Solid-Phase Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Study of β-ABpeptoids
Abstract
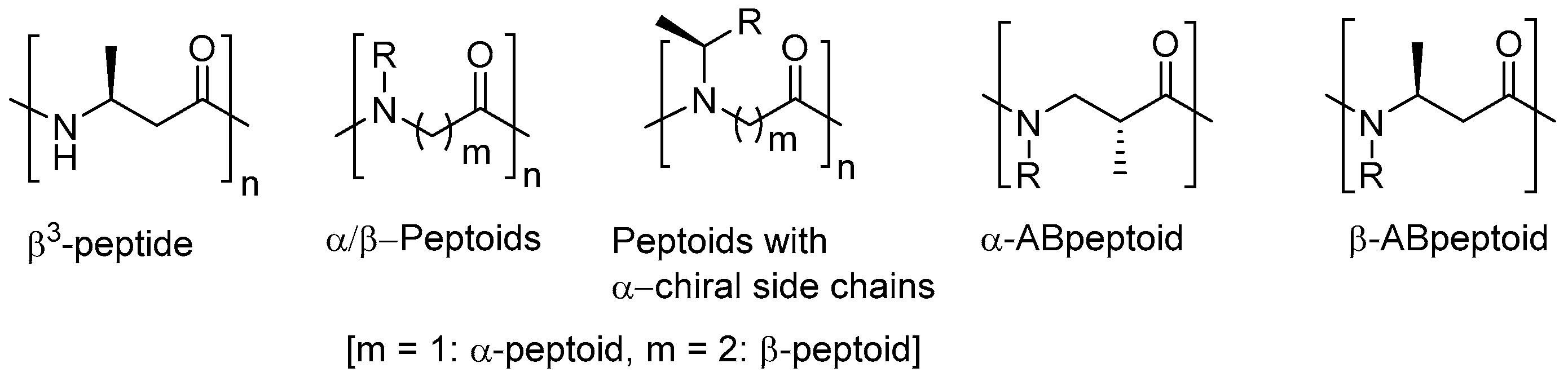
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
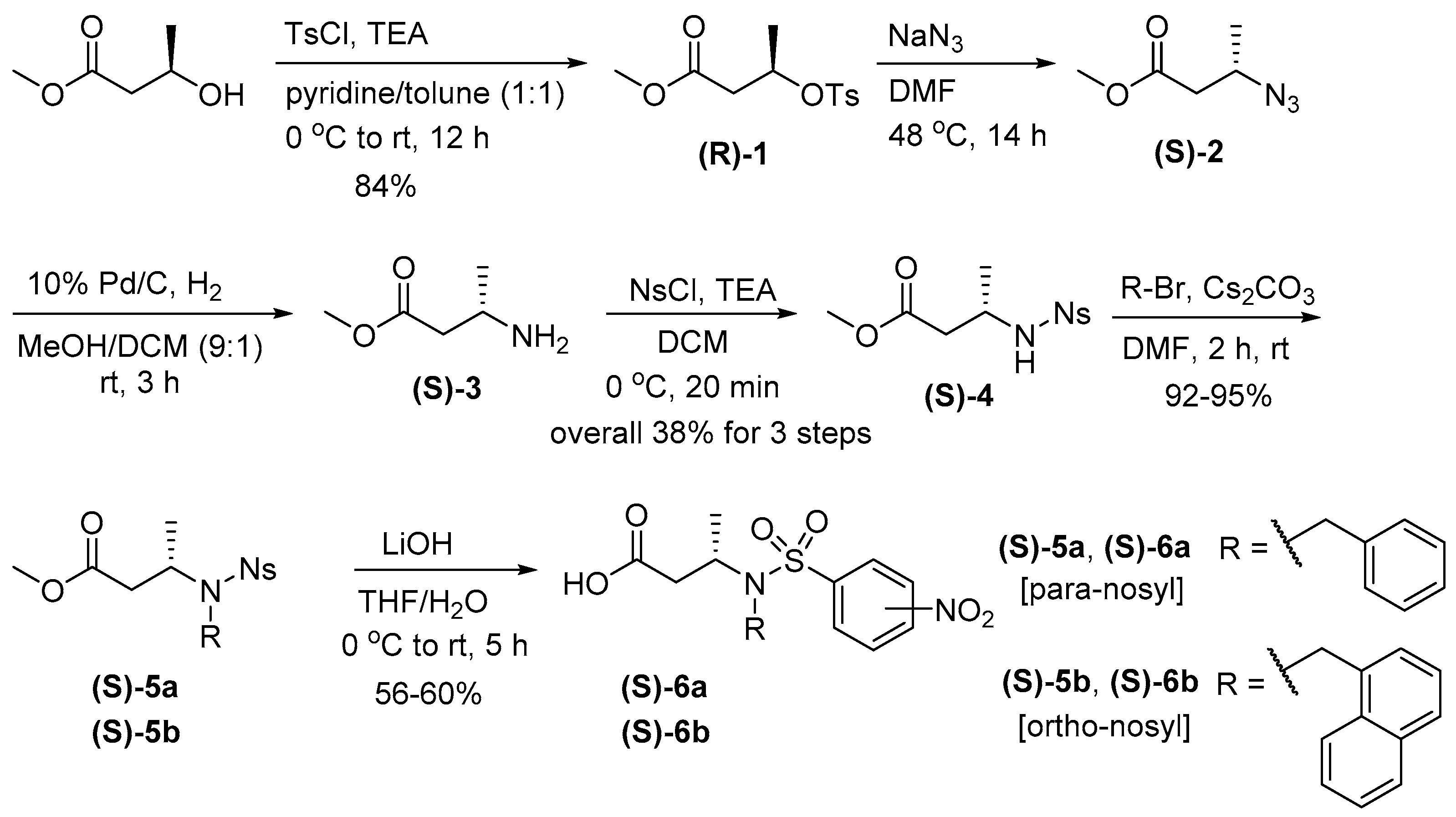
2.1. Synthesis of Monomer Building Blocks
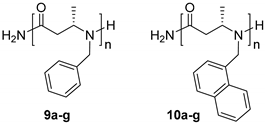
2.2. Solid-Phase Synthesis of β-ABpeptoid Oligomers
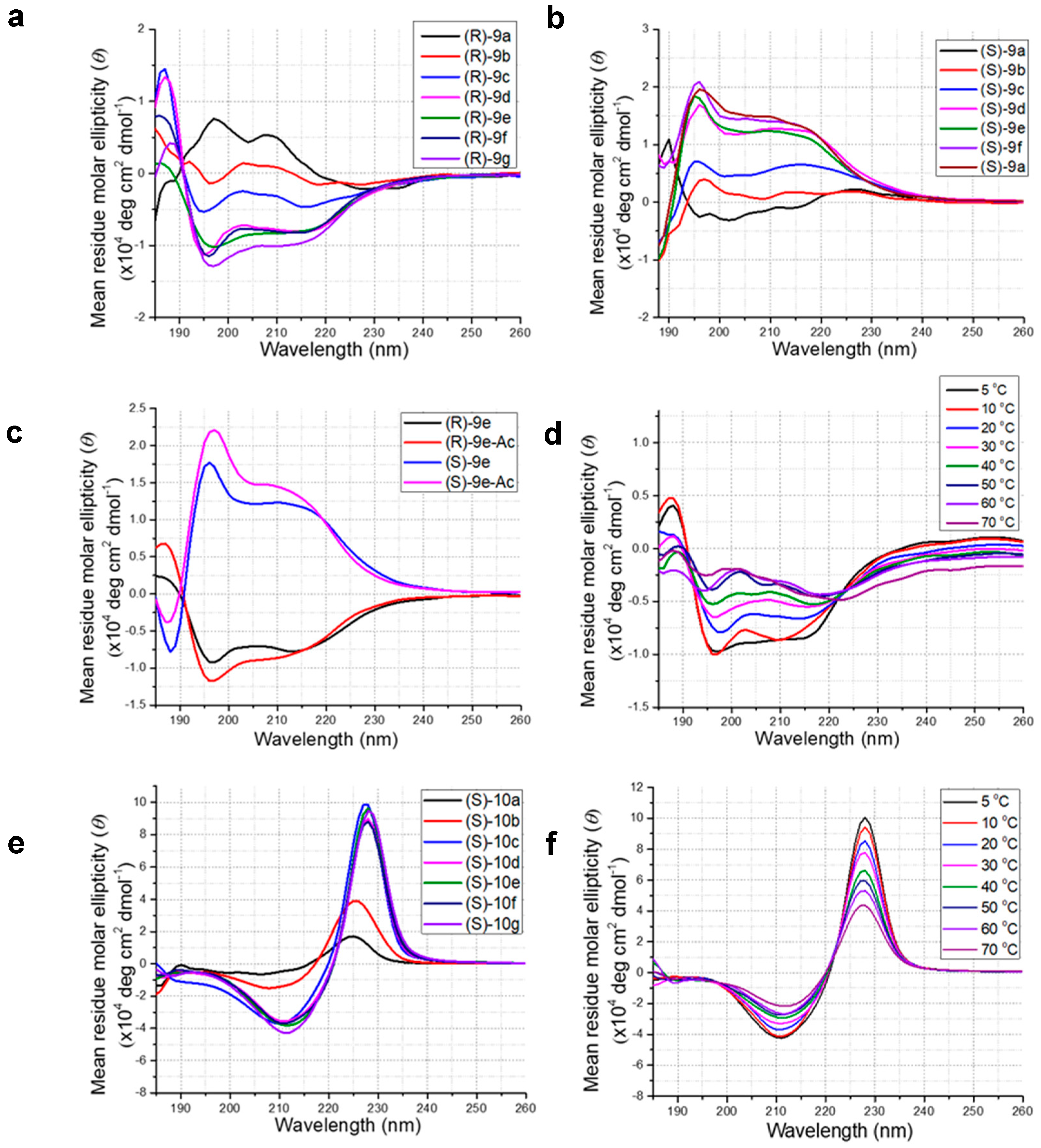
2.3. Structural Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Chemistry
3.2.1. Solution-Phase Synthesis Building Block Monomers and Intermediates
3.2.2. General Solid-Phase Synthesis Method for Oligomers Synthesis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, D.J.; Mio, M.J.; Prince, R.B.; Hughes, T.S.; Moore, J.S. A Field Guide to Foldamers. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3893–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.M.; Choi, S.; Shandler, S.; DeGrado, W.F. Foldamers as versatile frameworks for the design and evolution of function. Nat. chem. biol. 2007, 3, 10–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinek, T.A.; Fulop, F. Peptidic foldamers: Ramping up diversity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.P.; Gellman, S.H.; DeGrado, W.F. β-Peptides: From Structure to Function. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seebach, D.; Gardiner, J. β-Peptidic Peptidomimetics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritzer, J.A.; Lear, J.D.; Hodsdon, M.E.; Schepartz, A. Helical β-Peptide Inhibitors of the p53-hDM2 Interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9468–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, B.F.; Gellman, S.H. Impact of γ-Amino Acid Residue Preorganization on α/γ-Peptide Foldamer Helicity in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10766–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.-H.; Gellman, S.H. Impact of Backbone Pattern and Residue Substitution on Helicity in α/β/γ-Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violette, A.; Averlant-Petit, M.C.; Semetey, V.; Hemmerlin, C.; Casimir, R.; Graff, R.; Marraud, M.; Briand, J.-P.; Rognan, D.; Guichard, G. N,N′-Linked Oligoureas as Foldamers: Chain Length Requirements for Helix Formation in Protic Solvent Investigated by Circular Dichroism, NMR Spectroscopy, and Molecular Dynamics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2156–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collie, G.W.; Pulka-Ziach, K.; Lombardo, C.M.; Fremaux, J.; Rosu, F.; Decossas, M.; Mauran, L.; Lambert, O.; Gabelica, V.; Mackereth, C.D.; et al. Shaping quaternary assemblies of water-soluble non-peptide helical foldamers by sequence manipulation. