The ?-Cyclodextrin/Moringin Complex: A New Promising Antimicrobial Agent against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
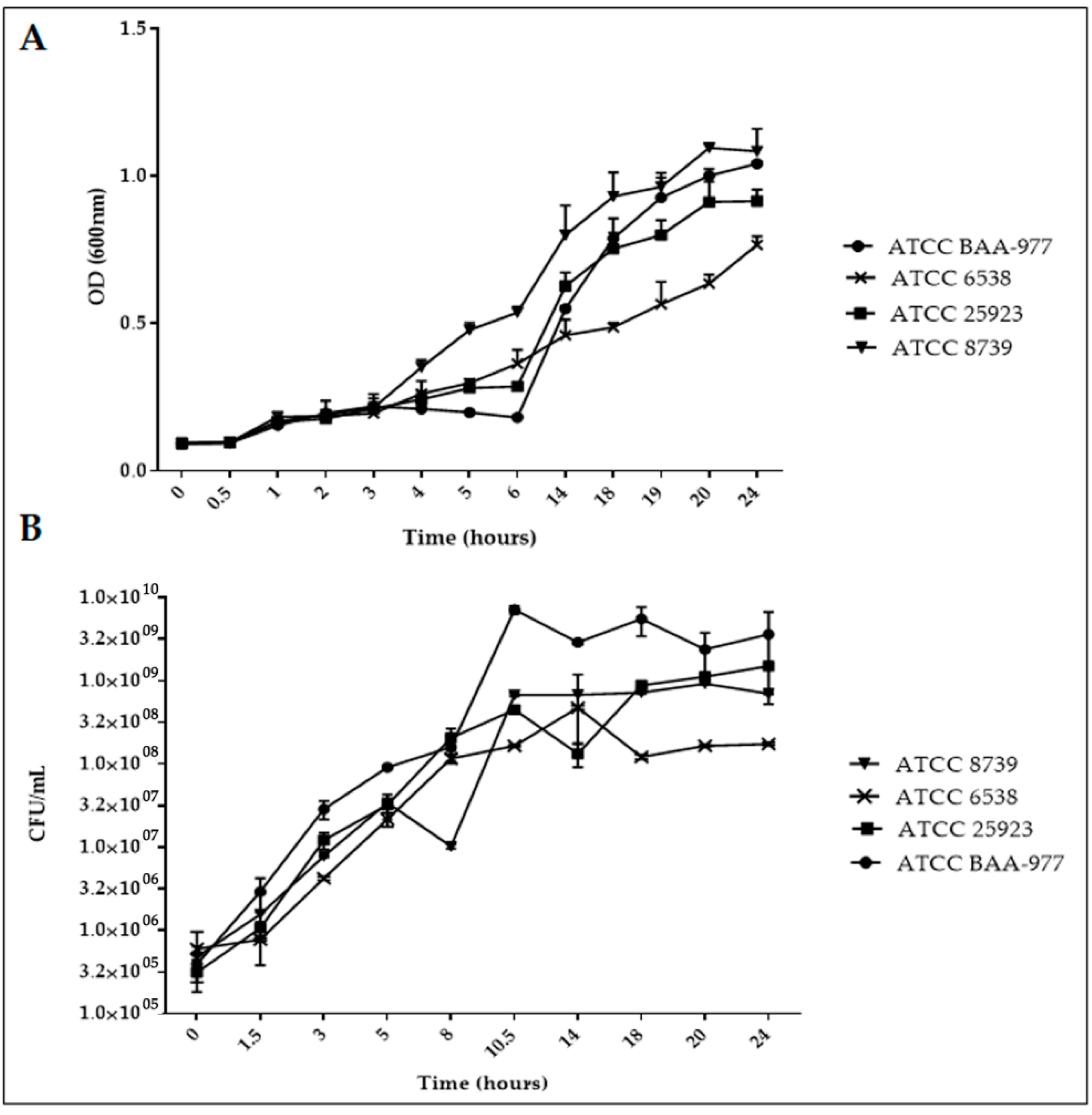
2.1. Bacterial Strain Growth Curve Determination into the Reference (MHB and CAMHB) Medium
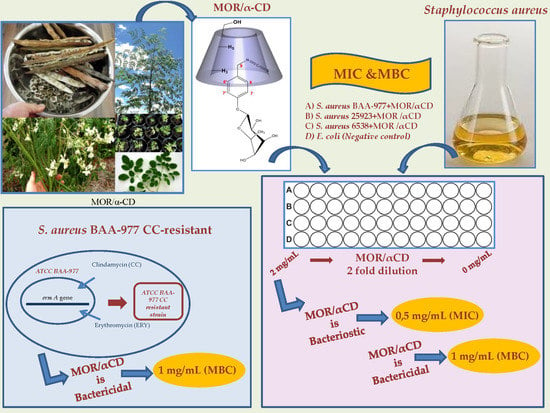
2.2. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration for MOR/α-CD
2.3. Determination of Minimum Bactericidal Concentration for MOR/α-CD
2.4. MOR/α-CD against BAA-977 Strain with a CC-Resistance Phenotype
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of MOR
4.2. Antibiotics and MOR/α-CD Dilution
4.3. S. aureus Strains and Growth Curve
4.4. MOR/α-CD Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.5. MOR/α-CD Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
4.6. MOR/α-CD Inhibitory (MIC) and Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) against S. aureus ATCC BAA-977 with CC-Resistant Phenotype Induced by Ery Treatment
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bottega, A.; Rodrigues, M.D.; Carvalho, F.A.; Wagner, T.F.; Leal, I.A.S.; Dos Santos, S.O.; Rampelotto, R.F.; Horner, R. Evaluation of constitutive and inducible resistance to clindamycin in clinical samples of Staphylococcus aureus from a tertiary hospital. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.S.; Jorgensen, J.H. Inducible clindamycin resistance in staphylococci: Should clinicians and microbiologists be concerned? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Waites, K.B.; Moser, S.A.; Cloud, G.A.; Hoesley, C.J. Prevalence of inducible clindamycin resistance among community- and hospital-associated Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2481–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, L.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Isothiocyanates: An overview of their antimicrobial activity against human infections. Molecules 2018, 23, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.; van Loon, J.; Ruschioni, S.; De Nicola, G.R.; Olsen, C.E.; Iori, R.; Agerbirk, N. Taste detection of the non-volatile isothiocyanate moringin results in deterrence to glucosinolate-adapted insect larvae. Phytochemistry 2015, 118, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padla, E.P.; Solis, L.T.; Levida, R.M.; Shen, C.C.; Ragasa, C.Y. Antimicrobial isothiocyanates from the seeds of moringa oleifera lam. Z. Naturforsch. C 2012, 67, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galuppo, M.; De Nicola, G.R.; Iori, R.; Dell’Utri, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Antibacterial activity of glucomoringin bioactivated with myrosinase against two important pathogens affecting the health of long-term patients in hospitals. Molecules 2013, 18, 14340–14348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Moringa isothiocyanate complexed with alpha-cyclodextrin: A new perspective in neuroblastoma treatment. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiron, D.; Iori, R.; Pilard, S.; Soundra Thangavelu, R.; Landy, D.; Mazzon, E.; Rollin, P.; Djedaïni-Pilard, F. A combined approach of nmr and mass spectrometry techniques applied to the alpha-cyclodextrin/moringin complex for a novel bioactive formulation. Molecules 2018, 23, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The a-cyclodextrin complex of the moringa isothiocyanate suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in raw 264.7 macrophage cells through akt and p38 inhibition. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 66, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, C.D.; Raney, P.M.; Morrell, A.K.; Williams, P.P.; McDougal, L.K.; Jevitt, L.; McGowan, J.E., Jr.; Tenover, F.C. Testing for induction of clindamycin resistance in erythromycin-resistant isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, M.; Inoue, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Endo, Y. New erm gene in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID). Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (mics) of antibacterial agents by broth dilution. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, ix–xv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, A.L.; Craig, W.A.; Nadler, H.; Reller, L.B.; Sanders, C.C.; Swenson, J.M. Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents: Approved Guideline, 18th ed.; NCCLS document M26-A; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards: Wayne, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Delaquis, P.J.; Mazza, G. Antimicrobial properties of isothiocyanates in food preservation. Food Technol. 1995, 49, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Roselli, C.; Perly, B.; Rollin, P. Complexes for Immobilizing Isothiocyanate Natural Precursors in Cyclodextrins, Preparation and Use. US Patent US6,716,827B1, 6 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, J.R.O.; Silva, G.C.; Costa, R.A.; Fontenelle, J.L.D.; Vieira, G.H.F.; Fonteles, A.A.F.; Vieira, R.H.S.D.F. In vitro antibacterial effect of aqueous and ethanolic moringa leaf extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klevens, R.M.; Morrison, M.A.; Nadle, J.; Petit, S.; Gershman, K.; Ray, S.; Harrison, L.H.; Lynfield, R.; Dumyati, G.; Townes, J.M.; et al. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the united states. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 298, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunelli, D.; Tavecchio, M.; Falcioni, C.; Frapolli, R.; Erba, E.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Barillari, J.; Manzotti, C.; Morazzoni, P.; et al. The isothiocyanate produced from glucomoringin inhibits nf-kb and reduces myeloma growth in nude mice in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: All the compounds (the antibiotics Ery and CC) are available from the authors but not the MOR/α-CD. |






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romeo, L.; Lanza Cariccio, V.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The ?-Cyclodextrin/Moringin Complex: A New Promising Antimicrobial Agent against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2018, 23, 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092097
Romeo L, Lanza Cariccio V, Iori R, Rollin P, Bramanti P, Mazzon E. The ?-Cyclodextrin/Moringin Complex: A New Promising Antimicrobial Agent against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 2018; 23(9):2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092097
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomeo, Letizia, Veronica Lanza Cariccio, Renato Iori, Patrick Rollin, Placido Bramanti, and Emanuela Mazzon. 2018. "The ?-Cyclodextrin/Moringin Complex: A New Promising Antimicrobial Agent against Staphylococcus aureus" Molecules 23, no. 9: 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092097
APA StyleRomeo, L., Lanza Cariccio, V., Iori, R., Rollin, P., Bramanti, P., & Mazzon, E. (2018). The ?-Cyclodextrin/Moringin Complex: A New Promising Antimicrobial Agent against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules, 23(9), 2097. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092097