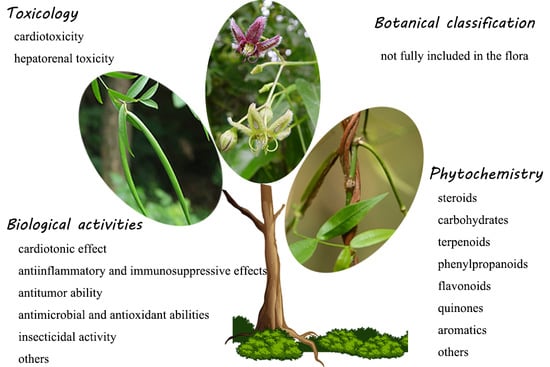
Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Botanical Classification of the Genus Periploca
3. Chemical Constituents from the Genus Periploca
3.1. Steroids
3.1.1. Cardenolides
3.1.2. C21 Pregnane-Type Steroids
3.1.3. Phytosterols
3.2. Carbohydrates
3.3. Terpenoids
3.4. Phenylpropanoids
3.5. Flavonoids
3.6. Quinones
3.7. Aromatics
3.8. Others
4. Biological Activities
4.1. Cardiotonic Effect
4.2. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects
4.3. Antitumor Ability
4.4. Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Abilities
4.5. Insecticidal Activity
4.6. Other Abilities
5. Toxicology
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, P.F. Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. 2017. Available online: http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/ (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Flora of China Editorial Committee. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1995; Volume 16, pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Beijing Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 257–258. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Board of Chinese Materia Medica, State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Miao Medicine Volume of Chinese Materia Medica; Guizhou science and technology press: Guiyang, China, 2005; Volume Miao Medicine, pp. 526–527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, F.P. Recent adcances of chemical constituents of Periploca plants. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2003, 15, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.R.; Fu, Q.J. Advances of research of Periploca Plants. J. Dali Univ. 2006, 5, 54–58. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, H.J.T. A revision of Periploca (Periplocaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 1997, 63, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, D.L.; Wang, F.P. Studies on chemical constituents of Periploca omeiensis. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2006, 18, 772–774. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, D.S.; Chen, X.C.; Ren, J.W. A new species of Periploca from Gansu province. Bull. Bot. Res. 2002, 22, 259–260. [Google Scholar]
- Azza, R.A.M.; Zeinab, A.K.; Ashraf, B.A.N.; Essam, A.S. A new triterpene and protective effect of Periploca somaliensis Browicz fruits against CCl4-induced injury on human hepatoma cell line (Huh7). Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, E. Active principles contained in the bark of periploca graeca. Arch. Der. Pharm. 1897, 235, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhou, L.; Tan, M.C.; Sun, Q.Y.; Hao, X.J. Study on chemical constituents of Periploca calophylla. China Pharm. (ChongqingChina) 2010, 21, 4463–4465. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.T.; Chen, D.L.; Wang, F.P. Chemical constituents from Periploca forestti. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2006, 37, 345–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma, S.; Ishizone, H.; Kawanishi, S.; Shoji, J. On the structure of glycoside G and K of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1969, 17, 2183–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Spera, D.; Siciliano, T.; Tommasi, N.; Braca, A.; Vessières, A. Antiproliferative cardenolides from Periploca graeca. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, J.; Kawanishi, S.; Sakuma, S.; Shibata, S. Studies on the chemical constituents of Chinese drug Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1967, 15, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, A.; Renz, J. Cardiac glucosides. XV. Periplocin, the true cardiac glucoside of Periploca graeca. Helv. Chim. Acta 1939, 22, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.R.; Wei, Y.P.; Yin, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y. A new cardenolide and two new pregnane glycosides from the root barks of Periploca sepium. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Yu, S.S.; Chen, X.G.; Wu, X.F.; Ma, S.G.; Qu, J.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, J.; Lv, H.N. Cytotoxic cardenolides from the stems of Periploca forrestii. Steroids 2012, 77, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.F.; Li, J.B.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, S.S.; Lv, H.N.; Qu, J.; Abliz, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; et al. Identification of cardiac glycosides in fractions from Periploca forrestii by high-performance liquid chromatography/diode-array detection/electrospray ionization multi-stage tandem mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.J.; Mu, Q.Z. The chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1989, 11, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, D.L.; Wang, F.P. Two novel cardiac glycosides from Periploca forestti. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 26, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K.; Itokawa, H. Pregnanes and cardenolides from Periploca sepium. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenker, E.; Hunger, A.; Reichstein, T. Glycosides and aglycons. CXXXIV. The glycosides of Periploca nigrescens Afzel. Helv. Chim. Acta 1954, 37, 1004–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, R.; Wehrli, W.; Reichstein, T. Die cardenolide von Parquetina nigrescens (Afzel) Bullock. Helv. Chim. Acta 1965, 48, 1634–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauli, R.; Tamm, C. Glycosides and aglycons. CLXXI. The glycosides of Periploca nigrescens. Helv. Chim. Acta 1957, 40, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, R.; Wehrli, W.; Reichstein, T. Die cardenolide von Parquetina nigrescens (Afzel) Bullock) 3. Mitt.) Die konstitution 5 neuer cardenolide (16-Dehydrostrophanthidin und verwandte substanzen). Helv. Chim. Acta 1965, 48, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.J.; Mu, Q.Z.; Zheng, Q.T.; He, C.H. New cardenolides of Periploca forrestii. Acta Chim. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 1990, 43, 714–719. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.Q.; Zhao, W.M. Complete 1H and 13C NMR assignments of four new oligosaccharides and two new glycosides from Periploca forrestii. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Du, J.; Deng, L.L.; Yang, F.M.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, D.P.; Zhang, Y.H. A new cardiac glycoside from Periploca forrestii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 2286–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Itokawa, H.; Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K. Studies on chemical constituents of antitumor fraction from Periploca sepium. IV. Structures of new pregnane glycosides, Periplocosides D, E, L and M. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1988, 36, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, Y.; Hirota, T.; Hikino, H. Periplosides A, B and C, steroidal glycosides of Periploca sepium root barks. Heterocycles 1987, 26, 2093–2098. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.Q.; Zhang, R.J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Tang, W.; Liu, Q.F.; Zuo, J.P.; Zhao, W.M. Immunosuppressive pregnane glycosides from Periploca sepium and Periploca forrestii. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 2716–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Zuo, J.P.; Zhao, W.M. Structural revision of periplocosides and periperoxides, natural immunosuppressive agents from the genus Periploca. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Zuo, J.P.; Zhao, W.M. Corrigendum to “Structural revision of periplocosides and periperoxides, natural immunosuppressive agents from the genus Periploca” [Phytochemistry 72/17 (2011) 2230-2236]. Phytochemistry 2013, 95, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itokawa, H.; Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K.; Watanabe, K.; Shoji, J. Studies on chemical constituents of antitumor fraction from Periploca sepium. II. Structures of new pregnane glycosides, Periplocosides A, B and C. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1988, 36, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokawa, H.; Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K. Studies on chemical constituents of antitumor fraction from Periploca sepium. V. Structures of new pregnane glycosides, Periplocosides J, K, F and O. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1988, 36, 4441–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.Y.; Qin, J.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Zuo, J.P.; Zhao, W.M. Absolute configuration of Periplosides C and F and isolation of minor spiro-orthoester group-containing pregnane-type steroidal glycosides from Periploca sepium and their T-Lymphocyte proliferation inhibitory activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.J.; Lin, Z.M.; Xu, Y.S.; Ren, J.W.; Zuo, J.P.; Zhao, W.M. Spiroorthoester group-containing pregnane glycosides from the root barks of Periploca chrysantha and their inhibitory activities against the proliferation of B and T lymphocytes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, D.M.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.L.; Yao, X.S.; Ye, W.C. Five new C21 steroidal glycosides from Periploca sepium. Steroids 2011, 76, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itokawa, H.; Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K. Studies on chemical constituents of antitumor fraction from Periploca sepium Bge. I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1987, 35, 4524–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.L.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.C.; Cai, J.Z.; Hu, Y.J.; Qiu, S.X. Chemical Constituents from Periploca forrestii. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 329–330. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.Y.; Wu, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Li, F.; Chen, B.; Yu, K.; Wang, M.K. C21 steroidal glycosides and oligosaccharides from the root bark of Periploca sepium. Fitoterapia 2017, 118, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.Q.; Shen, W.B.; Zhang, Q.W.; Ye, W.C. A new pregnane and a new diphenylmethane from the root barks of Periploca sepium. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 8, 1581–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.L.; Cai, J.Z.; Huang, R.M.; Jie, H.Y.; Yun, X.; Qiu, S.X. Chemical constituents from Periploca forestti. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 1909–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, X.N.; Wang, W.Z.; Luo, C.H.; Yan, Q.; Tian, M. Chemical constituents from the roots of Periploca sepium with insecticidal activity. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.J.; Zhang, J.W.; Gao, L.; Chen, C.C.; Ji, Z.Q.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. A new pregnane glycoside from the root barks of Periploca sepium. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2014, 49, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.W.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Fluorescence localization and comparative ultrastructural study of periplocoside NW from Periploca sepium Bunge in the midgut of the oriental amyworm, Mythimna separata Walker (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Toxins 2014, 6, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokawa, H.; Xu, J.P.; Takeya, K. Pregnane glycosides from an antitumour fraction of Periploca sepium. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, T.; Bader, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Morelli, I.; Braca, A. Sulfated pregnane glycosides from Periploca graeca. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, K.; Sumii, N.; Satoh, H.; Miyase, T.; Kuroyanagi, M.; Ueno, A. Studies on differentiation inducers. V. Steroid glycosides from Periplocae Radicis Cortex. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1995, 43, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, J. Steroids from the roots of Periploca sepium. Chin. Pharm. J. (BeijingChina) 2009, 44, 968–971. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma, S.; Kawanishi, S.; Shoji, J. Constituents of the Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” IX. Structure of glycoside H2, a patentiator of NGF-mediated nerve fiber outgrowth. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1980, 28, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, O.P.; Khare, A.; Khare, M.P. Structure of calocin. J. Nat. Prod. 1982, 45, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, D.; Khare, M.P.; Khare, A. A pregnane ester glycoside from Periploca calophylla. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, D.; Khare, M.P.; Khare, A. A pregnane ester diglycoside from Periploca calophylla. Indian J. Chem. B 1986, 25B, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, A.; Deepak, D.; Khare, M.P.; Khare, A. A novel pregnane glycoside from Periploca calophylla. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Q.; Zhao, W.M. Five new pregnane glycosides from the root barks of Periploca sepium. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, N.K.; Deepak, D.; Khare, A. Absolute configuration of calogenin and its 20-keto derivative. Indian J. Chem. B 2008, 47B, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, D.; Khare, M.P.; Khare, A. A pregnane ester diglycoside from Periploca calophylla. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 3015–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ou, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Qiao, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, S.H.; Liu, M.Y. A new C21 steroidal saponins from Periplocae Cortex. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 455–457. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma, S.; Kawanishi, S.; Shoji, J.; Shibata, S. Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” I. Studies on the aglycones of steroidal glycosides of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1968, 16, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.L.; Chen, L.; Xu, J.; Qu, W.; Guan, L.; Liu, W.Y.; Akihisa, T.; Feng, F.; Zhang, J. Melanogenesis-inhibitory and antioxidant activities of phenolics from Periploca forrestii. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.L.; Zhou, J.Y. Study on the chemical constituents of Periploca calophylla. Chin. Pharm. J. (BeijingChina) 2003, 38, 497–499. [Google Scholar]
- Askri, M.; Mighri, Z. Medicinal plants of Tunisia. The structure of Periplocadiol, a new elenmane-type sesquiterpene isolated from the roots of Periploca Laevigata. J. Nat. Prod. 1989, 52, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhao, Y.T. Study on chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii Schlecht. Chin. Pharm. J. (BeijingChina) 2011, 46, 823–826. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, G.; Anis, E.; Ahmed, S.; Anis, I.; Ahmed, H.; Malik, A.; Shahzad-ul-Hassan, S.; Choudhary, M.I. Lupene-type triterpenes from Periploca aphylla. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teresa, A.; Leah, N.; Cornelius, W.; Omollo, N.I. Triterpenoids from the stem bark of Periploca linearifolia (Asclepiadaceae). J. Kenya Chem. Soc. 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hichri, F.; Hammouda, O.; Ben Jannet, H.; Mighri, Z.; Abreu, P.J.M. Triterpenoids from the fruit bark of Periploca laevigata growing in Tunisia. J. Soc. Chim. Tunis. 2002, 4, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi, H.; Tomimoto, K. Components of Periploca aphylla. Constituents of Asclepiadaceae plants. Shoyakugaku Zasshi 1971, 25, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.L.; Zhou, J.Y. Study on the chemical constituents of Periploca calophylla (II). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2005, 36, 350–351. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.U.; Riaz, N.; Ahmad, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Malik, A. Phytochemical studies on Periploca aphylla. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2003, 25, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.B.; Yu, S.S. Chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiong, D.D.; Zou, H.; Ma, X.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.J. Chemical constituents from Periploca Radix. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizone, H.; Sakuma, S.; Kawanishi, S.; Shoji, J. Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” VII. On the structure of glycoside E of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1972, 20, 2402–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, S.; Sakuma, S.; Shoji, J. Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” V. On the structure of glycoside H1 of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1972, 20, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.G.; Zhang, X.R.; Peng, S.L.; Liao, X.; Ding, L.S. Chemical constituents from the roots of Biondia Hemsleyana. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2003, 24, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi, S.; Kasai, R.; Sakuma, S.; Shoji, J. Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” VIII. On the structures of new oligosaccharides C1, D2, F1, and F2 of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1977, 25, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Ye, W.C. Perisesaccharides A-E, new oligosaccharides from the root barks of Periploca sepium. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.M.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Liu, L.J. Chemical constituents in the root barks of Periploca sepium. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2011, 19, 521–522. [Google Scholar]
- Long, X.H.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tan, X.H.; Sun, Q.Y. A new oligosaccharide from Periploca calophylla. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Ma, Y.M.; Kong, Y.; Shi, Q.H. A study on chemical constituents of the stem of Periploca sepium. J. Northwest. Univ. 2005, 20, 145–146. [Google Scholar]
- Kawanishi, S.; Sakuma, S.; Okino, H.; Shoji, J. Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Wujiapi.” IV. On the structure of a new acetylbiose from steroidal glycosides of Bei-Wujiapi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1972, 20, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz-ur-Rehman; Malik, A.; Riaz, N.; Nawaz, H.R.; Ahmad, H.; Nawaz, S.A.; Choudhary, M.I. Lipoxygenase inhibitory constituents from Periploca aphylla. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, X.H.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, C.; Gong, X.J.; Chen, H.G. Chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii Schltr. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2009, 40, 708–710. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.M.; Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Feng, C.L. Chemical composition of the Periploca sepium. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2010, 46, 464–465. [Google Scholar]
- Ben nejma, A.; Besbes, M.; Guérineau, V.; Touboul, D.; Ben jannet, H.; Hamza, M.H.A. Isolation and structure elucidation of acetylcholinesterase lipophilic lupeol derivatives inhibitors from the latex of the Tunisian Periploca laevigata. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2767–S2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, X.H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.G.; Gong, X.J.; Zhao, C. Chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 3225–3228. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, O.P.; Khare, A.; Khare, M.P. Triterpenoids of Periploca calophylla. J. Nat. Prod. 1983, 46, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, X.H.; Zhou, X.; Chen, H.G.; Gong, X.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, D.P. Chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii Schltr. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2009, 17, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.M.; Shi, Q.H.; Kong, Y. Chemical constituents of stem bark from Periploca sepium. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.H.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Shen, W.B.; Zhao, S.X. Chemical constituents from root barks of Periploca sepium. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 32, 1300–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Q.H.; Ma, Y.M. Structural analysis on four compounds in root bark from Periploca sepium. J. Northwest. Univ. 2007, 22, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ogundaini, A.O.; Okafor, E.O. Isorhoifolin, a flavonoid glycoside from Periploca nigrescens leaves. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Yang, J.S.; Ren, F.Z.; Liu, G.S.; Zhang, J.; San, B.E.; Li, N. Study on anti-tumor active components of Periploca sepium. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2006, 37, 519–520. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.F.; Chen, J.X.; Du, J.; Qiu, D.W.; Qiu, M.H. Chemical constituents of Periploca forrestii and their cytotoxicity activity. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 3214–3216. [Google Scholar]
