Abstract
Fangchinoline (FCN) derived from Stephaniae tetrandrine S. Moore can be employed to treat fever, inflammation, rheumatism arthralgia, edema, dysuria, athlete’s foot, and swollen wet sores. FCN can exhibit a plethora of anti-neoplastic effects although its precise mode of action still remains to be deciphered. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) can closely regulate carcinogenesis and thus we analyzed the possible action of FCN may have on these two signaling cascades in tumor cells. The effect of FCN on NF-κB and AP-1 signaling cascades and its downstream functions was deciphered using diverse assays in both human chronic myeloid leukemia (KBM5) and multiple myeloma (U266). FCN attenuated growth of both leukemic and multiple myeloma cells and repressed NF-κB, and AP-1 activation through diverse mechanisms, including attenuation of phosphorylation of IκB kinase (IKK) and p65. Furthermore, FCN could also cause significant enhancement in TNFα-driven apoptosis as studied by various molecular techniques. Thus, FCN may exhibit potent anti-neoplastic effects by affecting diverse oncogenic pathways and may be employed as pro-apoptotic agent against various malignancies.
1. Introduction
Bioactive natural product compounds have been used in traditional medical practices especially in the Asian continent for centuries [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Recent advances in research and development have identified several novel molecules with potent bioactivity in several models of cancer [4,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Cancer especially in advanced stages is still considered incurable [29,30] and several pharmacological agents designated for cancer therapy can be obtained from Mother nature [21]. Leukemia comprises a group of hematological malignancies and is characterized by abnormal white cells that originate from the bone marrow and can affect both adults and children [31,32]. Despite remarkable progress in leukemia treatment, overall progress still remains riddled with frequent relapses and high mortality [33].
Hyperactivation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) is commonly seen in varying chronic conditions including cancers [13,14,31,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. NF-κB can be frequently activated in both solid tumors as well as in those of cells of blood-forming tissues [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. NF-κB may be activated by carcinogens, pro-oxidants, and growth factors and drives the oncogenic process [49,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64]. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα), was initially reported to be a potent anti-tumor cytokine that can abrogate tumor growth [65,66,67,68,69]. However, it was later found that TNFα can also function as a potent cytokine that is capable of inducing NF-κB signaling cascade and mediate tumorigenesis [65,70].
NF-κB, a complex of p50, p65, and IκBα, stays in the cytoplasm under unstimulated conditions [44,45,46,47,58,71]. Upon activation, several upstream kinases, such as IκB kinase (IKK), are phosphorylated and can ubiquitinate and degrade IκBα to release NF-κB which subsequently moves inside the nucleus and regulates transcription of genes controlling, apoptosis, angiogenesis, metastasis, and chemo- and radio-resistance [44,45,46,52,57,59,65,72,73]. Similarly, AP-1 has been reported to be overexpressed in different neoplastic cells and can also closely regulate the hallmarks of carcinogenesis [37,74,75]. Several AP-1 target genes, such as matrix metalloproteinases [MMPs] (MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-9), extracellular matrix associated proteins, and protein kinase C, have been implicated in carcinogenesis [76,77,78]. Furthermore, AP-1 has also been found to interact with NF-κB and augment cancer progression [38,79,80]. Therefore, dual targeting the NF-κB/AP-1 signaling axis may be effective for cancer therapy.
Fangchinoline (FCN) is a bisbenzylisoquinoline that belongs to the family Menispermaceae [10,31,81]. It can display significant anti-tumoral effects against malignant cells and in breast cancer cells, FCN inhibited cell proliferation and induced cell death that was driven by the mitochondrial pathway [82,83,84]. Similarly, FCN was observed to suppress the phosphorylation of AKT (phospho-Thr308), cyclin D1, and MMP-2, MMP-9 levels, as well as upregulate caspase-3 and -8 in MG63 and U2OS osteosarcoma cells [85]. In another report by Guo et al., FCN was noted to repress invasion by suppression of FAK-AKT and FAK-MEK-ERK1/2 pathways [86]. It has also been documented to mitigate metastasis of melanoma cells by modulating focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation [87].
In grade IV human glioblastoma multiforme cells (U87 MG and U118 MG), FCN interfered with AKT signaling pathway and caused apoptosis [88]. In another study, FCN negatively affected the multiplication in prostate cancer cells by suppressing the articulation of genes controlling cell-cycle regulation [89]. In SPC-A-1 lung adenocarcinoma cells, it also abrogated cellular growth and caused apoptosis [90]. Chronic myeloid leukemia is predominantly characterized by BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase deregulation. FCN can also affect the proliferation of K562 cells by causing arrest at G0/G1 phase, upregulating CDKN1A and MCL1 mRNA with concomitant downregulation of cyclin D1 mRNA [91]. Interestingly, FCN displayed autophagy mediated apoptosis in bladder cancer cells and caused a reduction in cellular ATP levels, upregulated LC3-II/LC3-1 ratio and caspase-3 and down regulated p62 protein levels [92]. In another study by Wang et al., it was found to promote autophagic cell death by modulating the p53/sestrin 2/AMPK signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells [93]. Interestingly, FCN could also inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth via modulating NR4A1 dependent apoptotic pathway [94].
In this study, we primarily deciphered the action of FCN in regulating NF-κB/AP-1 cell signaling and survival pathways and aimed to understand the effect of this alkaloid in regulating cytokine-induced apoptosis.
