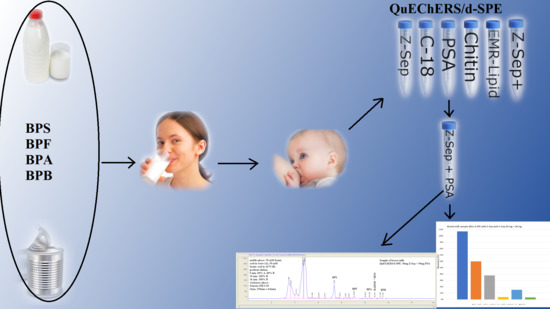
Method Development for Selected Bisphenols Analysis in Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QqQ-MS: Comparison of Sorbents (Z-SEP, Z-SEP Plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-Lipid) for Clean-Up of QuEChERS Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
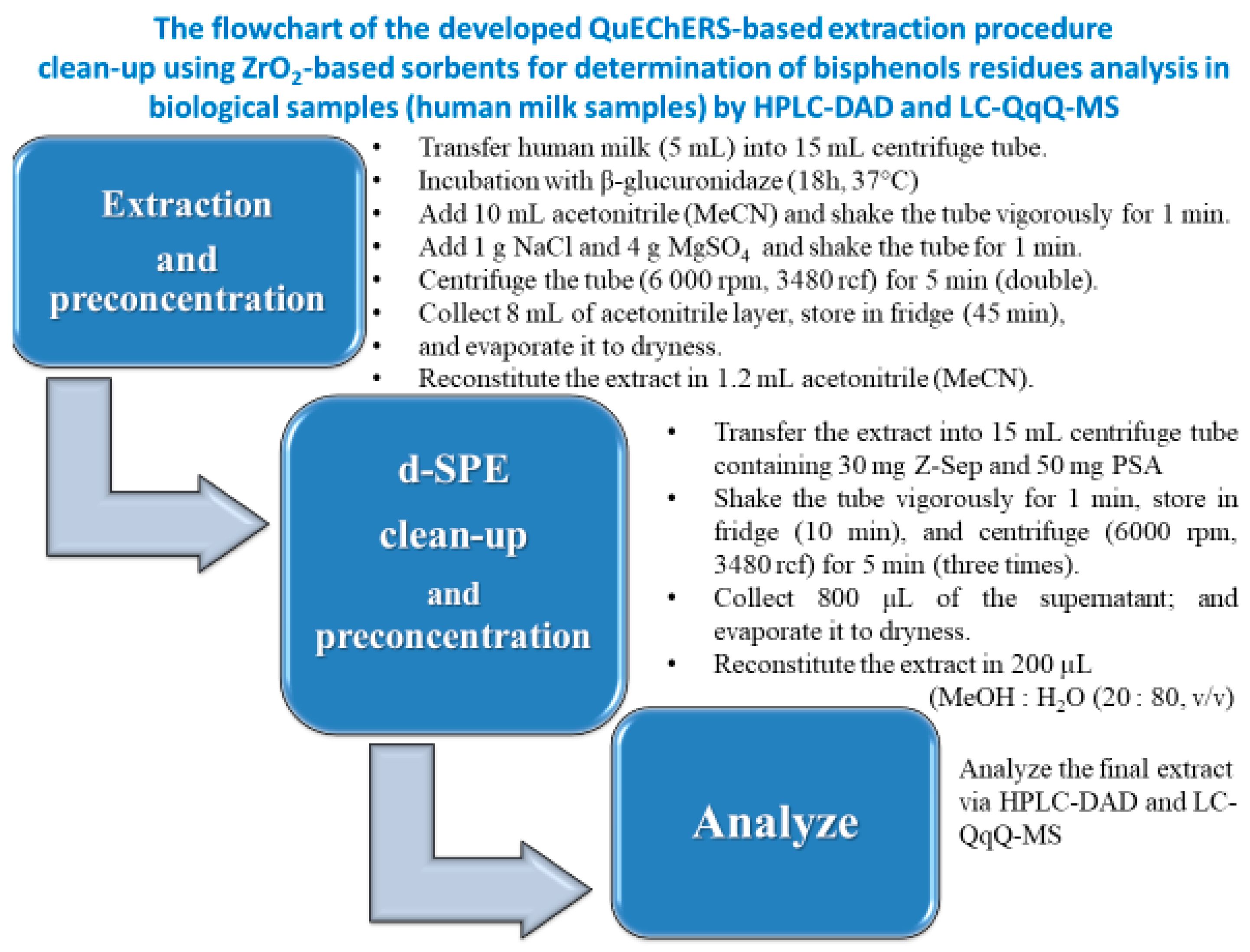
2.1. Sample Preparations
2.2. Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Optimization of QuEChERS-Based Procedure
2.4. Recovery Studies
2.5. Application of the Procedure to the Analysis of Natural Samples
2.5.1. Application of the Procedure to the Analysis of Sweetened Condensed Milk Samples from a Can
2.5.2. Application of the Procedure to the Analysis of Breast Milk Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.1.1. Analyte Standards
3.1.2. Solvents and Mobile-Phase Solutions
3.1.3. Enzymatic Standard and Solutions
3.1.4. QuEChERS Salts and Sorbents
3.2. Breast Milk Sample Collection
3.3. Sample Preparation of Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples
3.4. RP-HPLC
3.4.1. HPLC-DAD
3.4.2. LC-QqQ-MS
3.5. Method Optimization and Validation
3.5.1. HPLC Method Validation
3.5.2. Recovery and Precision Studies
3.5.3. Degree of the Matrix Interference Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halden, R.U. Plastics and Health Risks. Annu. Rev. Publ. Health 2010, 31, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caballero-Casero, N.; Lunar, L.; Rubio, S. Analytical methods for the determination of mixtures of bisphenols and derivatives in human and environmental exposure sources and biological fluids. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 908, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scientific Opinion of European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs: Executive summary. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. Available online: https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2015.3978 (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Scientific Opinion of European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. Part I: Exposure assessment. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wim_H_Jong/post/How_do_I_get_a_retention_time_for_Bisphenol-A_BPA/attachment/59d6297379197b8077987f3f/AS%3A335533382357010%401457008801036/download/EFSA+20150121+Part+1+Exposure+Assessment+BPA.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Scientific Opinion of European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) on the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs: PART II-Toxicological assessment and risk characterization. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3978. Available online: https://www.adeac.com/upload/pdf/www.efsa.europa.eu_en_efsajournal_doc_3978part2.pdf (accessed on 31 May 2019).
- Szczepańska, N.; Kudłak, B.; Namieśnik, J. Assessing ecotoxicity and the endocrine potential of selected phthalates, BADGE and BFDGE derivatives in relation to environmentally detectable levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the use of bisphenol A in varnishes and coatings intended to come into contact with food and amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as regards the use of that substance in plastic food contact materials (Text with EEA relevance). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2018/213/oj (accessed on 14 February 2018).
