Simultaneous Profiling and Holistic Comparison of the Metabolomes among the Flower Buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng by UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE-Based Metabolomics Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization and Development of a UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE Approach
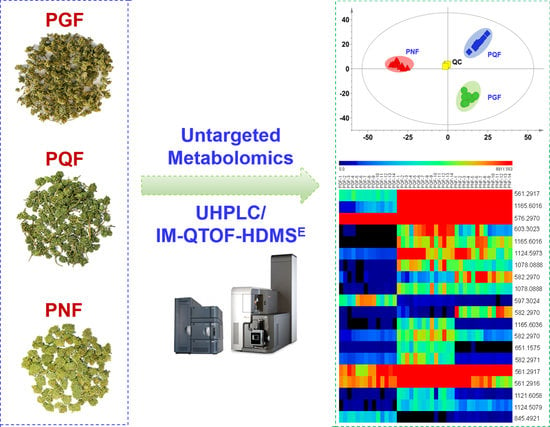
2.2. Systematic Comparison of the Metabolome Difference among PGF, PQF, and PNF by Untargeted Metabolomics
2.3. Identification of the Potential Marker Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Sample Preparation
3.3. Chromatographic Separation and MS Conditions
3.4. Date Processing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wu, W.Y.; Huang, L.Q.; Guo, D.A.; Liu, C.X. Approaches to establish Q-markers for the quality standards of traditional Chinese medicine. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2017, 7, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalov, J.J.; Marderosian, A.D.; Pierce, J.C. DNA identification of commercial Ginseng samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3744–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Chu, Y.; Bai, J.Q.; Gong, L.; Huang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.H.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z.H. Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis for OPT family genes in Panax ginseng and eleven flowering plants. Molecules 2019, 24, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Z.; Qiao, X.; Li, K.; Fan, J.R.; Bo, T.; Guo, D.A.; Ye, M. Identification and differentiation of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium, and Panax notoginseng by monitoring multiple diagnostic chemical markers. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Fu, L.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Wang, H.D.; Zuo, T.T.; Zhang, C.X.; Hu, Y.; Gao, X.M.; Han, L.F. Systematic profiling of the multicomponents and authentication of Erzhi Pill by UHPLC/Q-Orbitrap-Ms oriented rapid polarity-switching data-dependent acquisition and selective monitoring of the chemical markers deduced from fingerprint analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Yang, W.Z.; Guo, D.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.X.; Qiu, S.; Yao, C.L.; Cui, Y.J.; Wu, W.Y. Selective ion monitoring of quinochalcone C-glycoside markers for the simultaneous identification of Carthamus tinctorius L. in eleven Chinese patent medicines by UHPLC/QTOF MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 117, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.X.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Pei, J.; Huang, L.F. An integrated LC-MS-based strategy for the quality assessment and discrimination of three Panax species. Molecules 2018, 23, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Song, Q.Q.; Cao, Y.; Xie, N.; Li, Z.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Tu, P.F.; Song, Y.L.; Li, J. From 1H NMR-based non-targeted to LC-MS-based targeted metabolomics strategy for in-depth chemome comparisons among four Cistanche species. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 162, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yang, S.P.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhao, W.; Chen, L.Z.; Wen, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lu, K.Z.; et al. Strategy for comparative untargeted metabolomics revels honey markers of different floral and geographic origins using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1499, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yang, W.Z.; Yao, C.L.; Qiu, Z.D.; Shi, X.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Hou, J.J.; Wang, Q.R.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. Nontargeted metabolomic analysis and “commercial-homophyletic” comparison-induced biomarkers verification for the systematic chemical differentiation of five different parts of Panax ginseng. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1453, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.W.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, D.K.; Zhou, D.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.C.; Hu, B.; Ju, A.C.; Ye, Z.L. Nontargeted metabolomics approach for the differentiation of cultivation ages of mountain cultivated ginseng leaves using UHPLC/QTOF-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 141, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.L.; Lin, H.Q.; Tan, J.; Wang, G.Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.L.; Dong, Q.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.P. UPLC-QTOF/MS-based nontargeted metabolomic analysis of mountain- and garden-cultivated Ginseng of different ages in Northeast China. Molecules 2019, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.F.; Xu, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.N.