- Komissarenko, N.F.; Bagirov, R.B. Chemical study of Periploca graeca. Izv Akad Nauk Azerb Ssr. Biol. 1969, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.N.; Zhao, L.Y.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.; Deng, Y.R. Chemical constituents of the root barks of Periploca sepium. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2010, 32, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.L.; Zhou, J.Y. Isolation and structure elucidation of glycosides in n-butanol extracts from rhizome of Periploca calophylla. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2005, 30, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ishimaru, K.; Sudo, H.; Satake, M.; Shimomura, K. Phenyl glucosides grom a hairy root culture of Swertia japonica. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 3823–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Yu, J.P. Studies on chemical components of Periploca forrestii Schltr. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2008, 27, 560–562. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Xie, W.X. Study on the content of the chlorogenic ccid in water extract of Cortex periplocae at the different times by UV. North. Hortic. 2011, 35, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Komissarenko, N.F.; Khvorost, P.P.; Ivanov, V.D. Coumarins and cardenolides from Periploca sepium. Chem. Nat. Compound. 1983, 19, 98–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Jia, Z.J. Lignan, phenylpropanoid and iridoid glycosides from Pedicularis torta. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyama, T.; Ikawa, T.; Nishibe, S. The constituents of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. II. Isolation and structures of three new lignan glycosides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1985, 33, 3651–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhoud, S.; Aissaoui, H.; Derbre, S.; Mekkiou, R.; Richaume, P.; Benayache, S.; Benayache, F. Flavonoid glycosides from Periploca laevigata (Asclepiadaceae) from Algeria. Pharma. Chem. 2016, 8, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Gang, X.H.; Gong, X.J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, H.G. Glycosides from Periploca forrestii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2010, 35, 610–612. [Google Scholar]
- Al Musayeib, N.M.; Al-Massarani, S.M.; Amina, M.; El Dib, R.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Periplocain A, a new naphthalene derivative from Periploca aphylla growing in Saudi Arabia. Helv. Chim. Acta 2016, 99, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.G.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.Y. Preparative separation of the flavonoid fractions from Periploca forrestii Schltr. ethanol extracts using macroporous resin combined with HPLC analysis and evaluation of their biological activities. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F.; Shan, B.E.; Ren, F.Z.; Shan, T.Q.; Zhao, L.M.; Liu, L.H. Inhibitory effect of Baohuoside I from Cortex Periplocae on esophageal carcinoma cells and its transplantable models in nude mice. Canc. Res. Prev. Treat. 2009, 36, 635–638. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Qiao, S.Y. A diterpenoid quinone from Periploca forrestii. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2010, 35, 1648. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.T.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.P. Separation and identification of chemical compounds in Periploca forrestii Schltr. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2008, 27, 186–188. [Google Scholar]
- Solacolu, T.; Mavrodin, A.; Herrmann, G. The odoriferant principle of the plant Periploca graeca. J. Pharm. Chim. 1935, 22, 546–548. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.X.; Yamashita, T.; Todo, A.; Nitoda, T.; Izumi, M.; Baba, N.; Nakajima, S. Repellent from traditional chinese medicine, Periploca sepium Bunge. Z. Nat. C 2007, 62, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Antitumor and immunoregulatory effects of active components from Cortex Periplocae. Ph.D. Thesis, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Gang, X.H.; Gong, X.J.; Chen, H.G.; Zhou, X. Ceramides of Periploca forrestii. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2014, 20, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- MacKeith, M.H. Pharmacological properties of Periplocin. J. Pharm. 1926, 27, 449–466. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, A.; Vaccari, D. The use of the “greek” Periploca in heart diseases. Rev. Sud-Am. Endocrinol. Immunol. Quim. 1932, 15, 610. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, S.H.; Wang, T.E.; Wang, M.; Ho, K.; Mo, Y. Cardiotonic action of a glucosidal preparation obtained from Periploca forrestii. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1964, 11, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.X.; Wang, D.C.; He, G.B. Cardiotonic action of Periploca calophylla (Wight.) Falconer. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1980, 15, 245–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ji, Y.S.; Han, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y. Effect of periplocin on left ventricular structure and function in chronic heart failure rats by color doppler-echocardiography. J. Tianjin Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. (2006-) 2008, 27, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Y. Effect of Periplocin on expression of myocardial PLB and SERCA mRNA in rats with chronic heart failure. Jiangsu J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (2002-) 2009, 41, 71–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Gao, X.M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Hu, L.M.; Zhang, B.L. Gene expression profiling of the proliferative effect of periplocin on mouse cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2010, 16, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.T.; Zhou, K.; Deng, Y.R. Comparison of the effect of cardiac glycosides in Periplocae Cortex on isolated heart in rats. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2011, 29, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.J.; Dai, Y.L.; Yang, Y.M.; Li, C.X.; Wang, Z.G.; Luo, Y.H.; Liu, X.B. Experimental study on the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of Periploca forrestii Schlechter. Yunnan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2008, 29, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.R.; Zhang, X.R.; Sun, L.; Qi, C.H. Anti-inflammatory and immun modulation activities from active fraction of Periploca forrestii Schltr. Her. Med. 2010, 29, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.B.; Xi, G.P.; Yu, J.P. Anti-inflammatory effects and mechanism of emulsion of volatile oil from Periploca forrestii. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2012, 18, 252–255. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dong, Y.X.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.J.; Ni, J.M. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol fraction from Periploca forrestii Schltr. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2017, 23, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, N.; Tir, M.; Feriani, A.; Yahia, Y.; Allagui, M.S.; Saadaoui, E.; El Cafsi, M.; Nasri, N. Potential health advantages of Periploca laevigata: Preliminary phytochemical analysis and evaluation of in vitro antioxidant capacity and assessment of hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X. Pharmacology of Modern Chinese Medicine; Tianjin Science and Technology Press: Tianjing, China, 1997; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, W.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhao, A.G. Effect of periplogenin on mast cell degranulation and histamine release. China Pharm. (ChongqingChina) 2008, 19, 166–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Zhu, Y.N.; Feng, J.Q.; Chen, H.J.; Zhang, R.J.; Ni, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Hou, L.F.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Periplocoside A, a pregnane glycoside from Periploca sepium Bge, prevents Concanavalin A-induced mice hepatitis through inhibiting NKT-derived inflammatory cytokine productions. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.N.; Zhao, W.M.; Yang, Y.F.; Liu, Q.F.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, J.; Ni, J.; Fu, Y.F.; Zhong, X.G.; Tang, W. Periplocoside E, and effective compound from Periploca sepium Bge, inhibited T cell activation in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharm. Exp. 2005, 316, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.F.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.N.; Zeng, B.H.; Shi, S.H.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zhong, X.G. Effects of an immunosuppressive active component of Periplocae Cortex (Periploca sepium Bge.) on positive selection of thymocytes in vitro. J. Tradit. Chin. Med Sci. 2018, 5, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.J.; Tang, W.; Zhao, W.M.; Yang, Y.F.; Zuo, J.P. Periplocoside A prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing IL-17 production and inhibits differentiation of Th17 cells. Acta Pharm. Sin 2009, 30, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, B.E.