A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, VvMYBC2L2, Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. VvMYBC2L2 Sequence Analysis
2.2. VvMYBC2L2 Is Localized to the Nucleus
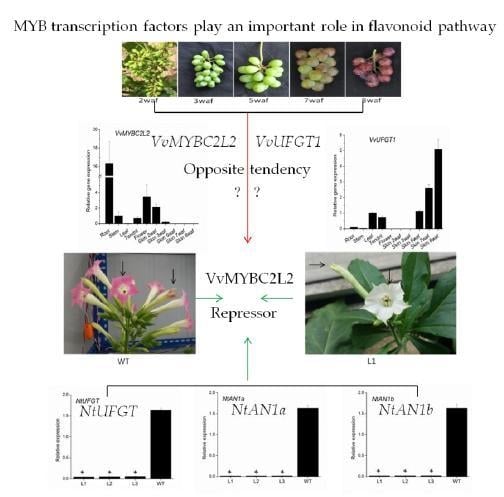
2.3. Transcript Profiles of VvMYBC2L2
2.4. Overexpression of VvMYBC2L2 in Tobacco Represses the Pigmentation of Petals
2.5. VvMYBC2L2-Regulated Flavonoid Biosynthetic Gene Expression in Tobacco Flowers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. Isolation of the VvMYBC2L2 Promoter Sequence
4.3. RNA Isolation and Expression Analysis
4.4. Subcellular Location of the VvMYBC2L2
4.5. Construct Assembly and Plant Transformation
4.6. Determination of Total Anthocyanin Content Concentration
4.7. Histochemical GUS Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.; Samec, D.; Tomczyk, M.; Milella, L.; Russo, D.; Habtemariam, S.; Suntar, I.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Xiao, J.; et al. Flavonoid biosynthetic pathways in plants: versatile targets for metabolic engineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.; Brandao, E.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Sensorial properties of red wine polyphenols: astringency and bitterness. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.Y.; Duan, C.Q. Astringency, bitterness and color changes in dry red wines before and during oak barrel aging: An updated phenolic perspective review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Paz-Ares, J. MYB transcription factors in plants. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.H.; Tian, Y.; Chen, K.Q.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, D.D.; Xie, X.B.; Cheng, C.G.; Cong, P.H.; Hao, Y.J. MdMYB9 and MdMYB11 are involved in the regulation of the JA-induced biosynthesis of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin in apples. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Putterill, J.; Stevenson, D.E.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Allan, A.C. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007, 49, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, D.G.; Sun, C.H.; Ma, Q.J.; You, C.X.; Cheng, L.; Hao, Y.J. MdMYB1 regulates anthocyanin and malate accumulation by directly facilitating their transport into vacuoles in apples. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Vimolmangkang, S.; Han, Y.; Wei, G.; Korban, S.S. An apple MYB transcription factor, MdMYB3, is involved in regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis and flower development. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Zhao, M.; Leavitt, J.M.; Lloyd, A.M. Regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway by the TTG1/bHLH/Myb transcriptional complex in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant. J. 2008, 53, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, S.; Keurentjes, J.; Bentsink, L.; Koornneef, M.; Smeekens, S. Sucrose-specific induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis requires the MYB75/PAP1 gene. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1840–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutanda-Perez, M.C.; Ageorges, A.; Gomez, C.; Vialet, S.; Terrier, N.; Romieu, C.; Torregrosa, L. Ectopic expression of VlmybA1 in grapevine activates a narrow set of genes involved in anthocyanin synthesis and transport. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeandet, P.; Clément, C.; Cordelier, S. Regulation of resveratrol biosynthesis in grapevine: new approaches for disease resistance? J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xi, H.; Dai, Z.; Lecourieux, F.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Patra, B.; Wei, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L. VvWRKY8 negatively regulates VvSTS through direct interaction with VvMYB14 to balance resveratrol biosynthesis in grapevine. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluc, L.; Barrieu, F.; Marchive, C.; Lauvergeat, V.; Decendit, A.; Richard, T.; Carde, J.P.; Merillon, J.M.; Hamdi, S. Characterization of a grapevine R2R3-MYB transcription factor that regulates the phenylpropanoid pathway. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deluc, L.; Bogs, J.; Walker, A.R.; Ferrier, T.; Decendit, A.; Merillon, J.M.; Robinson, S.P.; Barrieu, F. The transcription factor VvMYB5b contributes to the regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in developing grape berries. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrier, N.; Torregrosa, L.; Ageorges, A.; Vialet, S.; Verries, C.; Cheynier, V.; Romieu, C. Ectopic expression of VvMybPA2 promotes proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in grapevine and suggests additional targets in the pathway. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 1028–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czemmel, S.; Stracke, R.; Weisshaar, B.; Cordon, N.; Harris, N.N.; Walker, A.R.; Robinson, S.P.; Bogs, J. The grapevine R2R3-MYB transcription factor VvMYBF1 regulates flavonol synthesis in developing grape berries. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Numata, M.; Nakajima, I.; Goto-Yamamoto, N.; Matsumura, H.; Tanaka, N. Functional characterization of a new grapevine MYB transcription factor and regulation of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in grapes. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4433–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Umemura, Y.; Ohme-Takagi, M. AtMYBL2, a protein with a single MYB domain, acts as a negative regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008, 55, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbiati, M.; Matus, J.T.; Francia, P.; Rusconi, F.; Canon, P.; Medina, C.; Conti, L.; Cominelli, E.; Tonelli, C.; Arce-Johnson, P. The grapevine guard cell-related VvMYB60 transcription factor is involved in the regulation of stomatal activity and is differentially expressed in response to ABA and osmotic stress. BMC Plan. Biol. 2011, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharoni, A.; De Vos, C.H.; Wein, M.; Sun, Z.; Greco, R.; Kroon, A.; Mol, J.N.; O’Connell, A.P. The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 2001, 28, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.; Wang, G.; Wu, J.; Waheed, S.; Allan, A.C.; Zeng, L. Ectopic overexpression of a novel R2R3-MYB, NtMYB2 from Chinese narcissus represses anthocyanin biosynthesis in tobacco. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallini, E.; Matus, J.T.; Finezzo, L.; Zenoni, S.; Loyola, R.; Guzzo, F.; Schlechter, R.; Ageorges, A.; Arce-Johnson, P.; Tornielli, G.B. The phenylpropanoid pathway is controlled at different branches by a set of R2R3-MYB C2 repressors in grapevine. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1448–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, I.M.; Heim, M.A.; Weisshaar, B.; Uhrig, J.F. Comprehensive identification of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB transcription factors interacting with R/B-like BHLH proteins. Plant J. 2004, 40, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowicz, P.D.; Braun, E.L.; Wolfe, A.D.; Bowen, B.; Grotewold, E. Maize R2R3 Myb genes: sequence analysis reveals amplification in the higher plants. Genetics 1999, 153, 427–444. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czemmel, S.; Heppel, S.C.; Bogs, J. R2R3 MYB transcription factors: key regulators of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in grapevine. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagale, S.; Links, M.G.; Rozwadowski, K. Genome-wide analysis of ethylene-responsive element binding factor-associated amphiphilic repression motif-containing transcriptional regulators in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 1109–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; An, X.H.; Tian, Y.; Liu, D.D.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. MdHIR proteins repress anthocyanin accumulation by interacting with the MdJAZ2 protein to inhibit its degradation in apples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogt, T. Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis. Mol. Plant. 2010, 3, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Diaz, J.R.; Perez-Diaz, J.; Madrid-Espinoza, J.; Gonzalez-Villanueva, E.; Moreno, Y.; Ruiz-Lara, S. New member of the R2R3-MYB transcription factors family in grapevine suppresses the anthocyanin accumulation in the flowers of transgenic tobacco. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, J.B.; Cho, K.J.; Cheon, C.I.; Sung, M.K.; Choung, M.G.; Roh, K.H. Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB transcription factor AtMYB60 functions as a transcriptional repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Plant Cell Rep. 2008, 27, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Yamada, E.; Saito, M.; Fujita, K.; Nishihara, M. Heterologous expression of gentian MYB1R transcription factors suppresses anthocyanin pigmentation in tobacco flowers. Plant. cell rep. 2013, 32, 1925–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Kojima, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Tatsuzawa, F.; Doi, M.; Yazawa, S. Simultaneous post-transcriptional gene silencing of two different chalcone synthase genes resulting in pure white flowers in the octoploid dahlia. Planta 2011, 234, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Krol, A.R.; Lenting, P.E.; Veenstra, J.; van der Meer, I.M.; Koes, R.E.; Gerats, A.G.M.; Mol, J.N.M.; Stuitje, A.R. An anti-sense chalcone synthase gene in transgenic plants inhibits flower pigmentation. Nature 1988, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, K.; Xie, D.Y. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a dihydroflavonol 4-Reductase from Vitis bellula. Molecules 2018, 23, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Pattanaik, S.; Patra, B.; Werkman, J.R.; Xie, C.H.; Yuan, L. Flavonoid-related basic helix-loop-helix regulators, NtAn1a and NtAn1b, of tobacco have originated from two ancestors and are functionally active. Planta 2011, 234, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.E.; Olsson, N.; Schlosser, J.; Peng, F.; Lund, S.T. An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol. 2006, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutha, L.R.; Casassa, L.F.; Harbertson, J.F.; Naidu, R.A. Modulation of flavonoid biosynthetic pathway genes and anthocyanins due to virus infection in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.D.; Cho, Y.H.; Sheen, J. Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsch, R.B.; Fry, J.E.; Hoffmann, N.L.; Eichholtz, D.; Rogers, S.G.; Fraley, R.T. A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 1985, 227, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Khaldun, A.B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Lv, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y. A R2R3-MYB transcription factor regulates the flavonol biosynthetic pathway in a traditional chinese medicinal plant, pimedium sagittatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, R.A.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Bevan, M.W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Not available. |





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, B. A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, VvMYBC2L2, Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Molecules 2019, 24, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010092
Zhu Z, Li G, Liu L, Zhang Q, Han Z, Chen X, Li B. A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, VvMYBC2L2, Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Molecules. 2019; 24(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Ziguo, Guirong Li, Li Liu, Qingtian Zhang, Zhen Han, Xuesen Chen, and Bo Li. 2019. "A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, VvMYBC2L2, Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.)" Molecules 24, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010092
APA StyleZhu, Z., Li, G., Liu, L., Zhang, Q., Han, Z., Chen, X., & Li, B. (2019). A R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor, VvMYBC2L2, Functions as a Transcriptional Repressor of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Molecules, 24(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010092