- Szczepańska, N.; Kudłak, B.; Namieśnik, J. Recent advances in assessing xenobiotics migrating from packagingmateriale. A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.; Wielgomas, B.; Dziewirska, E.; Radwan, P.; Kałużny, P.; Klimowska, A.; Hanke, W.; Jurewicz, J. Urinary Bisphenol A Levels and Male Fertility. Am. J. Men’s Health 2018, 12, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gingrich, J.; Pu, Y.; Ehrhardt, R.; Karthikraj, R.; Kannan, K.; Veiga-Lopez, A. Toxicokinetics of bisphenol A, bisphenol S, and bisphenol F in a pregnancy sheep model. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Bishop, A.M.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. Automated on-line column-switching HPLC-MS/MS method with peak focusing for measuring parabens, triclosan, and other environmental phenols in human milk. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 622, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Needham, L.L.; Calafat, A.M. Measuring environmental phenols and chlorinated organic chemicals in breast milk using automated on-line column-switching–high performance liquid chromatography–isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 831, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B. Highly sensitive and high-throughput method for the analysis of bisphenol analogues and their halogenated derivatives in breast milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10452–10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, B.; Kim, C.; Yang, M. Biological monitoring of bisphenol A with HLPC/FLD and LC/MS/MS assays. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 2606–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. A review of recent developments and trends in the QuEChERS sample preparation approach. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 980–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. Recent Trends in Sample Preparation and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry for Pesticide Residue Analysis in Food and Related Matrixes. J. Aoac Int. 2015, 98, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzimski, T.; Sherma, J. Determination of Target Xenobiotics and Unknown Compound Residues in Food, Environmental, and Biological Samples; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; p. 424. ISBN 978-1-4987-8013-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tuzimski, T.; Pieniążek, D.; Buszewicz, G.; Teresiński, G. QuEChERS-based extraction procedures for the analysis of bisphenols S and A in breast milk samples by LC-QqQ-MS. J. Aoac Int. 2019, 102, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deceuninck, Y.; Bichon, E.; Marchand, P.; Boquien, C.; Legrand, A.; Boscher, C.; Antignac, J.P.; Le Bizec, B. Determination of bisphenol A and related substitutes/analogues in human breast milk using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2485–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dualde, P.; Pardo, O.; Corpas-Burgos, F.; Kuligowski, J.; Gormaz, M.; Vento, M.; Pastor, A.; Yusà, V. Biomonitoring