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryavtsev, K.V.; Ivantcova, P.M.; Churakov, A.V.; Wiedmann, S.; Luy, B.; Muhle-Goll, C.; Zefirov, N.S.; Bräse, S. Alternating Asymmetric Self-Induction in Functionalized Pyrrolidine Oligomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12736–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Teng, P.; Sang, P.; She, F.; Wei, L.; Cai, J. γ-AApeptides: Design, Structure, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teng, P.; Ma, N.; Cerrato, D.C.; She, F.; Odom, T.; Wang, X.; Ming, L.-J.; van der Vaart, A.; Wojtas, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Right-Handed Helical Foldamers Consisting of De Novo d-AApeptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 7363–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelo, N.G.; Arora, P.S. Nonpeptidic Foldamers from Amino Acids: Synthesis and Characterization of 1,3-Substituted Triazole Oligomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17134–17135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, R.; Hofmann, H.-J. Hydrazino Peptides as Foldamers: An Extension of the β-Peptide Concept. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proulx, C.; Sabatino, D.; Hopewell, R.; Spiegel, J.; García Ramos, Y.; Lubell, W.D. Azapeptides and their therapeutic potential. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1139–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.Y.; Moran, E.J.; Cherry, S.R.; Stephans, J.C.; Fodor, S.P.; Adams, C.L.; Sundaram, A.; Jacobs, J.W.; Schultz, P.G. An unnatural biopolymer. Science 1993, 261, 1303–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.-D.; Yang, D. α-Aminoxy Acids: New Possibilities from Foldamers to Anion Receptors and Channels. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.; Kirshenbaum, K. Peptoid architectures: Elaboration, actuation, and application. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.A.; Blackwell, H.E. Structure-function relationships in peptoids: Recent advances toward deciphering the structural requirements for biological function. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 1508–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, J.S.; Engel-Andreasen, J.; Olsen, C.A. β-Peptoid Foldamers at Last. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2696–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.J.; Kania, R.S.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Huebner, V.D.; Jewell, D.A.; Banville, S.; Ng, S.; Wang, L.; Rosenberg, S.; Marlowe, C.K. Peptoids: A modular approach to drug discovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9367–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckermann, R.N.; Kerr, J.M.; Kent, S.B.H.; Moos, W.H. Efficient method for the preparation of peptoids [oligo(N-substituted glycines)] by submonomer solid-phase synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10646–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.M.; Simon, R.J.; Ng, S.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Kerr, J.M.; Moos, W.H. Proteolytic studies of homologous peptide and N-substituted glycine peptoid oligomers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1994, 4, 2657–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Tullman, R.; Jewell, C.F., Jr.; Weetall, M.L.; Tse, F.L. Absorption and disposition of a tripeptoid and a tetrapeptide in the rat. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1999, 20, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, B.; Kodadek, T. A high-throughput assay for assessing the cell permeability of combinatorial libraries. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.C.; Yu, P.; Kwon, Y.U.; Kodadek, T. High-throughput evaluation of relative cell permeability between peptoids and peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 5853–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, M.-K.; Hyun, Y.-J.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, H.-S. Comparison of Cell Permeability of Cyclic Peptoids and Linear Peptoids. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.M.; Cobb, S.L. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Peptoid Macrocycles. Chemistry 2018, 24, 7560–7573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.B.Y.; Yoo, B.; Todaro, L.J.; Kirshenbaum, K. Cyclic Peptoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3218–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Meyer, A.M.; Lim, H.-S. A simple strategy for the construction of combinatorial cyclic peptoid libraries. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8615–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Lim, H.