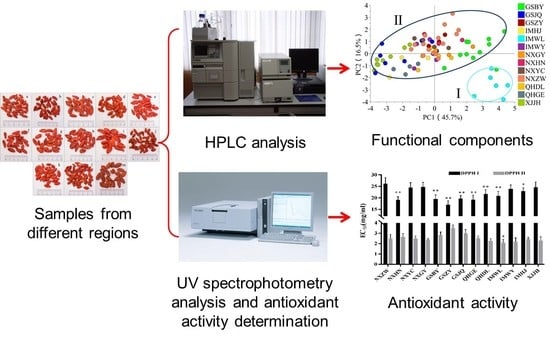
Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Carotenoid Content in Fruits of L. barbarum
2.1.1. Optimization of Extract Preparation
2.1.2. Development and Validation of the HPLC Method for Carotenoid Analysis
2.1.3. Analysis of Carotenoids in FLB from Different Regions
2.2. Total Phenolic Content and Flavonoid Content in FLB
2.2.1. Optimization of Extract Preparation
2.2.2. Analysis of Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents in FLB from Different Regions
2.3. Analysis of Total Polysaccharide Content (TLBP) in FLB from Different Regions
2.4. Antioxidant Activities of FLB from Different Regions
2.5. The Regional Characterization of Functional Components in FLB
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Reagents and Standards
3.3. Analysis of Total Carotenoid Content and Individual Carotenoids
3.3.1. Preparation of Standard Solutions
3.3.2. Preparation of Extract I for the Analysis of Carotenoids
3.3.3. Analysis of the Total Carotenoid Content (TCC) by Spectrophotometry
3.3.4. Analysis of Individual Carotenoids by HPLC-DAD
3.3.5. Method Validation for the Analysis of Individual Carotenoids
3.4. Analysis of Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Contents
3.4.1. Preparation of Standard Solutions
3.4.2. Preparation of Extract II for the Analysis of Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoids
3.4.3. Analysis of TPC and TFC by Spectrophotometry
3.5. Analysis of Polysaccharide Contents
3.6. Antioxidant Activity Assays
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Ulbricht, C.; Bryan, J.K.; Costa, D.; Culwell, S.; Giese, N.; Isaac, R.; Nummy, K.; Pham, T.; Rapp, C.; Rusie, E.; et al. An evidence-based systematic review of goji (Lycium spp.) by the natural standard research collaboration. J. Diet. Suppl. 2015, 12, 184–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagase, H.; Farnsworth, N.R. A review of botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, clinical relevance in efficacy and safety of Lycium barbarum, fruit (goji). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1702–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Heinrich, M.; Weckerle, C.S. The genus Lycium as food and medicine: A botanical, ethnobotanical and historical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.C.; So, K.F. Use of anti-aging herbal medicine, Lycium barbarum, against aging-associated diseases. what do we know so far? Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J.; Xi, W. Functional constituents and antioxidant activities of eight Chinese native goji genotypes. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, G.; Huang, L. Systematic review of chemical constituents in the genus Lycium (solanaceae). Molecules 2017, 22, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Fan, H.X.; He, R.R.; Xiao, J.; Tsoi, B.; Lan, K.H.; Kurihara, H.; So, K.F.; Yao, X.S.; Gao, H. Lycibarbarspermidines A-O, new dicaffeoylspermidine derivatives from wolfberry, with actives against Alzheimer’s disease and oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Xiao, J.; Fan, H.X.; Yu, Y.; He, R.R.; Feng, X.L.; Kurihara, H.; So, K.F.; Yao, X.S.; Gao, H. Polyphenols from wolfberry and their bioactivities. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Lu, H.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, B.H. Determination of carotenoids and their esters in fruits of Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MS. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2008, 47, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedor, J.; Burda, K. Potential role of carotenoids as antioxidants in human health and disease. Nutrients. 2014, 6, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczyński, B.; Gramza-Michałowska, A.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Kmiecik, D. The role of carotenoids in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease—Current state of knowledge. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F.; Chen, Z. Lycium barbarum: A traditional Chinese herb and a promising anti-aging agent. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 778–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.J.; Huang, R.F.; Kao, T.H.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Preparation of carotenoid extracts and nanoemulsions from Lycium barbarum L. and their effects on growth of HT-29 colon cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 135103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Suh, J.H.; Xi, Z.; Yu, W.; Ho, C.T. Identification and quantification of potential anti-inflammatory hydroxycinnamic acid amides from wolfberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneta, W.; Paulina, N.; Przemysław, B. Phenolic and carotenoid profile of new goji cultivars and their anti-hyperglycemic, anti-aging and antioxidant properties. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 632–642. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Yeo, J.D. Bioactivities of phenolics by focusing on suppression of chronic diseases: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Luo, S.; Luo, X.; Hu, M.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Huang, R. Fraction from Lycium barbarum polysaccharides reduces immunotoxicity and enhances antitumor activity of doxorubicin in mice. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Peng, L.; Li, R.; Li, H.; Mo, Z.; Dai, X.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, E.; Deng, H.; et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide protects HSF cells against ultraviolet-induced damage through the activation of Nrf2. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2018, 23, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masci, A.; Carradori, S.; Casadei, M.A.; Paolicelli, P.; Petralito, S.; Ragno, R.; Cesa, S. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides: Extraction, purification, structural characterisation and evidence about hypoglycaemic and hypolipidaemic effects. A review. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potterat, O. Goji (Lycium barbarum and L. chinense): Phytochemistry, pharmacology and safety in the perspective of traditional uses and recent popularity. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G.; Chiodelli, G.; Giuberti, G.; Ghisoni, S.; Baccolo, G.; Blasi, F.; Montesano, D.; Trevisan, M.; Lucini, L. UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS profile of polyphenols in goji berries (Lycium barbarum, L.) and its dynamics during in vitro, gastrointestinal digestion and fermentation. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M. Problems and developments strategies of goji export in China. In Practice in Foreign Economic Relations and Trade; Foreign Economic and Trade Practice Magazine: Wuhan, China, 2018; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, P.; Brand, E. The formation of daodi medicinal materials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Lam, S.C.; Cheong, K.L.; Feng, W.; Lin, P.C.; Long, Z.R.; Lv, X.R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, S.C. Simultaneous determination of molecular weights and contents of water-soluble polysaccharides and their fractions from Lycium barbarum, collected in china. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2016, 129, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wu, D.T.; Li, W.Z.; Ning, C.G.; Tang, Y.P.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.P. Effects of polysaccharides in Lycium barbarum berries from different regions of China on macrophages function and their correlation to the glycosidic linkages. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2411–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Carotenoid extraction methods: A review of recent developments. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, S.; Sun, W.; Wu, M.; Hu, W.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y. Comparative analysis of carotenoid accumulation in two goji (Lycium barbarum L. and L. ruthenicum murr.) fruits. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, L.C.; Sharpless, K.E.; Pursch, M. C30 stationary phases for the analysis of food by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 880, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.M.; Canelagarayoa, R. Analytical tools for the analysis of carotenoids in diverse materials. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, F.C.; Mercadante, A.Z. Composition by LC-MS/MS of new carotenoid esters in mango and citrus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8207–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH. Guidance for Industry, Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; ICH: Rockville, ML, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, F.C.O.L.; Sentanin, M.A.; Souza, D.D. Analytical methods in food additives determination: Compounds with functional applications. Food Chem. 2018, 272, 732–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowicka, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Fecka, I. Comparison of polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of strawberry fruit from 90 cultivars of Fragaria x ananassa Duch. Food Chem. 2018, 270, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Meng, J.; Deng, K.; Zhou, H.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of eighteen phenolic compounds from Lycium ruthenicum Murray by UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS and their antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Wei, J.; Hao, J.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z. Effect of sodium carbonate solution pretreatment on drying kinetics, antioxidant capacity changes, and final quality of wolfberry (Lycium barbarum) during drying. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 99, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skenderidis, P.; Petrotos, K.; Giavasis, L.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Tsakalof, A. Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of goji berry (Lycium barbarum) fruits and evaluation of extracts bioactivity. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, 12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiera, S.; Zaręba, M. Chromatographic Determination of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids in Lycium barbarum L. and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity. Food Anal. Method 2015, 8, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.T.; Cheong, K.L.; Deng, Y.; Lin, P.C.; Wei, F.; Lv, X.J.; Long, Z.R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, S.C.; Li, S.P. Characterization and comparison of polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum in China using saccharide mapping based on PACE and HPTLC. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 134, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.P.; Zhao, P.T. Chemical characterization of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides and their reducing myocardial injury in ischemia/reperfusion of rat heart. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Tang, W.; Jin, M.L.; Li, J.E.; Xie, M.Y. Recent advances in bioactive polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. Zizyphus jujuba Mill, Plantago spp. and Morus spp.: Structures and functionalities. Food Hydrocolloid. 2016, 60, 148–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.C.; Chang, S.C.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Isolation of carotenoids, flavonoids and polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. and evaluation of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Administration of Chinese pharmacopoeia Editorial Committee. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China; Chinese Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 249–250. [Google Scholar]
- Brandwilliams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lwt Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Riceevans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of fruits of Lycium barbarum in this study are available from the authors. |




