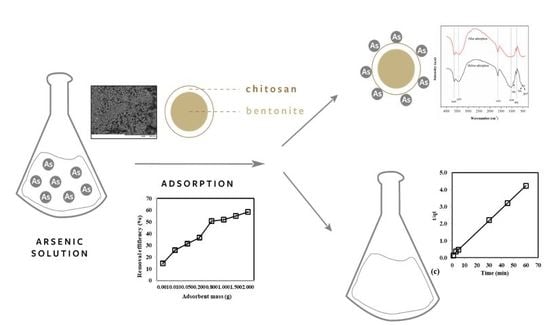
Treatment of Contaminated Groundwater via Arsenate Removal Using Chitosan-Coated Bentonite
Abstract
Share and Cite
Yee, J.-J.; Arida, C.V.J.; Futalan, C.M.; de Luna, M.D.G.; Wan, M.-W. Treatment of Contaminated Groundwater via Arsenate Removal Using Chitosan-Coated Bentonite. Molecules 2019, 24, 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132464
Yee J-J, Arida CVJ, Futalan CM, de Luna MDG, Wan M-W. Treatment of Contaminated Groundwater via Arsenate Removal Using Chitosan-Coated Bentonite. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132464
Chicago/Turabian StyleYee, Jurng-Jae, Carlo Vic Justo Arida, Cybelle Morales Futalan, Mark Daniel Garrido de Luna, and Meng-Wei Wan. 2019. "Treatment of Contaminated Groundwater via Arsenate Removal Using Chitosan-Coated Bentonite" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132464
APA StyleYee, J.-J., Arida, C. V. J., Futalan, C. M., de Luna, M. D. G., & Wan, M.-W. (2019). Treatment of Contaminated Groundwater via Arsenate Removal Using Chitosan-Coated Bentonite. Molecules, 24(13), 2464. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132464