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, R.N.; Li, Q.L.; Liu, J.H.; Li, Q.M.; Li, R.Q. Effects on differentiation and maturation of dendritic cells by lupane acetate of Cortex Periplocae. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 22, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, B.E.; Zhao, L.M.; Ai, J.; He, L.X.; Chen, S.H.; Ding, C.Y. Effect of Cortex Periplocae lupane acetate on immunoregulation of human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2008, 39, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, B.E.; Li, Q.M.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, R.N.; Ai, J. Immunoregulatory effects of Periplocin from Cortex Periplocae in tumor-bearing mice. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 25, 887–890. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.; Qi, C.H.; Zhou, W.X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Qiao, S.Y.; Sun, L. Cellular immunosuppression effect of polysaccharide HGT-5A from Periploca forrestii Schlechter and its possible active components. Chin. J. Pharm. Toxicol. 2011, 25, 538–542. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.G.; Zhou, X.; Deng, Q.F.; Hu, E.M.; Zhao, C.; Gong, X.J. Optimized microwave-assistant extraction combined ultrasonic pretreatment of flavonoids from Periploca forrestii Schltr. and evaluation of its anti-allergic activity. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokiwa, T.; Harada, K.; Matsumura, T.; Tukiyama, T. Oriental medicinal herb, Periploca sepium, extract inhibits growth and IL-6 production of human synovial fibroblast-like cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, B.J.; Liang, J. The mechanism of Periploca forrestii by regulating the inflammatory response on CIA rat model. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2018, 42, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.J.; Luo, C.L.; Guo, G.; Qiu, D.W.; Wang, W.Q. Effects and molecular mechanism of Periploca forrestii against rheumatoid arthritis. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2011, 17, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Ma, W.K.; Liu, Z.Q.; An, Y.; Yao, X.M.; Tang, Z.Y. Effects of Periploca forrestii ethanol extract (PFE) on proliferation, COX-2 expression, and PG2 expression of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from patients. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2015, 26, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.S.; Ke, X.; Qu, W.; Zhang, J.; Feng, F.; Liu, W. The therapeutic effects of Periploca forrestii Schltr. Stem extracts on collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting the activation of Src/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 202, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.M.; Zhao, X.L.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Q.L.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, H. Studies on the effective components of Periploca forrestii for anti-rheumatoid arthritis. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 649–651. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Li, M.H.; He, Q.H.; Yang, X.P.; Ruan, F.; Sun, G.C. Periploca forrestii saponin ameliorates murine CFA-induced arthritis by suppressing cytokine production. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 7941684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Sun, X.; Xing, C.C.; Zeng, L.T.; Sun, G.C. Periploca forrestii saponin ameliorates CIA via suppressing proinflammatory cytokines and nuclear factor kappa-B pathways. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, X.; He, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Dong, L.; Ma, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, G.C.; Zheng, J.; et al. In vivo and in vitro anti-arthritic effects of cardenolide-rich and caffeoylquinic acid-rich fractions of Periploca forrestii. Molecules 2018, 23, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Lu, G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, G.S.; Shan, B.E. Periplocin of Cortex Periplocae inhibits Stat3 signaling and induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7721. Acta Acad. Med. Mil. Tert. 2008, 30, 1448–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, B.E. Periplocin extracted from Cortex Periplocae induces apoptosis of SW480 cells through inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Chin. J. Cancer (1982–2010) 2009, 28, 456–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Shan, B.E.; Liu, J.H. Effects of Periplocin from Cortex Periplocae on apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells and expression of survivin. Her. Med. 2015, 34, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Shan, B.E.; Zhang, C. Effects of periplocin from Cortex Periplocae on cell cycle of MCF-7 cells and expression of p21WAFI/CIPI. Canc. Res. Prev. Treat. 2010, 37, 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.J.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Q.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Gou, L.T.; Yang, J.L.; Luo, F. Periplocin inhibits growth of lung cancer in vitro and in vivo by blocking AKT/ERK signaling pathways. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.F.; Lu, I.H.; Tseng, H.W.; Sun, C.Y.; Lin, L.T.; Kuo, Z.K.; Pan, I.H.; Ko, C.H. Antitumor effect of Periplocin in Trail-resistant human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of IAPs. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 958025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohberger, B.; Wagner, S.; Wohlmuther, J.; Kaltenegger, H.; Stuendl, N.; Leithner, A.; Rinner, B.; Kunert, O.; Bauer, R.; Kretschmer, N. Periplocin, the most anti-proliferative constituent of Periploca sepium, specifically kills liposarcoma cells by death receptor mediated apoptosis. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloise, E.; Braca, A.; De Tommasi, N.; Belisario, M.A. Pro-apoptotic and cytostatic activity of naturally occurring cardenolides. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2009, 64, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martey, O.N.K.; He, X.; Xing, H.Y.; Deng, F.C.; Feng, S.; Li, C.; Shi, X.Y. Periplocymarin is a potential natural compound for drug development: Highly permeable with absence of P-glycoprotein efflux and cytochrome P450 inhibitions. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Liu, H.Z.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Shan, B.E. Effect of Baohuoside-I on proliferat ion and cell cycle of human esophageal carcinoma cell Eca-109. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2009, 40, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Lu, A.; Liu, X.X.; Sang, M.X.; Shan, B.E.; Meng, F.R.; Cao, Q.; Ji, X. The flavonoid Baohuoside-I inhibits cell growth and downregulates survivin and cyclin D1 expression in esophageal carcinoma via β-catenin-dependent signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Lu, A.; Meng, F.R.; Cao, Q.; Shan, B.E. Inhibitory effects of lupeal acetate of Cortex periplocae on N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced rat esophageal tumorigenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.E.; Zhao, L.M.; He, L.X.; Di, H.Q.; Ren, F.Z. Effects of Periplocin on proliferation of human esophageal carcinoma cell TE-13 and its relation with Rb expression. Carcinog. Teratog. Mutagen. 2008, 20, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.M.; Ai, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, L.N.; Liu, L.H.; Wang, L.; Shan, B.E. Periplocin (a sort of ethanol from Cortexperiplocae) induces apoptosis of esophageal carcinoma cells by influencing expression of related genes. Tumor 2009, 29, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, X.H.; Shan, X.L.; Shan, B.E.; Chen, Y.M.; Ren, F.Z.; Liu, X.X. Ethylacetate extract from Cortex periplocae induced apoptosis of human esophageal carcinoma cellline TE-13. Tumor 2010, 30, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, C.P. Anti-tumor activity of extract from Periploca forrestii. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2011, 17, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.X.; Shan, B.E. The study of Cortex Periplocae extract on the differentiation of K562 cells. Carcinog. Teratog. Mutagen. 2008, 20, 449–450, 455. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, B.E.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, J. Inductive ef fect of Cortex Periplocae extract on apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells BGC-823. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2005, 36, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Hichri, F.; Jannet, H.B.; Cheriaa, J.; Jegham, S.; Mighri, Z. Antibacterial activities of a few prepared derivatives of oleanolic acid and of other natural triterpenic compounds. C. R. Chim. 2003, 6, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.B.; Xi, G.P.; Yu, J.P.; Ji, Y. Chemical constituents of petroleum ether extracts from Periploca forrestii and its antimicrobial effects. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2013, 24, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Hajji, M.; Masmoudi, O.; Souissi, N.; Triki, Y.; Kammoun, S.; Nasri, M. Chemical composition, angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the essential oil from Periploca laevigata root barks. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Dra, L.; Ait Sidi Brahim, M.; Boualy, B.; Aghraz, A.; Barakate, M.; Oubaassine, S.; Markouk, M.; Larhsini, M. Chemical composition, antioxidant and evidence antimicrobial synergistic effects of Periploca laevigata essential oil with conventional antibiotics. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, J.L.; Gao, H.F.; Zhou, L.A.; Liu, Z.L.; Chen, Y.Q.; Sui, P. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the root bark essential oil of Periploca sepium and its main component. Molecules 2010, 15, 5807–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, M.S.; Lee, H.S. Antimicrobial agents of 4-methoxysalicylaldehyde isolated from Periploca sepium oil against foodborne bacteria: Structure-activity relationship. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2018, 61, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Ons, M.; Yosra, E.-T.; Rayda, S.; Neji, G.; Moncef, N. Chemical composition and antioxidant and radical-scavenging activities of Periploca laevigata root bark extracts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.F.; Liu, Z.K.; Zhao, M.Q.; Liu, P.F. Purification, characterization, and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides isolated from Cortex Periplocae. Molecules 2017, 22, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, M.; Hamdi, M.; Sellimi, S.; Ksouda, G.; Laouer, H.; Li, S.; Nasri, M. Structural characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of a novel polysaccharide from Periploca laevigata root barks. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 206, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athmouni, K.; Belhaj, D.; Chawech, R.; Jarraya, R.; El Feki, A.; Ayadi, H. Characterization of polysaccharides isolated from Periploca angustifolia and its antioxidant activity and renoprotective potential against cadmium induced toxicity in HEK293 cells and rat kidney. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athmouni, K.; Belhaj, D.; El Feki, A.; Ayadi, H. Optimization, antioxidant properties and GC-MS analysis of Periploca angustifolia polysaccharides and chelation therapy on cadmium-induced toxicity in human HepG2 cells line and rat liver. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athmouni, K.; Belhaj, D.; Mkadmini Hammi, K.; El Feki, A.; Ayadi, H. Phenolic compounds analysis, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective effects of Periploca angustifolia extract on cadmium-induced oxidative damage in HepG2 cell line and rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khan, M.R.; Shah, S.A.; Batool, R.; Maryam, S.; Majid, M.; Zahra, Z. Protective aptitude of Periploca hydaspidis Falc against CCl4 induced hepatotoxicity in experimental rats. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 105, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, F.; Maqbool, Q.; Nazar, M.; Jabeen, N.; Hussain, S.Z.; Anwaar, S.; Mehmood, N.; Sheikh, M.S.; Hussain, T.; Iftikhar, S. Green synthesised zinc oxide nanostructures through Periploca aphylla extract shows tremendous antibacterial potential against multidrug resistant pathogens. Iet Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 11, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.S.; Qiao, X.W.; Wang, J.; Qin, S. Effects of the crude extracts from Periploca sepium Bunge on the bioactivity of imported cabbage worm Pieris rapae. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2006, 14, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.S.; Qiao, X.W.; Wang, J.; Qin, S. Study on antifeedant and insecticidal activities of extracts and fractions from Periploca sepium Bunge against Plutella xylostella (L.). Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 6, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Musayeib, N.M.; Mothana, R.A.; Al-Massarani, S.; Matheeussen, A.; Cos, P.; Maes, L. Study of the in vitro antiplasmodial, antileishmanial and antitrypanosomal activities of medicinal plants from Saudi Arabia. Molecules 2012, 17, 11379–11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.H.; Ma, Y.M.; Qin, H.Q. Chemical components and insecticidal activity of essential oil in Periploca sepium root bark to Schizaphis graminum. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2006, 26, 620–623. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, S.S.; Jiang, G.H.; Liu, W.L.; Liu, Z.L. Insecticidal activity of the root bark essential oil of Periploca sepium Bunge and its main component. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Cho, K.; Lee, H. Food protective effects of Periploca sepium oil and its active component against stored food mites. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zeng, X.N. Effects of periplocoside X on midgut cells and digestive enzymes activity of the soldiers of red imported fire ant. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2013, 93, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Shi, B.J.; Hu, Z.N. The insecticidal activity of Periplocoside NW. Chin. Bull. Entomol. 2008, 45, 950–952. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.X.; Shi, B.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J.; Wu, W. Histopathological effects and immunolocalization of Periplocoside NW from Periploca sepium Bunge on the midgut epithelium of Mythimna separata Walker larvae. Pestic Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 115, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.J.; Gao, L.T.; Ji, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.W.; Wu, W.J.; Hu, Z.N. Isolation of the insecticidal ingredients from Periploca sepium. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2012, 14, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.C.; Gao, L.T.; Shi, B.U.; Wen, W.D.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Effects of Periplocosides P and E from Periploca sepium on the proteinase activities in the midgut of larvae of Mythimna separata and Agrotis ypsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 412–419. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hu, Z.N. Effects of Periplocin P and E from Periploca sepium on activities of three detoxification enzymes in midgut of Mythimna separata and Agrotis ypsilon (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2016, 25, 939–944. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Qi, Z.J.; Qi, M.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Effects of Periplocoside P from Periploca sepium on the midgut transmembrane potential of Mythimna separata Larvae. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.X.; Li, Y.K.; Chen, X.T.; Wei, Q.S.; Wu, W.J.; Hu, Z.N. Comparative proteomic analysis of the effect of Periplocoside P from Periploca sepium on brush border membrane vesicles in midgut epithelium of Mythimna separata Larvae. Toxins 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.X.; He, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yan, X.F.; Zhang, J.W.; Hu, Z.N.; Wu, W.J. Isolation of the binding protein of Periplocoside E from BBMVs in midgut of the oriental amyworm Mythimna separata walker (lepidoptera: Noctuidae) through affinity chromatography. Toxins 2016, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Y.; Gong, L.L.; Dang, R.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Yang, Z.C. Experimental study on the treatment of nerve injury caused by Pristionchus pacificus by Periploca forrestii Schltr. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2012, 23, 2758–2759. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, A.; Muhammad, S.; Razaque, G.; Qadir, A.; Younis, M.; Ahmad, N.; Baloch, I.; Mustafa, G. Studies on neuropharmacological and analgesic effects of Periploca aphylla extract in mice. Pure Appl. Biol. 2016, 5, 1207–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.S.; Ke, X.; Sun, C.L.; Huang, X.X.; Jiang, P.; Feng, F.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhang, J. Chemical profiling and the potential active constituents responsible for wound healing in Periploca forrestii Schltr. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, P.; Li, J.S.; Xie, Z.J.; Xu, Y.H.; Qu, W.; Feng, F.; Liu, W.Y. Periplocin promotes wound healing through the activation of Src/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways mediated by Na/K-ATPase. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, W.Y.; Endale Gurmu, A.; Wubneh, Z.B. Antimalarial activity of stem bark of Periploca linearifolia during early and established plasmodium infection in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 4169397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Bao, Z.Y.; Huang, W.; Lv, L.L.; Zhang, Z.P.; Ren, H.Y. Experimental comparison study on mice’s acute toxicity of different composition in Cortex Periplocae. Chin. J. Pharm. 2010, 7, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, X.L.; Bao, Z.Y.; Sun, R. Experimental study on chronic toxicity in rats caused by different components of Cortex Periplocae radicis. Chin. J. Pharm. 2012, 9, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.T.; Sun, D.; Bi, B.; Zhao, C.F.; Zhou, K. The changed characteristics of electrocardiogram in guinea pigs’ poisoned by Cortex Periploca. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2010, 21, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.Y.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.N.; Sun, R. Experimental study on the “dose-time-toxicity” relationship of hepatotoxicity induced by different components from Cortex Periplocae in mice. Chin. J. Pharm. 2012, 9, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Huang, W.; Bao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. The research of oxidative damage mechanism in hepatical toxical injury caused by different components from Cortex Periplocae in mice. Chin. J. Pharm. 2012, 9, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.T.; Bi, B.; Zhou, K.; Deng, Y.R. Toxicity of periplocin in single administration. J. Health Toxicol. 2010, 24, 461–463. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; MA, Z.H.; Sun, D.; Chen, J.T.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y. Study on correlation of the content of periplocin with acute toxicity of Cortex Periplocae. Chin. J. Pharm. 2015, 12, 261–263. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, L.X.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Che, S.; Liu, W.T.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.H. Determination and pharmacokinetics of periplocin in rat plasma by LC-MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Bo, F.; Tu, Y.R.; Azietaku, J.T.; Dou, T.; Ouyang, H.Z.; Chang, Y.X.; Liu, H.; Gao, X.M. A validated LC-MS/MS assay for the simultaneous determination of periplocin and its two metabolites, periplocymarin and periplogenin in rat plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 114, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Zhang, D.D.; Tang, Z.D.; Sun, M.; Azietaku, J.T.; Ouyang, H.Z.; Chang, Y.X.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Gao, X.M. Tissue distribution study of periplocin and its two metabolites in rats by a validated LC-MS/MS method. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Name | Ref. |
