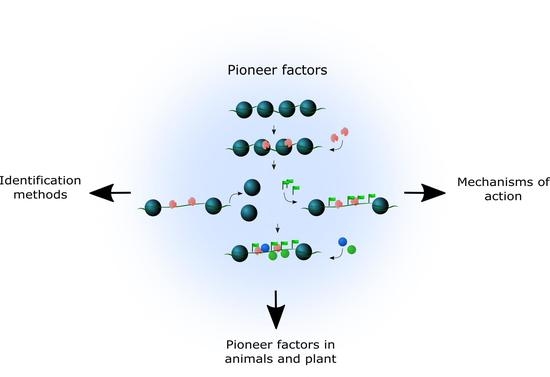
Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants—Colonizing Chromatin for Gene Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Identification of Pioneer Factors—Biochemical and Genome-Wide Studies
2.1. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays
2.2. ChIP-Seq and Variants
2.3. Chromatin Accessibility Assays
2.4. Chromosome Conformation Capture Assays
2.5. Loss/Gain-of-Function Experiments and Inducible Systems
2.6. A Cautionary Note
3. Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants
3.1. Mammalian Models
3.2. Plant Pioneer Factors
4. Mechanism of Action
4.1. Nucleosome-Compatible Binding and High Affinity
4.2. Pioneer Factors Recruit Chromatin Remodelers
4.3. Pioneer Factor Binding and Methylation of DNA and Histones
4.4. Pioneer Factors Impact the Epigenetic Landscape
5. Perspectives and Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balleza, E.; López-Bojorquez, L.N.; Martínez-Antonio, A.; Resendis-Antonio, O.; Lozada-Chávez, I.; Balderas-Martínez, Y.I.; Encarnación, S.; Collado-Vides, J. Regulation by transcription factors in bacteria: Beyond description. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelli, K.M.; Slattery, M.; Mann, R.S. Disentangling the Many Layers of Eukaryotic Transcriptional Regulation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2012, 46, 43–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; López-Vidriero, I.; Carrasco, J.L.; Godoy, M.; Vera, P.; Solano, R. DNA-binding specificities of plant transcription factors and their potential to define target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudinier, A.; Brady, S.M. Mapping Transcriptional Networks in Plants: Data-Driven Discovery of Novel Biological Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 575–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, S.A.; Jolma, A.; Campitelli, L.F.; Das, P.K.; Yin, Y.; Albu, M.; Chen, X.; Taipale, J.; Hughes, T.R.; Weirauch, M.T. The Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2018, 172, 650–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, Z.; Mirny, L.A. Different gene regulation strategies revealed by analysis of binding motifs. Trends Genet. 2009, 25, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, D.; Flicek, P.; Odom, D.T. Evolution of transcription factor binding in metazoans — mechanisms and functional implications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, K.; Dechassa, M.L.; Tremethick, D.J. New insights into nucleosome and chromatin structure: An ordered state or a disordered affair? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Morozov, A.V. Gene regulation by nucleosome positioning. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualdi, R.; Bossard, P.; Zheng, M.; Hamada, Y.; Coleman, J.R.; Zaret, K.S. Hepatic specification of the gut endoderm in vitro: Cell signaling and transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1670–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossard, P.; Zaret, K.S. GATA transcription factors as potentiators of gut endoderm differentiation. Development 1998, 125, 4909–4917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zaret, K.S. Regulatory phases of early liver development: Paradigms of organogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, L.A.; Lin, F.R.; Cuesta, I.; Friedman, D.; Jarnik, M.; Zaret, K.S. Opening of compacted chromatin by early developmental transcription factors HNF3 (FoxA) and GATA-4. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, L.; Eeckhoute, J.; Lupien, M. Pioneer factors: Directing transcriptional regulators within the chromatin environment. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, J. Minireview: Pioneer Transcription Factors in Cell Fate Specification. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwafuchi-Doi, M.; Zaret, K.S. Pioneer transcription factors in cell reprogramming. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2679–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmich, A.I.; Tyulkina, D.V.; Vinogradova, T.V.; Sverdlov, E.D. Pioneer transcription factors in normal development and carcinogenesis. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2015, 41, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, K.S.; Mango, S.E. Pioneer transcription factors, chromatin dynamics, and cell fate control. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 37, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaret, K.S.; Lerner, J.; Iwafuchi-Doi, M. Chromatin Scanning by Dynamic Binding of Pioneer Factors. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwafuchi-Doi, M.; Zaret, K.S. Cell fate control by pioneer transcription factors. Development 2016, 143, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinstead, E.E.; Paakinaho, V.; Presman, D.M.; Hager, G.L. Pioneer factors and ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling factors interact dynamically: A new perspective. BioEssays 2016, 38, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayran, A.; Drouin, J. Pioneer transcription factors shape the epigenetic landscape. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, jbc.R117.001232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufi, A.; Garcia, M.F.; Jaroszewicz, A.; Osman, N.; Pellegrini, M.; Zaret, K.S. Pioneer transcription factors target partial DNA motifs on nucleosomes to initiate reprogramming. Cell 2015, 161, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, T.; Muthurajan, U.M.; Luger, K.; Tulin, A.V.; Zaret, K.S. Nucleosome-binding affinity as a primary determinant of the nuclear mobility of the pioneer transcription factor FoxA. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, T.; Zaret, K.S. Repression by Groucho/TLE/Grg Proteins: Genomic Site Recruitment Generates Compacted Chromatin In Vitro and Impairs Activator Binding In Vivo. Mol. Cell 2007, 28, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Fornes, O.; Stigliani, A.; Gheorghe, M.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; Van Der Lee, R.; Bessy, A.; Chèneby, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Tan, G.; et al. JASPAR 2018: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D260–D266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-T.; Chen, H.-M.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Lee, N.K.; Burger, A.; Zaret, K.; Liu, T.; Levine, E.; Mango, S.E. Recruitment of RNA polymerase II by the pioneer transcription factor PHA-4. Science 2015, 348, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Gadue, P.; Chen, K.; Jiao, Y.; Tuteja, G.; Schug, J.; Li, W.; Kaestner, K.H. Foxa2 and H2A.Z mediate nucleosome depletion during embryonic stem cell differentiation. Cell 2012, 151, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaku, M.; Grimm, S.A.; Shimbo, T.; Perera, L.; Menafra, R.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Archer, T.K.; Machida, S.; Kurumizaka, H.; Wade, P.A. GATA3-dependent cellular reprogramming requires activation-domain dependent recruitment of a chromatin remodeler. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufi, A.; Donahue, G.; Zaret, K.S. Facilitators and impediments of the pluripotency reprogramming factors’ initial engagement with the genome. Cell 2012, 151, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, H.W.; Klose, R.J. The pioneer factor OCT4 requires the chromatin remodeller BRG1 to support gene regulatory element function in mouse embryonic stem cells. Elife 2017, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronis, C.; Fiziev, P.; Papp, B.; Butz, S.; Bonora, G.; Sabri, S.; Ernst, J.; Plath, K. Cooperative Binding of Transcription Factors Orchestrates Reprogramming. Cell 2017, 168, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, R.I.; Hashimoto, T.; O’Donnell, C.W.; Lewis, S.; Barkal, A.A.; Van Hoff, J.P.; Karun, V.; Jaakkola, T.; Gifford, D.K. Discovery of directional and nondirectional pioneer transcription factors by modeling DNase profile magnitude and shape. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domcke, S.; Bardet, A.F.; Adrian Ginno, P.; Hartl, D.; Burger, L.; Schübeler, D. Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1. Nature 2015, 528, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayran, A.; Khetchoumian, K.; Hariri, F.; Pastinen, T.; Gauthier, Y.; Balsalobre, A.; Drouin, J. Pioneer factor Pax7 deploys a stable enhancer repertoire for specification of cell fate. Nat. Genet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Georgakilas, G.; Petrovic, J.; Kurachi, M.; Cai, S.; Harly, C.; Pear, W.S.; Bhandoola, A.; Wherry, E.J.; Vahedi, G. Lineage-Determining Transcription Factor TCF-1 Initiates the Epigenetic Identity of T Cells. Immunity 2018, 48, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapinski, O.L.; Vierbuchen, T.; Qu, K.; Lee, Q.Y.; Chanda, S.; Fuentes, D.R.; Giresi, P.G.; Ng, Y.H.; Marro, S.; Neff, N.F.; et al. Hierarchical mechanisms for direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to neurons. Cell 2013, 155, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.I.; Guilhamon, P.; Desai, K.; McAdam, R.F.; Langille, E.; O’Connor, M.; Lan, X.; Whetstone, H.; Coutinho, F.J.; Vanner, R.J.; et al. ASCL1 Reorganizes Chromatin to Direct Neuronal Fate and Suppress Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, B.H.; Kollipara, R.K.; Pozo, K.; Johnson, J.E. Intrinsic DNA binding properties demonstrated for lineage-specifying basic helix-loop- helix transcription factors. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oevelen, C.; Collombet, S.; Vicent, G.; Hoogenkamp, M.; Lepoivre, C.; Badeaux, A.; Bussmann, L.; Sardina, J.L.; Thieffry, D.; Beato, M.; et al. C/EBPα Activates Pre-existing and de Novo Macrophage Enhancers during Induced Pre-B Cell Transdifferentiation and Myelopoiesis. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boller, S.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Akbas, D.; Nechanitzky, R.; Burger, L.; Murr, R.; Schübeler, D.; Grosschedl, R. Pioneering Activity of the C-Terminal Domain of EBF1 Shapes the Chromatin Landscape for B Cell Programming. Immunity 2016, 44, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataskar, A.; Jung, J.; Smialowski, P.; Noack, F.; Calegari, F.; Straub, T.; Tiwari, V.K. NeuroD1 reprograms chromatin and transcription factor landscapes to induce the neuronal program. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallberg, A.E.; Neely, K.E.; Hassan, A.H.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Workman, J.L.; Wright, A.P. Recruitment of the SWI-SNF chromatin remodeling complex as a mechanism of gene activation by the glucocorticoid receptor tau1 activation domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinstead, E.E.; Miranda, T.B.; Paakinaho, V.; Baek, S.; Goldstein, I.; Hawkins, M.; Karpova, T.S.; Ball, D.; Mazza, D.; Lavis, L.D.; et al. Steroid Receptors Reprogram FoxA1 Occupancy through Dynamic Chromatin Transitions. Cell 2016, 165, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballaré, C.; Castellano, G.; Gaveglia, L.; Althammer, S.; González-Vallinas, J.; Eyras, E.; Le Dily, F.; Zaurin, R.; Soronellas, D.; Vicent, G.P.; et al. Nucleosome-Driven Transcription Factor Binding and Gene Regulation. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, A.J.; Yang, P.; Conway, A.E.; Cinghu, S.; Freudenberg, J.M.; Yellaboina, S.; Jothi, R. Histone-Fold Domain Protein NF-Y Promotes Chromatin Accessibility for Cell Type-Specific Master Transcription Factors. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, S.; Benner, C.; Spann, N.; Bertolino, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Laslo, P.; Cheng, J.X.; Murre, C.; Singh, H.; Glass, C.K. Simple Combinations of Lineage-Determining Transcription Factors Prime cis-Regulatory Elements Required for Macrophage and B Cell Identities. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barozzi, I.; Simonatto, M.; Bonifacio, S.; Yang, L.; Rohs, R.; Ghisletti, S.; Natoli, G. Coregulation of Transcription Factor Binding and Nucleosome Occupancy through DNA Features of Mammalian Enhancers. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nili, E.L.; Field, Y.; Lubling, Y.; Widom, J.; Oren, M.; Segal, E. p53 binds preferentially to genomic regions with high DNA-encoded nucleosome occupancy. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammons, M.A.; Zhu, J.; Drake, A.M.; Berger, S.L. TP53 engagement with the genome occurs in distinct local chromatin environments via pioneer factor activity. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younger, S.T.; Rinn, J.L. P53 regulates enhancer accessibility and activity in response to DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9889–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Buck, M.J. Defining p53 pioneering capabilities with competitive nucleosome binding assays. Bioarxiv 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddie, S.C.; John, S.; Sabo, P.J.; Thurman, R.E.; Johnson, T.A.; Schiltz, R.L.; Miranda, T.B.; Sung, M.H.; Trump, S.; Lightman, S.L.; et al. Transcription Factor AP1 Potentiates Chromatin Accessibility and Glucocorticoid Receptor Binding. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, S.M.; Sun, Y.; Lim, B.; Ziukaite, R.; O’Brien, K.; Nien, C.Y.; Kirov, N.; Shvartsman, S.Y.; Rushlow, C.A. Zelda potentiates morphogen activity by increasing chromatin accessibility. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, K.N.; Bondra, E.R.; Moshe, A.; Villalta, J.E.; Lieb, J.D.; Kaplan, T.; Mckay, D.J.; Harrison, M.M.; Hill, C.; Hill, C.; et al. Zelda is differentially required for chromatin accessibility, transcription factor binding, and gene expression in the early Drosophila embryo. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshe, A.; Kaplan, T. Genome-wide search for Zelda-like chromatin signatures identifies GAF as a pioneer factor in early fly development. Epigenetics Chromatin 2017, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Atkins, M.; Davie, K.; Imrichova, H.; Romanelli, L.; Christiaens, V.; Hulselmans, G.; Potier, D.; Wouters, J.; Taskiran, I.I.; et al. The transcription factor Grainy head primes epithelial enhancers for spatiotemporal activation by displacing nucleosomes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, K.; Kopp, W.; Wu, G.; Heising, S.; Greber, B.; Stehling, M.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Boerno, S.T.; Timmermann, B.; Vingron, M.; et al. Esrrb Unlocks Silenced Enhancers for Reprogramming to Naive Pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayou, C.; Nanao, M.H.; Jamin, M.; Pose, D.; Thevenon, E.; Gregoire, L.; Tichtinsky, G.; Denay, G.; Ott, F.; Llobet, M.P.; et al. A SAM oligomerization domain shapes the genomic binding landscape of the LEAFY transcription factor. Nat. Commun. 2016, 48, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajoro, A.; Madrigal, P.; Muiño, J.M.; Matus, J.T.; Jin, J.; Mecchia, M.A.; Debernardi, J.M.; Palatnik, J.F.; Balazadeh, S.; Arif, M.; et al. Dynamics of chromatin accessibility and gene regulation by MADS-domain transcription factors in flower development. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Shen, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y. Embryonic epigenetic reprogramming by a pioneer transcription factor in plants. Nature 2017, 551, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasinathan, S.; Orsi, G.A.; Zentner, G.E.; Ahmad, K.; Henikoff, S. High-resolution mapping of transcription factor binding sites on native chromatin. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentner, G.E.; Kasinathan, S.; Xin, B.; Rohs, R.; Henikoff, S. ChEC-seq kinetics discriminates transcription factor binding sites by DNA sequence and shape in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skene, P.J.; Henikoff, S. An efficient targeted nuclease strategy for high-resolution mapping of DNA binding sites. Elife 2017, 6, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutin, J.; Sadeh, R.; Bodenheimer, N.; Joseph-Strauss, D.; Klein-Brill, A.; Alajem, A.; Ram, O.; Friedman, N. Fine-Resolution Mapping of TF Binding and Chromatin Interactions. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2601–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Carey, M.; Workman, J.L. The Role of Chromatin during Transcription. Cell 2007, 128, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, C.M.; Strømme, C.B.; Huang, H.; Patel, D.J.; Groth, A. Histone chaperone networks shaping chromatin function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, J.; Marti-Renom, M.A.; Mirny, L.A. Exploring the three-dimensional organization of genomes: Interpreting chromatin interaction data. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbert, P.B.; Henikoff, S. Histone variants on the move: substrates for chromatin dynamics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesh, S.; Workman, J.L. Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesselberth, J.R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sabo, P.J.; Sandstrom, R.; Reynolds, A.P.; Thurman, R.E.; Neph, S.; Kuehn, M.S.; Noble, W.S.; et al. Global mapping of protein-DNA interactions in vivo by digital genomic footprinting. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.H.; Meyer, C.A.; Hu, S.S.; Chen, M.W.; Zang, C.; Liu, Y.; Rao, P.K.; Fei, T.; Xu, H.; Long, H.; et al. Refined DNase-seq protocol and data analysis reveals intrinsic bias in transcription factor footprint identification. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumbie, J.S.; Filichkin, S.A.; Megraw, M. Improved DNase-seq protocol facilitates high resolution mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites in roots in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Methods 2015, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.A.; Liu, X.S. Identifying and mitigating bias in next-generation sequencing methods for chromatin biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohy, H.; Down, T.A.; Hubbard, T.J. Chromatin Accessibility Data Sets Show Bias Due to Sequence Specificity of the DNase I Enzyme. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingwall, C.; Lomonossoff, G.P.; Laskey, R.A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, V, 2659–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giresi, P.G.; Kim, J.; Mcdaniell, R.M.; Giresi, P.G.; Kim, J.; Mcdaniell, R.M.; Iyer, V.R.; Lieb, J.D. FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Giresi, P.G.; Zaba, L.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corces, M.R.; Trevino, A.E.; Hamilton, E.G.; Greenside, P.G.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.A.; Vesuna, S.; Satpathy, A.T.; Rubin, A.J.; Montine, K.S.; Wu, B.; et al. An improved ATAC-seq protocol reduces background and enables interrogation of frozen tissues. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. ATAC-seq: A method for assaying chromatin accessibility genome-wide. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2015, 109, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Litzenburger, U.M.; Ruff, D.; Gonzales, M.L.; Snyder, M.P.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. Single-cell chromatin accessibility reveals principles of regulatory variation. Nature 2015, 523, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada-Iglesias, A.; Grosveld, F.G.; Papantonis, A. Forces driving the three-dimensional folding of eukaryotic genomes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eagen, K.P. Principles of Chromosome Architecture Revealed by Hi-C. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinodoz, S.A.; Ollikainen, N.; Tabak, B.; Palla, A.; Schmidt, J.M.; Detmar, E.; Lai, M.; Shishkin, A.; Bhat, P.; Trinh, V.; et al. Higher-order inter-chromosomal hubs shape 3-dimensional genome organization in the nucleus. Cell 2017, 02215, 219683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, M.; Ibrahim, D.M.; Andrey, G.; Schwarzer, W.; Heinrich, V.; Schöpflin, R.; Kraft, K.; Kempfer, R.; Jerković, I.; Chan, W.L.; et al. Formation of new chromatin domains determines pathogenicity of genomic duplications. Nature 2016, 538, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Luo, O.J.