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Xue, X.; Xiong, H.; Lin, R.C.; et al. Chemical comparison of two drying methods of mountain cultivated ginseng by UPLC-QOTF-MS/MS and multivariate statistical analysis. Molecules 2017, 27, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Yang, W.Z.; Li, S.R.; Yao, S.; Qi, P.; Yang, Z.; Feng, Z.J.; Hou, J.J.; Cai, L.Y.; Yang, M.; et al. An intelligentized strategy for endogenous small molecules characterization and quality evaluation of earthworm from two geographic origins by ultra-high performance HILIC/QTOF MSE and Progenesis QI. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3881–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.J.; Yang, W.Z.; Qiu, S.; Hou, J.J.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. Systematic profiling and comparison of the lipidomes from Panax ginseng, P. quinquefolius, and P. notoginseng by ultrahigh performance supercritical fluid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry and ion mobility-derived collision cross section measurement. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1548, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.T.; Yin, Y.X. Strategies for large-scale targeted metabolomics quantitation by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2016, 141, 6362–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Li, Y.L.; Ye, G.Z.; Lu, X.; Lin, X.H.; Xu, G.W. A novel approach to transforming a non-targeted metabolic profiling method to a pseudo-targeted method using the retention time locking gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-selected ions monitoring. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1255, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.N.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.X.; Hu, C.X.; Li, Y.L.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, L.L.; Chang, Y.W.; Wang, F.; et al. Metabolic response of rice leaves and seeds under transgenic backcross breeding and pesticide stress by pseudotargeted metabolomics. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1802–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirok, B.W.J.; Stoll, D.R.; Schoenmakers, P.J. Recent developments in two-dimensional liquid chromatography: Fundamental improvements for practical applications. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 240–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yang, W.Z.; Shi, X.J.; Yao, C.L.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, B.H.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. A green protocol for efficient discovery of novel natural compounds: Characterization of new ginsenosides from the stem and leaves of Panax ginseng. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, Q.; Lin, Z.Z.; Lu, J.Q.; Qiao, Y.J. Rapid screening and identification of target constituents using full scan-parent ions list dynamic exclusion acquisition coupled to diagnostic product ions analysis on a hybrid LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Talanta 2014, 124, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.L.; Ding, H.; Han, L.F.; Jia, L.; Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Hu, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Gao, X.M.; Guo, D.A. Simultaneously targeted and untargeted multicomponent characterization of Erzhi Pill by offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography/quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1584, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Reinke, S.N.; Mathon, C.; Blankley, R.; Chaleckis, R.; Wheelock, C.E. Development of a liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry metabolomics method with high specificity for metabolite identification using all ion fragmentation acquisition. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7933–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.W.; Jin, Y.R.; Hou, L.D.; Ma, Y.H.; Xu, H.J.; Zhang, K.R.; Zhang, L.T.; Du, Y.F. A practical strategy for the characterization of ponicidin metabolites in vivo and in vitro by UHPLC-Q-TOR-MS based on nontargeted SWATH data acquisition. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atri, V.D.; Causon, T.; Hernandez-Alba, O.; Mutabazi, A.; Veuthey, J.L.; Cianferani, S.; Guillarme, D. Adding a new separation dimension to MS and LC-MS: What is the utility of ion mobility spectrometry? J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 20–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, D.; Li, H.H.; Wang, H.; Tan, H.S.; Xu, H.X. Diagnostic filtering to screen polycyclic polyprenylated acylphloroglucinols from Garcinia oblongifolia by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography coupled with ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 912, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, D.A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Min, H. Ginseng, the ‘immunity boost’: The effects of Panax ginseng on immune system. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Guo, R.X.; Zhou, G.H.; Zhou, X.D.; Kou, Z.Z.; Sui, F.; Li, C.; Ling, L.Y.; Wang, Z.J. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 188, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Huang, L.L.; Cai, X.J.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.T.; Wan, J.B. Fatty acid variability in three medicinal herbs of Panax species. Chem. Central J. 2013, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, R.; Martinelli, E.M.; Sardone, N.; Combarieu, E.D.E. Metabolomic evaluation of ginsenosides distribution in Panax genus (Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius) using multivariate statistical analysis. Fitoterapia 2015, 101, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.Z.; Bo, T.; Ji, S.; Qiao, X.; Guo, D.A.; Ye, M. Rapid chemical profiling of saponins in the flower buds of Panax notoginseng by integrating MCI gel column chromatography and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.B.; Zhang, Q.W.; Hong, S.J.; Li, P.; Li, S.P.; Wang, Y.T. Chemical investigation of saponins in different parts of Panax notoginseng by pressurized liquid extraction and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2012, 17, 5836–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.R.; Cheung, K.K.; Zhou, X.; Xie, R.F.; Cheng, P.P.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Hoi, P.M.; Wang, Y.H.; et al. Amelioration of acute myocardial infarction by saponins from flower buds of Panax notoginseng via pro-angiogenesis and anti-apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 181, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lv, C.N.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Song, D.; Liu, P.P.; Zhang, D.D.; Lu, J.C. Chemical and bioactive comparison of flowers of Panax ginseng Meyer, Panax quinquefolius L., and Panax notoginseng Burk. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.X.; Zhang, C.X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Qian, Y.X.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.Z.; Jiang, M.M.; Guo, D.A. Application of multiple chemical and biological approaches for quality assessment of Carthamus tinctorius L. (safflower) by determining both the primary and secondary metabolites. Phytomedicine 2019, 58, 152826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, J.X.; Yao, C.L.; Qiu, S.; Chen, M.; Pan, H.Q.; Shi, X.J.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. Method development and application of offline two-dimensional liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry-fast data directed analysis for comprehensive characterization of the saponins from Xueshuantong Injection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 128, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.M.; Zheng, D.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, C.W.; Xiao, L.B.; Xu, H.X. A multidimensional analytical approach based on time-decoupled online comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography coupled with ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the analysis of ginsenosides from white and red ginseng. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 163, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J.; Bijlsma, S.; van der Werff-van der Vat, B.J.C.; Jellema, R.H. Fusion of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6729–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.L.; Yang, W.Z.; Zhang, J.X.; Qiu, S.; Chen, M.; Shi, X.J.; Pan, H.Q.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach to compare the saponins compositions of Xueshuantong injection and Xuesaitong Injection. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.S.; Jian, D.M.; Jiang, L.; Wang, W.; Ju, K.; Quan, C.M.; Mu, E.T.; Zhou, J.L. Study on identification of notoginseng flower and its adulterants. J. Gansu Univ. Chin. Med. 2018, 35, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Paglia, G.; Angel, P.; Williams, J.P.; Richardson, K.; Olivos, H.J.; Thompson, J.W.; Menikarachchi, L.; Lai, S.; Walsh, C.; Moseley, A.; et al. Ion mobility-derived collision cross section as an additional measure for lipid fingerprinting and identification. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.J.; Yang, W.Z.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.J.; Qiu, S.; Yao, C.L.; Feng, Z.J.; Wei, W.L.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. Direct screening of malonylginsenosides from nine Ginseng extracts by an untargeted profiling strategy incorporating in-source collision-induced dissociation, mass tag, and neutral loss scan on a hybrid linear ion-trap/Orbitrap mass spectrometer coupled to ultra-high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Yang, W.Z.; Yao, C.L.; Shi, X.J.; Li, J.Y.; Lou, Y.; Duan, Y.N.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. Malonylginsenosides with potential antidiabetic activities from the flower buds of Panax ginseng. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.J.; Yang, W.Z.; Qiu, S.; Yao, C.L.; Shen, Y.; Pan, H.Q.; Bi, Q.R.; Yang, M.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. An in-source multiple collision-neutral loss filtering based nontargeted metabolomics approach for the comprehensive analysis of malonyl-ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, P. quinquefolius, and P. notoginseng. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 952, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the flower buds of three Panax species are available from the authors. |







