Bioactive Compound Fingerprint Analysis of Aged Raw Pu’er Tea and Young Ripened Pu’er Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
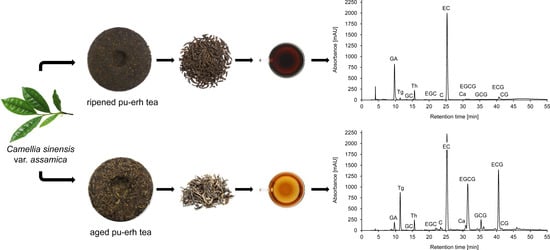
2.1. Identification and Quantification of Chemical Components Using LC-DAD/ESI-MS
2.1.1. Flavan-3-ols
2.1.2. Flavonols
2.1.3. Caffeoylquinic Acids
2.1.4. Methylxanthines
2.2. Time-Temperature Relation with Bioactive Compounds Extraction
2.3. Outcome of Multivariate Data Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.3.1. Plant Material
3.3.2. Preparation of the Infusions
3.4. Quantification of Chemical Components Using LC-DAD/ESI-MS
3.5. Characterization of Chemical Components Using Folin-Ciocalteu Assay
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hung, P.-Y. Tea Production, Land Use Politics, and Ethnic Minorities: Struggling over Dilemmas in China’s Southwest Frontier; Palgrave MacMillan: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-349-57364-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.M.; Wang, C.F.; Shen, S.M.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, P.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Du, S.S.; Liu, Z.L.; Deng, Z.W. Antioxidant phenolic compounds from Pu-erh tea. Molecules 2012, 17, 14037–14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiong, S.; Xishuang, Y. History of Pu’er Tea and comparative study for the effect of its various extracts on lipid-lowering diet. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Hwang, L.S. Polyphenol contents of Pu-Erh teas and their abilities to inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis in Hep G2 cell line. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, K.-L.; Weng, M.-S.; Chiang, C.-T.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Lin, J.-K. Comparative Studies on the Hypolipidemic and Growth Suppressive Effects of Oolong, Black, Pu-erh, and Green Tea Leaves in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.X.; Duan, W.H.; Wu, H.Y.; Si, Z.M. Investigation and analysis of consumptive request for Chinese premium teas. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2013, 30, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.-P.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Lin, Z.; Liang, Y.-R. Processing and chemical constituents of Pu-erh tea: A. review. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Durgo, K.; Chisti, Y.; Gong, J.; Sirisansaneeyakul, S.; Komes, D. Physicochemical properties and biological activities of a high-theabrownins instant Pu-erh tea produced using Aspergillus tubingensis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 90, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Zhu, L.; Peng, W.-L.; He, X.-C.; Chen, H.-L.; Li, J.; Yu, T.; Liang, Z.-T.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Chen, H.-B. Comparison of ten major constituents in seven types of processed tea using HPLC-DAD-MS followed by principal component and hierarchical cluster analysis. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, N.; Ma, Z.-Z.; Tu, P.-F. Comparison of the Chemical Constituents of Aged Pu-erh Tea, Ripened Pu-erh Tea, and Other Teas Using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8754–8760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komes, D.; Horžić, D.; Belščak, A.; Ganić, K.K.; Vulić, I. Green tea preparation and its influence on the content of bioactive compounds. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Xie, D.; Lu, M.; Li, P.; Lv, H.; Yang, C.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Characterization of white tea metabolome: Comparison against green and black tea by a nontargeted metabolomics approach. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbowy, M.E.; Balentine, D.A.; Davies, A.P.; Cai, Y. Tea Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2010, 16, 415–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Umeki, H.; Nagai, S.; Shii, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kouno, I. Transformation of tea catechins and flavonoid glycosides by treatment with Japanese post-fermented tea acetone powder. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.-K.; Lin, C.-L.; Liang, Y.-C.; Lin-Shiau, S.-Y.; Juan, I.-M. Survey of Catechins, Gallic Acid, and Methylxanthines in Green, Oolong, Pu-erh, and Black Teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, P.D.; Yen, G.C.; Yen, W.J.; Wang, B.S.; Chang, L.W. Effects of Pu-erh tea on oxidative damage and nitric oxide scavenging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 8169–8176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, S.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, I.; Kim, G.-B. Effect of fermentation on the antioxidant activity in plant-based foods. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattem, D.A.; Shetty, K. Ellagic acid production and phenolic antioxidant activity in cranberry pomace (Vaccinium macrocarpon) mediated by Lentinus edodes using a solid-state system. Process Biochem. 2003, 39, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, D.; Strahsburger, E.; Lopez de Lacey, A.M.; Bregola, V.; Marotti, I.; Aloisio, I.; Biavati, B.; Dinelli, G. Flavonoid bioconversion in Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum B7003: A potential probiotic strain for functional food development. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, L.; Yang, B.; Jiang, G.; Gao, H.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Y. Production of quercetin, kaempferol and their glycosidic derivatives from the aqueous-organic extracted residue of litchi pericarp with Aspergillus awamori. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, N.T.; Van Camp, J.; Smagghe, G.; Raes, K. Improved Release and Metabolism of Flavonoids by Steered Fermentation Processes: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19369–19388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landete, J.M.; Curiel, J.A.; Rodríguez, H.; de las Rivas, B.; Muñoz, R. Aryl glycosidases from Lactobacillus plantarum increase antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds. J. Funct. Foods. 2014, 7, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, P.C.H.; Buijsman, M.N.C.P.; van Gameren, Y.; Cnossen, P.J.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Katan, M.B. The sugar moiety is a major determinant of the absorption of dietary flavonoid glycosides in man. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Song, J.L.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, J.S.; Park, K.Y. Fermented Pu-erh Tea increases in vitro anticancer activities in HT-29 Cells and has antiangiogenetic effects on HUVECs. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2013, 32, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, P.; Lin, L.; Harnly, J.M.; Yu, L.; Li, Z. Tentative identification, quantitation, and principal component analysis of green pu-erh, green, and white teas using UPLC/DAD/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, W.; Powell, C.; Clifford, M.N. The Analysis by HPLC of Green, Black and Pu’er Teas Produced in Yunnan. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1995, 69, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozuma, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Kohori, J.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I. Antihypertensive effect of green coffee bean extract on mildly hypertensive subjects. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurow, T.; Lee, S.-O. Effect of Chlorogenic Acid and Neochlorogenic Acid on Human Colon Cancer Cells. Stud. J. Dale Bump. Coll. Agric. Food Life Sci. 2012, 13, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Unno, T.; Sugimoto, A.; Kakuda, T. Scavenging effect of tea catechins and their epimers on superoxide anion radicals generated by a hypoxanthine and xanthine oxidase system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 80, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosińska, A.; Andlauer, W. Antioxidant Capacity of Tea: Effect of Processing and Storage. Process. Impact Antioxid. Beverages 2014, 12, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, P.; Vollmer, M.; Rohn, S. Phenolic compounds in Cistus incanus herbal infusions—Antioxidant capacity and thermal stability during the brewing process. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A. Analysis of Antioxidant Activity, Chlorogenic Acid, and Rutin Content of Camellia sinensis Infusions Using Response Surface Methodology Optimization. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Burillo, S.; Giménez, R.; Rufián-Henares, J.A.; Pastoriza, S. Effect of brewing time and temperature on antioxidant capacity and phenols of white tea: Relationship with sensory properties. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Ye, M.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Y.; Su, M.; Huang, H.; Qiu, M.; Zhao, A.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, T.; et al. Characterization of Pu-erh Tea Using Chemical and Metabolic Profiling Approaches. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3046–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchuk, A.; Jayasinghe, L.; Nikolai, K. Differentiation of black tea infusions according to origin, processing and botanical varieties using multivariate statistical analysis of LC-MS data. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y. Simultaneous determination of catechins, caffeine and gallic acids in green, Oolong, black and pu-erh teas using HPLC with a photodiode array detector. Talanta 2002, 57, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Ji, W.B.; Yu, P.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, F.; Yin, J.F. Effect of extraction methods on the chemical components and taste quality of green tea extract. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singleton, V.L. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Jones, A.; Acquaviva, A.; Dennis, G.R.; Shalliker, R.A.; Soliven, A. Bioactive screening of complex tea samples using the ferric reducing antioxidant power assay incorporating reaction flow HPLC columns for post column derivatisations. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Variety | Origin | Name | Year of Production | Producing Company | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shu 1 | Menghai (Bulang) | Gaoshan bing | 2016 | Lang he | n/a |
| 2 | Shu 2 | Lincang (Fengqing) | Tianlai bing | 2016 | Long run | n/a |
| 3 | Shu 3 | Menghai | Dayi 8592 | 2016 | Dayi | n/a |
| 4 | Shu 4 | Dali | Xiaguan zhuan | 2016 | Xiaguan | n/a |
| 5 | Shu 5 | Dali | Jinque bing | 2016 | Xiaguan | n/a |
| 6 | Shu 6 | Lincang (Fengqing) | Ruyi bing | 2017 | Zhong cha | n/a |
| 7 | Shu 7 | Menghai | Dayi 7572 | 2017 | Dayi | n/a |
| 8 | Shu 8 | Menghai | Laotongzhi bing | 2017 | Lao tong zhi | n/a |
| 9 | Shu 9 | Lincang (Fengqing) | Runxinhao bing | 2017 | Long run | n/a |
| 10 | Shu 10 | Pu’er | Lancang bing | 2017 | Lancang gu cha | n/a |
| 11 | Shu 1980 | Xishuangbanna | n/a | 1980 | n/a | n/a |
| 12 | Shu 1994 | Xishuangbanna | n/a | 1994 | n/a | n/a |
| 13 | Sheng 1 | Dali | Canger tuo | 2005 | Xiaguan | Kunming |
