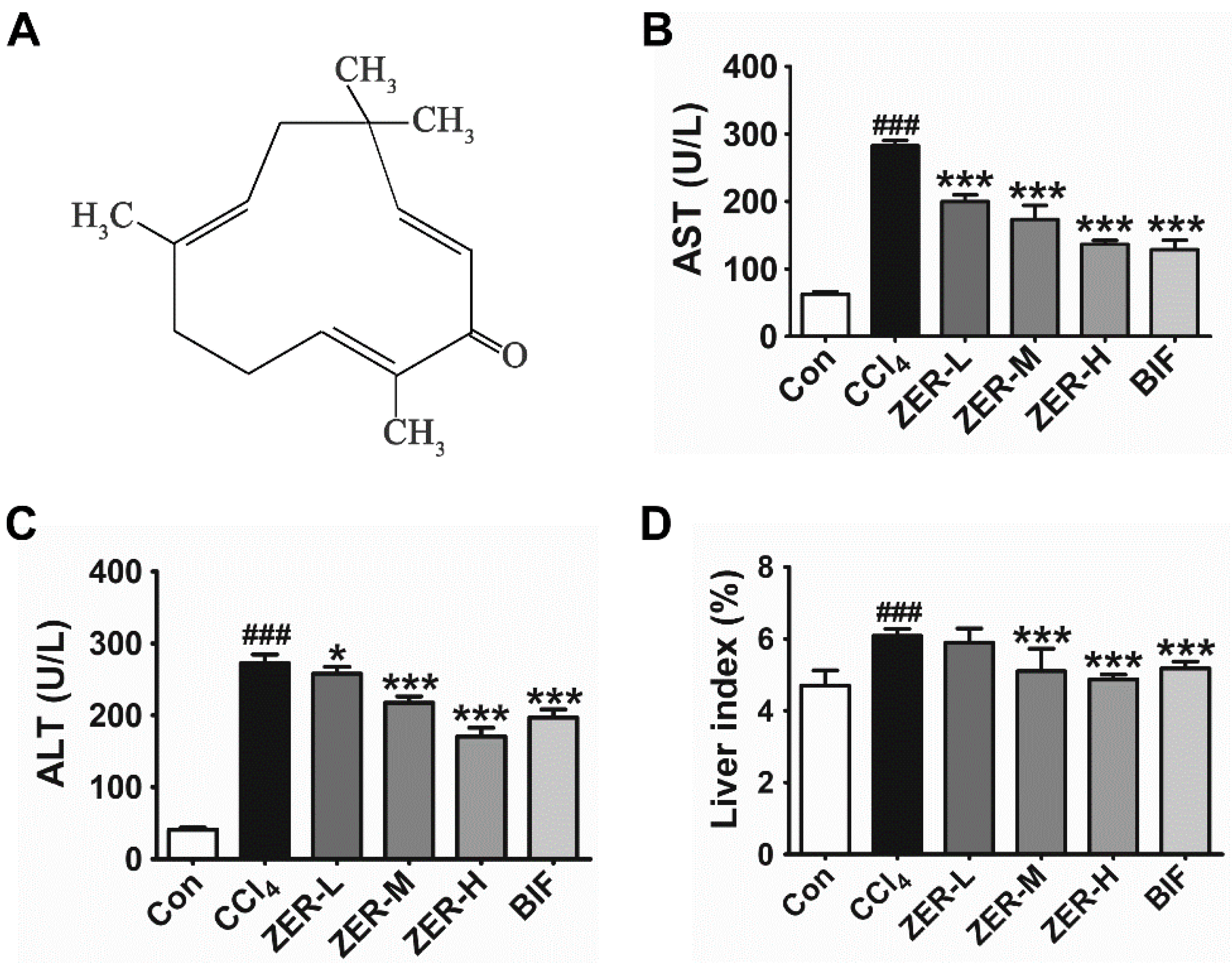
Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of ZER on Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), and Liver Index
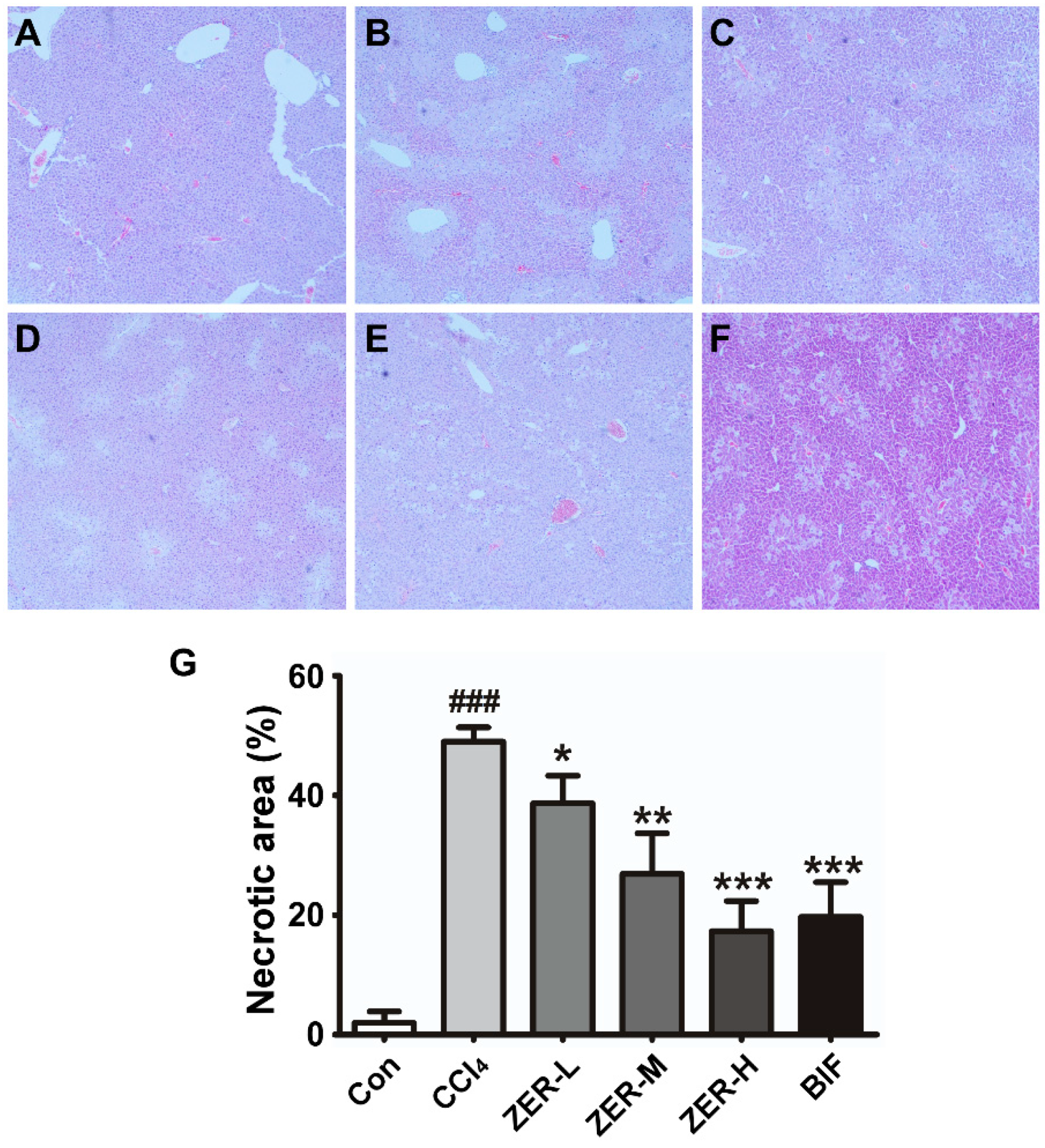
2.2. Histopathological Effect of ZER in Liver
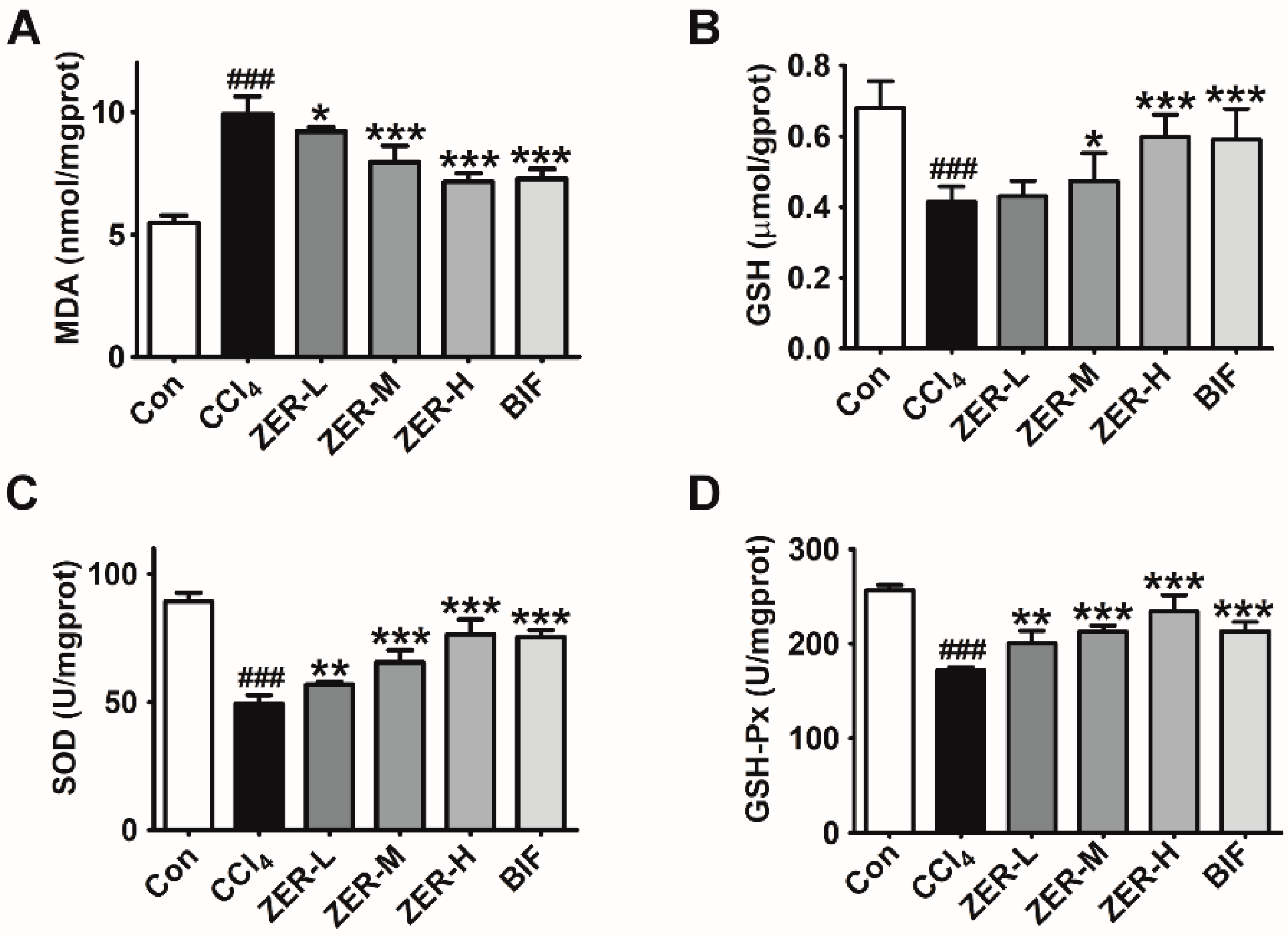
2.3. Effects of ZER on Oxidative Stress Parameters
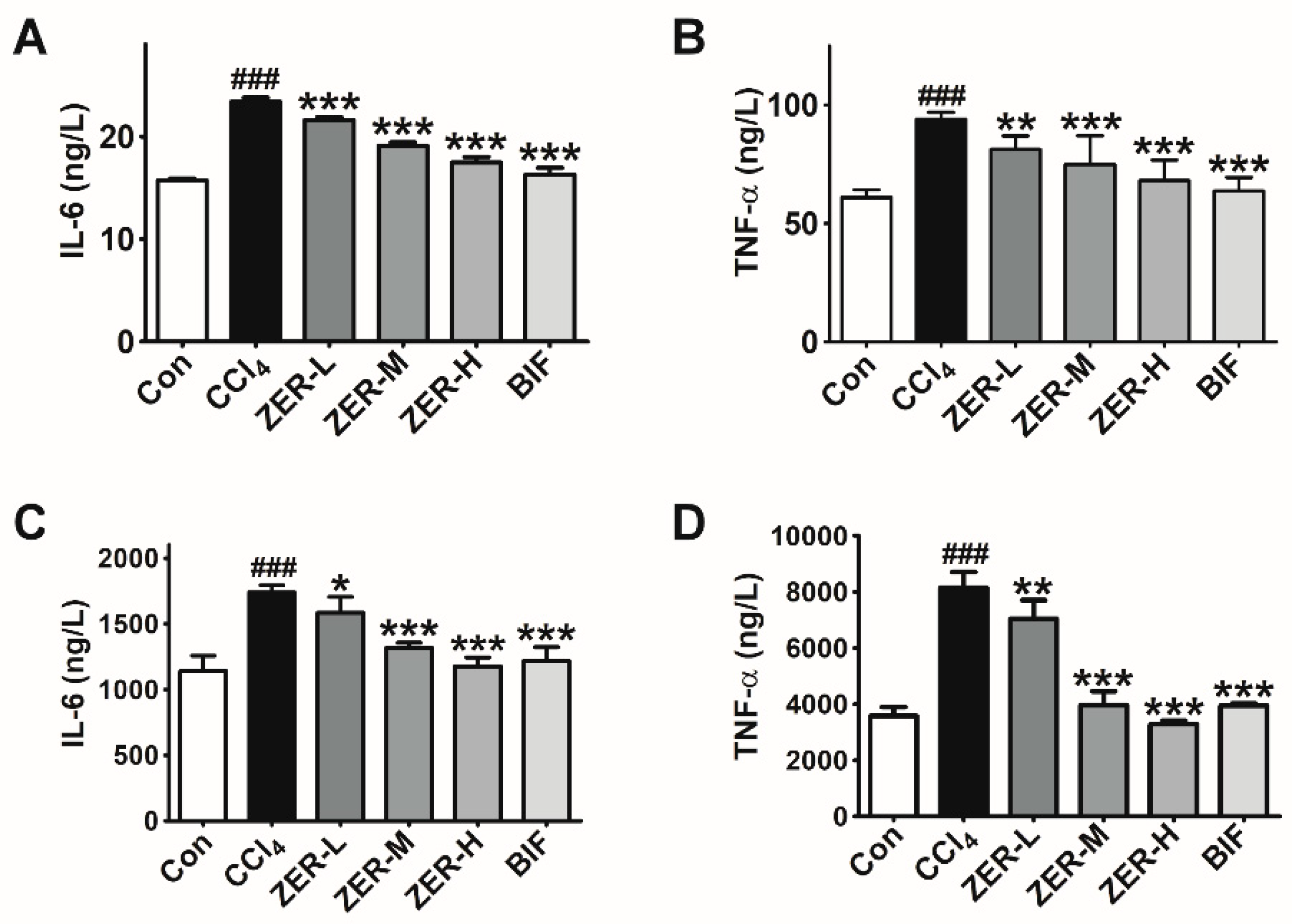
2.4. Effects of ZER on the Levels of TNF-α and IL-6 In Vivo
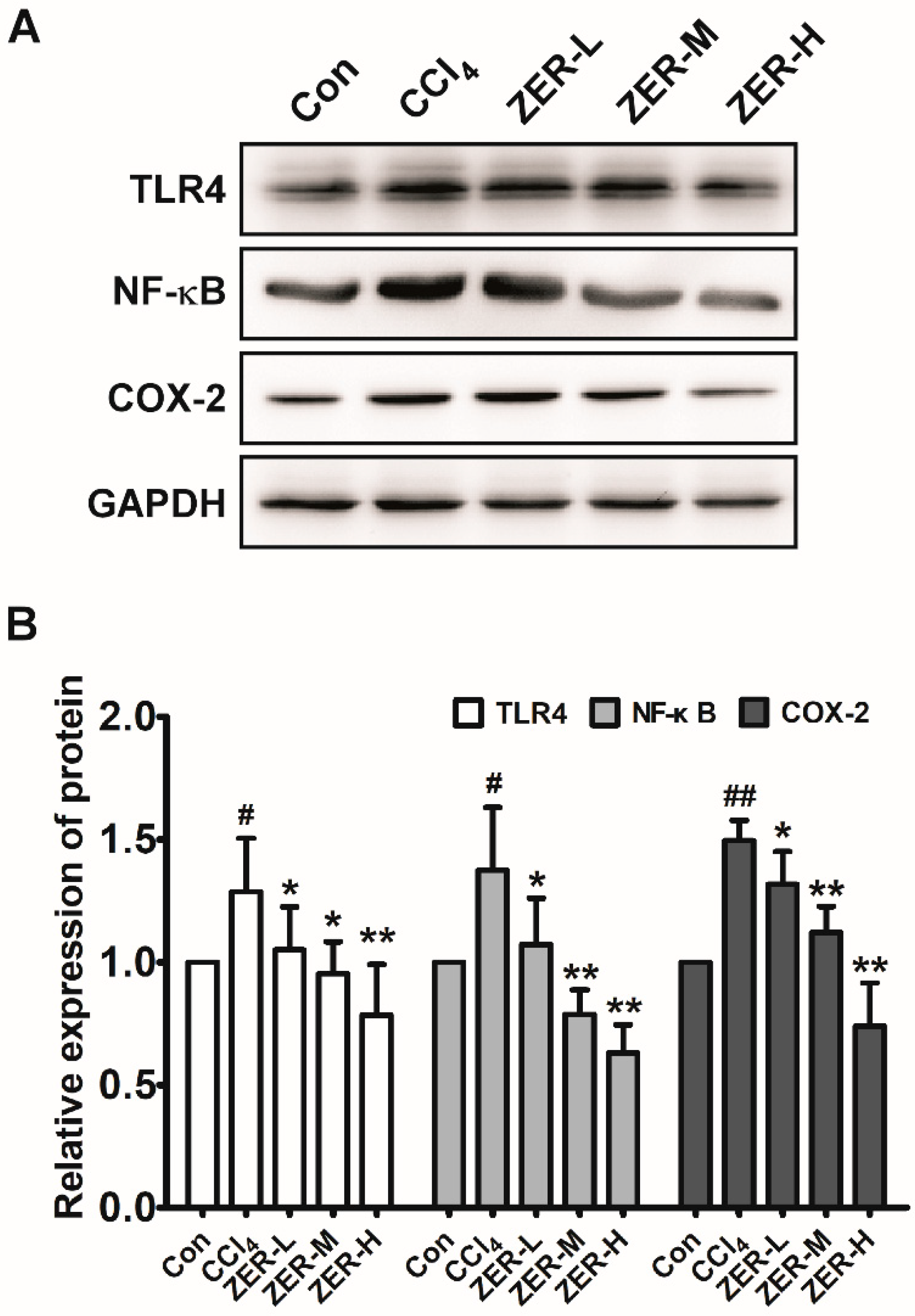
2.5. Effects of ZER on TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling In Vivo
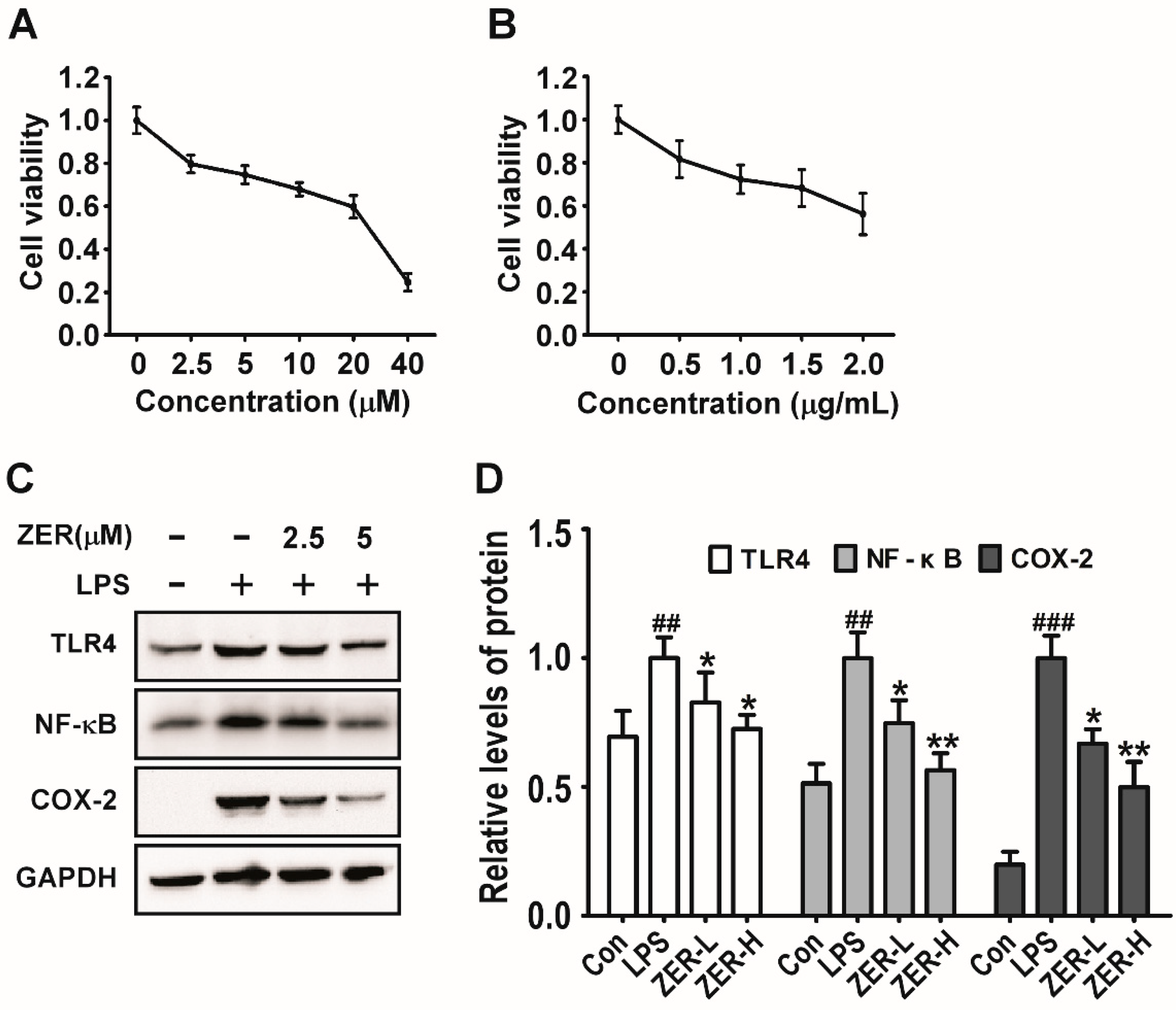
2.6. Effects of ZER on TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Design
4.4. Detections of Biochemistry Indexes
4.5. Histopathological Analysis
4.6. Detections of Inflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α
4.7. Cell Culture and LPS Treatment
4.8. Cytotoxicity Assessment of ZER and LPS by MTT Assay
4.9. Western Blotting Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| ALI | Acute liver injury |
| ZER | Zerumbone |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TLR4 | Toll-like Receptor 4 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor -κB |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| HMGB1 | High mobility group box-1 protein |
| DAMPs | Damage associated molecular patterns |
| BIF | Bifendate |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
References
- Patten, D.A.; Shepherd, E.L.; Weston, C.J.; Shetty, S. Novel Targets in the Immune Microenvironment of the Hepatic Sinusoids for Treating Liver Diseases. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Liu, Y.; Shang, J.; Xie, Q.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Xu, J.M.; Niu, J.Q.; Liu, J.J.; Paul, B.W.; et al. Incidence and Etiology of Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Mainland China. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepotec, Z.; Lichtenegger, E.; Plank, C.; Aneja, M.K.; Rudolph, C. Delivery of mRNA Therapeutics for the Treatment of Hepatic Diseases. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reyes-Gordillo, K.; Shah, R.; Muriel, P. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Hepatic Diseases: Current and Future Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 3140673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Xiao, X.; Li, D.; Tun, S.; Wang, Y.; Velkov, T.; Tang, S.S. Chloroquine ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice via the concomitant inhibition of inflammation and induction of apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitazaki, S.; Kotajima, N.; Matsuda, S.; Ida, N.; Iide, M.; Honma, S.; Suto, M.; Kato, N.; Kurode, N.; Hiraiwa, K.; et al. Dimethylthiourea ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in ovariectomized mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Cai, E.; Zhu, H.; He, Z.M.; Gao, Y.G.; Li, P.Y.; Zhao, Y. Sesquiterpenoids from the root of Panax Ginseng protect CCl4-induced acute liver injury by anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative capabilities in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, A.; Jeyachandran, R.; Cindrella, L.; Thangadurai, D.; Veerapur, V.P.; Muralidha, P. Hepatocurative potential of sesquiterpene lactones of Taraxacum officinale on carbon tetrachloride induced liver toxicity in mice. Acta Biol. Hung. 2010, 61, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, B.; Gagliano, N.; Fusaro, L.M.; Parmeggiani, L.; Tagliabue, J.; Galetti, P.; Castri, D.D.; Moscheni, C.; Annoni, G. Aloe-Emodin quinone pretreatment reduces acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 87, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; He, K.; Li, J.; Li, Z.J.; Gong, J.P. The role of Kupffer cells in hepatic diseases. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 85, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, E.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, P.Y. Triterpenoids from fruits of Sorbus pohuashanensis inhibit acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wang, Z.; Liang, S.; Tang, Z.; Liu, J.; Xin, Y.; Kuang, H.; Wang, Q. Hepatoprotective effect of a polysaccharide from Radix Cyathulae officinalis Kuan against CCl4-induced acute liver injury in rat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Jaeschke, H. Sterile inflammation in acute liver injury: Myth or mystery? Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Kou, R.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhao, N.; Zeng, T.; Xie, K. Diallyl sulfide treatment protects against acetaminophen-/carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.Y.; Kao, C.L.; Liu, C.M. The Cancer Prevention, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidation of Bioactive Phytochemicals Targeting the TLR4 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cai, X.; Luo, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, L. Emodin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury via Inhibiting the TLR4 Signaling Pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, M.; Izawa, T.; Pervin, M.; Bondoc, A.; Kuwamura, M.; Yamate, J. The kinetics of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and toll-like receptors during thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Srivastava, M.; Saqib, U.; Liu, D.; Faisal, S.M.; Sugathan, S.; Bishnoi, S.; Baij, M.S. Potential therapeutic targets for inflammation in toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, S.; Nobili, V.; Alisi, A. Toll-like receptor-mediated signaling cascade as a regulator of the inflammation network during alcoholic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16443–16451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girisa, S.; Shabnam, B.; Monisha, J.; Fan, L.; Halim, C.E.; Arfuso, F.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Potential of Zerumbone as an Anti-Cancer Agent. Molecules 2019, 24, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, T.Y.; Huang, S.K.; Lee, C.J.; Tsai, P.W.; Wang, C.C. Antinociceptive and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Zerumbone against Mono-Iodoacetate-Induced Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y.; Tzeng, T.F.; Liu, I.M. Zerumbone, a Bioactive Sesquiterpene, Ameliorates Diabetes-Induced Retinal Microvascular Damage through Inhibition of Phospho-p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-kappaB Pathways. Molecules 2016, 21, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, T.F.; Liou, S.S.; Chang, C.J.; Liu, I.M. Zerumbone, a tropical ginger sesquiterpene, ameliorates streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats by reducing the hyperglycemia-induced inflammatory response. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemn, H.O.; Noordin, M.M.; Rahman, H.S.; Hazilawati, H.; Zuki, A.; Chartrand, M.S. Antihypercholesterolemic and antioxidant efficacies of zerumbone on the formation, development, and establishment of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4173–4208. [Google Scholar]
- Zulazmi, N.A.; Gopalsamy, B.; Min, J.C.; Farouk, A.A.; Sulaiman, M.R.; Bharatham, B.H.; Perimal, E.K. Zerumbone Alleviates Neuropathic Pain through the Involvement of l-Arginine-Nitric Oxide-cGMP-K(+) ATP Channel Pathways in Chronic Constriction Injury in Mice Model. Molecules 2017, 22, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Chen, S.P.; Su, C.H.; Ho, Y.C.; Yang, M.L.; Lee, S.S.; Huang, L.R.; Yang, C.P.; Chan, C.J.; Kuan, Y.H. Zerumbone from Zingiber zerumbet Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced ICAM-1 and Cytokines Expression via p38 MAPK/JNK-IkappaB/NF-kappaB Pathway in Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury. Chin. J. Physiol. 2018, 61, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannan, R.; Kalesh, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Nachiyappan, A.; Ramachandran, L.; Nguyen, A.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lakshmanan, M.; Sethi, G. Key cell signaling pathways modulated by zerumbone: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzeng, T.F.; Liou, S.S.; Chang, C.J.; Liu, M.H. Zerumbone, a Natural Cyclic Sesquiterpene of Zingiber zerumbet Smith, Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Hamsters Fed on High-Fat Diet. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 303061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Yang, D.; Jeong, H.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, B. Dietary zerumbone, a sesquiterpene, ameliorates hepatotoxin-mediated acute and chronic liver injury in mice. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.; Lee, L.S.; Karim, S.R.; Jufri, N.F. Hepatoprotective Effects of Zerumbone against Paracetamol-Induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Jaeschke, H. The impact of sterile inflammation in acute liver injury. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2017, 3, 170–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalantari, K.; Moniri, M.; Boroumand, M.A.; Abdul Rahim, R.; Bin Ariff, A.; Izadiyan, Z.; Mohamad, R.; et al. A Review of the Biomedical Applications of Zerumbone and the Techniques for Its Extraction from Ginger Rhizomes. Molecules 2017, 22, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Rui, D.; Yan, Y.; Xu, S.; Niu, Q.; Feng, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Jing, M. Oxidative Damage Induced by Arsenic in Mice or Rats: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 176, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazalee, N.S.; Jantan, I.; Arshad, L.; Haque, M.A. Immunosuppressive effects of the standardized extract of Zingiber zerumbet on innate immune responses in Wistar rats. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.L.; Lee, C.L.; Korivi, M.; Liao, J.W.; Rajendran, P.; Wu, J.J.; Hseu, Y.C. Zerumbone protects human skin keratinocytes against UVA-irradiated damages through Nrf2 induction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhel Abbas Albaayit, S.; Maharjan, R.; Liao, J.W.; Rajendran, P.; Wu, J.J.; Hseu, Y.C. Immunomodulation of Zerumbone via Decreasing the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species from Immune Cells. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 21, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Suhaimi, E.A.; Al-Riziza, N.A.; Al-Essa, R.A. Physiological and therapeutical roles of ginger and turmeric on endocrine functions. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zou, S.; Cui, Z.; Guo, P.; Meng, Q.; Shi, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, G.; Han, Z. Zerumbone protects INS-1 rat pancreatic beta cells from high glucose-induced apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithara, T.; Dhanya, B.P.; Arun, K.B.; Sini, S.; Dan, M.; Kokkuvayil-Vasu, R.; Nisha, P. Zerumbone, a Cyclic Sesquiterpene from Zingiber zerumbet Induces Apoptosis, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Antimigratory Effects in SW480 Colorectal Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ren, M.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Feng, S.J.; Li, S.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, C.X.; Gao, S.Q.; Zhang, G.Q. Zerumbone inhibits melanoma cell proliferation and migration by altering mitochondrial functions. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2397–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajan, I.; Jayasree, P.R.; Kumar, P.R. Zerumbone induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis via increased calcium, generation of reactive oxygen species and upregulation of soluble histone H2AX in K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8479–8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. Promotion of p53 expression and reactive oxidative stress production is involved in zerumbone-induced cisplatin sensitization of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biochimie 2014, 107, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobhan, P.K.; Seervi, M.; Deb, L.; Varghese, S.; Soman, A.; Joseph, J.; Mathew, K.A.; Raghu, G.; Thomas, G. Calpain and reactive oxygen species targets Bax for mitochondrial permeabilisation and caspase activation in zerumbone induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, T.F.; Liou, S.S.; Tzeng, Y.C.; Liu, I.M. Zerumbone, a Phytochemical of Subtropical Ginger, Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Retinal Damage in Experimental Diabetic Rats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Yun, J.M. Molecular Mechanism of the Protective Effect of Zerumbone on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation of THP-1 Cell-Derived Macrophages. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Jantan, I.; Harikrishnan, H. Zerumbone suppresses the activation of inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated U937 macrophages through MyD88-dependent NF-kappaB/MAPK/PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 55, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.W.; Qian, G.B.; Jiang, M.J.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.Z. Inhibition of microRNA-495 suppresses chondrocyte apoptosis through activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway by regulating CCL4 in osteoarthritis. Gene Ther. 2019, 26, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.; Liu, D.; Abdulrahim, Y.; Khan, A.; Qian, G.; Huang, G. Inactivation of Kupffer cells by selenizing astragalus polysaccharides prevents CCl4-Induced hepatocellular necrosis in the male Wistar rat. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 179, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Petrasek, J.; Gyongyosi, B.; Abhishek, S.; Patrick, L.; Karen, K.; Donna, C.; Charles, D.; Calenda, E.; Kurt, J.; Katherine, A.; Gyongyi, S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatocellular death pathways mediate liver injury and fibrosis via stimulator of interferon genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26794–26805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K.; Lu, M.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.N.; Bian, H.J. MFGE8 protects against CCl4 -induced liver injury by reducing apoptosis and promoting proliferation of hepatocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, T.Y.; Nie, C.H.; Wan, D.L.; Zheng, S.S. Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone, suppresses tumor growth through inducing apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of mTOR pathway regulated by ROS generation in liver cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, T.; Ao, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, L.; Tong, B.; Ren, B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Total sesquiterpene glycosides from Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) leaf alleviate high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through cytochrome P450 2E1 inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yang, W.; Yasen, M.; Zhao, H.; Aisa, H. The mechanism of hepatoprotective effect of sesquiterpene rich fraction from Cichorum glandulosum Boiss. et Huet on immune reaction-induced liver injury in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, P.; Schultze, N.; Niehs, S.; Albrecht, D.; Methling, K.; Wurster, M.; Wachlin, G.; Lalk, M.; Lindequist, U.; Haertel, B. Differential effects of Helenalin, an anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone, on the proteome, metabolome and the oxidative stress response in several immune cell types. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 40, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Murias, M.; Bloszyk, E. Effect of sesquiterpene lactones on antioxidant enzymes and some drug-metabolizing enzymes in rat liver and kidney. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilin, W.; Jingling, N.; Lei, G.; Yang, G.; Shegan, G. Zerombone inhibits migration in ESCC via promoting Rac1 ubiquitination. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Niu, J.; Ou, L.; Deng, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway. Molecules 2019, 24, 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101964
Wang M, Niu J, Ou L, Deng B, Wang Y, Li S. Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway. Molecules. 2019; 24(10):1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101964
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Meilin, Jingling Niu, Lina Ou, Bo Deng, Yingyi Wang, and Sanqiang Li. 2019. "Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway" Molecules 24, no. 10: 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101964
APA StyleWang, M., Niu, J., Ou, L., Deng, B., Wang, Y., & Li, S. (2019). Zerumbone Protects against Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4)-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice via Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and the Inflammatory Response: Involving the TLR4/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathway. Molecules, 24(10), 1964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24101964