|---|---|
| P. sepium Bunge | [2,7] |
| P. forrestii Schlechter | [2] |
| P. graeca L | [7] |
| P. calophylla (Wight) Falconer | [2,7] |
| P. aphylla Decne | [7] |
| P. nigrescens Afz. | [7] |
| P. linearifolia, Quart.-Dill. and A. Rich | [7] |
| P. laevigata Ait | [7] |
| P. hydaspidis Falc | [7] |
| P. angustifolia Labill | [7] |
| P. somaliensis Browicz | [10] |
| P. omeiensis Z. Y. Zhu | [8] |
| P. chrysantha D. S. Yao, X. C. Chen et J. W. Ren | [9] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardenolide-type steroids | ||||
| 1 | periplocin | P. graeca P. omeiensis P. calophylla P. forrestii P. sepium | bark whole plant stems whole plant cortex | [11] [8] [12] [13] [14] |
| 2 | periplogenin | P. graeca P. calophylla P. forrestii P. sepium | bark, stems stems whole plant cortex | [11,15] [12] [13] [16] |
| 3 | periplocymarin | P. graeca P. sepium P. forrestii | stalks and bark cortex whole plant | [15,17] [14] [13] |
| 4 | biondianoside A | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 5 | periplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 6 | periplogenin 3-[O-β-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-sarmentopyranoside] | P. sepium | root bark | [18] |
| 7 | periplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-β-D-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [19,20] |
| 8 | periplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-β-digitaloside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 9 | periplogenin 3-O-β-d-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 10 | 7β-hydroxy-periplogenin | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 11 | 7-hydroxyl-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 12 | 7-hydroxyl-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 13 | 7-hydroxyl-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-β-d-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 14 | 8β-hydroxy-periplogenin | P. forrestii | rhizome, stems | [19,21] |
| 15 | 8-hydroxyl-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 16 | periforoside G | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 17 | periforoside H | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 18 | 7,8-dihydroxyl-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 19 | periforgenin C | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 20 | periforoside F | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 21 | 7,8-epoxy-periplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| 22 | periploforgeside A | P. forrestii | unknown | [22] |
| 23 | periploforgeside B | P. forrestii | unknown | [22] |
| 24 | echubioside | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 25 | xysmalogenin | P. sepium | root bark | [23] |
| 26 | 3β,5β-dihydroxy-14-en-card-20(22)-enolide | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 27 | periforoside E | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 28 | strophanthidin | P. nigrescens | branches | [24,25] |
| 29 | strophanthidol | P. nigrescens | branches | [24] |
| 30 | strophanthidin-β-d-glucoside | P. nigrescens | branches | [26] |
| 31 | strophadogenin | P. nigrescens | branches | [25] |
| 32 | convallatoxin | P. nigrescens | branches | [25] |
| 33 | 16β-acetoxystrophanthidin | P. nigrescens | branches | [27] |
| 34 | 3-O-rhamnosyl-16β-acetoxystrophanthidin | P. nigrescens | branches | [27] |
| 35 | 16-dehydrostrophanthidin | P. nigrescens | branches | [27] |
| 36 | 16-dehydrostrophanthidol | P. nigrescens | branches | [27] |
| 37 | 3-O-digitoxosyl-16-dehydrostrophanthidin | P. nigrescens | branches | [27] |
| 38 | alloperiplogenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 39 | alloperiplogenin | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 40 | biondianoside B | P. graeca | stems | [15] |
| 41 | periforgenin A | P. forrestii | rhizome, stems | [19] |
| 42 | periforoside I | P. forrestii | rhizome, stems | [19,28] |
| 43 | periforgenin A 3-O-β-cymaropyranoside | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 44 | periforgenin A-3-O-β-digitoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [30] |
| 45 | periforoside D | P. forrestii | stems | [19] |
| 46 | periforgenin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-β-d-glucopyranosyl-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [20] |
| C21 pregnane-type steroids | ||||
| 47 | periploside A (periplocoside E) | P. sepium P. calophylla | root bark stems | [31,32,33,34,35] [12] |
| 48 | periploside B | P. sepium | root bark | [32] |
| 49 | periploside C (periplocoside A) | P. sepium | root bark | [32,33,34,35,36] |
| 50 | periploside D (periplocoside D) | P. sepium | root bark | [31,33,34,35] |
| 51 | periploside E (periperoxide A) | P. sepium | root bark | [33,34,35] |
| 52 | periploside F (periplocoside F) | P. sepium | root bark | [33,34,35,37] |
| 53 | periploside G (periperoxide B) | P. forrestii | root bark | [33,34,35] |
| 54 | periploside H (periperoxide E) | P. forrestii | root bark | [33,34,35] |
| 55 | periploside I (periperoxide C) | P. forrestii | root bark | [33,34,35] |
| 56 | periploside J (periplocoside J) | P. sepium | root bark | [34,35,37] |
| 57 | periploside K (periplocoside K) | P. sepium | root bark | [34,35,37] |
| 58 | periploside L (periperoxide D) | P. forrestii | root bark | [33,34,35] |
| 59 | periploside M (periplocoside B) | P. sepium | root bark | [34,35,36] |
| 60 | periploside N (periplocoside C) | P. sepium | root bark | [34,35,36] |
| 61 | periploside O | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 62 | periploside P | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 63 | periploside Q | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 64 | periploside R | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 65 | periploside S | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 66 | periploside T | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 67 | periploside U | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 68 | periploside V | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 69 | 3-O-formyl-periploside A | P. sepium | root bark | [38] |
| 70 | periploside W | P. chrysantha | root bark | [39] |
| 71 | periploside X | P. chrysantha | root bark | [39] |
| 72 | periploside Y | P. chrysantha | root bark | [39] |
| 73 | 3-O-formyl-periploside F | P. chrysantha | root bark | [39] |
| 74 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,17α,20(S)-triol | P. sepium | root bark | [31,40] |
| 75 | periplocogenin | P. sepium | root bark | [41] |
| 76 | periplocoside L | P. sepium P. forrestii | root bark rhizome | [31] [42] |
| 77 | periplocoside M periploside B | P. sepium P. forrestii P. calophylla P. sepium | root bark stems stems root bark | [31,43] [30] [12] [44] |
| 78 | periplocoside N | P. sepium P. forrestii | root bark root bark | [31] [45] |
| 79 | periplocoside O | P. sepium | root bark | [37] |
| 80 | periplocoside X | P. sepium | roots | [46] |
| 81 | periplocoside P | P. sepium | root bark | [47] |
| 82 | periplocoside NW | P. sepium | root bark | [48] |
| 83 | (3β,20S)-pregn-5-ene-3,17,20-triol 20-[O-β-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-canaropyranoside] | P. sepium | root bark | [18] |
| 84 | periseoside A | P. sepium | root bark | [40] |
| 85 | periseoside B | P. sepium | root bark | [40] |
| 86 | perisepiumoside I | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| 87 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,20(S)-diol | P. sepium | root bark | [44,49] |
| 88 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,20(S)-diol 3-O-[β-d-digitalopyranosyl (1→4)β-d-cymaropyranoside] 20-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl (1→2)-β-d-digitalopyranoside] | P. sepium P. graeca | root bark small branches | [49] [50] |
| 89 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,20(S)-diol 3-O-[2-O-acetyl-β-d-digitalopyranosyl (1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside] 20-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→2)-β-d-digitalopyranoside] | P. sepium | root bark | [49] |
| 90 | plocoside A | P. sepium | root bark | [49,51] |
| 91 | biondianoside C | P. sepium | root bark | [52] |
| 92 | biondianoside D | P. sepium | root bark | [52] |
| 93 | periseoside C | P. sepium | root bark | [40] |
| 94 | periseoside D | P. sepium | root bark | [40] |
| 95 | 5-pregnen-3β,20β-diol glucoside | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| 96 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,20(R)-diol 3-O-monoacetate | P. sepium | root bark | [31] |
| 97 | glycoside H2 | P. sepium P. graeca | cortex, root bark small branches | [40,49,53] [50] |
| 98 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,16α,20(S)-triol | P. sepium | root bark | [16,49] |
| 99 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,16α,20(S)-triol 20-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→2)-β-d-digitalopyranoside | P. sepium | root bark | [49,52] |
| 100 | plocoside B | P. sepium | root bark | [40,51] |
| 101 | periseoside E | P. sepium | root bark | [40] |
| 102 | 16α-[(6-O-sulfo-β-d-glucopyranosyl)oxy] pregn-5-en-20-ol-3β-yl O-(2-O-acetyl-β-d-digitalopyranosyl)-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 103 | 16α-[(6-O-sulfo-β-d-glucopyranosyl) oxy] pregn-5-en-20-ol-3β-yl O-β-d-oleandropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-oleandropyranoside | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 104 | 16α-[(6-O-sulfo-β-d-glucopyranosyl)oxy] pregn-5-en-20-ol-3β-yl O-β-d-oleandropyranoside | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 105 | 16α-[(6-O-sulfo-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy] pregn-5-ene-3β,20-diol | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 106 | 20-O-[(β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-d-digitalopyranosyl)oxy] pregn-5-en-16β-ol-3β-yl O-β-d-digitalopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 107 | 3β,16β,20-trihydroxy-pregn-5-en-3-O-2,4-diacetyl-β-digitalopyranosyl-(1→4)-O-β-cymaropyranosyl-20-O-β-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-digitalopyranoside | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 108 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,16β,20(R)-triol | P. sepium | root bark | [49] |