| 14 | Sheng 2 | Menghai | Changtai bing | 2005 | Chang tai | Zhejiang |
| 15 | Sheng 3 | Lincang | Qingzhuan | 2005 | Bai cha tang | Shanghai |
| 16 | Sheng 4 | Menghai | Dadugang bing | 2005 | Da du gang | Zhejiang |
| 17 | Sheng 5 | Menghai | Ziya bing | 2005 | Da du gang | Zhejiang |
| 18 | Sheng 1980 | Xishuangbanna | n/a | 1980 | n/a | n/a |
| 19 | Sheng 1992 | Xishuangbanna | n/a | 1992 | n/a | n/a |
| No. | Identification | Abbr. | RT [min] | UV [nm] | LOD [mg/L] | LOQ [mg/L] | ATP | YPT | MW [g/mol] | [M + H]+ [m/z] | Major Fragments [M + H]+ [m/z] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gallic acid | GA | 9.4 | 280 | 1.6 | 4.9 | x | X | 170.12 | 171.1 | 153.1 | 394.0 | - |
| 2 | Theogallin | Tg | 11.4 | 280 | 18.2 | 55.2 | X | x | 344.27 | 345.1 | 153.0 | 367.0 | 545.8 |
| 3 | (−)-Gallocatechin | GC | 15.0 | 280 | 147 | 446 | X | x | 306.27 | 307.0 | 139.0 | 288.7 | 419.2 |
| 4 | Theobromine | Tb | 15.2 | 280 | 4.0 | 12.3 | X | x | 180.16 | 181.1 | - | - | - |
| 5 | (−)-Epigallocatechin | EGC | 22.0 | 280 | 49.9 | 151.3 | X | x | 306.27 | 307.1 | 139.0 | 629.8 | - |
| 6 | (+)-Catechin | C | 23.8 | 280 | 20.6 | 62.3 | X | x | 290.27 | 291.1 | 123.0 | - | - |
| 7 | Caffeine | Caf | 25.4 | 280 | 19.3 | 58.5 | X | x | 194.19 | 195.1 | - | - | - |
| 8 | (−)-Epicatechin | EC | 31.1 | 280 | 11.3 | 34.2 | X | x | 290.27 | 291.0 | 123.1 | 139.2 | 165.3 |
| 9 | (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate | EGCG | 31.7 | 280 | 6.5 | 19.6 | X | x | 458.37 | 459.1 | 139.1 | 289.1 | 547.1 |
| 10 | (−)-Gallocatechin gallate | GCG | 34.3 | 280 | 5.0 | 15.3 | X | x | 458.37 | 459.0 | 139.0 | 289.6 | 884.1 |
| 11 | (−)-Epicatechin gallate | ECG | 40.3 | 280 | 13.6 | 41.2 | X | x | 442.37 | 443.1 | 123.1 | 139.0 | 273.1 |
| 12 | (−)-Catechin gallate | CG | 41.1 | 280 | 6.9 | 20.9 | X | x | 442.37 | 443.1 | - | - | - |
| 13 | Neochlorogenic acid | 3-CQA | 18.2 | 320 | 10.0 | 30.3 | X | x | 354.31 | 355.1 | 163.0 | 393.1 | - |
| 14 | Chlorogenic acid | 5-CQA | 24.2 | 320 | 10.6 | 32.2 | X | x | 354.31 | 355.0 | 163.0 | 393.1 | - |
| 15 | Cryptochlorogenic acid | 4-CQA | 26.1 | 320 | 10.1 | 30.7 | X | x | 354.31 | 355.0 | 163.1 | - | - |
| 16 | Quercetin-3-O-galactoside | Q-gal | 42.1 | 360 | 18.0 | 54.6 | X | x | 464.37 | 465.1 | 303.0 | - | - |
| 17 | Quercetin-3-O-glucoside | Q-glu | 43.0 | 360 | 23.1 | 69.9 | X | x | 464.37 | 465.0 | 303.0 | - | - |
| 18 | Kaempferol-3-O-rutinoside | K-rut | 44.6 | 360 | 19.4 | 58.8 | X | x | 594.52 | 595.1 | 287.1 | 449.0 | - |
| 19 | Kaempferol-3-O-glucoside | K-glu | 45.6 | 360 | 19.3 | 58.6 | X | x | 448.38 | 449.1 | 287.0 | - | - |
| 20 | Quercetin | Q | 52.8 | 360 | 2.1 | 6.3 | x | X | 302.24 | 303.0 | - | - | - |
| 21 | Kaempferol | K | 56.9 | 360 | 19.3 | 58.4 | x | X | 286.24 | 287.0 | - | - | - |
| 22 * | Theophylline | Tp | 19.4 | 280 | - | - | - | - | 180.16 | 181.0 | 124.2 | - | - |
| 23 * | Theaflavin | Tf | 51.5 | 280 | - | - | - | - | 564.49 | 565.1 | 121.0 | 1128.8 | 1693.3 |
| 24 * | Luteolin-6-C-glucoside | L-glu | 37.6 | 360 | - | - | - | - | 448.38 | 449.1 | - | - | - |
| 25 * | Luteolin | L | 52.9 | 360 | - | - | - | - | 286.24 | 287.0 | - | - | - |
| 26 * | Quercetin-3-O-rutinoside | Q-rut | 41.9 | 360 | - | - | - | - | 610.52 | 611.0 | 302.8 | 465.0 | - |
| 27 * | Quercetin-3-O-glucuronid | Q-glc | 42.6 | 360 | - | - | - | - | 478.36 | 479.0 | 303.0 | - | - |
| 28 * | Apigenin | A | 56.5 | 320 | - | - | - | - | 270.24 | 271.0 | - | - | - |
| No. | TPC | Tg | Caf | Tb | GA | GC | EGC | C | EC | EGCG | GCG | ECG | CG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shu 1 | 114 ± 2 | 1.44 ± 0.1 | 29.01 ± 0.66 | 1.73 ± 0.04 | 10.27 ± 0.26 | 3.59 ± 0.18 | 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 1.62 ± 0.02 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.00 | 2.35 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.02 |