-S. Design and Facile Solid-Phase Synthesis of Conformationally Constrained Bicyclic Peptoids. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5012–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Lim, H.-S. Facile Method To Sequence Cyclic Peptides/Peptoids via One-Pot Ring-Opening/Cleavage Reaction. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5710–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniraj, P.J.; Maayan, G. A Facile Strategy for the Construction of Cyclic Peptoids under Microwave Irradiation through a Simple Substitution Reaction. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2110–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, M.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, H.; Hyun, Y.-J.; Lim, H.-S. A Chemical Inhibitor of the Skp2/p300 Interaction that Promotes p53-Mediated Apoptosis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Kirshenbaum, K.; Goldsmith, R.A.; Farr-Jones, S.; Barron, A.E.; Truong, K.T.V.; Dill, K.A.; Mierke, D.F.; Cohen, F.E.; Zuckermann, R.N.; et al. NMR determination of the major solution conformation of a peptoid pentamer with chiral side chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.W.; Sanborn, T.J.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Barron, A.E. Peptoid Oligomers with α-Chiral, Aromatic Side Chains: Effects of Chain Length on Secondary Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2958–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Kirshenbaum, K.; Sanborn, T.J.; Patch, J.A.; Huang, K.; Dill, K.A.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Barron, A.E. Structural and Spectroscopic Studies of Peptoid Oligomers with α-Chiral Aliphatic Side Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 13525–13530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, J.R.; Crapster, J.A.; Guzei, I.A.; Blackwell, H.E. Extraordinarily Robust Polyproline Type I Peptoid Helices Generated via the Incorporation of α-Chiral Aromatic N-1-Naphthylethyl Side Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15559–15567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, O.; Dumonteil, G.; Faure, S.; Jouffret, L.; Kriznik, A.; Taillefumier, C. Homogeneous and Robust Polyproline Type I Helices from Peptoids with Nonaromatic α-Chiral Side Chains. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13533–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, J.S.; Harris, P.; Fristrup, P.; Olsen, C.A. Triangular prism-shaped β-peptoid helices as unique biomimetic scaffolds. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.J.; Lee, W.S.; Yun, H.; Hyun, Y.-J.; Seo, C.D.; Lee, C.W.; Lim, H.-S. Oligomers of N-Substituted β2-Homoalanines: Peptoids with Backbone Chirality. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 3678–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sable, G.A.; Lee, K.J.; Shin, M.-K.; Lim, H.-S. Submonomer Strategy toward Divergent Solid-Phase Synthesis of α-ABpeptoids. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 2526–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshenbaum, K.; Barron, A.E.; Goldsmith, R.A.; Armand, P.; Bradley, E.K.; Truong, K.T.V.; Dill, K.A.; Cohen, F.E.; Zuckermann, R.N. Sequence-specific polypeptoids: A diverse family of heteropolymers with stable secondary structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.W.; Sanborn, T.J.; Huang, K.; Zuckermann, R.N.; Barron, A.E. Peptoid Oligomers with α-Chiral, Aromatic Side Chains: Sequence Requirements for the Formation of Stable Peptoid Helices. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6778–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sable, G.A.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Lim, S.-J.; Jang, S.; Lim, D. Solid-Phase Total Synthesis of the Proposed Structure of Coibamide A and Its Derivative: Highly Methylated Cyclic Depsipeptides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 7043–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, G.A.; Park, J.; Lim, S.-J.; Lim, D. Solid-phase Total Synthesis of Amide Analogues of Coibamide A: Azacoibamide A and O-Desmethyl Azacoibamide A. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2016, 37, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, J.; Fukuda, Y.; Sando, S. Solid-Phase Synthesis of beta-Peptoids with Chiral Backbone Substituents Using Reductive Amination. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5912–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgren, A.S.; Zhang, S.; Arvidsson, P.I. Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Spectroscopic Investigations of Oligomeric β-Peptoids with α-Chiral Side Chains. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 4533–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorske, B.C.; Stringer, J.R.; Bastian, B.L.; Fowler, S.A.; Blackwell, H.E. New Strategies for the Design of Folded Peptoids Revealed by a Survey of Noncovalent Interactions in Model Systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16555–16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (S)-6a, (R)-6a, (S)-6b, 9a–g, (S)-10a–g, 9e-Ac and, (S)-10e-Ac are available from the authors. |