2. Results
2.1. FCN Abrogates NF-κB/AP-1 Activation
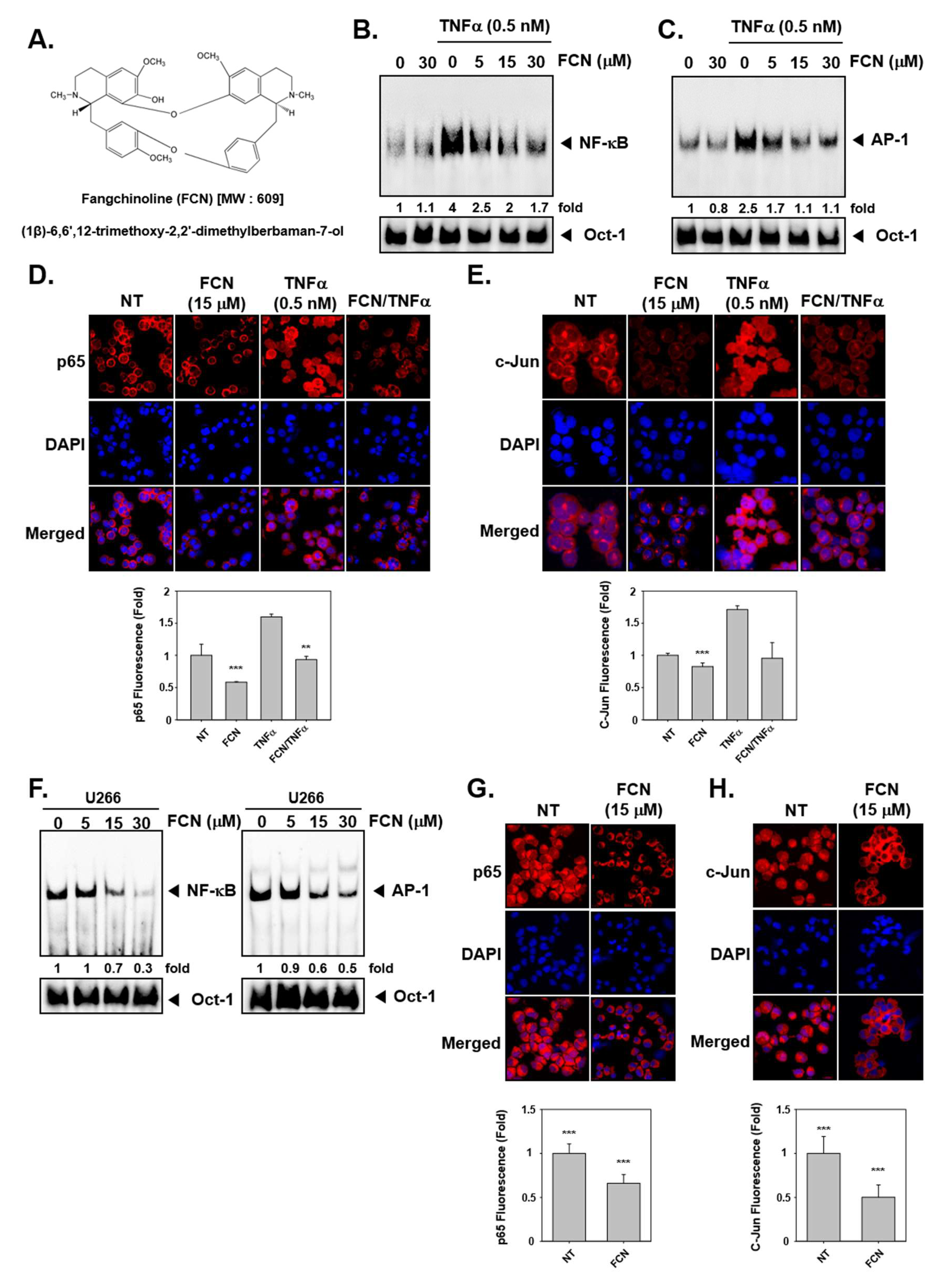
To evaluate whether FCN can regulate TNFα-induced NF-κB/AP-1 activation in KBM5 cells, we performed an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) assay. We had previously measured cytotoxicity with of FCN in KBM5 cells and found that IC50 (half-maximal inhibitory concentration) was 10 μM at 72 h. So we selected the concentration in the range 0 to 30 μM, around the IC50 value for duration up to 24 h and no significant toxicity was noted in this dose range. The results indicated that NF-κB/AP-1 proteins can be activated by TNFα (0.5 nM) exposure and suppressed by FCN treatment in concentration response studies (Figure 1B,C). In addition, in immunocytochemistry results, nuclear translocation of p65 and c-Jun was induced by TNFα and FCN suppressed this activity (Figure 1D,E). Interestingly, similar effects on DNA binding and nuclear translocation was observed in myeloma U266 cells (Figure 1F–H).
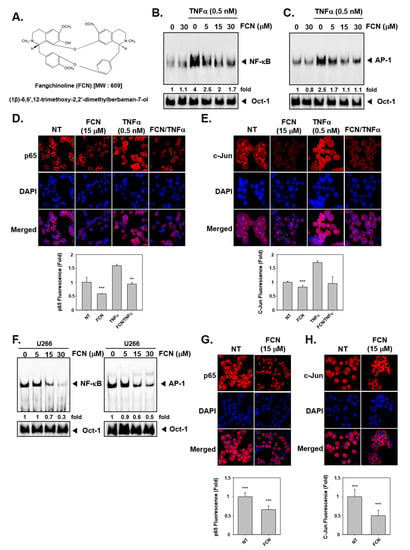
Figure 1.
Fangchinoline (FCN) affects the activation of oncogenic transcription factors. (A) The chemical structure of FCN. (B,C) FCN was added in different concentrations to KBM5 cells. After 2 h of treatment, 0.5 nM of TNFα was added for 15 min. Nuclear extracts (NE) were prepared for electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) assay to evaluate Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) expression. Oct-1 was used as loading control. (D,E) KBM5 cells were treated as described above. Immunocytochemistry was done to analyze p65 and c-Jun translocation to the nucleus, results were compared between non-treated (NT) and FCN treated cells. (F) Changes in constitutive NF-κB and AP-1 expression upon FCN treatment in U266 cells was evaluated by EMSA assay. Oct-1 was used as loading control. (G,H) p65 and c-Jun nuclear translocation was evaluated by immunocytochemistry in U266 cells. The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.
