.; Hauck, B.; Donnison, I.; Winters, A. Isolation, identification and quantitation of hydroxycinnamic acid conjugates, potential platform chemicals, in the leaves and stems of Miscanthus × giganteus using LC-ESI-MSn. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnert, N.; Said, I.H.; Jaiswal, R. Assignment of Regio- and Stereochemistry of Natural Products Using Mass Spectrometry Chlorogenic Acids and Derivatives as a Case Study. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2014, 42, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R.; Kuhnert, N. Identification and Characterization of the Phenolic Glycosides of Lagenaria siceraria Stand. (Bottle Gourd) Fruit by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, R.; Halabi, E.A.; Karar, M.G.E.; Kuhnert, N. Identification and characterisation of the phenolics of Ilex glabra L. Gray (Aquifoliaceae) leaves by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, R.; Müller, H.; Müller, A.; Karar, M.G.; Kuhnert, N. Identification and characterization of chlorogenic acids, chlorogenic acid glycosides and flavonoids from Lonicera henryi L. (Caprifoliaceae) leaves by LC-MSn. Phytochemistry 2014, 108, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Yan, Y.; Guo, D.A. Characterization of phenolic compounds in the Chinese herbal drug Tu-Si-Zi by liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyckens, F.; Claeys, M. Mass spectrometry in the structural analysis of flavonoids. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (Hyperoside, Isoquercitrin, Astragalin, Luteolin-7-O-glucoside, Isorhamnetin, Quercetin, Kaempferol, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid, 3-caffeoylquinic acid, 4-caffeoylquinic acid, p-hydroxycinnamic acid, caffeic acid, 5-O-Feruloylquinic acid) are not available from the authors. |








| No. | tR(min) | Identification | [M − H] or [M+FA-H] | Molecular Formula | Exact Mass | [M − H]-m/z | Characteristic m/z of Ions in Negative Ion Mode |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.18 | Caffeoyl glucoside | M+FA-H | 539.1653 | MS2:503(100), 341(73) MS3:179(100), 323(25), 341(10) | ||
| 2 | 1.31 | 6-O-caffeoyl-β-glucose | M − H | C15H18O9 | 342.0951 | 341.1068 | MS2:179(100), 281(2), 221(1) MS3:135(100) |
| 3 | 1.32 | Caffeoyl diglucoside | M − H | 503.1590 | MS2:179(100), 221(51), 323(22), 161(15), 341(15) MS3:161(100),143(63), 131(14) | ||
| 4 | 1.46 | 3,4-diCQA | M − H | C25H24O12 | 516.1268 | 515.1378 | MS2:353(100), 191(62), 178(9), 173(2) |
| 5 | 1.58 | 6-O-Caffeoyl-α-glucose | M − H | C15H18O9 | 342.0951 | 341.1075 | MS2:179(100), 281(2) MS3:135(100) |
| 6 | 2.34 | 3,5-diCQA | M − H | C25H24O12 | 516.1268 | 515.1400 | MS2:179(100), 353(69), 191(22), 335(3), 173(3), MS3:191(100), 179(10), 135(4) |
| 7 | 2.93 | 4,5-diCQA | M − H | C25H24O12 | 516.1479 | 515.1403 | MS2:353(100), 191(63), 179(2) MS3:191(100), 179(5) |
| 8 | 4.01 | 3-O-(4′-O-Caffeoylglucosyl)quinic acid | M − H | C22H28O14 | 516.1434 | 515.1397 | MS2:341(100), 353(87), 191(4), 173(41), 179(57) |
| 9 | 4.04 | p-Hydroxycinnamic acid | M − H | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | 163.0398 | MS2:119(100) MS3:119(100), 75(46) |