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, J.J.; Szalaj, P.; Trzaskoma, P.; Magalska, A.; Wlodarczyk, J.; Ruszczycki, B.; et al. CTCF-Mediated Human 3D Genome Architecture Reveals Chromatin Topology for Transcription. Cell 2015, 163, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Jin, W.; Cui, K.; Rodrigez, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Larson, D.R.; Zhao, K. CTCF-Mediated Enhancer-Promoter Interaction Is a Critical Regulator of Cell-to-Cell Variation of Gene Expression. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.E.; Corces, V.G. CTCF: Master Weaver of the Genome. Cell 2009, 137, 1194–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Enge, M.; Whitington, T.; Dave, K.; Liu, J.; Sur, I.; Schmierer, B.; Jolma, A.; Kivioja, T.; Taipale, M.; et al. Transcription factor binding in human cells occurs in dense clusters formed around cohesin anchor sites. Cell 2013, 154, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.P.; Huang, S.C.; Glenn St Hilaire, B.; Engreitz, J.M.; Perez, E.M.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.R.; Sanborn, A.L.; Johnstone, S.E.; Bascom, G.D.; Bochkov, I.D.; et al. Cohesin Loss Eliminates All Loop Domains. Cell 2017, 171, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupiáñez, D.G.; Spielmann, M.; Mundlos, S. Breaking TADs: How Alterations of Chromatin Domains Result in Disease. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadhouders, R.; Vidal, E.; Serra, F.; Di Stefano, B.; Le Dily, F.; Quilez, J.; Gomez, A.; Collombet, S.; Berenguer, C.; Cuartero, Y.; et al. Transcription factors orchestrate dynamic interplay between genome topology and gene regulation during cell reprogramming. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotelo-silveira, M.; Montes, R.A.C.; Sotelo-silveira, J.R.; Marsch-martínez, N.; De Folter, S. Entering the Next Dimension: Plant Genomes in 3D. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Ren, B. The Three-Dimensional Organization of Mammalian Genomes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullwood, M.J.; Liu, M.H.; Pan, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Mohamed, Y.B.; Orlov, Y.L.; Velkov, S.; Ho, A.; Mei, P.H.; Chew, E.G.Y.; et al. An oestrogen-receptor-α-bound human chromatin interactome. Nature 2009, 462, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumbach, M.R.; Rubin, A.J.; Flynn, R.A.; Dai, C.; Khavari, P.A.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Chang, H.Y. HiChIP: Efficient and sensitive analysis of protein-directed genome architecture. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Cauchy, P.; Ramamoorthy, S.; Boller, S.; Chavez, L.; Grosschedl, R. Dynamic EBF1 occupancy directs sequential epigenetic and transcriptional events in B-cell programming. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.A.; Chereji, R.V.; Stavreva, D.A.; Morris, S.A.; Hager, G.L.; Clark, D.J. Conventional and pioneer modes of glucocorticoid receptor interaction with enhancer chromatin in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwafuchi-Doi, M.; Donahue, G.; Kakumanu, A.; Watts, J.A.; Mahony, S.; Pugh, B.F.; Lee, D.; Kaestner, K.H.; Zaret, K.S. The Pioneer Transcription Factor FoxA Maintains an Accessible Nucleosome Configuration at Enhancers for Tissue-Specific Gene Activation. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Desbordes, S.C.; Xie, H.; Tillo, E.S.; Pixley, F.; Stanley, E.R.; Graf, T. PU.1 and C/EBPalpha/beta convert fibroblasts into macrophage-like cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6057–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieda, M.; Fu, J.D.; Delgado-Olguin, P.; Vedantham, V.; Hayashi, Y.; Bruneau, B.G.; Srivastava, D. Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors. Cell 2010, 142, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addis, R.C.; Ifkovits, J.L.; Pinto, F.; Kellam, L.D.; Esteso, P.; Rentschler, S.; Christoforou, N.; Epstein, J.A.; Gearhart, J.D. Optimization of direct fibroblast reprogramming to cardiomyocytes using calcium activity as a functional measure of success. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 60, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vierbuchen, T.; Ostermeier, A.; Pang, Z.P.; Kokubu, Y.; Südhof, T.C.; Wernig, M. Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors. Nature 2010, 463, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, S.; Suzuki, A. Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors. Nature 2011, 475, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; He, Z.; Ji, S.; Sun, H.; Xiang, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hui, L. Induction of functional hepatocyte-like cells from mouse fibroblasts by defined factors. Nature 2011, 475, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel, A.; Song, J.; Dean, C.; Howard, M. A Polycomb-based switch underlying quantitative epigenetic memory. Nature 2011, 476, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.B.; Sung, S. Vernalization-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing by a Long Intronic Noncoding RNA. Science 2011, 331, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardini, M.; Gnesutta, N.; Donati, G.; Gatta, R.; Forni, C.; Fossati, A.; Vonrhein, C.; Moras, D.; Romier, C.; Bolognesi, M.; et al. Sequence-specific transcription factor NF-Y displays histone-like DNA binding and H2B-like ubiquitination. Cell 2013, 152, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, J.D.; Pavesi, G.; Benatti, P.; Imbriano, C.; Mantovani, R.; Struhl, K. NF-Y coassociates with FOS at promoters, enhancers, repetitive elements, and inactive chromatin regions, and is stereo-positioned with growth-controlling transcription factors. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyroud, E.; Kusters, E.; Monniaux, M.; Koes, R.; Parcy, F. LEAFY blossoms. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, J. Genome-Wide Identification of Regulatory DNA Elements and Protein-Binding Footprints Using Signatures of Open Chromatin in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 2719–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Sang, Y.; Bezhani, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Han, S.; Li, Z.; Su, Y.; Slewinski, T.L.; Wagner, D. SWI2/SNF2 chromatin remodeling ATPases overcome polycomb repression and control floral organ identity with the LEAFY and SEPALLATA3 transcription factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3576–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alejandra Mandel, M.; Gustafson-Brown, C.; Savidge, B.; Yanofsky, M.F. Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis floral homeotic gene APETALA1. Nature 1992, 360, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaz, S.; Ditta, G.S.; Baumann, E.; Wisman, E.; Yanofsky, M.F. B and C floral organ identity functions require SEPALLATA MADS-box genes. Nature 2000, 405, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, T.; Goto, K. Complexes of MADS-box proteins are sufficient to convert leaves into floral organs. Nature 2001, 409, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mech, L.D. A Gray Wolf (Canis lupus) Delivers Live Prey to a Pup. Can. Field-Nat. 2014, 128, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugouvieux, V.; Silva, C.S.; Jourdain, A.; Stigliani, A.; Charras, Q.; Conn, V.; Conn, S.J.; Carles, C.C.; Parcy, F.; Zubieta, C. Tetramerization of MADS family transcription factors SEPALLATA3 and AGAMOUS is required for floral meristem determinacy in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4966–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaczniak, C.; Immink, R.G.H.; Muiño, J.M.; Blanvillain, R.; Busscher, M.; Busscher-Lange, J.; Dinh, Q.D.P.; Liu, S.; Westphal, A.H.; Boeren, S. Characterization of MADS-domain transcription factor complexes in Arabidopsis flower development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.; Meyerowitz, E.M. SPLAYED, a novel SWI/SNF ATPase homolog, controls reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezhani, S.; Winter, C.; Hershman, S.; Wagner, J.D.; Kennedy, J.F.; Kwon, C.S.; Pfluger, J.; Su, Y.; Wagner, D. Unique, Shared, and Redundant Roles for the Arabidopsis SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling ATPases BRAHMA and SPLAYED. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutinen, P.; Rahkama, V.; Rytinki, M.; Palvimo, J.J. Nuclear Mobility and Activity of FOXA1 with Androgen Receptor Are Regulated by SUMOylation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrou, S.; Hellqvist, M.; Samuelsson, L.; Enerbäck, S.; Carlsson, P. Cloning and characterization of seven human forkhead proteins: Binding site specificity and DNA bending. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, L.A.; McPherson, C.E.; Bossard, P.; Stevens, K.; Cherian, S.; Shim, E.Y.; Clark, K.L.; Burley, S.K.; Zaret, K.S. Binding of the winged-helix transcription factor HNF3 to a linker histone site on the nucleosome. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.L.; Halay, E.D.; Lai, E.; Burley, S.K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature 1993, 364, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolfini, D.; Gatta, R.; Mantovani, R. NF-Y and the transcriptional activation of CCAAT promoters. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laloum, T.; De Mita, S.; Gamas, P.; Baudin, M.; Niebel, A. CCAAT-box binding transcription factors in plants: Y so many? Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, K.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Gnesutta, N.; Calvenzani, V.; Fornari, M.; Tonelli, C.; Holt, B.F.; Mantovani, R. The Promiscuous Life of Plant NUCLEAR FACTOR Y Transcription Factors. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4777–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnesutta, N.; Saad, D.; Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Mantovani, R.; Nardini, M. Crystal Structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana L1L/NF-YC3 Histone-fold Dimer Reveals Specificities of the LEC1 Family of NF-Y Subunits in Plants. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamès, C.; Ptchelkine, D.; Grimm, C.; Thevenon, E.; Moyroud, E.; Gérard, F.; Martiel, J.-L.; Benlloch, R.; Parcy, F.; Müller, C.W. Structural basis for LEAFY floral switch function and similarity with helix-turn-helix proteins. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 2628–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rümpler, F.; Theißen, G.; Melzer, R. A conserved leucine zipper-like motif accounts for strong tetramerization capabilities of SEPALLATA-like MADS-domain transcription factors. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theißen, G.; Melzer, R.; Rümpler, F. MADS-domain transcription factors and the floral quartet model of flower development: linking plant development and evolution. Development 2016, 143, 3259–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Schones, D.E.; Cui, K.; Ybarra, R.; Northrup, D.; Tang, Q.; Gattinoni, L.; Restifo, N.P.; Huang, S.; Zhao, K. Regulation of nucleosome landscape and transcription factor targeting at tissue-specific enhancers by BRG1. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnakumar, R.; Chen, A.F.; Pantovich, M.G.; Danial, M.; Parchem, R.J.; Labosky, P.A.; Blelloch, R. FOXD3 Regulates Pluripotent Stem Cell Potential by Simultaneously Initiating and Repressing Enhancer Activity. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattler, A.; Farnham, P.J. Cross-talk between site-specific transcription factors and DNA methylation states. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34287–34294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kribelbauer, J.F.; Laptenko, O.; Chen, S.; Martini, G.D.; Freed-Pastor, W.A.; Prives, C.; Mann, R.S.; Bussemaker, H.J. Quantitative Analysis of the DNA Methylation Sensitivity of Transcription Factor Complexes. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaghey, J.; Thakurela, S.; Charlton, J.; Chen, J.S.; Smith, Z.D.; Gu, H.; Pop, R.; Clement, K.; Stamenova, E.K.; Karnik, R.; et al. Genetic determinants and epigenetic effects of pioneer-factor occupancy. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.S.; Nicetto, D.; Zaret, K.S. H3K9me3-Dependent Heterochromatin: Barrier to Cell Fate Changes. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.C.; Martin, C.; Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Quail, P.H.; Huq, E.; Heim, M.A.; Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. Update on the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Gene Family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englbrecht, C.C.; Schoof, H.; Böhm, S. Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. BMC Genom. 2004, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, C.; Muro-pastor, M.I.; Florencio, F.J. The GATA Family of Transcription Factors in Arabidopsis and Rice 1. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1718–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behringer, C.; Schwechheimer, C. B-GATA transcription factors—insights into their structure, regulation, and role in plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pioneer TFs | Species | Organ/Cell Type | Biological Process | Identification | Pioneer Activity | Co-Factors | Epigenetic Effects | Other Features and Cautious Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forkhead box TFs | Human and mouse | Many, such as endoderm | Cell differentiation and organogenesis | EMSAs and ChIP-seq | Resembles H1 and binds nucleosomal DNA | N/A | N/A (not applicable) | PHA-4 recruits Pol-II [27]; FOXA2 recruits nucleosome disassembly complexes [28] | [13,27] |
| GATA family | Human and mouse | Many, such as endoderm | Cell differentiation and organogenesis | EMSAs | Binds nucleosomal DNA and create accessible chromatin | BRG1 of BAF complexes | N/A | N/A | [11,13,29] |
| OCT4 | Human and mouse | Embryonic cells or fibroblast | Embryonic development or reprogram somatic cells to pluripotent cells | Activity of reprogramming cell fate; ATAC-seq, ChIP-seq and DNase-seq | Open closed chromatin by recruiting BRG1 | BRG1 | Facilitate H3K4me1/2/3, H3K9ac and H3K27ac deposition | N/A | [30,31] |
| SOX2 | Human and mouse | Embryonic cells or fibroblast | Embryonic development or reprogram somatic cells to pluripotent cells | DNase-seq; Activity of reprogramming cell fate specification | Binds nucleosomal DNA and create accessible chromatin | N/A | N/A | [30] | |
| KLF4 | Human and mouse | Embryonic cells or fibroblast | Embryonic development or reprogram somatic cells to pluripotent cells | Activity of reprogramming cell fate; DNase-seq | Binds nucleosomal DNA and create accessible chromatin | N/A | N/A | [30,32] | |
| NRF1 | Human and mouse | Embryonic cells | Cellular growth | DNase-seq; ChIP-seq | Create DNase-hypersensitive sites upon binding | N/A | N/A | Sensitive to DNA-methylation [22] | [33,34] |
| PAX7 | Mouse | Melanotrope | Specifies intermediate pituitary melanotrope cell identity | ATAC-seq | Open closed chromatin | p300 | Reduce DNA methylation and acquire epigenetic memory | Binds enhancers rapidly, but gene activation are slower [35] | [35] |
| TCF-1 | Human and mouse | T cells | T cell lineage establishment | ATAC-seq | Open closed chromatin | N/A | Erase H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 | N/A | [36] |
| ASCL | Human and Mouse | Glioblastoma Stem Cells or embryonic stem cells | Neurogenesis, conversion of fibroblasts into induced neuronal cells [37] | ATAC-seq, MNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Open closed chromatin | N/A | Induce H3K37ac deposition | N/A | [37,38,39] |