2.2. FCN Mitigates TNFα -Induced IKK Phosphorylation
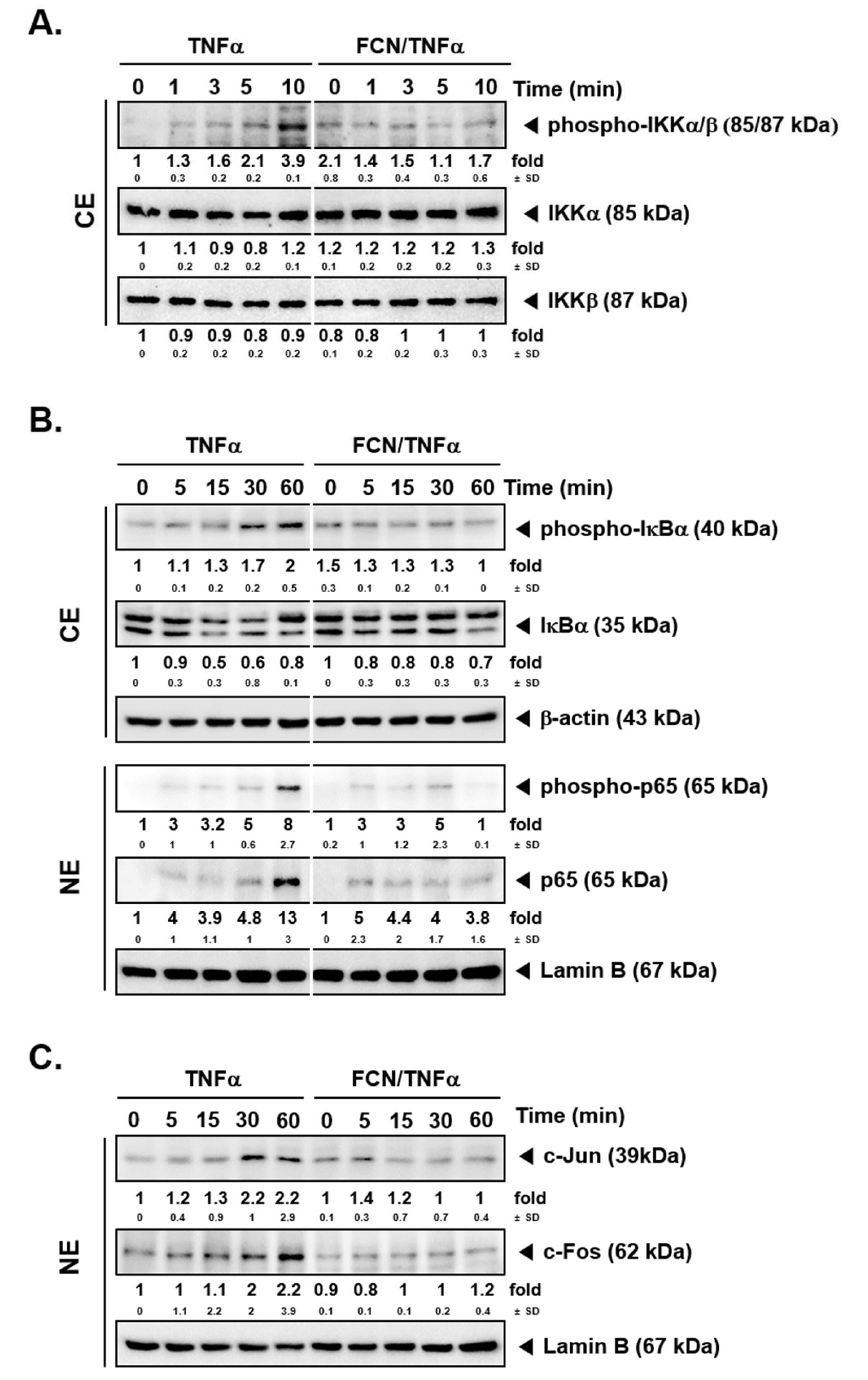
To determine whether FCN has modulatory effects on IKK activation, FCN (15 μM) pre-treated KBM5 cells were first stimulated with TNFα. Western blot experiments carried out thereafter suggest that FCN suppressed phospho-IKKα/β activation (Figure 2A). Because IκBα degradation can lead to NF-κB nuclear translocation activation, we evaluated whether FCN can also inhibit IκBα degradation. As shown, FCN can effectively abrogate IκBα degradation as well as phosphorylation of p65 driven by TNFα exposure (Figure 2B), and it also attenuated the expression of c-Jun and c-Fos proteins (Figure 2C).
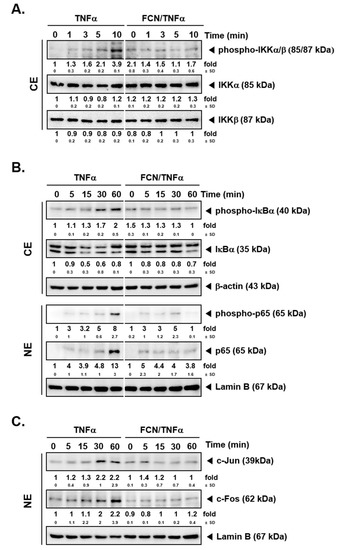
Figure 2.
FCN affects NF-κB activation and IκBα degradation in KBM5 cells. KBM5 cells were pre-treated with 15 μM of FCN for 2 h. After pre-treatment, 0.5 nM TNFα was added for the indicated time intervals. (A) Cytoplasmic extracts (CE) were prepared to evaluate the expression of phospho-IKKα/β, IKKα, and IKKβ by Western blot analysis. (B) Cytoplasmic extracts (CE) and nuclear extracts (NE) were analyzed to evaluate NF-κB activation and IκBα degradation. (C) AP-1 related c-Jun and c-Fos expression was determined by Western blot analysis using nuclear extracts (NE). The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.