| 10 | 4.73 | 5-O-(3′-O-Caffeoylglucosyl)quinic acid | M − H | C22H28O14 | 516.1479 | 515.1396 | MS2:323(100), 191(26), 353(24), 341(16), 179(3) |
| 11 | 5.35 | Quercetin-3-O-galactoside-7-O-glucoside | M − H | C27H30O17 | 626.1483 | 625.1390 | MS2:463(100),505(3), 301(2) MS3:301(100), 179(1) |
| 12 | 5.47 | Quinic acid | M − H | C7H12O6 | 192.0634 | 191.0553 | MS2:127(100), 85(86), 173(63), 93(58) MS3:85(100), 99(40), 109(27) |
| 13 | 5.51 | 3-O-Caffeoylqunic acid | M − H | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | 353.0856 | MS2:191(100), 179(3) MS3:127(100), 173(76) |
| 14 | 5.85 | Caffeic acid | M − H | C9H8O4 | 180.0423 | 179.0347 | MS2:135(100), 107(27) MS3:107(100), 78(68) |
| 15 | 6.01 | Quercetin-3-O-caffeoylgalactoside | M − H | C27H30O17 | 626.1483 | 625.1396 | MS2:463(100), 301(33), 505(5) MS3:301(100), 343(10) |
| 16 | 6.48 | Coumaroyl caffeoylglycoside | M − H | C24H24O11 | 488.1319 | 487.1449 | MS2:265(100), 163(85), 307(71), 235(60), 145(53), 325(30), 341(15), 323(6) |
| 17 | 6.58 | Kaempferol-dihexoside | M − H | C27H30O16 | 610.1534 | 609.1452 | MS2:447(100), 285(16) MS3:284(100), 285(52), 327(22), 255(14) |
| 18 | 7.56 | Coumaroyl-tricaffeoylquinic acid | M − H | 823.2269 | MS2:661(100) MS3:487(100), 353(94), 515(34), | ||
| 19 | 7.73 | 5-FQA | M − H | C17H20O9 | 368.1107 | 367.1025 | MS2:191(100), 173(100) MS3:127(100), 85(83), 173(81), 93(46), 111(36) |
| 20 | 9.01 | Quercetin-3-O-apiosyl-(1→2)-galactoside | M − H | C26H28O16 | 596.1377 | 595.1292 | MS2:300(100), 301(48), 463(24) MS3:271(100), 255(58), 179(1) |
| 21 | 10.03 | Hyperoside | M − H | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 463.0860 | MS2:301(100), 300(33), 343(4) MS3:179(100), 151(79), 273(18), 257(12) |
| 22 | 10.40 | Isoquercitrin | M − H | C21H20O12 | 464.0955 | 463.0866 | MS2:301(100) MS3:179(100), 151(91), 273(16), 255(9) |
| 23 | 10.65 | Kaempferol-3-apiosyl-(1→2)-glucoside | M − H | C26H28O15 | 580.1428 | 579.1344 | MS2:285(100), 284(60), 447(24), 255(15) MS3:257(100), 151(69), 241(46) |
| 24 | 11.50 | Isorhamnetin-3-apiosyl-(1→2)-hexoside | M − H | C27H30O16 | 610.1534 | 609.1448 | MS2:315(100), 314(29), 300(22), 459(13) MS3:300(100), 287(5) |
| 25 | 11.86 | Quercetin 3-(2′′-acetylgalactoside) | M − H | C23H22O13 | 506.1060 | 505.0979 | MS2:301(100), 300(53), 463(23) MS3:179(100), 151(89) |
| 26 | 12.04 | Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside | M − H | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 447.0926 | MS2:284(100), 285(61), 327(14) MS3:255(100), 227(9) |
| 27 | 13.29 | Astragalin | M − H | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 447.0927 | MS2:284(100), 285(58), 327(12) MS3:255(100), 256(17), 227(13) |
| 28 | 13.42 | Isorhamnetin-7-glucoside | M − H | C22H22O12 | 478.1111 | 477.1029 | MS2:314(100), 315(71), 357(18), 449(8) MS3:285(100), 271(74), 300(34), 243(27) |
| 29 | 14.31 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside | M − H | C22H22O12 | 478.1111 | 477.1033 | MS2:314(100), 315(36), 285(9), 300(3) MS3:285(100), 271(77), 300(35), 243(25), |