of bisphenols A, F, S in human milk and probabilistic risk assessment for breastfed infants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruve, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I.; Kruve, A.; Herodes, K.; Leito, I. Accounting for matrix effects of pesticide residue liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation mass spectrometric determination by treatment of background mass spectra with chemometric tools. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







| No | Analyte | tR (min) | λ (nm) | Range (ng mL−1) | Without Incubation with β-Glucuronidase | Incubation with β-Glucuronidase | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Curve | R2 | LOD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) | Calibration Curve | R2 | LOD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) | |||||
| 1 | BPS | ~7.3 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0907x − 1.8053 | 0.9881 | 140 | 423 | y = 0.0893x + 2.4926 | 0.9717 | 665 | 2014 |
| 2 | BPF | ~9.1 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0505x − 0.179 | 0.9948 | 53 | 159 | y = 0.0506x − 1.233 | 0.980 | 549 | 1663 |
| 3 | BPA | ~10.35 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0482x − 4.1544 | 0.989 | 92 | 277 | y = 0.043x + 5.1191 | 0.9689 | 142 | 430 |
| 4 | BADGE *H2O | ~10.8 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0206x − 0.6918 | 0.9883 | 76 | 230 | y = 0.0192x − 1.8587 | 0.9894 | 693 | 2102 |
| 5 | BPB | ~11.375 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0392x + 0.0659 | 0.9952 | 237 | 720 | y = 0.036x + 3.1957 | 0.957 | 165 | 500 |
| 6 | BADGE * 2HCl | ~13.75 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0215x + 1.1725 | 0.9945 | 272 | 824 | y = 0.0206x − 0.0784 | 0.987 | 366 | 1110 |
| 7 | BADGE | ~14.5 | 280 | 250–2000 | y = 0.0245x − 1.4438 | 0.9894 | 306 | 926 | y = 0.0143x + 1.9757 | 0.9657 | 260 | 787 |
| Analyte | Calibration Data | Recovery c (%) (RSD%) | MI% d | Recovery c (%) (RSD%) | MI% d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range (ng mL−1) | Calibration Curve | R2 | SD of Slope a | SD of Intercept a | mLOQ b (ng mL−1) | 5 ng mL−1 | 5 ng mL−1 | 50 ng mL−1 | 50 ng mL−1 | |
| BPS | 1-50 | y = 3986x + 7542 | 0.9999 | 68 | 950 | 0.25 | 102 (8) | 12 | 95 (15) | 13 |
| BPF | 1-50 | y = 285x + 604 | 0.9998 | 13 | 180 | 0.13 | 68 (9) | 11 | 63 (9) | 10 |
| BPA | 1-50 | y = 203x + 547 | 0.9991 | 11 | 150 | 0.10 | 39 (7) | 10 | 35 (17) | 12 |
| Breast Milk Sample | Concentration in Breast Milk Sampleng mL−1 (Urban Area) | Breast Milk Sample | Concentration in Breast Milk Sampleng mL−1 (Rural Area) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | BPS | BPF | BPB | BPA | BPS | BPF | BPB | ||
| 1 | 0.35 | - | - | - | 26 | - | 0.62 | - | + |
| 2 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.29 | - | 27 | 0.31 | - | - | - |
| 3 | 0.41 | - | - | - | 28 | 0.39 | - | - | - |
| 4 | - | 0.29 | - | - | 29 | 0.51 | 0.52 | - | - |
| 5 | 0.68 | 0.41 | - | + | 30 | 0.39 | - | 0.34 | - |
| 6 | 0.33 | - | - | - | 31 | 0.42 | - | - | - |
| 7 | 0.49 | - | - | - | 32 | 0.52 | 0.51 | - | - |