2.3. FCN down Regulates Levels of Diverse Oncogenic Proteins
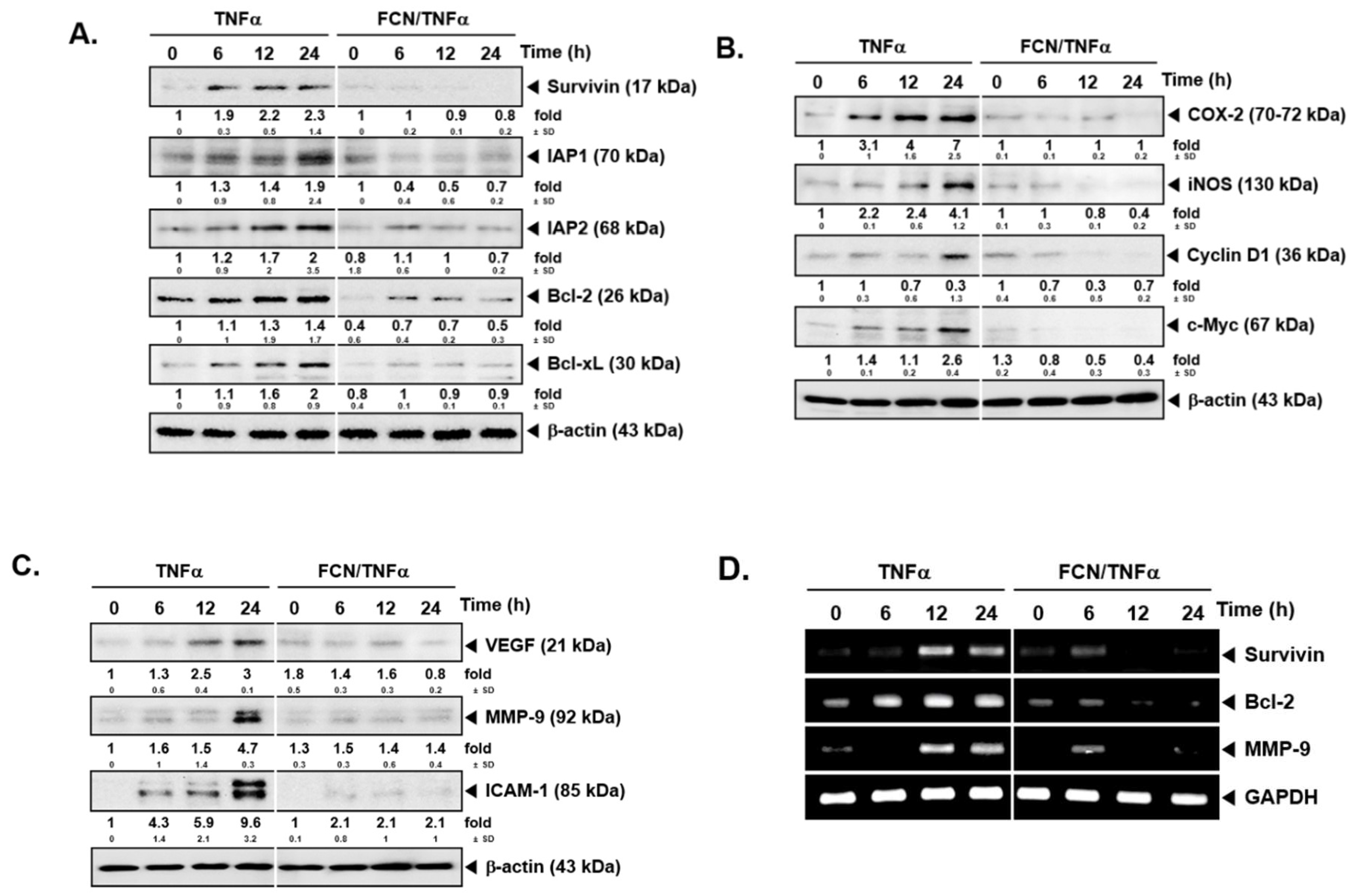
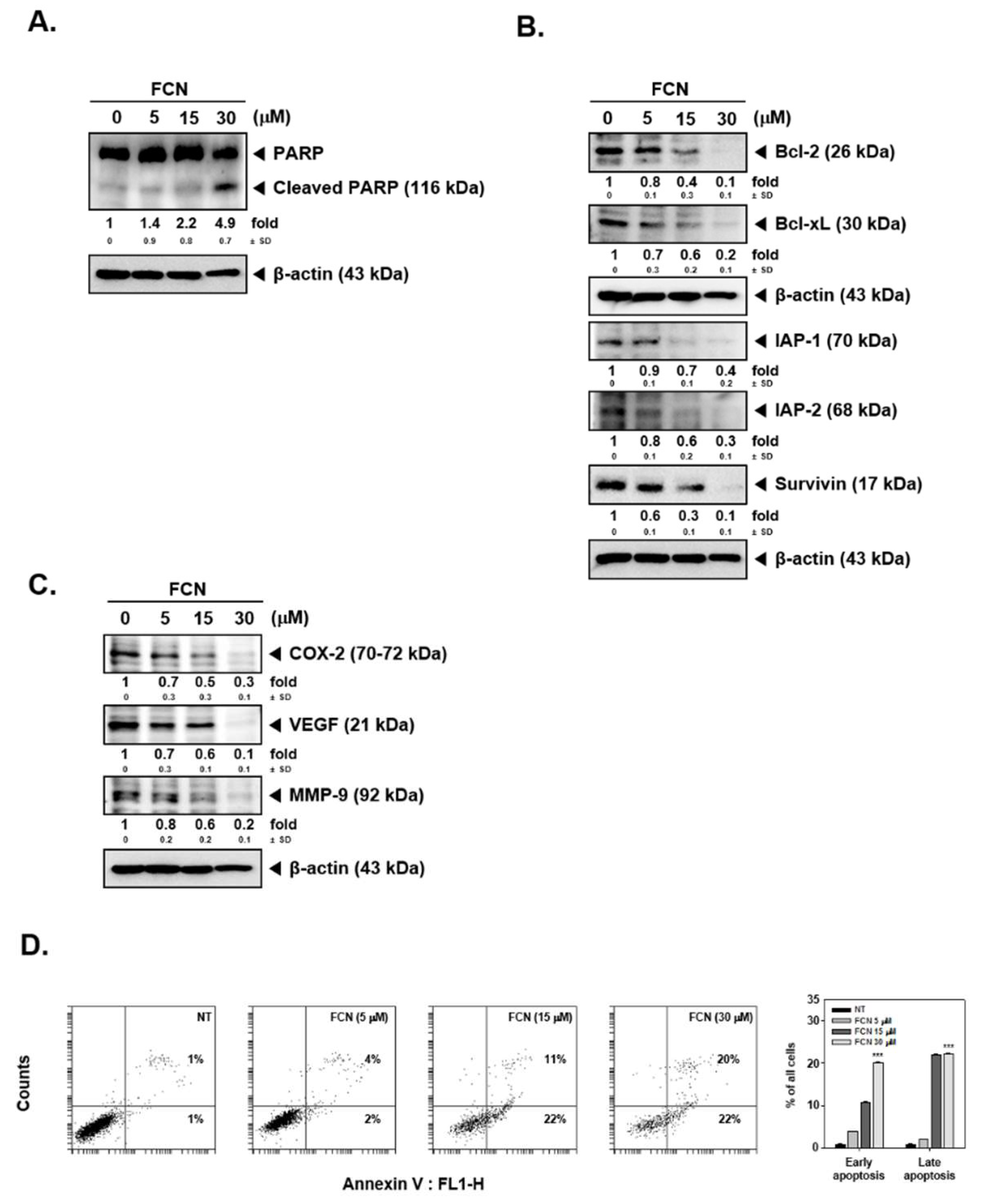
To analyze whether FCN has potential effects on the levels of various gene products, we performed Western blot analysis and RT-PCR. Among various gene products, first, we evaluated the effect of FCN on survivin, IAP-1, IAP2, Bcl-2, and Bcl-xl proteins. As shown on Figure 3A, TNFα caused an increase but FCN treatment downmodulated the expression of these proteins. Additionally, we found that FCN treatment could mitigate COX-2, Cyclin D1, and c-Myc expression (Figure 3B). Moreover, tumor cell metastasis related gene products, such as VEGF, MMP-9, and ICAM-1, could be mitigated by FCN (Figure 3C). Furthermore, we have selected few significant markers, such as survivin, Bcl-2, and MMP-9, for RT-PCR analysis that may represent important hallmarks of cancer [95], and the appearance of survivin, Bcl-2, and MMP-9 genes were substantially repressed upon FCN exposure (Figure 3D).
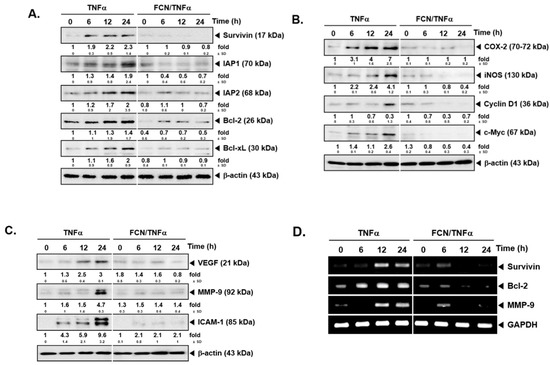
Figure 3.
FCN influences the expression of various oncogenic genes. KBM5 cells were pre-treated with 15 μM of FCN for 2 h. After 2 h, 0.5 nM TNFα was added for 24 h. (A) Western blot analysis was performed to check the expression of various proteins. (B) The levels of proliferative gene products were analyzed by Western blot analysis. (C) The expression of metastatic gene products were analyzed by Western blot analysis. (D) RT-PCR was done to check the mRNA level of various genes. The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments.
2.4. FCN Enhances TNFα-Induced Apoptosis through Affecting Caspase-3 Activation
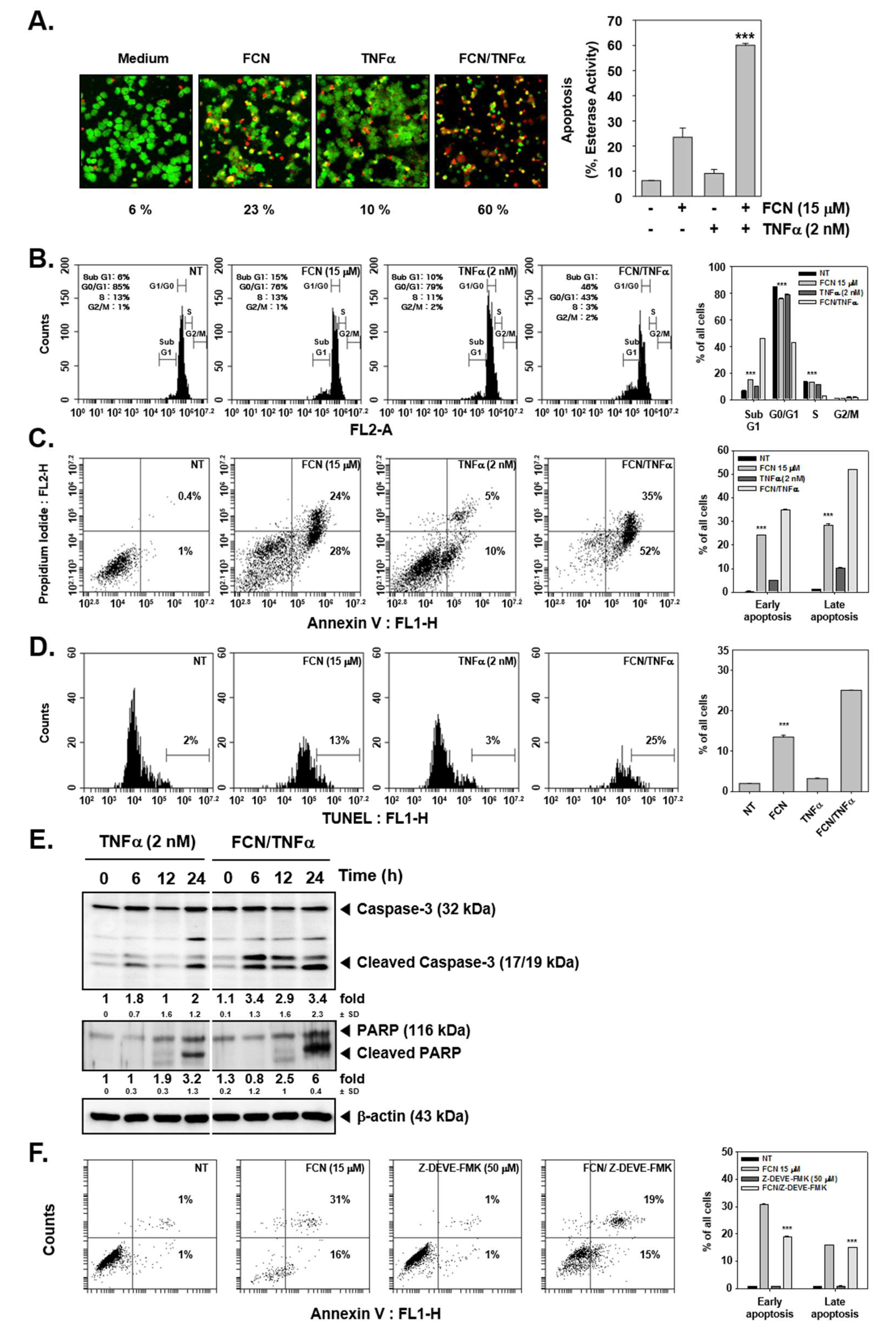