| Shu 2 | 99 ± 1 | 0.80 ± 0.01 | 29.58 ± 0.05 | 1.46 ± 0.01 | 3.97 ± 0.01 | 2.22 ± 0.01 | 0.56 ± 0.02 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 1.57 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 1.53 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.00 |
| Shu 3 | 115 ± 4 | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 30.96 ± 0.71 | 1.53 ± 0.04 | 5.28 ± 0.16 | 2.19 ± 0.24 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.02 | 1.18 ± 0.04 | 0.54 ± 0.02 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.04 |
| Shu 4 | 85 ± 2 | 0.72 ± 0.01 | 26.58 ± 0.25 | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 4.48 ± 0.02 | 1.86 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.50 ± 0.01 | 1.02 ± 0.13 | 0.50 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.00 | 1.49 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 5 | 83 ± 1 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 34.04 ± 0.28 | 2.24 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.07 | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.89 ± 0.11 | 0.40 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 1.64 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 6 | 111 ± 1 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 27.36 ± 0.32 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | 5.21 ± 0.09 | 2.28 ± 0.16 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 2.03 ± 0.01 | 1.16 ± 0.04 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 2.28 ± 0.04 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 7 | 120 ± 2 | 1.00 ± 0.01 | 31.86 ± 0.13 | 1.72 ± 0.01 | 6.72 ± 0.04 | 2.40 ± 0.03 | 0.69 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 1.57 ± 0.02 | 0.67 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 1.76 ± 0.02 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 8 | 116 ± 1 | 1.28 ± 0.03 | 31.12 ± 0.39 | 1.98 ± 0.03 | 11.18 ± 0.13 | 2.64 ± 0.11 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 0.68 ± 0.02 | 1.26 ± 0.03 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.00 | 1.82 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 9 | 93 ± 2 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 29.18 ± 0.35 | 1.38 ± 0.02 | 2.33 ± 0.04 | 1.70 ± 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 1.75 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 1.60 ± 0.00 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| Shu 10 | 109 ± 3 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 31.89 ± 0.31 | 1.47 ± 0.01 | 4.53 ± 0.11 | 2.44 ± 0.24 | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 0.71 ± 0.02 | 1.84 ± 0.07 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.00 | 1.35 ± 0.05 | 0.06 ± 0.00 |
| Mean Shu 1-10 | 105 ± 13 | 0.94 ± 0.25 | 30.16 ± 2.26 | 1.60 ± 0.33 | 5.50 ± 3.17 | 2.23 ± 0.67 | 0.57 ± 0.16 | 0.66 ± 0.11 | 1.47 ± 0.37 | 0.66 ± 0.23 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 1.76 ± 0.33 | 0.16 ± 0.07 |
| Shu 1980 | 100 ± 2 | 1.47 ± 0.02 | 24.83 ± 0.35 | 1.06 ± 0.01 | 4.21 ± 0.11 | 2.44 ± 0.04 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.07 | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | 2.22 ± 0.08 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
| Shu 1994 | 148 ± 2 | 1.07 ± 0.71 | 26.74 ± 0.28 | 1.10 ± 0.01 | 17.81 ± 0.27 | 5.94 ± 0.10 | 1.25 ± 0.17 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 3.40 ± 0.03 | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 0.42 ± 0.00 | 3.01 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.03 |
