An Established HPLC-MS/MS Method for Evaluation of the Influence of Salt Processing on Pharmacokinetics of Six Compounds in Cuscutae Semen
Abstract
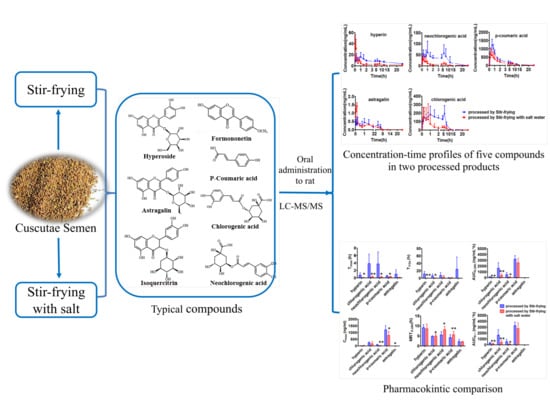
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Internal Standard (IS) Selection
2.2. Optimization of LC-MS/MS Conditions
2.3. Quantification of the Six Compounds in Two Processed CS Extracts
2.4. Method Validations
2.4.1. Linearity and LLOQ
2.4.2. Selectivity
2.4.3. Accuracy and Precision
2.4.4. Stability
2.4.5. Matrix Effects and Recoveries
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Application
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Apparatus and LC-MS/MS Conditions
3.3. Preparation of SF-CS and SP-CS Extract
3.4. Preparation of Standard and Quality Control (QC) Samples
3.5. Plasma Samples Preparation
3.6. Method Validation
3.6.1. Linearity and LLOQ
3.6.2. Selectivity
3.6.3. Accuracy and Precision
3.6.4. Stability
3.6.5. Matrix Effects and Recoveries
3.7. Pharmacokinetic and Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajimehdipoor, H.; Kondori, B.M.; Amin, G.R.; Adib, N.; Rastegar, H.; Shekarchi, M. Development of a validated HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of compounds in Cuscuta chinensis Lam. by ultra-violet detection. DARU J. Fac. Pharm. 2012, 20, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial Committee of the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mavlonov, G.T.; Ubaidullaeva, K.A.; Kadryaeva, G.V.; Kuznetsova, N.N. Cytotoxic components of Cuscuta. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2008, 44, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnapee, S.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Ge, A.H.; Donkor, P.O.; Gao, X.M.; Chang, Y.X. Cuscuta chinensis Lam.: A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 157, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Xu, X.F.; Xue, X.; Liu, M.N.; Xu, S.Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.R. Compounds identification in Semen Cuscutae by Ultra-High-Performance liquid chromatography (UPLCs) coupled to electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Molecules 2018, 23, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Lee, S.G.; Chuang, E.S.; Lim, S.J.; Kim, W.S.; Yoon, H.; Kim, S.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Jang, Y.P.; Bae, H. Neuroprotective effects of cuscutae semen in a mouse modle of Parkinson’s disease. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 22, 150153. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lee, M.S.; Chiu, Y.J.; Chao, W.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, M.K.; Peng, Y.H. Antinociceptive and anti-flammatory activities of Cuscuta chinensis seeds in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.X.; Yao, S.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, T.S. Protective effect Cuscuta chinensis Lam. extract on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Chin. Pharma. Bull. 2011, 27, 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.X.; Zhou, C.; Qiu, W.Y.; Wu, H.W.; Li, J.; Peng, J.T.; Qiu, M.; Liang, C.; Gao, J.; Luo, S.P. Total compounds from Semen Cuscutae target MMP9 and promote invasion of EVT cells via Notch/AKT/MAPK signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, Z.T.; Xie, Y.; Duan, Z.W.