| 30 | 14.4 | Luteolin-hexoside | M − H | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 447.0927 | MS2:285(100), 327(5) MS3:285(100), 151(32), 257(20), 229(10), 241(20) |
| 31 | 16.12 | Luteolin-7-O-glucoside | M − H | C21H20O11 | 448.1006 | 447.0926 | MS2:285(100), 284(13), 327(5), 257(2) MS3:151(100), 257(32), 241(22) |
| 32 | 16.73 | 4-O-Caffeoylqunic acid | M − H | C16H18O9 | 354.0951 | 353.0871 | MS2:173(100), 179(47), 191(16), 135(7) MS3:93(100), 111(77) |
| 33 | 21.23 | Kaempferol-3-O-p-hydroxybenzoylglucoside | M − H | C28H24O13 | 568.1217 | 567.1135 | MS2:284(100), 285(97), 447(37), 255(30), 429(11), 327(9) MS3:285(100), 151(6) |
| 34 | 22.17 | cis-4-pCoQA | M − H | C16H18O8 | 338.1002 | 337.0922 | MS2:173(100), 163(9) MS3:93(100), 111(58) |
| 35 | 22.76 | Apigenin | M − H | C15H10O5 | 270.0528 | 269.0928 | MS2:225(100) |
| 36 | 23.23 | Cuscutoside D | M − H | C37H46O21 | 826.2532 | 825.2439 | MS2:369(100), 663(76), 323(43) MS3:219(100), 339(74), 311(54), 323(11) |
| 37 | 23.32 | Quercetin-3-O-coumaroylgalactoside | M − H | C30H26O14 | 610.1323 | 609.1242 | MS2:463(100), 301(13) MS3:301(100), 343(3) |
| 38 | 23.75 | Quercetin | M − H | C15H10O7 | 302.0427 | 301.0349 | MS2:151(100), 179(97) |
| 39 | 24.69 | Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside-7-rhamnoside | M − H | C30H26O13 | 594.1373 | 593.1289 | MS2:447(13), 285(100), 327(1) MS3:257(81),285(100), 151(63), 241(45), 229(3) |
| 40 | 25.17 | Kaempferol-3-O-coumaroylglucoside | M − H | C30H26O13 | 594.1373 | 593.1290 | MS2:285(100), 447(12), 307(6) MS3:285(100), 257(70), 151(59), 229(36), 241(35) |
| 41 | 25.21 | trans-4-pCoQA | M − H | C16H18O8 | 338.1002 | 337.0923 | MS2:173(100), 163(8) MS3:93(100), 111(57) |
| 42 | 25.74 | pCoQA isomer | M − H | C16H18O8 | 338.1002 | 337.0923 | MS2:173(100), 322(57), 306(14) MS3:93(100), 111(62), 155(36), |
| 43 | 27.12 | Cuscutoside A | M − H | 663.1917 | MS2:369(100) MS3:219(100), 339(77), 311(45) | ||
| 44 | 27.77 | Kaempferol | M − H | C15H10O6 | 286.0477 | 285.0392 | MS2:285(100), 229(17) |
| 45 | 28.54 | Isorhamnetin | M − H | C16H12O7 | 316.0583 | 315.0502 | MS2:300(100) MS3:271(100), 151(91), 272(62), 255(30) |
| No. | tR(min) | Compound | Molecular Formula | New or Not | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.18 | Caffeoyl glucoside | + | 4 | |
| 2 | 1.31 | 6-O-caffeoyl-β-glucose | C15H18O9 | + | 2 |
| 3 | 1.32 | Caffeoyl diglucoside | + | 3 | |
| 4 | 1.46 | 3,4-diCQA | C25H24O12 | - | 1 |
| 5 | 1.58 | 6-O-Caffeoyl-α-glucose | C15H18O9 | + | 4 |
| 6 | 2.34 | 3,5-diCQA | C25H24O12 | - | 1 |
| 7 | 2.93 | 4,5-diCQA | C25H24O12 | - | 1 |
| 8 | 4.01 | 3-O-(4′-O-Caffeoylglucosyl)quinic acid | C22H28O14 | + | 3 |
| 9 | 4.04 | p-Hydroxycinnamic acid | C9H8O3 | - | 1 |
| 10 | 4.73 | 5-O-(3′-O-Caffeoylglucosyl)quinic acid | C22H28O14 | + | 4 |
| 11 | 5.35 | Quercetin-3-O-galactoside-7-O-glucoside | C27H30O17 | - | 3 |
| 12 | 5.47 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | - | 4 |
| 13 | 5.51 | 3-O-Caffeoylqunic acid | C16H18O9 | - | 2 |
| 14 | 5.85 | Caffeic acid | C9H8O4 | + | 1 |