| 109 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,16β,20(R)-triol 3-O-[2-O-acetyl-β-d-digitalopyranosyl (1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside] 20-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→2)-β-d-digitalopyranoside] | P. sepium P. graeca | root bark small branches | [49] [50] |
| 110 | Δ5-pregnene-3β,16β,20(R)-triol 20-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl (l→2)-β-d-digitalopyranoside | P. sepium | root bark | [49] |
| 111 | calocin | P. calophylla | twigs | [54] |
| 112 | plocin | P. calophylla | twigs | [55] |
| 113 | plocigenin | P. calophylla | twigs | [55] |
| 114 | locin | P. calophylla | twigs | [56] |
| 115 | calocinin | P. calophylla | twigs | [57] |
| 116 | calogenin 3-O-β-d-digitalopyranoside-20-O-β-d-canaropyranoside | P. graeca | small branches | [50] |
| 117 | (3β,14β)-3,14-dihydroxy-21-methoxypregn-5-en-20-one | P. sepium | root bark | [44] |
| 118 | perisepiumosides E | P. sepium | root bark | [58] |
| 119 | (3β,14β,17α)-3,14,17-trihydroxy-21-methoxypregn-5-en-20-one 3-[O-β-oleandropyranosyl-(1→4)-O-β-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-cymaropyranoside] | P. sepium | root bark | [18] |
| 120 | (3β,14β,17α)-3,14,17-trihydroxy-21-methoxypregn-5-en-20-one | P. sepium | root bark | [18] |
| 121 | perisepiumoside G | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| 122 | perisepiumoside H | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| 123 | calogenin | P. calophylla | unknown | [59] |
| 124 | plocinine | P. calophylla | twigs | [60] |
| 125 | 21-O-methyl-5-pregnene-3β,14β,17β,20,21-pentaol | P. sepium | root bark | [23] |
| 126 | perisepiumosides A | P. sepium | root bark | [58] |
| 127 | perisepiumosides B | P. sepium | root bark | [58] |
| 128 | perisepiumoside F | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| 129 | (3β,14β,17β)-3,14,17-trihydroxy-21-methoxypregn-5-en-20-one | P. sepium | root bark | [23] |
| 130 | perisepiumosides C | P. sepium | root bark | [58] |
| 131 | perisepiumosides D | P. sepium | root bark | [58] |
| 132 | 21-O-methyl-Δ5-pregnene-3β,14β,17β,21-tetraol-20-one-3-O-β-d-oleandropyranosyl(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranosyl (periplocoside P) | P. sepium | root bark | [61] |
| 133 | 21-O-methyl-5,14-pregndiene-3β,17β,20,21-tetraol | P. sepium | root bark | [23] |
| 134 | Δ5,16-pregnadiene-3β,20α-diol diacetate | P. sepium | root bark | [62] |
| 135 | neridienone A | P. sepium | root bark | [41] |
| 136 | 5α-pregn-6-ene-3β,17α,20(S)-triol-20-O-β-d-digtoxopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 137 | teikagenin-3-O-β-d-dignitalosyl-20-O-β-d-canaroside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 138 | 3-O-β-d-digitalosyl-3β,17α,20α-tihydroxy-5α-pregn-6-ene | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| Phytosterol-type steroids | ||||
| 139 | β-sitosterol | P. omeiensis P. calophylla P. laevigata P. forrestii P. aphylla P. linearifolia | whole plant root bark roots stems whole plant stem bark | [8] [64] [65] [66] [67] [68] |
| 140 | β-daucosterol | P. omeiensis P. calophylla P. forrestii P. sepium P. laevigata P. aphylla | whole plant root bark root bark root bark fruit bark above ground part | [8] [64] [21] [62] [69] [70] |
| 141 | (6′-O-palmitoyl)-sitosterol-3-O-β-d-glucoside | P. calophylla | root bark | [71] |
| 142 | stigmasterol | P. aphylla | unknown | [72] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 143 | cymarose | P. calophylla | twigs | [55] |
| 144 | β-d-glucopyranose | P. laevigata | roots | [65] |
| 145 | α-d-glucopyranose | P. laevigata | roots | [65] |
| 146 | sucrose | P. sepium | stems | [82] |
| 147 | 4-O-(2-O-acetyl-β-d-digitalopyranosyl)-d-cymaropyranose | P. sepium | cortex, root bark | [49,83] |
| 148 | methyl 4-O-(2-O-acetyl-β-d-digitalopyranosyl)-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. sepium | cortex | [83] |
| 149 | methyl β-d-digitalopyranosyl(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranoside | P. sepium | root bark | [49] |
| 150 | oligosaccharide C1 | P. sepium | cortex | [78] |
| 151 | oligosaccharide D2 | P. sepium | cortex, root bark | [33,78] |
| 152 | oligosaccharide F1 | P. sepium | cortex | [78] |
| 153 | oligosaccharide F2 | P. sepium | cortex, root bark | [33,78] |
| 154 | perisaccharide A | P. sepium | root bark | [33] |
| 155 | perisaccharide B | P. sepium P. calophylla | root bark stems | [33,43] [81] |
| 156 | perisaccharide C | P. sepium | root bark | [33] |
| 157 | perifosaccharide A | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 158 | perifosaccharide B | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 159 | perifosaccharide C | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 160 | perifosaccharide D | P. forrestii | roots | [29] |
| 161 | perisesaccharide A | P. sepium | root bark | [79] |
| 162 | perisesaccharide B | P. sepium | root bark | [43,79] |
| 163 | perisesaccharide C | P. sepium | root bark | [43,79] |
| 164 | perisesaccharide D | P. sepium | root bark | [79] |
| 165 | perisesaccharide E | P. sepium | root bark | [79] |
| 166 | perisesaccharide F | P. sepium | root bark | [80] |
| 167 | 4-O-acetyl-β-cymaropyranosyl(1→4)-O-β-d-cymaropyranosyl(1→4)-O-β-d-canaropyranosyl(1→4)-O-β-d-cymaropyranosy(l→4)-O-oleandronic acid-δ-lactone | P. calophylla | stems | [81] |
| 168 | 2-O-acetyl-β-D-digitalopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranosyl- (1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-cymaropyranosyl- (1→4)-β-d-oleandronic-δ-lactone | P. sepium | root bark | [43] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 169 | loliolide | P. forrestii | whole plant | [73] |
| 170 | periplocadiol | P. laevigata | roots | [65] |
| 171 | 2α,6α-dihydroxy-5-[(E)-3′-hydroxy-3′-methyl-1′-butenyl]-6-methyl-4-cyclohexen-3-one | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 172 | oleanolic acid | P. forrestii P. sepium P. laevigata P. aphylla | unknown leaves roots above ground part | [85] [86] [65] [70] |
| 173 | hederagenin | P. omeiensis P. forrestii | whole plant whole plant | [8] [13] |
| 174 | 2α,3β,5,24-tetrahydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid | P. forrestii | stems | [66] |
| 175 | masilinic acid | P. laevigata P. aphylla | fruit bark above ground part | [69] [70] |
| 176 | arjunolic acid | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 177 | 12α-hydroxy-δ-lactone of oleanolic acid | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 178 | 11α,12α-Epoxy-3β-hydroxy-olean-13β,28-olide | P. somaliensis | fruits | [10] |
| 179 | 3-O-acety loleanolic acid | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 180 | 3β-hydroxy-11,13(18)-diene-olean-28-oicacid | P. forrestii | unknown | [85] |
| 181 | β-amyrin | P. calophylla P. laevigata P. forrestii P. sepium P. linearifolia | twigs roots unknown stem bark stem bark | [89] [65] [90] [91] [68] |
| 182 | β-amyrin acetate | P. forrestii P. sepium | unknown root bark, stem bark | [90] [92,93] |
| 183 | P1 | P. calophylla | twigs | [89] |
| 184 | P2 | P. calophylla | twigs | [89] |
| 185 | P3 | P. calophylla | twigs | [89] |
| 186 | ursolic acid | P. omeiensis P. calophylla P. forrestii P. somaliensis P. aphylla P. nigrescens | whole plant rhizome rhizome fruits unknown leaves | [8] [64] [21] [10] [72] [94] |
| 187 | 2α,3β-dihydroxy ursolic acid | P. forrestii P. calophylla P. aphylla | stems stems unknown | [88] [64] [72] |
| 188 | asiatic acid | P. laevigata P. calophylla P. forrestii P. aphylla | roots stems stems unknown | [65] [12] [30] [72] |
| 189 | 12-ursen-3β-acetyl-11-one | P. forrestii | unknown | [85] |
| 190 | jacoumaric acid | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 191 | 14-ursen-3-ol-1-one | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 192 | taraxasterol | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 193 | α-amyrin | P. forrestii P. sepium P. laevigata | unknown root bark roots | [90] [92] [65] |
| 194 | 27-hydroxy-α-amyrin | P. omeiensis P. forrestii | whole plant unknown | [8] [90] |
| 195 | α-amyrin acetate | P. calophylla P. forrestii P. sepium | twigs unknown root bark | [89] [90] [95] |
| 196 | 3β-hydroxy-urs-11-en-13β,28-olide | P. somaliensis | fruits | [10] |
| 197 | lupeol | P. laevigata P. aphylla | roots, latex above ground part | [65,87] [70] |
| 198 | lupeol acetate | P. calophylla P. laevigata P. sepium P. aphylla | rhizome latex cortex above ground part | [64] [87] [95] [70] |
| 199 | lupeol arachidate | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 200 | procrim a | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 201 | procrim b | P. laevigata P. linearifolia | latex stem bark | [87] [68] |
| 202 | laevigatin I | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 203 | laevigatin II | P. laevigata | latex | [87] |
| 204 | lupeol-20(29)-en-3-nonadecanoate | P. forrestii | roots | [96] |
| 205 | 3β,6α-dihydroxylup-20(29)-ene | P. aphylla | stems | [67,72] |
| 206 | 6α-hydroxylup-20(29)-en-3β-octadecanoate | P. aphylla | stems | [67,72] |
| 207 | betuline | P. aphylla | unknown | [72] |
| 208 | (24R)-9,19-cycloart-25-ene-3β,24-diol | P. sepium | root bark | [92] |
| 209 | (24S)-9,19-cycloart-25-ene-3β,24-diol | P. sepium | root bark | [92] |
| 210 | cycloeucalenol | P. sepium | root bark | [92] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 211 | sinapic acid | P. calophylla | rhizome | [71] |
| 212 | sinapate glucose-1-ester | P. calophylla | rhizome | [99,100] |
| 213 | E-p-hydroxy-cinnamic acid | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 214 | caffeic acid | P. forrestii | stems | [88] |
| 215 | ethyl caffeate | P. forrestii P. sepium | stems root bark | [101] [98] |
| 216 | (E)-1-(2,4-dihydroxy phenyl)-ethyl acrylate | P. forrestii | stems | [101] |
| 217 | trans-3,4-methylenedioxy cinnamyl alcohol | P. forrestii | whole plant | [73] |
| 218 | 6′-O-(E)-feruloyl sucrose | P. forrestii | whole plant | [73] |