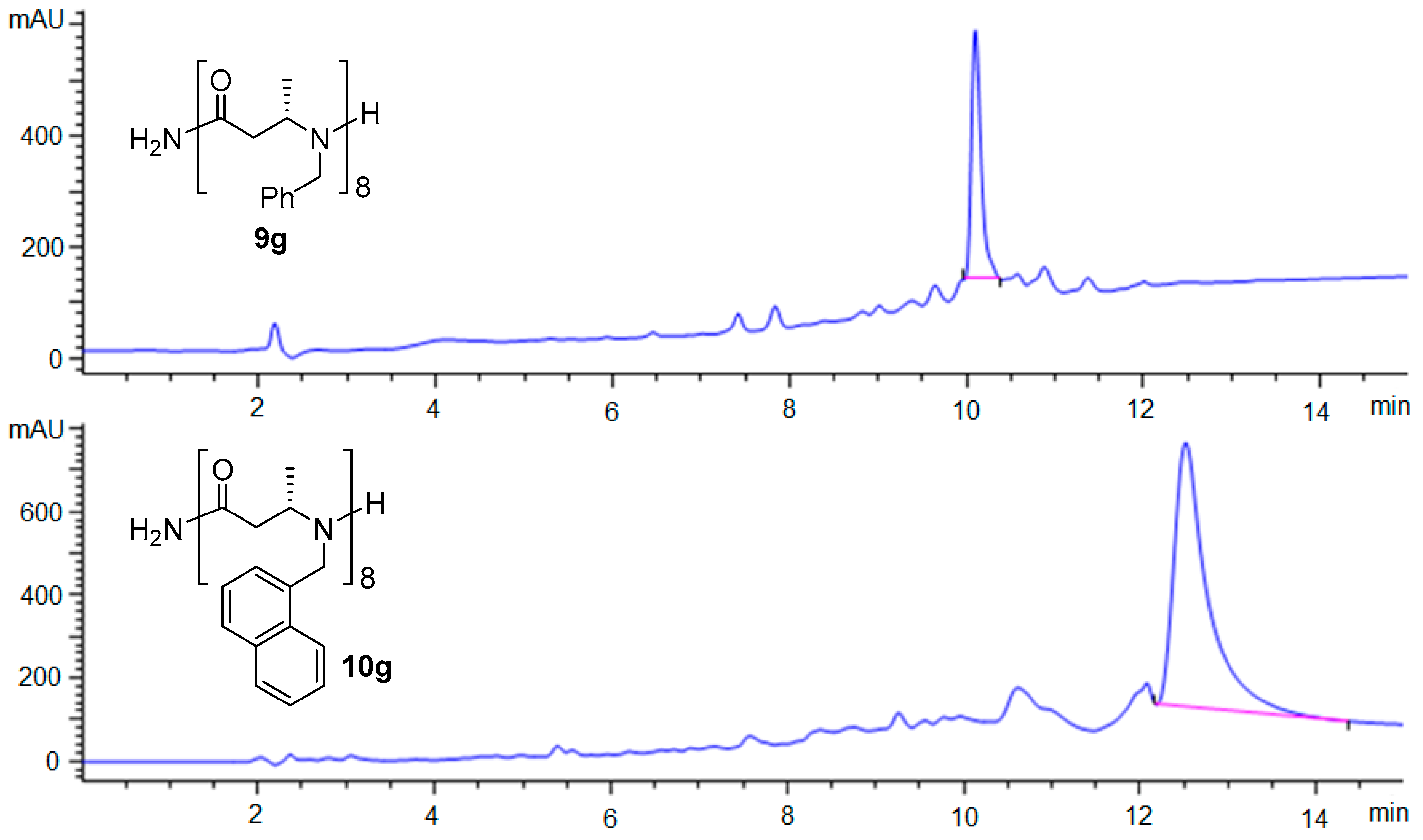
| Compd No. | Chain Length | % Purity a | Calcd Mass | Obsd Mass b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (S)-9a | 2 | 65 | 367.23 | 368.2 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9b | 3 | 68 | 542.33 | 543.3 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9c | 4 | 77 | 717.43 | 718.4 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9d | 5 | 78 | 892.53 | 893.4 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9e | 6 | 79 | 1067.62 | 1068.5 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9f | 7 | 73 | 1242.72 | 1243.6 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-9g | 8 | 71 | 1417.82 | 1440.9 [M + H]+c |
| (S)-9e-Ac d | 6 | 70 | 1109.64 | 1132.5 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10a | 2 | 94 | 467.26 | 468.2 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10b | 3 | 82 | 692.37 | 693.4 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10c | 4 | 94 | 917.49 | 918.4 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10d | 5 | 92 | 1142.60 | 1144.5 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10e | 6 | 87 | 1367.72 | 1368.6 [M + H]+ |
| (S)-10f | 7 | 85 | 1592.83 | 1614.8 [M + Na]+c |
| (S)-10g | 8 | 81 | 1817.95 | 1839.9 [M + Na]+c |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sable, G.A.; Lee, K.J.; Lim, H.-S. Solid-Phase Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Study of β-ABpeptoids. Molecules 2019, 24, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010178
Sable GA, Lee KJ, Lim H-S. Solid-Phase Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Study of β-ABpeptoids. Molecules. 2019; 24(1):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010178
Chicago/Turabian StyleSable, Ganesh A., Kang Ju Lee, and Hyun-Suk Lim. 2019. "Solid-Phase Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Study of β-ABpeptoids" Molecules 24, no. 1: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010178
APA StyleSable, G. A., Lee, K. J., & Lim, H.-S. (2019). Solid-Phase Synthesis and Circular Dichroism Study of β-ABpeptoids. Molecules, 24(1), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010178