| 15 | 6.01 | Quercetin-3-O-caffeoylgalactoside | C27H30O17 | - | 2 |
| 16 | 6.48 | Coumaroyl caffeoylglycoside | C24H24O11 | + | 4 |
| 17 | 6.58 | Kaempferol-dihexoside | C27H30O16 | - | 1 |
| 18 | 7.56 | Coumaroyl-tricaffeoylquinic acid | - | 3 | |
| 19 | 7.73 | 5-FQA | C17H20O9 | + | 3 |
| 20 | 9.01 | Quercetin-3-O-apiosyl-(1→2)-galactoside | C26H28O16 | - | 2 |
| 21 | 10.03 | Hyperoside | C21H20O12 | - | 4 |
| 22 | 10.40 | Isoquercitrin | C21H20O12 | - | 4 |
| 23 | 10.65 | Kaempferol-3-apiosyl-(1→2)-glucoside | C26H28O15 | + | 1 |
| 24 | 11.50 | Isorhamnetin-3-apiosyl-(1→2)-hexoside | C27H30O16 | + | 2 |
| 25 | 11.86 | Quercetin 3-(2′′-acetylgalactoside) | C23H22O13 | + | 1 |
| 26 | 12.04 | Kaempferol-3-O-galactoside | C21H20O11 | - | 1 |
| 27 | 13.29 | Astragalin | C21H20O11 | - | 1 |
| 28 | 13.42 | Isorhamnetin 7-glucoside | C22H22O12 | - | 1 |
| 29 | 14.31 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside | C22H22O12 | + | 1 |
| 30 | 14.40 | Luteolin-hexoside | C21H20O11 | + | 1 |
| 31 | 16.12 | Luteolin-7-O-glucoside | C21H20O11 | + | 1 |
| 32 | 16.73 | 4-O-Caffeoylqunic acid | C16H18O9 | - | 1 |
| 33 | 21.23 | Kaempferol-3-O-p-hydroxybenzoylglucoside | - | 1 | |
| 34 | 22.17 | cis-4-pCoQA | C16H18O8 | + | 2 |
| 35 | 22.76 | Apigenin | C15H10O5 | - | 1 |
| 36 | 23.23 | Cuscutoside D | C37H46O21 | - | 1 |
| 37 | 23.32 | Quercetin-3-O-coumaroylgalactoside | C30H26O14 | - | 1 |
| 38 | 23.75 | Quercetin | C15H10O7 | - | 1 |
| 39 | 24.69 | Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside-7-rhamnoside | C30H26O13 | - | 2 |
| 40 | 25.17 | Kaempferol-3-O-coumaroylglucoside | C30H26O13 | + | 1 |
| 41 | 25.21 | trans-4-pCoQA | C16H18O8 | + | 2 |
| 42 | 25.74 | pCoQA isomer | C16H18O8 | + | 2 |
| 43 | 27.12 | Cuscutoside A | - | 1 | |
| 44 | 27.77 | Kaempferol | C15H10O6 | - | 4 |
| 45 | 28.54 | Isorhamnetin | C16H12O7 | - | 2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Xu, X.; Xue, X.; Liu, M.; Xu, S.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Compounds Identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLCs) Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 23, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051199
Zhang Y, Xiong H, Xu X, Xue X, Liu M, Xu S, Liu H, Gao Y, Zhang H, Li X. Compounds Identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLCs) Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2018; 23(5):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051199
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Hui Xiong, Xinfang Xu, Xue Xue, Mengnan Liu, Shuya Xu, Huan Liu, Yan Gao, Hui Zhang, and Xiangri Li. 2018. "Compounds Identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLCs) Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 23, no. 5: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051199
APA StyleZhang, Y., Xiong, H., Xu, X., Xue, X., Liu, M., Xu, S., Liu, H., Gao, Y., Zhang, H., & Li, X. (2018). Compounds Identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLCs) Coupled to Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 23(5), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23051199