| 8 | 0.46 | - | - | - | 33 | 0.41 | - | - | - |
| 9 | 0.29 | - | - | - | 34 | 0.22 | - | - | - |
| 10 | 0.28 | 0.43 | - | - | 35 | 0.22 | - | - | - |
| 11 | 0.48 | - | - | - | 36 | 0.39 | 0.32 | - | - |
| 12 | 0.67 | - | - | + | 37 | 0.24 | - | - | - |
| 13 | - | 0.45 | 0.25 | - | 38 | 0.41 | 0.39 | - | - |
| 14 | 0.26 | - | - | - | 39 | - | - | - | - |
| 15 | 0.61 | 0.51 | - | + | 40 | - | - | - | - |
| 16 | 0.31 | - | - | - | 41 | 0.26 | - | - | - |
| 17 | 0.36 | - | - | - | 42 | 0.41 | 0.32 | - | + |
| 18 | 0.69 | 0.68 | - | + | 43 | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | 0.61 | - | 0.22 | + | 44 | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | - | 0.43 | - | - | 45 | 0.21 | - | - | - |
| 21 | 0.43 | - | - | - | 46 | - | 0.33 | - | - |
| 22 | 0.23 | 0.36 | - | - | 47 | 0.46 | - | 0.55 | - |
| 23 | 0.44 | - | - | - | 48 | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | - | 0.41 | - | 49 | - | - | - | - | |
| 25 | 0.39 | - | - | - | 50 | 0.31 | - | - | - |
| Compounds | Precursor Ion [m/z] | Product Ion [m/z] | Fragmentor [V] | Collision Energy [V] | Polarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d16-BPA | 241 | 225 * 151 | 100 | 15 30 | negative negative |
| d8-BPS | 249 | 257 * 112 | 166 | 20 20 | negative negative |
| d10-BPF | 209 | 199 * 97 | 98 | 20 20 | negative negative |
| BPA | 227 | 212 * 133 | 98 | 15 25 | negative negative |
| BPS | 249 | 108 * 156 | 166 | 20 25 | negative negative |
| BPF | 209 | 199 * 105 | 98 | 20 20 | negative negative |
| BADGE | 358 | 191 * 161 | 98 | 5 25 | positive positive |
| BADGE-2H2O | 394 | 209 * 135 | 98 | 20 30 | positive positive |
| BADGE-2HCl | 430 | 227 * 135 | 98 | 15 40 | positive positive |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuzimski, T.; Szubartowski, S. Method Development for Selected Bisphenols Analysis in Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QqQ-MS: Comparison of Sorbents (Z-SEP, Z-SEP Plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-Lipid) for Clean-Up of QuEChERS Extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112093
Tuzimski T, Szubartowski S. Method Development for Selected Bisphenols Analysis in Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QqQ-MS: Comparison of Sorbents (Z-SEP, Z-SEP Plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-Lipid) for Clean-Up of QuEChERS Extract. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112093
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuzimski, Tomasz, and Szymon Szubartowski. 2019. "Method Development for Selected Bisphenols Analysis in Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QqQ-MS: Comparison of Sorbents (Z-SEP, Z-SEP Plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-Lipid) for Clean-Up of QuEChERS Extract" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112093
APA StyleTuzimski, T., & Szubartowski, S. (2019). Method Development for Selected Bisphenols Analysis in Sweetened Condensed Milk from a Can and Breast Milk Samples by HPLC–DAD and HPLC-QqQ-MS: Comparison of Sorbents (Z-SEP, Z-SEP Plus, PSA, C18, Chitin and EMR-Lipid) for Clean-Up of QuEChERS Extract. Molecules, 24(11), 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112093