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.H. High resolution UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous separation and determination of six compounds from Semen Cuscutae extract in rat plasma: Application to comparative pharmacokinetic studies in normal and kindey-deficient rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.K.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, K.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lee, M.S.; Yang, M.J.; Cheng, H.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, D.C.; Chu, C.L. Kaempferol from Semen cuscutae attenuates the immune function of dendritic cells. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.M. Enlightening Primer of Materia Medical; Traditional Chinese Medicine Ancient Books Press: Beijing, China, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Xu, H.F.; Zhao, B.S.; Li, S.S.; Li, T.T.; Xu, X.F.; Zhang, T.J.; Lin, R.C.; Li, J.; Li, X.R. The difference of chemical components and biological activities of the crude product and salt-processed product from Semen Cuscutae. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 8656740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, W.F.; Li, J.; He, J.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, B.L.; Gao, X.M.; Chang, Y.X. Influence of processing on pharmacokinetic of typical constituents in radix Polygoni multiflori after oral administration by LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 148, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Mi, S.Q.; Luo, S.P.; Luo, Y.H. The determination of quercetin content by semen cuscutacae intragastric administration in rat and its pharmacokinetic study. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2004, 22, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.X. Take the Cuscuta as the Example, the Discussion Traditional Chinese Medicine Pharmacokinetic of Related Question Research. Ph.D. Thesis, Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China, 2010; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J. Study on Processing Technology and Standardization of Quality Standard of Cuscutae Semen (Tusizi). Master’s Thesis, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang, China, 2010; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry Bioanaly Method Validation. Fed. Regist. 2001, 66, 206–207. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds hyperin, chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, p-coumaric acid, astragalin, formononetin and isoquercitrin are available from the authors. |





| Compounds | Q1 | Q3 | Dwell Time (ms) | DP (V) | EP (V) | CE (eV) | CXP (V) | Retention (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neochlorogenic acid | 353.0 | 190.9 | 100 | −40 | −4.5 | −30 | −3.0 | 3.01 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 353.0 | 191.0 | 100 | −40 | −5.5 | −25 | −1.0 | 3.83 |
| P-coumaric acid | 162.8 | 119.0 | 100 | −35 | −5.5 | −20 | −2.0 | 10.07 |
| Hyperin | 463.0 | 300.0 | 100 | −70 | −6.0 | −39 | −1.0 | 12.51 |
| Isoquercitrin | 462.9 | 300.0 | 100 | −60 | −7.0 | −40 | −1.5 | 13.61 |