| Sheng 1 | 221 ± 7 | 24.92 ± 0.67 | 36.79 ± 0.95 | 1.87 ± 0.05 | 2.24 ± 0.07 | 2.49 ± 0.18 | 6.94 ± 0.12 | 3.73 ± 0.45 | 8.41 ± 0.31 | 53.94 ± 1.51 | 6.76 ± 0.57 | 45.32 ± 1.29 | 1.35 ± 0.12 |
| Sheng 2 | 212 ± 7 | 16.69 ± 0.13 | 30.40 ± 0.16 | 1.13 ± 0.01 | 2.70 ± 0.04 | 2.60 ± 0.09 | 4.48 ± 0.07 | 3.33 ± 0.03 | 7.98 ± 0.12 | 34.30 ± 0.32 | 4.38 ± 0.05 | 40.77 ± 0.38 | 1.20 ± 0.06 |
| Sheng 3 | 206 ± 6 | 14.16 ± 0.21 | 29.57 ± 0.40 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 1.88 ± 0.02 | 2.24 ± 0.03 | 3.61 ± 0.08 | 3.82 ± 0.04 | 9.09 ± 0.11 | 30.50 ± 0.40 | 4.70 ± 0.07 | 44.03 ± 0.65 | 1.00 ± 0.06 |
| Sheng 4 | 207 ± 3 | 11.66 ± 0.17 | 29.80 ± 0.16 | 1.33 ± 0.02 | 1.85 ± 0.10 | 3.40 ± 0.13 | 6.19 ± 0.01 | 4.16 ± 0.06 | 10.19 ± 0.09 | 32.24 ± 0.37 | 1.68 ± 0.02 | 39.93 ± 0.18 | 1.51 ± 0.02 |
| Sheng 5 | 205 ± 10 | 13.25 ± 0.40 | 27.36 ± 0.85 | 0.92 ± 0.02 | 2.13 ± 0.06 | 4.61 ± 0.30 | 5.28 ± 0.26 | 2.95 ± 0.17 | 7.27 ± 0.36 | 24.59 ± 1.13 | 5.15 ± 0.22 | 30.64 ± 1.41 | 1.39 ± 0.13 |
| Mean Sheng 1-5 | 210 ± 6 | 16.13 ± 5.24 | 30.78 ± 3.55 | 1.24 ± 0.39 | 2.16 ± 0.35 | 3.07 ± 0.97 | 5.30 ± 1.32 | 3.60 ± 0.47 | 8.59 ± 1.11 | 35.11 ± 11.13 | 4.54 ± 1.84 | 40.14 ± 5.76 | 1.29 ± 0.20 |
| Sheng 1980 | 155 ± 2 | 8.67 ± 0.21 | 26.67 ± 0.22 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.80 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 2.05 ± 0.05 | 9.25 ± 0.08 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 21.81 ± 0.14 | 0.79 ± 0.04 |
| Sheng 1992 | 154 ± 3 | 7.96 ± 0.05 | 22.29 ± 0.22 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 3.01 ± 0.06 | 3.60 ± 0.05 | 1.72 ± 0.05 | 1.89 ± 0.02 | 5.64 ± 0.10 | 12.71 ± 0.15 | 1.04 ± 0.00 | 21.74 ± 0.49 | 1.03 ± 0.05 |
| No. | 3-CQA | 5-CQA | 4-CQA | Kaempferol | K-rut | K-glu | Quercetin | Q-gal | Q-glu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shu 1 | 93 ± 2 | 47 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 | 122 ± 3 | 421 ± 13 | 422 ± 10 | 357 ± 12 | 229 ± 5 | 440 ± 19 |
| Shu 2 | 57 ± 1 | 30 ± 1 | 35 ± 1 | 107 ± 1 | 262 ± 4 | 223 ± 1 | 309 ± 6 | 204 ± 2 | 208 ± 2 |
| Shu 3 | 65 ± 2 | 34 ± 1 | 23 ± 1 | 92 ± 1 | 268 ± 10 | 247 ± 6 | 329 ± 7 | 206 ± 8 | 302 ± 8 |
| Shu 4 | 169 ± 19 | 60 ± 3 | 345 ± 16 | 85 ± 1 | 930 ± 10 | 497 ± 26 | 210 ± 2 | 556 ± 28 | 871 ± 54 |
| Shu 5 | 58 ± 1 | 32 ± 1 | 30 ± 1 | 82 ± 1 | 124 ± 3 | 167 ± 3 | 192 ± 4 | 141 ± 6 | 138 ± 3 |
| Shu 6 | 48 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 107 ± 1 | 334 ± 6 | 271 ± 5 | 278 ± 2 | 248 ± 3 | 259 ± 5 |
| Shu 7 | 69 ± 1 | 37 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 107 ± 2 | 350 ± 7 | 290 ± 1 | 311 ± 14 | 200 ± 3 | 287 ± 3 |
| Shu 8 | 100 ± 1 | 47 ± 1 | 28 ± 3 | 113 ± 1 | 329 ± 8 | 314 ± 5 | 320 ± 2 | 185 ± 2 | 317 ± 4 |
| Shu 9 | 46 ± 1 | 25 ± 1 | 36 ± 1 | 108 ± 1 | 205 ± 1 | 227 ± 1 | 351 ± 6 | 205 ± 3 | 224 ± 3 |
| Shu 10 | 28 ± 2 | 18 ± 1 | 20 ± 1 | 49 ± 2 | 196 ± 8 | 213 ± 9 | 96 ± 3 | 183 ± 8 | 199 ± 10 |
| Mean Shu 1-10 | 73 ± 40 | 35 ± 13 | 59 ± 101 | 97 ± 21 | 342 ± 224 | 287 ± 102 | 275 ± 84 | 236 ± 116 | 324 ± 209 |
| Shu 1980 | 34 ± 2 | 20 ± 1 | 48 ± 4 | 83 ± 2 | 348 ± 19 | 255 ± 13 | 223 ± 7 | 220 ± 19 | 291 ± 15 |
| Shu 1994 | 74 ± 1 | 30 ± 1 | 93 ± 3 | 55 ± 1 | 462 ± 3 | 282 ± 7 | 145 ± 6 | 244 ± 2 | 404 ± 1 |
| Sheng 1 | 497 ± 8 | 412 ± 10 | 1902 ± 27 | 39 ± 1 | 1428 ± 64 | 753 ± 25 | 83 ± 3 | 464 ± 16 | 718 ± 24 |
| Sheng 2 | 605 ± 2 | 281 ± 1 | 1178 ± 5 | 41 ± 1 | 1190 ± 19 | 543 ± 5 | 81 ± 1 | 545 ± 6 | 780 ± 26 |
| Sheng 3 | 609 ± 11 | 258 ± 4 | 1117 ± 14 | 42 ± 1 | 1394 ± 6 | 556 ± 6 | 72 ± 1 | 616 ± 9 | 775 ± 8 |
| Sheng 4 | 147 ± 18 | 53 ± 2 | 309 ± 19 | 65 ± 4 | 721 ± 37 | 385 ± 27 | 148 ± 14 | 447 ± 27 | 696 ± 38 |