| 219 | 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii P. sepium | roots and stems roots | [74] [102] |
| 220 | 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 221 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 222 | 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 223 | 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 224 | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid methyl ester | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 225 | 1,3-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 226 | 3,4-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 227 | 3,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 228 | 4,5-di-O-caffeoylquinic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 229 | scopoletin | P. forrestii P. sepium P. nigrescens | whole plant cortex and seedlings bark, leaves, seeds | [73,85] [103] [97] |
| 230 | cleomiscosin A | P. forrestii P. calophylla | root bark, stems rhizome | [45,66] [71] |
| 231 | cleomiscosin B | P. forrestii | stems | [66] |
| 232 | (+)-lyoniresinol | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 233 | (+)-lyoniresinol-3α-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 234 | (-)-lyoniresinol-3α-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 235 | tortoside B | P. sepium | root bark | [98,104] |
| 236 | (-)-gentioluteol-9-O-β-d-glucoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 237 | (-)-berchemol 9-O-β-d-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 238 | (7S,8R)-dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 9-O-β-d-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)- O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 239 | 7S,7′S,8R,8′R-lcariol A2-9-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 240 | (+)-1-hydroxypinoresinol | P. omeiensis P. forrestii | whole plant whole plant | [8] [13] |
| 241 | syringaresinol | P. forrestii | whole plant | [13,73] |
| 242 | (+)-syringaresinol-4′-O-β-d-monoglucoside | P. forrestii P. calophylla | whole plant rhizome | [73] [99,105] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 243 | kaempferol | P. forrestii | unknown | [85] |
| 244 | kaempferol-3-O-α-d-arabinopyranoside | P. calophylla | rhizome | [99] |
| 245 | kaempferol-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. calophylla P. laevigata P. graeca | rhizome aerial parts bark, leaves, and seeds | [99] [106] [97] |
| 246 | kaempferol-3-O-β-d-galactopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [107] |
| 247 | kaempferol-3-O-β-l-arabinopyranoside | P. forrestii P. laevigata | stems aerial parts | [107] [106] |
| 248 | rutin | P. laevigata P. aphylla P. graeca | aerial parts aerial parts bark, leaves, and seeds | [106] [108] [97] |
| 249 | quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii P. sepium P. laevigata P. aphylla P. graeca | stems leaves aerial parts aerial parts bark, leaves, and seeds | [107] [86] [106] [108] [97] |
| 250 | quercetin | P. forrestii P. sepium | unknown leaves | [85] [86] |
| 251 | quercetin-3-O-β-l-arabinopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [107] |
| 252 | 6′-Methyl ester of quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucuronide | P. sepium | leaves | [86] |
| 253 | quercetin-3-O-α-l-rhamnopyranoside | P. aphylla | aerial parts | [108] |
| 254 | quercetin-3-O-α-l-arabinopyranoside | P. forrestii | unknown | [109] |
| 255 | baohuoside I | P. sepium | cortex | [110] |
| 256 | quercetin-7-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | unknown | [109] |
| 257 | apigenin | P. nigrescens | leaves | [94] |
| 258 | isorhoifolin | P. nigrescens | leaves | [94] |
| 259 | wogonin | P. forrestii | rhizome | [42] |
| 260 | negletein | P. forrestii | rhizome | [42] |
| 261 | liquiritigenin | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 262 | 3′,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxy-flavanone-2(S)-3′-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. calophylla | rhizome | [99] |
| 263 | isoliquiritigenin | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 264 | daidzein | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 265 | formononetin | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 266 | (−)-epicatechin | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 267 | cinchonain Ia | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 268 | cinchonain Ib | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 269 | proanthocyanidin A2 | P. forrestii | stems | [63,88] |
| 270 | aesculitannin B | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 271 | catechin-(3′→O→3′’’)-afzelechin | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 272 | epicatechin-(3′→O→7′’)-epiafzelechi | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 273 | (−)-maackiain | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 274 | physcion | P. calophylla P. forrestii | rhizome rhizome, root bark | [64] [45,112] |
| 275 | physcion-8-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [107] |
| 276 | emodin | P. forrestii | stems | [90] |
| 277 | emodin-8-O-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [107] |
| 278 | emodin-8-methyl ether | P. forrestii | stems | [66] |
| 279 | chrysophanol | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 280 | 1,3,6-trihydroxy-2,5-dimethoxyxanthone | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 281 | tanshinone IIA | P. forrestii | unknown | [111] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 282 | vanillic acid | P. calophylla P. forrestii | rhizome unknown | [64] [66] |
| 283 | protocatechuic acid | P. forrestii | root bark | [45] |
| 284 | salicylic acid | P. calophylla P. forrestii | rhizome roots and stems | [71] [74] |
| 285 | 4-methoxysalicylic acid | P. sepium | root bark | [92] |
| 286 | syringic acid | P. forrestii | stems, roots and stems | [74,90] |
| 287 | p-hydroxybenzoic acid | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 288 | 2,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester | P. forrestii | whole plant | [13] |
| 289 | 2-ethylhexyl benzoate | P. aphylla | aerial parts | [108] |
| 290 | o-phthalic acid bis(2-ethylnonyl) ester | P. aphylla | whole plant | [84] |
| 291 | erigeside C | P. calophylla | rhizome | [99] |
| 292 | 4′-hydroxy-3′-methoxy-phenol-β-d-[6-O-9-(4′’-hydroxy-3′’,5′’-dimethoxy benzoate)] glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 293 | 4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl 6′-O-syringoyl-β-d-glucopyranoside | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 294 | 4-methoxy salicylaldehyde | P. graeca P. sepium | bark root bark | [113] [16,114] |
| 295 | 4-methoxybenzaldehyde-2-O-[β-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranoside] | P. sepium | root bark | [115] |
| 296 | 4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy benzaldehyde | P. calophylla | rhizome | [64] |
| 297 | 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyl benzaldehyde | P. calophylla P. sepium P. forrestii | rhizome root bark whole plant | [71] [92] [73] |
| 298 | 4-methoxy salicylaldehyde lactoside | P. sepium | root bark | [93] |
| 299 | isovanillin | P. sepium P. forrestii | root bark rhizome | [92] [42] |
| 300 | protocatechuic aldehyde | P. forrestii | roots and stems | [74] |
| 301 | 2-hydroxy-5-(2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzyl)-4-methoxybenzaldehyde | P. sepium | root bark | [44] |
| 302 | 3-propyl anisole | P. forrestii | rhizome | [116] |
| 303 | 2,6-dimethoxy-4-hydroxyphenol-1-O-β-d-glucoside | P. calophylla | rhizome | [116] |
| 304 | periplocain A | P. aphylla | aerial parts | [108] |
| No. | Compounds | Sources | Parts of Plants | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 305 | 1-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(2S,3S,4R,10E)-2-[(2R)-2-hydroxytetracosanoylamino]-10-octadecene-3,4-diol | P. forrestii | whole plant | [116] |
| 306 | (2S,3S,4R,10E)-2-[(2R)-2-hydroxytetracosanoylamino]-10-octadecene-1,3,4-triol | P. forrestii | whole plant | [116] |
| 307 | N-(4-ethoxyphenyl)-acetamide | P. forrestii | rhizome | [112] |
| 308 | malonic acid | P. forrestii | whole plant | [13] |
| 309 | palmitic acid | P. forrestii | unknown | [85] |
| 310 | n-heptadecane | P. forrestii | unknown | [85] |
| 311 | 1-triacontanol | P. calophylla | rhizome | [71] |
| 312 | methyl (9S,12S,13S)-9,12,13-trihydroxy-10E-octadecenoate | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 313 | methyl (9S,12R,13S)-9,12,13-trihydroxy-10E-octadecenoate | P. forrestii | stems | [63] |
| 314 | obaculactone | P. sepium | root bark | [80] |
| Biological Activities | Interrelated Species 1 | Primarily Active Components |
|---|---|---|
| cardiotonic effect | b, c, d | periplocin |
| anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects | a | periplosides; periplocin; several triterpenoids |
| antitumor ability | a, b, d, e | periplocin; periplocymarin; several pregnane glycosides; several oligosaccharides; baohuoside I; lupeol acetate |
| antimicrobial and antioxidant abilities | a, b, e, f | 4-methoxy salicylaldehyde; several lignins; several flavanes; several polysaccharides |
| insecticidal activity | a | 4-methoxysalicylaldehyde; periplosides |
| other abilities | a, b | several pregnane glycosides; several cardenolides; several triterpenes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Shen, S.; Luo, C.; Ren, Y. Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology. Molecules 2019, 24, 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152749
Huang M, Shen S, Luo C, Ren Y. Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology. Molecules. 2019; 24(15):2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152749
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Mingjin, Shoumao Shen, Chunli Luo, and Yan Ren. 2019. "Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology" Molecules 24, no. 15: 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152749
APA StyleHuang, M., Shen, S., Luo, C., & Ren, Y. (2019). Genus Periploca (Apocynaceae): A Review of Its Classification, Phytochemistry, Biological Activities and Toxicology. Molecules, 24(15), 2749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24152749