| Astragalin | 447.1 | 284.0 | 100 | −68 | −5.5 | −38 | −1.0 | 15.81 |
| Formononetin (IS) | 267.0 | 251.8 | 100 | −60 | −2 | −27 | −16 | 19.25 |
| Compounds | Regression Equation | r | Linearity Range (ng·mL−1) | LLOQ (ng·mL−1) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperin | Y = 0.00406X + 0.000488 | 0.9996 | 1–250 | 1 | 104 | 7.9 |
| Chlorogenic acid | Y = 0.00113X + 0.00233 | 0.9992 | 0.1–1500 | 0.1 | 104 | 15 |
| Neochlorogenic acid | Y = 0.00134X + 0.00254 | 0.9990 | 4–1000 | 4 | 102 | 4.6 |
| P-coumaric acid | Y = 0.00366X + 0.00276 | 0.9993 | 4–10000 | 4 | 98.3 | 4.7 |
| Astragalin | Y = 0.00613X + 0.000874 | 0.9991 | 0.1–25 | 0.1 | 90.4 | 17 |
| Isoquercitrin | Y = 0.00286X + 0.000841 | 0.9994 | 2–500 | 2 | 102 | 10 |
| Compounds | Concentration (ng·mL−1) | Intra-day | Inter-day | Recovery | Matrix Effect | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Hyperin | 3.0 | 94.8 | 12.7 | 98.9 | 4.20 | 93.0 | 6.0 | 95.0 | 5.0 |
| 10 | 106 | 7.80 | 108 | 3.70 | 83.0 | 5.0 | 91.0 | 5.0 | |
| 250 | 107 | 12.5 | 100 | 6.40 | 87.0 | 8.0 | 92.0 | 7.0 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.3 | 114 | 14.7 | 106 | 7.10 | 65.0 | 11.0 | 109 | 13.0 |
| 60 | 88.9 | 6.00 | 94.2 | 6.30 | 75.0 | 9.0 | 106 | 10.0 | |
| 1500 | 101 | 5.50 | 90.2 | 11.0 | 77.0 | 8.0 | 112 | 7.0 | |
| Neochlorogenic acid | 12 | 103 | 3.70 | 99.3 | 3.90 | 76.0 | 8.0 | 117 | 7.0 |
| 40 | 80.3 | 5.80 | 98.3 | 16.2 | 66.0 | 7.0 | 95.0 | 6.0 | |
| 1000 | 104 | 7.80 | 101 | 3.40 | 60.0 | 8.0 | 99.0 | 8.0 | |
| P-coumaric acid | 12 | 108 | 1.80 | 97.2 | 10.0 | 61.0 | 6.0 | 101 | 9.0 |
| 400 | 81.0 | 5.00 | 101 | 17.0 | 96.0 | 5.0 | 95.0 | 4.0 | |
| 10000 | 113 | 5.90 | 95.2 | 15.9 | 96.0 | 6.0 | 96.0 | 4.0 | |
| Astragalin | 0.3 | 87.0 | 12.9 | 96.2 | 9.30 | 117 | 9.0 | 117 | 14.0 |
| 1.0 | 113 | 9.50 | 112 | 8.00 | 94.0 | 11.0 | 99.0 | 8.0 | |
| 25 | 105 | 12.8 | 96.1 | 8.60 | 91.0 | 7.0 | 89.0 | 5.0 | |
| Isoquercitrin | 6.0 | 86.0 | 12.7 | 93.5 | 6.00 | 95.0 | 9.0 | 100 | 8.0 |
| 20 | 109 | 7.80 | 105 | 5.70 | 90.0 | 12.0 | 93.0 | 4.0 | |
| 500 | 110 | 13.2 | 100 | 10.9 | 89.0 | 8.0 | 92.0 | 7.0 | |
| Compounds | Concentration (ng·mL−1) | Freeze-Thaw Cycles | −80 °C for 1 Month | Auto-Sampler for 24 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | Accuracy (%) | RSD (%) | ||
| Hyperin | 3.0 | 104 | 14.8 | 103 | 6.20 | 90.2 | 13.6 |
| 10 | 116 | 10.7 | 92.5 | 3.80 | 107 | 13.2 | |
| 250 | 107 | 12.0 | 102 | 3.90 | 100 | 10.8 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.3 | 107 | 13.1 | 104 | 6.70 | 94.4 | 12.0 |
| 60 | 119 | 12.6 | 105 | 13.5 | 115 | 13.9 | |
| 1500 | 104 | 14.2 | 99.8 | 10.1 | 119 | 9.20 | |
| Neochlorogenic acid | 12 | 99.9 | 12.4 | 103 | 12.3 | 98.9 | 13.3 |
| 40 | 102 | 8.30 | 103 | 14.3 | 115 | 9.00 | |
| 1000 | 116 | 8.10 | 90.6 | 9.50 | 117 | 4.90 | |
| P-coumaric acid | 12 | 98.8 | 10.4 | 91.5 | 12.7 | 88.8 | 15.1 |
| 400 | 112 | 8.30 | 100 | 11.9 | 116 | 8.30 | |
| 10000 | 111 | 4.20 | 93.6 | 8.40 | 115 | 8.60 | |
| Astragalin | 0.3 | 91.7 | 12.1 | 113 | 12.8 | 96.0 | 9.90 |
| 1.0 | 104 | 11.9 | 103 | 12.6 | 92.0 | 12.7 | |
| 25 | 102 | 12.8 | 92.9 | 12.0 | 95.2 | 12.7 | |
| Isoquercitrin | 6.0 | 107 | 11.7 | 106 | 12.1 | 111 | 11.5 |