We first evaluated whether TNFα-induced apoptosis may be augmented upon FCN exposure by live and dead assay, cell cycle analysis, annexin V, and TUNEL assays. First, FCN and TNFα treated cells were probed with calcein AM and Ethd-1. Because live cells can disaggregate the calcein, cells appeared in green color. On the contrary, dead cells exhibited damage in their cell membranes, so Ethd-1 can invade into the cells through ruptured membranes and the cells thus appeared as red colored (Figure 4A). Moreover, it was observed that FCN exposure increased sub G1 phase from 6% to 15%, TNFα increased sub G1 phase from 6% to 10%, and combination treatment clearly enhanced distribution in sub G1 phase to 46% (Figure 4B).
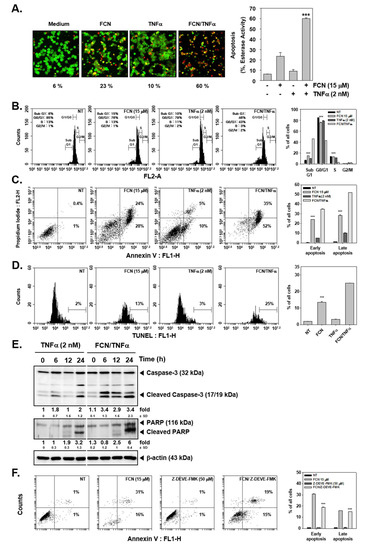
Figure 4.
FCN can augment cytokine caused apoptosis. KBM5 cells were pre-treated with 15 μM of FCN and 2 nM TNFα was thereafter added for a total of 24 h. (A) Cytotoxicity of FCN and TNFα was analyzed by live and dead assay. Live cells were stained with Calcein AM (green) and dead cells were stained with Ethd-1 (red). The graph (right) shows the rate of dead cells by quantification. (B) Cells were treated as described above and then fixed with EtOH overnight. RNase A (10 μg/mL) was treated for 1 h and then cells were stained with propidium iodide, analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) FCN and TNFα treated cells were stained with Annexin V Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)/propidium iodide, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) After FCN and TNFα treatment, cells were subjected to Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. (E) KBM5 cells were treated as described above and Western blot analysis was performed. (F) KBM5 cell were treated with