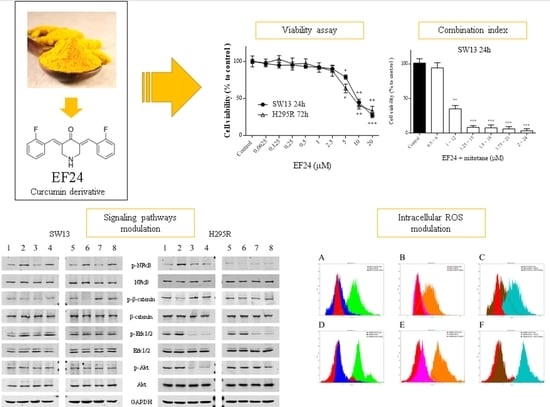
Biological Effects of EF24, a Curcumin Derivative, Alone or Combined with Mitotane in Adrenocortical Tumor Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Viability Assays, Combination Index, and Drug Synergism
2.2. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.3. Motility Assay (Wound Healing Assay)
2.4. Assessment of Cell Morphology by Wright’s Staining
2.5. Clonogenic Cell Survival Assay
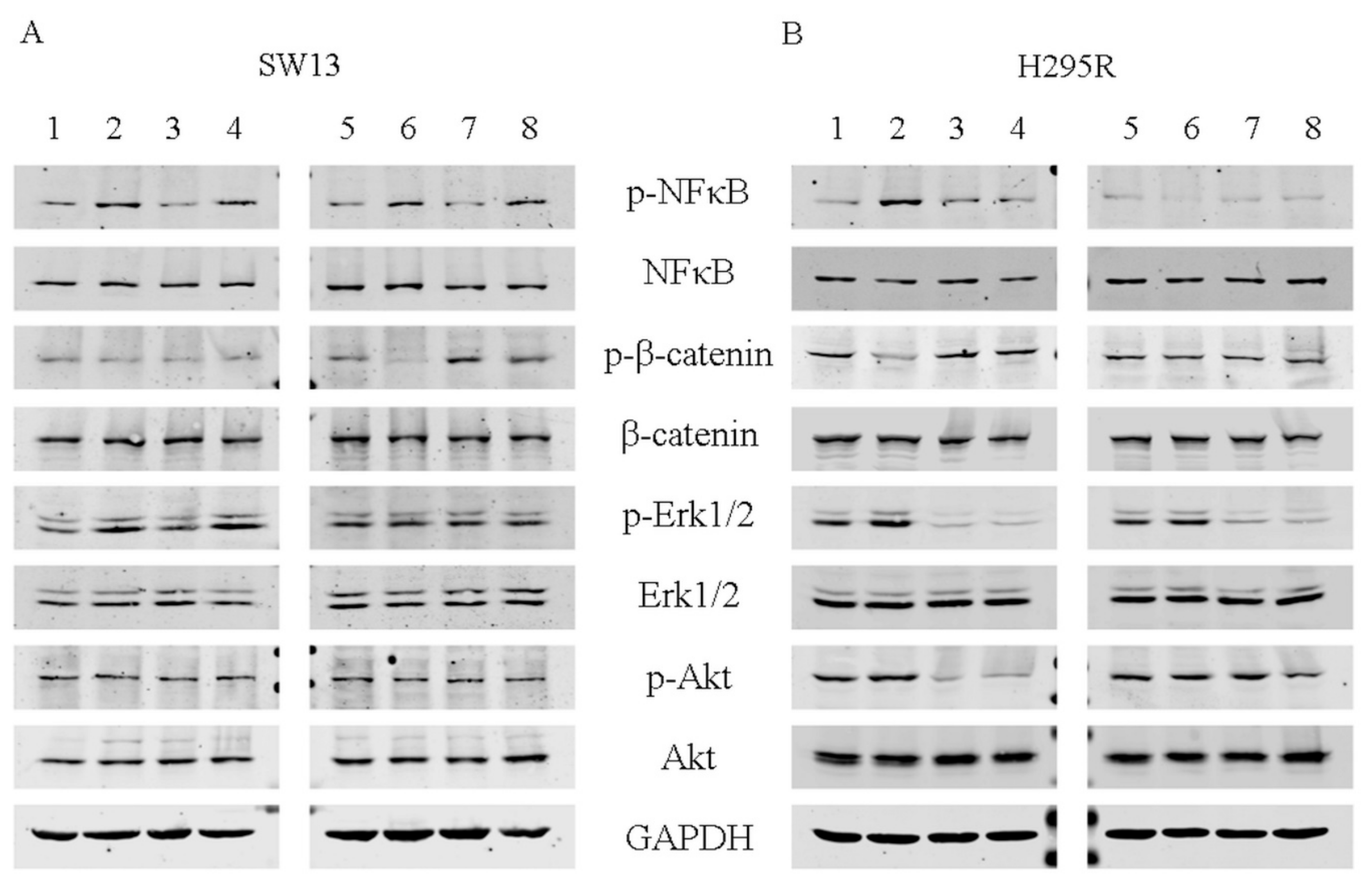
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Levels (DCFH-DA Assay)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Cell Cultures and Maintenance
4.3. Cell Viability Assays, Combination Index, and Drug Synergism
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Motility Assay (Wound Healing Assay)
4.6. Assessment of Cell Morphology by Wright’s Staining
4.7. Clonogenic Cell Survival Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Levels (DCFH-DA Assay)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Else, T.; Kim, A.C.; Sabolch, A.; Raymond, V.M.; Kandathil, A.; Caoili, E.M.; Jolly, S.; Miller, B.S.; Giordano, T.J.; Hammer, G.D. Adrenocortical carcinoma. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 282–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American_Cancer_Society Adrenal cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Stigliano, A.; Cerquetti, L.; Lardo, P.; Petrangeli, E.; Toscano, V. New insights and future perspectives in the therapeutic strategy of adrenocortical carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Konda, B.; Kirschner, L.S. Novel targeted therapies in adrenocortical carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2016, 23, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Cherniack, A.D.; Dewal, N.; Moffitt, R.A.; Danilova, L.; Murray, B.A.; Lerario, A.M.; Else, T.; Knijnenburg, T.A.; Ciriello, G.; et al. Comprehensive pan-genomic characterization of adrenocortical carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assie, G.; Letouze, E.; Fassnacht, M.; Jouinot, A.; Luscap, W.; Barreau, O.; Omeiri, H.; Rodriguez, S.; Perlemoine, K.; Rene-Corail, F.; et al. Integrated genomic characterization of adrenocortical carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzani, R. Adrenocortical carcinoma: In the search for a pre-operative biomarker. Acta Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 340–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, E.; Romano, B.; Izzo, A.A.; Borrelli, F. The clinical efficacy of curcumin-containing nutraceuticals: An overview of systematic reviews. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 134, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, C.A.; Liotta, D.C.; Snyder, J.P. Highly active anticancer curcumin analogues. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 595, 77–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unlu, A.; Nayir, E.; Dogukan Kalenderoglu, M.; Kirca, O.; Ozdogan, M. Curcumin (Turmeric) and cancer. J. Buon. 2016, 21, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam, D.; May, R.; Sureban, S.M.; Lee, K.B.; George, R.; Kuppusamy, P.; Ramanujam, R.P.; Hideg, K.; Dieckgraefe, B.K.; Houchen, C.W.; et al. Diphenyl difluoroketone: A curcumin derivative with potent in vivo anticancer activity. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1962–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.K.; Ferstl, E.M.; Davis, M.C.; Herold, M.; Kurtkaya, S.; Camalier, R.F.; Hollingshead, M.G.; Kaur, G.; Sausville, E.A.; Rickles, F.R.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel curcumin analogs as anti-cancer and anti-angiogenesis agents. Bioorga. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Sun, H.; Kong, Q. Bioactivities of EF24, a novel curcumin analog: A review. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Rainey, W.E. Human adrenocortical carcinoma cell lines. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 351, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Sidell, N.; Mancini, A.; Huang, R.P.; Shenming, W.; Horowitz, I.R.; Liotta, D.C.; Taylor, R.N.; Wieser, F. Multiple anticancer activities of EF24, a novel curcumin analog, on human ovarian carcinoma cells. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 17, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Feng, C.; Vinothkumar, R.; Chen, W.; Dai, X.; Chen, X.; Ye, Q.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Curcumin analog EF24 induces apoptosis via ROS-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tian, L.; Song, R.; Han, T.; Pan, S.; Liu, L. In vivo and in vitro suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma by EF24, a curcumin analog. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Tin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Jin, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. EF24 suppresses invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro via inhibiting the phosphorylation of Src. BioMed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8569684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Ben, W.; Yang, Y.; Ning, N.; Lu, M.; Guan, Y. Therapeutic role of EF24 targeting glucose transporter 1-mediated metabolism and metastasis in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Lou, B.; Du, Y.; Purcell, J.; Snyder, J.P.; Khuri, F.R.; Liotta, D.; Fu, H. Activation of the p38 pathway by a novel monoketone curcumin analog, EF24, suggests a potential combination strategy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariniello, B.; Rosato, A.; Zuccolotto, G.; Rubin, B.; Cicala, M.V.; Finco, I.; Iacobone, M.; Frigo, A.C.; Fassina, A.; Pezzani, R.; et al. Combination of sorafenib and everolimus impacts therapeutically on adrenocortical tumor models. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.; Regazzo, D.; Redaelli, M.; Mucignat, C.; Citton, M.; Iacobone, M.; Scaroni, C.; Betterle, C.; Mantero, F.; Fassina, A.; et al. Investigation of N-cadherin/beta-catenin expression in adrenocortical tumors. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13545–13555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tello Velasquez, J.; Nazareth, L.; Quinn, R.J.; Ekberg, J.A.; St John, J.A. Stimulating the proliferation, migration and lamellipodia of Schwann cells using low-dose curcumin. Neuroscience 2016, 324, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantara, C.; O’Connell, M.; Sarkar, S.; Moya, S.; Ullrich, R.; Singh, P. Curcumin promotes autophagic survival of a subset of colon cancer stem cells, which are ablated by DCLK1-siRNA. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiraly, O.; Gong, G.; Olipitz, W.; Muthupalani, S.; Engelward, B.P. Inflammation-induced cell proliferation potentiates DNA damage-induced mutations in vivo. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Han, Y. Inflammation-induced CD69(+) Kupffer cell feedback inhibits T cell proliferation via membrane-bound TGF-beta1. Science China. Life Sci. 2016, 59, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowla, S.N.; Perkins, N.D.; Jat, P.S. Friend or foe: Emerging role of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells in cell senescence. OncoTargets Ther. 2013, 6, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, S. ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebratu, Y.; Tesfaigzi, Y. How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Hottiger, M.O. Crosstalk between Wnt/beta-Catenin and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway during Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.K.; Cai, J.; Armstrong, J.; Herold, M.; Lu, Y.J.; Sun, A.; Snyder, J.P.; Liotta, D.C.; Jones, D.P.; Shoji, M. EF24, a novel synthetic curcumin analog, induces apoptosis in cancer cells via a redox-dependent mechanism. Anti-cancer Drugs 2005, 16, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Xia, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Ying, S.; Feng, Z.; Chen, T.; Ye, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, C.; et al. EF24 induces ROS-mediated apoptosis via targeting thioredoxin reductase 1 in gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18050–18064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, R.A.; Harris, I.S.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A.; Humpton, T.J.; Gopinathan, A.; Wei, C.; Frese, K.; Mangal, D.; Yu, K.H.; Yeo, C.J.; Calhoun, E.S.; et al. Oncogene-induced Nrf2 transcription promotes ROS detoxification and tumorigenesis. Nature 2011, 475, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertazza, L.; Sensi, F.; Cavedon, E.; Watutantrige-Fernando, S.; Censi, S.; Manso, J.; Vianello, F.; Casal Ide, E.; Iacobone, M.; Pezzani, R.; et al. EF24 (a curcumin analog) and ZSTK474 emphasize the effect of cabozantinib in medullary thyroid cancer. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 2348–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijnsdorp, I.V.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J. Analysis of drug interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.; Manso, J.; Monticelli, H.; Bertazza, L.; Redaelli, M.; Sensi, F.; Zorzan, M.; Scaroni, C.; Mian, C.; Iacobone, M.; et al. Crude extract of Origanum vulgare L. induced cell death and suppressed MAPK and PI3/Akt signaling pathways in SW13 and H295R cell lines. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzani, R.; Rubin, B.; Bertazza, L.; Redaelli, M.; Barollo, S.; Monticelli, H.; Baldini, E.; Mian, C.; Mucignat, C.; Scaroni, C.; et al. The aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680 shows anti-cancer effects in primary metastatic cells and the SW13 cell line. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds EF24 and mitotane are available from the authors. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bertazza, L.; Barollo, S.; Mari, M.E.; Faccio, I.; Zorzan, M.; Redaelli, M.; Rubin, B.; Armanini, D.; Mian, C.; Pezzani, R. Biological Effects of EF24, a Curcumin Derivative, Alone or Combined with Mitotane in Adrenocortical Tumor Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122202
Bertazza L, Barollo S, Mari ME, Faccio I, Zorzan M, Redaelli M, Rubin B, Armanini D, Mian C, Pezzani R. Biological Effects of EF24, a Curcumin Derivative, Alone or Combined with Mitotane in Adrenocortical Tumor Cell Lines. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122202
Chicago/Turabian StyleBertazza, Loris, Susi Barollo, Maria Elena Mari, Irene Faccio, Maira Zorzan, Marco Redaelli, Beatrice Rubin, Decio Armanini, Caterina Mian, and Raffaele Pezzani. 2019. "Biological Effects of EF24, a Curcumin Derivative, Alone or Combined with Mitotane in Adrenocortical Tumor Cell Lines" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122202
APA StyleBertazza, L., Barollo, S., Mari, M. E., Faccio, I., Zorzan, M., Redaelli, M., Rubin, B., Armanini, D., Mian, C., & Pezzani, R. (2019). Biological Effects of EF24, a Curcumin Derivative, Alone or Combined with Mitotane in Adrenocortical Tumor Cell Lines. Molecules, 24(12), 2202. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122202