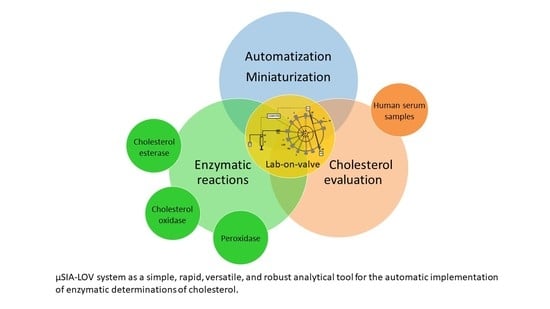
Enzymatic Reactions in a Lab-on-Valve System: Cholesterol Evaluations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Studies
2.2. µSIA-LOV System Optimization
2.3. Evaluation of Total Cholesterol Concentrations in Serum Samples Using the Developed µSIA-LOV Methodology
2.4. Comparison between the Developed Methodology and Other Flow-based Methodologies Used for Cholesterol Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solutions
3.2. Apparatus
3.3. Micro Sequential Injection Procedure
3.4. Comparison Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silvestre, C.I.C.; Pinto, P.; Segundo, M.A.; Saraiva, M.; Lima, J. Enzyme based assays in a sequential injection format: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 689, 160–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, A.N.; Lima, J.; Pinto, P.; Saraiva, M. Enzymatic determination of glucose in milk samples by sequential injection analysis. Anal. Sci. 2009, 25, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzicka, J.; Marshall, G.D. Ssequential injection - A new concept for chemical sensors, process analysis and laboratory assays. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 237, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzicka, J. Lab-on-valve: Universal microflow analyzer based on sequential and bead injection. Analyst 2000, 125, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuir, M.; Boden, H.; Carroll, A.; Ruzicka, J. Principles of micro sequential injection analysis in the lab-on-valve format andiIts introduction into a teaching laboratory. J. Flow Injection Anal. 2007, 24, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Vidigal, S.; Toth, I.V.; Rangel, A. Sequential injection-LOV format for peak height and kinetic measurement modes in the spectrophotometric enzymatic determination of ethanol: Application to different alcoholic beverages. Talanta 2008, 77, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ruzicka, J. Accelerated micro-sequential injection in lab-on-valve format, applied to enzymatic assays. Analyst 2004, 129, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.; Passos, M.L.C.; Azevedo, A.M.O.; Saraiva, M. Automatic evaluation of peroxidase activity using different substrates under a micro sequential injection analysis/lab-on-valve (mu SIA-LOV) format. Microchem. J. 2017, 134, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidigal, S.; Toth, I.V.; Rangel, A. Sequential injection lab-on-valve system for the determination of the activity of peroxidase in vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2071–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidigal, S.; Toth, I.V.; Rangel, A. Sequential injection lab-on-valve system for the on-line monitoring of hydrogen peroxide in lens care solutions. Microchem. J. 2009, 91, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Carroll, A.D.; Scampavia, L.; Ruzicka, J. Automated method, based on micro-sequential injection, for the study of enzyme kinetics and inhibition. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlicek, O.; Polasek, M.; Foltyn, M.; Cabal, J. Automated detection of organophosphate warfare gases (nerve agents) in air based on micro-SIA - lab-on-valve system. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013, 11, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krug, A.; Gobel, R.; Kellner, R. Flow-injection analysis for total cholesterol with photometric detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 287, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman; Pundir, C.S. Co-immobilization of cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase and peroxidase onto alkylamine glass beads for measurement of total cholesterol in serum. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2003, 3, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Allain, C.C.; Poon, L.S.; Chan, C.S.G.; Richmond, W.; Fu, P.C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin. Chem. 1974, 20, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.; Dickinson, M.A.; Albers, J.J.; Havel, R.J.; Cheung, M.C.; Vigne, J.L. The effect of a high cholesterol and saturated fat diet on serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, apoprotein-A-I, and apoprotein-E levels in normolipidemic humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1980, 33, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, A.J.; O’Reilly, E.J.; Moriarty, R.D.; Bertoncello, P.; Keyes, T.E.; Forster, R.J.; Dennany, L. A Cholesterol biosensor based on the NIR electrogenerated-chemiluminescence (ECL) of water-soluble CdSeTe/ZnS quantum dots. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 157, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.; Armitage, J.; Parish, S.; Sleight, P.; Peto, R.; Heart Protect Study, C. Effects of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin on stroke and other major vascular events in 20 536 people with cerebrovascular disease or other high-risk conditions. Lancet 2004, 363, 757–767. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, W.P.; Anderson, K. A population at risk - Prevalence of high cholesterol levels in hypertensive patients in the Framingham-study. Am. J. Med. 1986, 80, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Murray, C.J.L.; Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, F.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Benn, M. Familial Hypercholesterolemia and risk of peripheral arterial disease and chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4491–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, I.; Hara, K.; Matsuoka, H.; Suzuki, S. Amperometric determination of total cholesterol in serum with use of immobilized cholesterol esterase and cholesterol oxidase. Anal. Chim. Acta 1982, 139, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Yuki, H. Determination of cholesterol with a laboratory-built chemiluminescence system. Anal. Chim. Acta 1986, 188, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolti, N.L.; Pilosof, D.; Nieman, T.A. Determination of cholesterol with a microporous membrane chemiluminescence cell with cholesterol oxidase in solution. Anal. Chim. Acta 1985, 170, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, H.; Faridbod, F.; Ganjali, M.R. Flow injection analysis of cholesterol using FFT admittance voltammetric biosensor based on MWCNT-ZnO nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 100, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Malik, J.; Prashant, A.; Jaiwal, P.K.; Pundir, C.S. Amperometric determination of serum total cholesterol with nanoparticles of cholesterol esterase and cholesterol oxidase. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 500, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Sun, X.T.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.R. Boron nitride nanosheet/CuS nanocomposites as mimetic peroxidase for sensitive colorimetric detection of cholesterol. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 246, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cui, L.J.; Xue, Y.W.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhu, N.X.; Liang, J.T.; Li, G.Y. Ultrasensitive cholesterol biosensor based on enzymatic silver deposition on gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandezromero, J.M.; Decastro, M.D.L.; Valcarcel, M. Enzymatic determination of total cholesterol in serum by flow-injection analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1987, 5, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Wasa, T. Flow-injection system for simultaneous assay of free and total cholesterol in blood-serum by use of immobilized enzymes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1988, 207, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, A.; Suleiman, A.A.; Guilbault, G.G.; Kellner, R. Colorimetric determination of free and total cholesterol by flow-injection analysis with fiber optic detector. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1992, 14, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Situmorang, M.; Alexander, P.W.; Hibbert, D.B. Flow injection potentiometry for enzymatic assay of cholesterol with a tungsten electrode sensor. Talanta 1999, 49, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.N.; Catita, J.A.M.; Lima, J. Monosegmented flow-analysis of serum cholesterol. Farmaco 1999, 54, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.K.; Reis, B.F.; Galhardo, C.X.; Martelli, P.B. A multicommuted flow procedure for the determination of cholesterol in animal blood serum by chemiluminescence. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 3011–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaldi, D.C.; Reschiglian, P.; Zattoni, A.; Johann, C. Enzymatic determination of cholesterol and triglycerides in serum lipoprotein profiles by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation with on-line, dual detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 654, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisitsoraat, A.; Sritongkham, P.; Karuwan, C.; Phokharatkul, D.; Maturos, T.; Tuantranont, A. Fast cholesterol detection using flow injection microfluidic device with functionalized carbon nanotubes based electrochemical sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, W. Use of cholesterol oxidase for assay of total and free cholesterol in serum by continuous-flow analysis. Clin. Chem. 1976, 22, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples are not available from the authors. |




| Mode | Methodology | Enzymes | Matrix | Analytes | Detection Mode | Sample Treatment | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | Amperometry | Dilution with ethanol and triton X-100 | 100–400 mg·dL−1 | n.a. | [22] | |
| CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | Chemiluminescence | Dilution with phosphate buffer solution | n.a. | n.a. | [23] | ||
| CO, CE, POD | Serum | Free and total cholesterol | Chemiluminescence | Dilution with triton X-100 | 0.4–40 mg·dL−1 | 0.2 mg·dL−1 | [24] | ||
| CO | - | Free cholesterol | Voltammetry | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 0.2–60.0 nmol·L−1 | 0.05 nmol·L−1 | [25] | ||
| CO, CE | Serum | Total cholesterol | Amperometry | Dilution with triton X-100 | 10–700 mg·dL−1 | 0.1 mg·dL−1 | [26] | ||
| CO, CE | Serum | Total cholesterol | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | Dilution with triton X-100 | 10–100 µmol·L−1 | 2.9 µmol·L−1 | [27] | ||
| CO, CE | - | Total cholesterol | Voltammetry | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 5–5000 µg·mL−1 | 3.0 µg·mL−1 | [28] | ||
| Flow analysis | FIA | CO, CE, POD | - | Total cholesterol | UV-Vis spectrophotometry and fluorimetry | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 0.02–0.20 g·L−1 0.005–0.05 g·L−1 | 0.0020 g·L−1 0.0004 g·L−1 | [29] |
| FIA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Free and total cholesterol | Potentiometry | Dilution with triton X-100 | Up to around 10−3 mol·L−1 | 3.0 × 10−3 mol·L−1 | [30] | |
| FIA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Free and total cholesterol | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 0.5–0.8 mmol·L−1 | n. a. | [31] | |
| FIA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | Dilution with triton X-100 | 0.11–0.86 mmol·L−1 | n. a. | [13] | |
| FIA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | Potentiometry | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 0.05–3.0 mmol·L−1 | 0.01 mmol·L−1 | [32] | |
| MFA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | Dilution with phenol and triton X-100 | Up to 10.3 mmol·L−1 | n. a. | [33] | |
| MCFIA | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Total cholesterol | Chemiluminescence | Dilution with isopropanol and triton X-100 | 25–125 mg·L−1 | 3.7 mg·L−1 | [34] | |
| AF4-PFRD | CO, CE, POD | Serum | Cholesterol and triglycerides | UV-Vis spectrophotometry | - | 10–250 mg·dL−1 | n. a | [35] | |
| FIA microfluidic chip | CO | - | Free cholesterol | Amperometry | Dilution with triton X-100 | 50–400 mg·dL−1 | 10 mg·dL−1 | [36] |
| Kind of Sample | Sample | Standard Concentrations (mg·dL−1) | Calculated Concentrations (mg·dL−1) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference samples | 1 | 109 | 113.9 ± 0.7 | 4.5 |
| 2 | 109 | 105.5 ± 0.6 | −3.2 | |
| 3 | 109 | 108.6 ± 1.5 | −0.3 | |
| 4 | 104 | 109.3 ± 0.2 | 5.1 | |
| 5 | 104 | 105.0 ± 0.0 | 1.0 | |
| Real samples | 6 | 223 | 228.1 ± 0.1 | 2.3 |
| 7 | 283 | 283.3 ± 1.3 | 0.1 | |
| 8 | 279 | 263.6 ± 3.7 | −5.5 | |
| 9 | 272 | 269.2 ± 1.8 | −1.0 | |
| 10 | 225 | 214.4 ± 0.2 | −4.7 | |
| 11 | 272 | 257.4 ± 2.0 | −5.4 | |
| 12 | 279 | 274.7 ± 3.3 | −1.5 | |
| 13 | 211 | 213.5 ± 0.5 | 1.2 | |
| 14 | 283 | 292.3 ± 1.1 | 3.3 |
| Step | Position | Volume (µL) | Time (s) | Flow Rate (mL·min−1) | Direction | Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Chromogenic reagent |
| 2 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Cholesterol oxidase |
| 3 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Cholesterol esterase |
| 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Sample |
| 5 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Cholesterol esterase |
| 6 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Sample |
| 7 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Cholesterol oxidase |
| 8 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 0.15 | Aspiration | Chromogenic reagent |
| 9 | 9 | - | 360 | 0 | Stopped flow | Stopped flow in the holding coil |
| 10 | 9 | 10,000 | 75 | 1.25 | Propulsion | Propulsion to the detector |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
S. Barbosa, J.; L.C. Passos, M.; A. Korn, M.d.G.; M.F.S. Saraiva, M.L. Enzymatic Reactions in a Lab-on-Valve System: Cholesterol Evaluations. Molecules 2019, 24, 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162890
S. Barbosa J, L.C. Passos M, A. Korn MdG, M.F.S. Saraiva ML. Enzymatic Reactions in a Lab-on-Valve System: Cholesterol Evaluations. Molecules. 2019; 24(16):2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162890
Chicago/Turabian StyleS. Barbosa, Jucineide, Marieta L.C. Passos, M. das Graças A. Korn, and M. Lúcia M.F.S. Saraiva. 2019. "Enzymatic Reactions in a Lab-on-Valve System: Cholesterol Evaluations" Molecules 24, no. 16: 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162890
APA StyleS. Barbosa, J., L.C. Passos, M., A. Korn, M. d. G., & M.F.S. Saraiva, M. L. (2019). Enzymatic Reactions in a Lab-on-Valve System: Cholesterol Evaluations. Molecules, 24(16), 2890. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24162890