FCN (15 μM) and Z-Asp(O-Me)-Glu(O-Me)-Val-Asp(O-Me) fluoromethyl ketone (Z-DEVD-FMK) (50 μM, caspase inhibitor) for 24 h. Cells were stained with Annexin V FITC/propidium iodide and then analyzed by flow cytometry. The results shown are representative at least three independent experiments.
Interestingly in annexin V assay, FCN treatment could increase both early and late apoptosis form 0.4% and 1% to 24% and 28%. TNFα also exacerbated early and late apoptosis to 5% and 10%. Interestingly, combination treatment enhanced apoptosis to 35% and 52% (Figure 4C). In addition, we analyzed the effect on apoptosis by TUNEL assay. We noted that FCN induced apoptosis from 2% to 13% and combination treatment prominently enhanced apoptosis to 25% (Figure 4D). We later examined the mechanism(s) behind enhancement of apoptosis observed upon FCN treatment. As shown in Figure 4E, TNFα treatment induced apoptosis and FCN exposure clearly augmented cell death through augmentation in caspase-3 as well as PARP cleavage. We additionally confirmed that FCN indeed caused apoptosis through caspase cleavage. KBM5 cells were treated with Z-DEVD-FMK (50 μM), known as caspase inhibitor, and FCN (15 μM) and as illustrated in Figure 4F, FCN can induce substantial apoptosis but Z-DEVD-FMK treatment could attenuate apoptosis. Overall, the results demonstrated that FCN induced apoptosis through the caspase and PARP dependent pathways.
Moreover, as shown in Figure 5A,B, FCN treatment induced PARP cleavage and attenuated the level of diverse oncogenic proteins in myeloma cells as well. Furthermore, cell death in these cells increased dramatically with increasing concentrations of FCN (0, 5, 15, 30 μM), (Figure 5C).
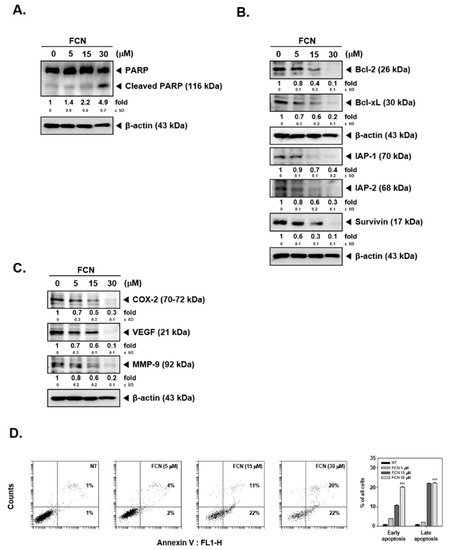
Figure 5.