| No. | VIP | tR (min) | m/z | CCS (Å2) | Identification | PGF | PQF | PNF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 8.59 | 24.76 | 1077.5881 | 357.30 | ginsenoside Rb3 | L | H | M |
| M2 * | 7.84 | 22.09 | 1209.6274 | 355.12 | ginsenoside Ra1 | L | L | H |
| M3 | 6.97 | 27.74 | 1163.5880 | 370.72 | isomer of m-Rc/m-Rb2/m-Rb3 | L | M | H |
| M4 * | 6.63 | 25.37 | 1209.6274 | 356.45 | isomer of ginsenoside Ra1/Ra2 | L | L | H |
| M5 | 6.53 | 19.71 | 1107.5973 | 350.29 | ginsenoside Rb1 | M | L | H |
| M6 * | 6.43 | 17.52 | 1239.6379 | 283.47 | isomer of ginsenoside Ra3 | L | L | H |
| M7 * | 5.25 | 19.42 | 1209.6274 | 358.21 | isomer of ginsenoside Ra1/Ra2 | L | L | H |
| M8 * | 5.21 | 21.07 | 1209.6274 | 351.82 | isomer of ginsenoside Ra1/Ra2 | L | L | H |
| M9 * | 5.06 | 20.97 | 1325.6383 | 368.56 | isomer of m-Ra3 | L | L | H |
| M10 * | 4.61 | 22.80 | 1341.6696 | 379.05 | notoginsenoside Q/S or isomer | L | L | H |
| M11 | 4.46 | 29.77 | 1249.5896 | 358.00 | dimal-Rc/Rb2/Rb3 or isomer | L | H | M |
| M12 | 4.41 | 27.06 | 1163.5885 | 377.51 | isomer of m-Rc/m-Rb2/m-Rb3 | L | H | M |
| M13 * | 4.33 | 16.82 | 1341.6696 | 372.35 | notoginsenoside Q/S or isomer | L | L | H |
| M14 | 4.00 | 25.70 | 1163.5880 | 347.14 | isomer of m-Rc/m-Rb2/m-Rb3 | L | M | H |
| M15 | 3.85 | 25.83 | 1193.5976 | 357.85 | isomer of m-Rb1 | H | M | L |
| M16 | 3.84 | 25.12 | 1163.5878 | 337.60 | isomer of m-Rc/m-Rb2/m-Rb3 | M | M | H |
| M17 * | 3.82 | 26.37 | 1295.6327 | 365.60 | m-Ra2 or isomer | L | L | H |
| M18 | 3.79 | 30.19 | 1249.5886 | 365.80 | dimal-Rc/Rb2/Rb3 or isomer | L | H | M |
| M19 | 3.78 | 26.75 | 1163.5880 | 337.60 | m-Rb3 | L | H | M |
| M20 * | 3.76 | 19.54 | 1341.6696 | 375.59 | notoginsenoside Q/S or isomer | L | L | H |
| M21 | 3.72 | 5.35 | 695.1473 | 229.84 | m-kaempferol-GlcGlc | M | H | L |
| M22 | 3.51 | 29.51 | 1163.5880 | 371.94 | isomer of m-Rc/m-Rb2/m-Rb3 | M | H | L |
| M23 | 3.50 | 21.91 | 1077.5879 | 338.39 | ginsenoside Rc | L | M | H |
| M24 * | 3.37 | 17.89 | 815.4830 | 301.49 | ginsenoside F3 | H | L | L |
| M25 * | 3.36 | 18.71 | 1209.6274 | 351.14 | isomer of ginsenoside Ra1/Ra2 | L | L | H |
| M26 | 3.33 | 23.90 | 1077.5879 | 360.22 | ginsenoside Rb2 | M | H | M |
| M27 * | 3.29 | 29.13 | 793.4395 | 282.26 | chikusetsusaponin IVa | M | H | L |
| M28 * | 3.21 | 19.55 | 716.3369 | 354.60 | unknown | L | L | H |
| M29 * | 3.20 | 13.10 | 845.4921 | 298.26 | 24(R)-pseudoginsenoside F11 | L | H | L |
| M30 * | 3.11 | 14.72 | 1371.6802 | 386.06 | notoginsenoside D/T or isomer | L | L | H |
| M31 | 3.09 | 15.00 | 845.4921 | 302.65 | ginsenoside Rf | H | L | M |
| M32 * | 3.03 | 23.72 | 1295.6327 | 362.76 | m-Ra2 or isomer | L | L | H |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, L.; Zuo, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Qian, Y.; Yang, W.; Yu, H. Simultaneous Profiling and Holistic Comparison of the Metabolomes among the Flower Buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng by UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE-Based Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112188
Jia L, Zuo T, Zhang C, Li W, Wang H, Hu Y, Wang X, Qian Y, Yang W, Yu H. Simultaneous Profiling and Holistic Comparison of the Metabolomes among the Flower Buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng by UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE-Based Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules. 2019; 24(11):2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112188
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Li, Tiantian Zuo, Chunxia Zhang, Weiwei Li, Hongda Wang, Ying Hu, Xiaoyan Wang, Yuexin Qian, Wenzhi Yang, and Heshui Yu. 2019. "Simultaneous Profiling and Holistic Comparison of the Metabolomes among the Flower Buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng by UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE-Based Metabolomics Analysis" Molecules 24, no. 11: 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112188
APA StyleJia, L., Zuo, T., Zhang, C., Li, W., Wang, H., Hu, Y., Wang, X., Qian, Y., Yang, W., & Yu, H. (2019). Simultaneous Profiling and Holistic Comparison of the Metabolomes among the Flower Buds of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng by UHPLC/IM-QTOF-HDMSE-Based Metabolomics Analysis. Molecules, 24(11), 2188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24112188