| C/EBPα | Mouse | B cells | Pre-B-cell to macrophage trans-differentiation | MNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Create de novo chromatin accessibility | Cooperative binding with PU.1 | N/A | N/A | [40] |
| EBF1 | Mouse | B cells | Lymphopoiesis | DNase-seq | Promoted chromatin accessibility | N/A | Promote DNA demethylation | N/A | [41] |
| NeuroD1 | Mouse | Neuron | Neuronal specification | ChIP-seq and FAIRE-seq | Conversion of heterochromatin to euchromatin | N/A | Promote H3K27ac and reduce H3K27me3 | N/A | [42] |
| ER and GR | Human | Many | Many | DNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Enhance binding of pioneer factor FOXA1 | SWI/SNF complex [43] | N/A | Pioneer activity under strong debate [18] | [44] |
| PR | Human | Breast cancer cells | Breast tumorigenesis | DNase-seq, MNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Initiate chromatin binding and remodeling | N/A | N/A | N/A | [45] |
| NF-Y | Mouse | Embryonic cells and neurons | Maintenance of embryonic cell identity | ChIP-seq | Mimic histone proteins | N/A | Promote H3K4me1 and H3K27ac deposition and reduce H3K27me3 | N/A | [46] |
| PU.1 | Mouse | myeloid and lymphoid cells | myeloid and lymphoid development | MNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Create the macrophage-specific repertoire of accessible cis-regulatory elements | N/A | Promote H3K4me deposition. | N/A | [47,48] |
| p53 | Human | Many | Tumor suppressor | EMSAs, ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq | Targets heterochromatin and binds to nucleosome in vitro | N/A | Promote H3K27ac and H4K16ac deposition | N/A | [49,50,51,52] |
| AP-1 | Mouse | Many | Cell differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis | ChIP-seq and DNase-seq | Potentiate chromatin accessibility | N/A | N/A | N/A | [53] |
| ZELDA | Drosophila | Germ cells | Reprogramming specified germ cell to pluripotent cells (Zygotic genome activation) | FAIRE-seq | Open chromatin | N/A | N/A | Chromatin remains open even in the absence of ZELDA | [54,55] |
| GAF | Drosophila | Embryonic cells | Zygotic genome activation | ChIP-seq | Establish open chromatin and activate regulatory regions | N/A | Promote H3K4me1 deposition and H3K27me3 depletion | N/A | [56] |
| GRAINY | Human and Drosophila | Epithelial tissue | Epithelial cell-fate specification | ATAC-seq and ChIPmentation | Establish tissue-specific accessible chromatin landscapes | N/A | N/A | GRAINY binding open epithelial enhancers but not for gene activation | [57] |
| MYOD1 | Mouse | Embryonic stem cells | Embryonic development | ATAC-seq, MNase-seq and ChIP-seq | Bind to inaccessible chromatin and open chromatin | N/A | Promote H3K37ac deposition | N/A | [39] |
| ESRRB | Mouse | Epiblast stem cells (EpiSCs) | Reprograming of EpiSCs to ESCs | ChIP-seq | Binds to silenced enhancers containing stable nucleosomes and hypermethylated DNA | Cooperative binding with OCT4, SOX2 and NANOG | Promote loss of DNA methylation and engagement of p300 | N/A | [58] |
| Pioneer TFs | Species | Organ/Cell Type | Biological Process | Identification | Pioneer Activity | Co-Factors | Epigenetic Effects | Other Features and Cautious Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEAFY | Arabidopsis thaliana | Inflorescence meristem | Flower meristem establishment | ChIP-seq and RNA-seq | Bind to cognate sites in closed chromatin region | BRAHMA and SPLAYD | Counteract with PRC2 for H3K27me3 elimination | Oligomerization activity likely involve in targeting binding sites in closed chromatin | [59] |
| AP1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Flower organs | Flower organ specification | DNase-seq | Open closed chromatin | [60] | |||
| SEP3 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Flower organs | Flower organ specification | DNase-seq | Open closed chromatin | [60] | |||
| LEC1 | Arabidopsis thaliana | Embryonic cells | Vernalization | ChIP-qPCR | Establish stable epigenetic markers | N/A | Promote H3K36me3 deposition, and counteract with PRC2 for H3K27me3 elimination | N/A | [61] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, X.; Verhage, L.; Hugouvieux, V.; Zubieta, C. Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants—Colonizing Chromatin for Gene Regulation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081914
Lai X, Verhage L, Hugouvieux V, Zubieta C. Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants—Colonizing Chromatin for Gene Regulation. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081914
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Xuelei, Leonie Verhage, Veronique Hugouvieux, and Chloe Zubieta. 2018. "Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants—Colonizing Chromatin for Gene Regulation" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081914
APA StyleLai, X., Verhage, L., Hugouvieux, V., & Zubieta, C. (2018). Pioneer Factors in Animals and Plants—Colonizing Chromatin for Gene Regulation. Molecules, 23(8), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081914