FCN induced apoptosis in U266 cells. U266 cells were treated with FCN (0, 5, 15, and 30 μM) for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were prepared to analyze the expression of (A) PARP and (B) various oncogenic gene products such as Bcl-2, Bcl-xl, IAP-1, IAP-2, survivin, as well as (C) COX-2, VEGF, and MMP-9. (D) FCN-induced apoptosis in U266 cells was analyzed by annexin V assay. Cells were treated with FCN for 24 h. The results shown are representative at least three independent experiments.
3. Discussion
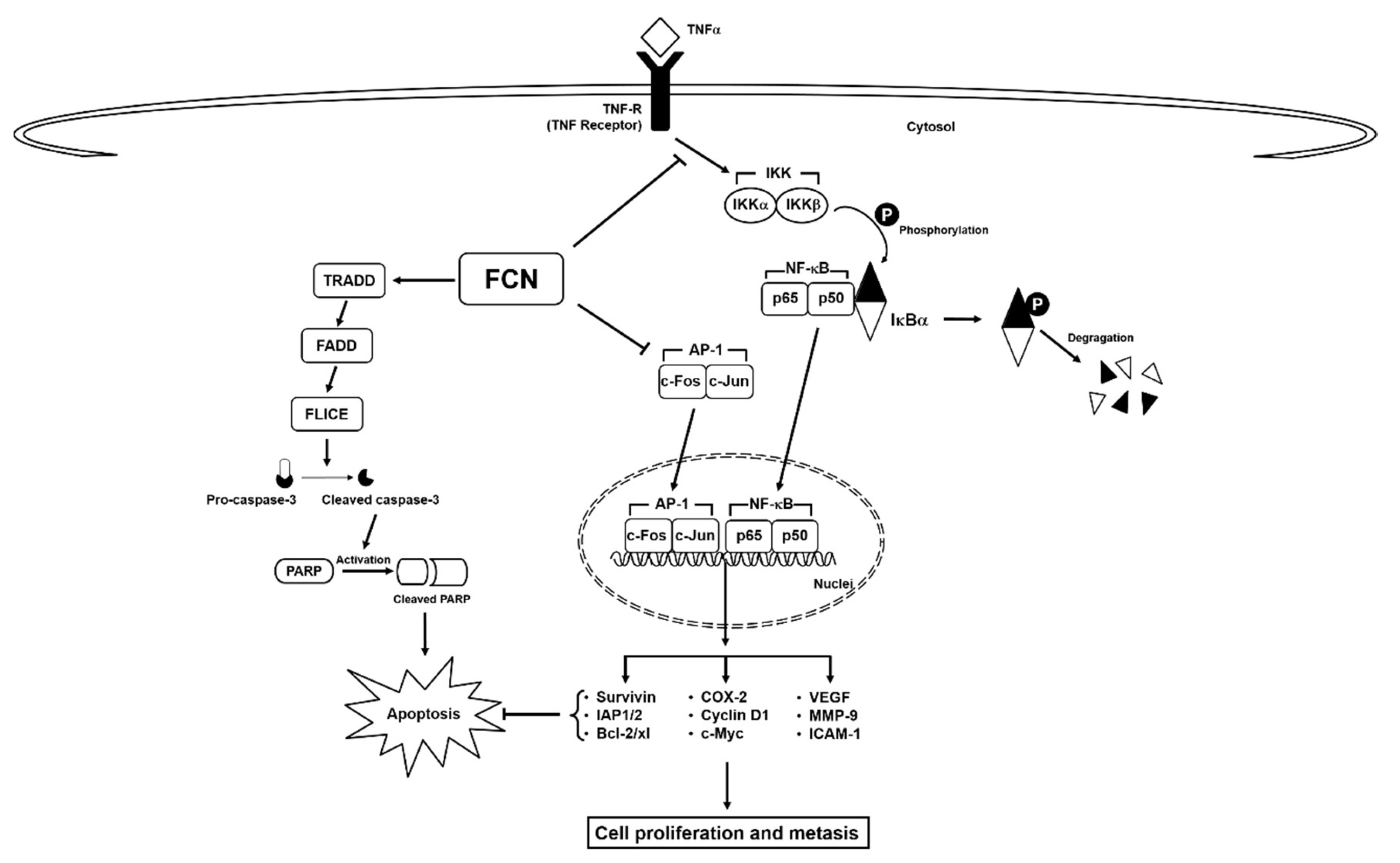
Here, we deciphered the anti-neoplastic actions of FCN in abrogating the survival of chronic myeloid leukemia cells. FCN is a bisbenzylisoquinoline based alkaloid that has been documented to act as a potent anti-neoplastic agent against different malignancies [10]. Leukemia, a cancer characterized by abnormal growth of blood cells [96], can exist in various forms, such as acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and chronic myeloid leukemia [32,79,97,98,99,100]. NF-κB has been known to play an important role in the regulation of cell survival, proliferation, and metastasis [101]. It is also well known that cytokine TNFα can regulate the robust activation of master transcription factor NF-κB [65,70], and persistent NF-κB overexpression/phosphorylation has been detected in leukemia as well as multiple myeloma [54,102,103,104,105]. FCN has been found to inhibit the growth of chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells, but detailed mode of its anti-cancer actions still remains unclear [91]. Thus, in this study we employed both human chronic myeloid leukemia and myeloma cell lines to decipher the primary mode(s) of action regulating the anti-neoplastic actions of FCN. We noted that FCN effectively suppressed both constitutive and induced NF-κB and AP-1 activation as well as modulated the survival potential of the tumor cells (Figure 6).
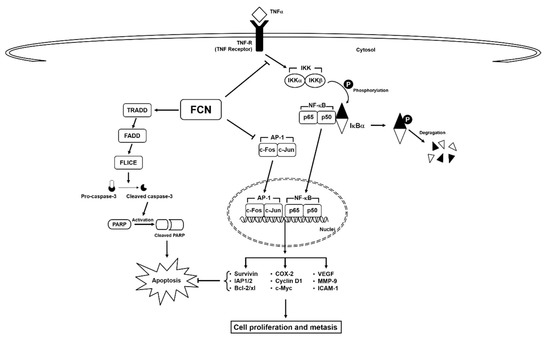
Figure 6.