| Regions | Contents of Analytes (mean ± SD, n ≥ 3) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeaxanthin | β-Cryptoxanthin | β-Carotene | Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate | TCC 4 | TFC 4 | TP 4 | Rutin | Ferulic Acid | TLBP 4 | |
| Daodi herbs region | ||||||||||
| NXZW 1 | 0.0856 ± 0.0216 c 2 | 0.0009 ± 0.0002 cd | 0.0615 ± 0.0197 cd | 7.375 ± 2.307 abc | 17.71 ± 3.94 cde | 5.545 ± 0.769 abc | 8.253 ± 0.839 a | 0.2609 ± 0.0566 cdef | 0.1659 ± 0.0405 a | 31.41 ± 5.30 bc |
| Non-Daodi herbs region | ||||||||||
| NXHN | 0.0497 ± 0.0127 de** 3 | 0.0007 ± 0.0002 de | 0.0830 ± 0.0376 bcd | 8.002 ± 1.024 abc | 20.75 ± 3.10 abcd | 4.942 ± 0.606 bcd | 7.902 ± 0.587 ab | 0.2874 ± 0.0517 bcde | 0.1453 ± 0.0573 abc | 42.45 ± 2.79 a* |
| NXYC | 0.0277 ± 0.0112 e** | 0.0003 ± 0.0001 fg** | 0.0702 ± 0.0258 cd | 8.301 ± 1.491 abc | 19.62 ± 2.57 bcd | 4.692 ± 0.767 cde* | 7.707 ± 0.714 ab | 0.3400 ± 0.0654 bc* | 0.1305 ± 0.0198 abc | 34.19 ± 5.04 b |
| NXGY | 0.0651 ± 0.0164 cd | 0.0010 ± 0.0001 cd | 0.0980 ± 0.0310 abc | 9.766 ± 1.904 ab | 21.69 ± 3.87 abc | 5.936 ± 0.606 a | 7.555 ± 0.301 ab | 0.3771 ± 0.0289 ab ** | 0.1335 ± 0.0132 abc | 27.80 ± 2.74 bcd |
| GSBY | 0.1139 ± 0.0157 b** | 0.0014 ± 0.0003 b** | 0.1133 ± 0.0363 ab** | 10.04 ± 2.13 a** | 23.71 ± 3.37 ab** | 6.144 ± 0.710 a* | 7.663 ± 0.477 a* | 0.4391 ± 0.0999 a** | 0.1726 ± 0.0340 a | 31.91 ± 4.51 bc |
| GSZY | 0.0487 ± 0.0192 de** | 0.0004 ± 0.0002 f** | 0.0788 ± 0.0096 bcd | 9.681 ± 1.206 ab | 21.25 ± 0.34 abc | 5.821 ± 0.303 ab | 7.966 ± 0.586 ab | 0.2413 ± 0.0309 def | 0.1390 ± 0.0328 abc | 29.64 ± 1.40 bcd |
| GSJQ | 0.0554 ± 0.0224 de** | 0.0006 ± 0.0002 ef** | 0.0549 ± 0.0263 de | 5.565 ± 2.531 cd | 14.72 ± 4.05 f | 4.737 ± 0.610 cde* | 7.443 ± 0.907 ab* | 0.1812 ± 0.0727 f** | 0.1147 ± 0.0289 bc** | 30.161 ± 5.65 bcd |
| QHDL | 0.0324 ± 0.0171 e** | 0.0010 ± 0.0001 c | 0.0544 ± 0.0101 de | 7.757 ± 1.814 abc | 17.09 ± 2.06 cde | 3.859 ± 0.540 ef* | 7.711 ± 0.563 ab | 0.3283 ± 0.0763 bcd* | 0.1122 ± 0.0225 bc* | 27.54 ± 5.25 bcd |
| QHGE | 0.0317 ± 0.0193 e** | 0.0011 ± 0.0001 c* | 0.0752 ± 0.0208 cd | 9.403 ± 2.732 ab | 20.73 ± 3.28 abcd | 3.546 ± 0.362 f* | 6.960 ± 0.237 b* | 0.211 ± 0.0559 ef | 0.1027 ± 0.0184 c** | 23.62 ± 2.15 d* |
| IMWL | 0.2857 ± 0.0190 a** | 0.0031 ± 0.0002 a** | 0.1301 ± 0.0307 a** | 10.07 ± 1.65 a* | 25.35 ± 1.91 a** | 4.906 ± 0.455 bcd* | 7.176 ± 0.624 ab* | 0.3457 ± 0.0479 bc** | 0.1588 ± 0.0300 ab | 30.35 ± 4.81 bcd |
| IMWY | 0.0538 ± 0.0105 de** | 0.0005 ± 0.0001 ef** | 0.0672 ± 0.0204 cd | 8.300 ± 2.001 abc | 20.12 ± 3.47 bcd | 5.977 ± 0.646 a | 7.219 ± 0.860 ab* | 0.2357 ± 0.609 def | 0.0994 ± 0.0180 c** | 25.13 ± 2.50 cd* |
| IMHJ | 0.0482 ± 0.0243 de** | 0.0005 ± 0.0001 ef** | 0.0607 ± 0.0211 cd | 6.654 ± 2.078 bcd | 15.78 ± 2.40 ef | 4.011 ± 0.598 def* | 6.899 ± 0.765 b* | 0.2566 ± 0.0093 cdef | 0.1059 ± 0.0228 c* | 25.17 ± 3.64 cd* |
| XJJH | 0.0429 ± 0.0252 de** | 0.0001 ± 0.0000 g** | 0.0229 ± 0.0090 e** | 4.260 ± 1.451 d** | 12.93 ± 2.87 f** | 3.177 ± 0.659 f* | 7.239 ± 0.803 ab* | 0.2274 ± 0.0343 ef | 0.1309 ± 0.0269 abc* | 26.78 ± 3.88 cd* |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.-W.; Wang, H.-Q.; Jin, L.; Duan, J.-A. Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China. Molecules 2019, 24, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122228
Lu Y, Guo S, Zhang F, Yan H, Qian D-W, Wang H-Q, Jin L, Duan J-A. Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China. Molecules. 2019; 24(12):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122228
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Youyuan, Sheng Guo, Fang Zhang, Hui Yan, Da-Wei Qian, Han-Qing Wang, Ling Jin, and Jin-Ao Duan. 2019. "Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China" Molecules 24, no. 12: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122228
APA StyleLu, Y., Guo, S., Zhang, F., Yan, H., Qian, D. -W., Wang, H. -Q., Jin, L., & Duan, J. -A. (2019). Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China. Molecules, 24(12), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24122228