| Sheng 5 | 598 ± 21 | 239 ± 25 | 1626 ± 45 | 41 ± 1 | 1204 ± 56 | 568 ± 28 | 102 ± 2 | 767 ± 30 | 1132 ± 50 |
| Mean Sheng 1-5 | 491 ± 198 | 248 ± 129 | 1226 ± 606 | 45 ± 11 | 1187 ± 282 | 561 ± 131 | 97 ± 30 | 568 ± 130 | 820 ± 178 |
| Sheng 1980 | 250 ± 9 | 163 ± 5 | 334 ± 11 | 45 ± 1 | 1235 ± 7 | 651 ± 7 | 94 ± 2 | 666 ± 5 | 913 ± 26 |
| Sheng 1992 | 285 ± 13 | 119 ± 3 | 694 ± 15 | 64 ± 1 | 903 ± 11 | 456 ± 7 | 210 ± 1 | 654 ± 12 | 913 ± 17 |
| Bioactive compounds | Infusion Temperature [°C] | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 98 | ||||||
| Sheng 1 | Shu 1 | Sheng 1 | Shu 1 | Sheng 1 | Shu 1 | Sheng 1 | Shu 1 | Sheng 1 | Shu 1 | |
| TPC [mg GAE/g] | 37 ± 1 | 20 ± 3 | 40 ± 3 | 26 ± 2 | 44 ± 3 | 32 ± 4 | 68 ± 6 | 34 ± 4 | 71 ± 6 | 36 ± 2 |
| Gallic acid | 1.2 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 0.1 ± 0.1 |
| Theogallin | 10.1 ± 1.9 | 9.8 ± 1.8 | 12.4 ± 0.6 | 10.8 ± 0.4 | 13.6 ± 6.9 | 12.0 ± 1.5 | 19.4 ± 1.1 | 12.7 ± 2.0 | 19.3 ± 1.3 | 14.1 ± 4.2 |
| GC | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 3.8 ± 0.1 | 5.3 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 5.4 ± 0.4 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.1 |
| Theobromine | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 1.0 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.83 ± 0.0 |
| EGC | 1.6 ± 0.3 | n.d. | 2.4 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 2.5 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 |
| (+)-Catechin | 1.8 ± 0.3 | n.d. | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| Caffeine | 8.6 ± 1.3 | 9.5 ± 1.5 | 13.5 ± 2.9 | 14.2 ± 1.1 | 15.6 ± 1.3 | 19.2 ± 2.6 | 23.9 ± 1.1 | 21.5 ± 1.5 | 24.8 ± 2.5 | 22.3 ± 0.5 |
| (−)-Epicatechin | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 1.3 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 0.9 ± 0.0 |
| EGCG | 6.7 ± 1.8 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 10.4 ± 2.5 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 12.0 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 18.9 ± 1.9 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 19.4 ± 1.1 | 0.7 ± 0.0 |
| GCG | 1.01 ± 0.2 | n.d. | 1.41 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 1.9 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.0 |
| ECG | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 1.3 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 0.7 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 15.0 ± 1.9 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 13.9 ± 0.8 | 0.6 ± 0.5 |
| CG | 0.3 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 0.3 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 0.7 ± 0.1 | n.d. | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.0 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedan, V.; Rohn, S.; Holinger, M.; Hühn, T.; Chetschik, I. Bioactive Compound Fingerprint Analysis of Aged Raw Pu’er Tea and Young Ripened Pu’er Tea. Molecules 2018, 23, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081931
Pedan V, Rohn S, Holinger M, Hühn T, Chetschik I. Bioactive Compound Fingerprint Analysis of Aged Raw Pu’er Tea and Young Ripened Pu’er Tea. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081931
Chicago/Turabian StylePedan, Vasilisa, Sascha Rohn, Mirjam Holinger, Tilo Hühn, and Irene Chetschik. 2018. "Bioactive Compound Fingerprint Analysis of Aged Raw Pu’er Tea and Young Ripened Pu’er Tea" Molecules 23, no. 8: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081931
APA StylePedan, V., Rohn, S., Holinger, M., Hühn, T., & Chetschik, I. (2018). Bioactive Compound Fingerprint Analysis of Aged Raw Pu’er Tea and Young Ripened Pu’er Tea. Molecules, 23(8), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081931