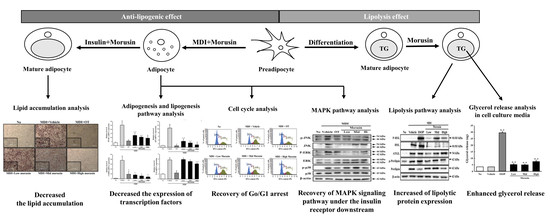
Morusin Functions as a Lipogenesis Inhibitor as Well as a Lipolysis Stimulator in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and Primary Adipocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Adipocyte Differentiation
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.3. Oil Red-O Staining
2.4. Care and Use of Laboratory Animals
2.5. Isolation and Culture of Primary Adipocytes
2.6. Real Time-PCR Analysis
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Cell Cycle Assay
2.9. Measurement of Free Glycerol Release
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cytotoxicity of Morusin
3.2. Inhibitory Effect of Morusin on Lipid Accumulation
3.3. Suppression of Adipogenic Transcription Factors and Lipogenic Proteins after Morusin Exposure
3.4. Effect of Morusin on the Insulin Receptor Downstream Signaling Pathway
3.5. Effect of Morusin on the Regulation of the Cell Cycle
3.6. Effect of Morusin on Lipolysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ko, H.H.; Yu, S.M.; Ko, F.N.; Teng, C.M.; Lin, C.N. Bioactive constituents of Morus australis and Broussonetia papyrifera. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.H.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, J.P.; Lin, C.N. Chemistry and biological activities of constituents from Morus australis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1428, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.Z.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Y.Q. Preparation of morusin from Ramulus ori and its effects on mice with transplanted H22 hepatocarcinoma. Biofactors 2014, 40, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, X.; Ma, C.; Lv, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, P. Morusin induces paraptosis-like cell death through mitochondrial calcium overload and dysfunction in epithelial ovarian cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 283, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Dong, L.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Gao, L.; Wang, X. Morusin suppresses breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo through C/EBPβ and PPARγ mediated lipoapoptosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, P.; Wang, X. Morusin inhibits glioblastoma stem cell growth in vitro and in vivo through stemness attenuation, adipocyte transdifferentiation, and apoptosis induction. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.W.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, E.Y.; Nam, D.W.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Sim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S. Blockage of STAT3 signaling pathway by morusin induces apoptosis and inhibits invasion in human pancreatic tumor cells. Pancreas 2016, 45, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Yi, C.; Wang, X. Morusin shows potent antitumor activity for human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo through apoptosis induction and angiogenesis inhibition. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 1789–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.W.; Na, W.J.; Choi, M.J.; Kang, S.J.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, C.Y. Autophagy inhibits cell death induced by the anti-cancer drug morusin. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, D.; Mao, J.; Ke, X.X.; Zhang, R.; Yin, C.; Gao, N.; Cui, H. Morusin inhibits cell proliferation and tumor growth by down-regulating c-Myc in human gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57187–57200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellik, Y.; Boukraâ, L.; Alzahrani, H.A.; Bakhotmah, B.A.; Abdellah, F.; Hammoudi, S.M.; Iguer-Ouada, M. Molecular mechanism underlying anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of phytochemicals: an update. Molecules 2013, 18, 322–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, H.Y.; Son, K.H.; Kwon, C.S.; Kwon, G.S.; Kang, S.S. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of 18 prenylated flavonoids isolated from medicinal plants: Morus alba L., Morus mongolica Schneider, Broussnetia papyrifera (L.) Vent, Sophora flavescens Ait and Echinosophora koreensis Nakai. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.G.; Matsuzaki, K.; Takamatsu, S.; Kitanaka, S. Inhibitory effects of constituents from Morus alba var. multicaulis on differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 6010–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Koh, P.O.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, K.S.; Chung, B.Y.; Kim, G.S.; Cho, J.H. Anti-obesity effect of Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 cells and high fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Jung, H.K.; Cho, K.H.; Youn, K.S.; Hong, J.H. Anti-obesity Effect of Grape Skin Extract in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−∆∆C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehart, H.; Kumpf, S.; Ittner, A.; Ricci, R. MAPK signaling in cellular metabolis: Stress or wellness? EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.J.; Koo, H.J.; Sohn, E.H.; Kang, S.C.; Rhee, D.K.; Pyo, S.N. Theobromine inhibits differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells during the early stage of adipogenesis via AMPK and MAPK signaling pathways. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Peng, K.Y.; Day, Y.J.; Hung, L.M. Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects in high-fat diet obese mice and displays differential dosage effects on cytotoxicity differentiation, and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. Endor. J. 2016, 63, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jang, Y.J.; Park, B.K.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Rhee, D.K.; Pyo, S.K. Ramalin inhibits differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and suppresses adiposity and body weight in a high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 257, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Xie, J.; Xu, Q.; Pan, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, J. Anti-obesity effects of zeaxanthin on 3T3-L1 pradipocyte and high fat induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3327–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Min, K.; Kwon, T.K.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, J.O. Eupatilin inhibits adipogenesis through suppression of PPARγ activity in 3T3-L1 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, S.; Wakai, E.; Shibano, M.; Fujimori, K. Anti-obesity effects of Asian dayflower, commelina communis, in mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity and in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Lane, M.D. Activation and centromeric localization of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins during the mitotic clonal expansion of adipocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gregoire, F.M.; Smas, C.M.; Sul, H.S. Understanding adipocyte differentiation. Physicol. Rev. 1998, 78, 783–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, Y.M.; Lane, M.D. Mitotic clonal expansion during preadipocyte differentiation: calpain-mediated turnover of p27. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17653–17660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, B.; Lim, S.W.; Ki, H.H.; Nepali, S.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, D.K. Dioscin inhibits adipogenesis through the AMPK/ MAPK pathway in 3T3-L1 cells and modulates fat accumulation in obese mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Rhee, D.K.; Kim, B.O.; Pyo, S. Inhibitory effect of sinigrin on adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells: Involvement of AMPK and MAPK pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 12, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.Q.; Otto, T.C.; Lane, M.D. Mitotic clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Morusin is not available from the authors. |







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.R.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, J.J.; Kim, H.R.; Song, B.R.; Park, J.W.; Kang, M.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Morusin Functions as a Lipogenesis Inhibitor as Well as a Lipolysis Stimulator in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and Primary Adipocytes. Molecules 2018, 23, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082004
Lee MR, Kim JE, Choi JY, Park JJ, Kim HR, Song BR, Park JW, Kang MJ, Choi YW, Kim KM, et al. Morusin Functions as a Lipogenesis Inhibitor as Well as a Lipolysis Stimulator in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and Primary Adipocytes. Molecules. 2018; 23(8):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082004
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Mi Rim, Ji Eun Kim, Jun Young Choi, Jin Ju Park, Hye Ryeong Kim, Bo Ram Song, Ji Won Park, Mi Ju Kang, Young Whan Choi, Kyung Mi Kim, and et al. 2018. "Morusin Functions as a Lipogenesis Inhibitor as Well as a Lipolysis Stimulator in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and Primary Adipocytes" Molecules 23, no. 8: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082004
APA StyleLee, M. R., Kim, J. E., Choi, J. Y., Park, J. J., Kim, H. R., Song, B. R., Park, J. W., Kang, M. J., Choi, Y. W., Kim, K. M., & Hwang, D. Y. (2018). Morusin Functions as a Lipogenesis Inhibitor as Well as a Lipolysis Stimulator in Differentiated 3T3-L1 and Primary Adipocytes. Molecules, 23(8), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23082004