| 20 | 109 | 14.2 | 91.4 | 13.2 | 103 | 8.00 | |
| 500 | 114 | 14.9 | 99.1 | 8.90 | 104 | 8.00 | |
| Compound | Hyperin | Chlorogenic Acid | Neochlorogenic Acid | P-coumaric Acid | Astragalin | Isoquercitrin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | A | B | |
| dosage (mg/kg) | 21.8 | 27.5 | 31.1 | 49.0 | 6.09 | 6.64 | 0.59 | 0.87 | 1.87 | 1.30 | 1.98 | 1.99 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.74 | 0.11 | 3.84 | 0.28 | 3.75 | 0.26 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.99 | 0.17 | ||
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 21.3 ± 6.98 | 36.6 ± 21.9 | 257 ± 53 | 175.2 ± 167.7 | 88.6 ± 39.6 | 31.8 ± 17.3 ** | 1213 ± 310 | 805 ± 307 * | 0.65 ± 0.39 | 1.43 ± 0.21 * | - | - |
| T1/2ka (h) | 2.15 ± 4.21 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.63 ± 0.87 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.12 ± 1.66 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.12 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 2.27 ± 5.13 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | - | - |
| T1/2α (h) | 11.7 ± 6.73 | 0.46 ± 0.30 ** | 6.53 ± 5.20 | 0.84 ± 0.42 * | 7.72 ± 7.50 | 3.35 ± 4.31 | 1.32 ± 0.86 | 1.40 ± 0.95 | 24.6 ± 33.2 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | - | - |
| AUC0–24h (ng/mL·h) | 172 ± 38 | 63.0 ± 27.8 ** | 1662 ± 931 | 417 ± 281 ** | 548 ± 384 | 129 ± 38 * | 3198 ± 635 | 2567 ± 792 | 1.27 ± 0.76 | 1.31 ± 0.27 | - | - |
| AUC0–∞ (ng/mL·h) | 331 ± 80 | 185 ± 153 * | 1671 ± 931 | 438 ± 289 ** | 567 ± 376 | 178 ± 22 * | 3286 ± 591 | 2804 ± 951 | 11.2 ± 10.8 | 2.33 ± 0.72 | - | - |
| MRT0–24h (h) | 9.19 ± 1.50 | 8.66 ± 2.37 | 4.81 ± 0.35 | 5.06 ± 1.10 * | 5.57 ± 1.74 | 8.18 ± 1.66 * | 4.24 ± 1.45 | 5.68 ± 1.69 ** | 2.30 ± 0.98 | 2.13 ± 0.20 | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zou, S.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Hao, J.; He, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, E.; Chang, Y. An Established HPLC-MS/MS Method for Evaluation of the Influence of Salt Processing on Pharmacokinetics of Six Compounds in Cuscutae Semen. Molecules 2019, 24, 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132502
Liu J, Zou S, Liu W, Li J, Wang H, Hao J, He J, Gao X, Liu E, Chang Y. An Established HPLC-MS/MS Method for Evaluation of the Influence of Salt Processing on Pharmacokinetics of Six Compounds in Cuscutae Semen. Molecules. 2019; 24(13):2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132502
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiao, Shuhan Zou, Wei Liu, Jin Li, Hui Wang, Jiao Hao, Jun He, Xiumei Gao, Erwei Liu, and Yanxu Chang. 2019. "An Established HPLC-MS/MS Method for Evaluation of the Influence of Salt Processing on Pharmacokinetics of Six Compounds in Cuscutae Semen" Molecules 24, no. 13: 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132502
APA StyleLiu, J., Zou, S., Liu, W., Li, J., Wang, H., Hao, J., He, J., Gao, X., Liu, E., & Chang, Y. (2019). An Established HPLC-MS/MS Method for Evaluation of the Influence of Salt Processing on Pharmacokinetics of Six Compounds in Cuscutae Semen. Molecules, 24(13), 2502. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132502