A schematic diagram of FCN effects on NF-κB/AP-1 in tumor cells.
Interestingly, we found that FCN-induced NF-κB may be caused by the abrogation of inhibitor kappa kinase (IKK) activation and suppression of IκBα phosphorylation. These steps are important for the transcription of myriad of genes controlled by NF-κB [14,44,79,100]. Next, FCN was observed to mitigate nuclear localization of p65 and effectively promote a down-modulation in the levels of pro-survival as well as oncogenic proteins. As known, translocation of NF-κB complexes into the nucleus is an essential step for its reported oncogenic functions [43,44]. Interestingly, in a previous study, FCN was noted to promote cell death and suppress migration via regulation of NF-κB activation in mammary tumor cells [22]. The AP-1 complex can drive oncogenesis in different malignancies including leukemia and myeloma [13,106]. Uncontrolled cellular proliferation has been correlated to activation of c-fos and c-jun proteins and inadequate response to chemotherapeutic agents [14,38]. Moreover, c-fos and c-jun can be overexpressed, and mediate process of oncogenic transformation in leukemic cells, however, normal lymphocytes did not express c-Jun [32,75,80]. However, whether FCN can affect NF-κB and AP-1 activation by modulating the phosphorylation of an upstream signaling molecule that may regulate both these signaling cascades requires additional experiments.
It is understood that simultaneously attenuating both NF-κB and AP-1 pathways can be an important approach to target oncogenesis [1,107,108]. FCN could significantly enhance cytokine-induced apoptosis and this effect was found to be mediated via its action in inducing capase-3 activation and subsequent PARP cleavage. Thus, our finding suggests that NF-κB and AP-1 may augment pro-survival signaling mechanism(s) in malignant cells and therapeutic targeting of these two potent transcription factors by FCN could abrogate tumor growth as well as survival (Figure 5). Overall, it appears that FCN can act as a promising anti-cancer drug whose potential remains to be validated in appropriate tumor models. In addition, further studies are needed to determine whether FCN can be employed along with existing treatment modalities for cancer therapy.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
Fangchinoline (FCN, Figure 1A) was purchased from Chem faces (Wuhan, Hubei, China). FCN was stored in 100 mM stock solution with dimethyl sulfoxide at −20 °C and diluted in cultured media for in vitro experiments. LightShift® Chemiluminescent EMSA kit was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Alexa Fluor® 594 donkey anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) antibody was obtained from Life Technologies (Grand Island, NY, USA). Z-DEVD-FMK (caspase-3 inhibitor) was purchased from CALBIOCHEM (San Diego, CA, USA).
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
Human chronic myeloid leukemia (KBM5) cells as described before [109] were cultured in IMDM medium containing 10% inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Human multiple myeloma (U266) cells as described before [54] were cultured with RPMI medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin.
4.3. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
NF-κB and AP-1 DNA binding were analyzed by EMSA as reported before [38,109].
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
Western blot assay was done as explained before [110,111].
4.5. RT-PCR
RT-PCR was carried out as elaborated before [112].
4.6. Immunocytochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was done as described previously [109].
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
To evaluate apoptotic effects of FCN, cells were pre-treated with FCN (15 μM) for 2 h and TNFα (2 nM) treated for total 24 h. After treatment, cells were washed by 1× PBS and fixed with 100% EtOH for overnight at 4 °C. Cells were resuspended with fresh 1× PBS as well as RNase A (1 μg/mL) treated at 37 °C for 1 h and then stained with propidium iodide. Thereafter analysis was carried out by BD Accuri™ C6 Plus Flow Cytometer (BD Biosciences, Becton-Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
4.8. TUNEL Assay
Annexin V assay was done as explained before [113].
4.9. Live and Dead Assay
KBM5 cells were pre-treated with FCN (15 μM) and TNFα (2 nM) for total 24 h. After treatment, cells were incubated with 5 μM Calcein AM and 5 μM Ethd-1(Ethidium homodimer-1) at 37 °C for 30 min. Thereafter Olympus FluoView FV1000 confocal microscope was used for analysis (Tokyo, Japan).
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance was calculated by Mann–Whitney U test. Significance was set at p < 0.05.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y.J. and K.S.A.; methodology, Y.Y.J., M.K.S., A.C., S.A.A. and O.H.S.; formal analysis, Y.Y.J. and J.-Y.U.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Y.J., G.S. and K.S.A.; writing—review and editing, G.S. and K.S.A.; project administration, G.S. and K.S.A.; funding acquisition, G.S. and K.S.A.
Funding
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (NRF-2015R1A4A1042399 and 2018R1D1A1B07042969). The authors also thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding of this research through the Research Group Number (RG-1435-081).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Abbreviations
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| AP-1 | activator protein 1 |
| TNFα | tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IKKs | inhibitory kappa B kinases |
| IκBα | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| MMP | mitochondrial membrane potential |
| PARP | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| IC50 | half maximal inhibitory concentration |
References
- Yang, S.F.; Weng, C.J.; Sethi, G.; Hu, D.N. Natural bioactives and phytochemicals serve in cancer treatment and prevention. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 698190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kannaiyan, R.; Sethi, G. Targeting cell signaling and apoptotic pathways by dietary agents: Role in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.S.; Yang, S.F.; Sethi, G.; Hu, D.N. Natural bioactives in cancer treatment and prevention. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 182835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G. Bioactive natural products in cancer prevention and therapy: Progress and promise. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarla, N.S.; Bishayee, A.; Sethi, G.; Reddanna, P.; Kalle, A.M.; Dhananjaya, B.L.; Dowluru, K.S.; Chintala, R.; Duddukuri, G.R. Targeting arachidonic acid pathway by natural products for cancer prevention and therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 48–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanpourghadi, M.; Looi, C.Y.; Pandurangan, A.K.; Sethi, G.; Wong, W.F.; Mustafa, M.R. Phytometabolites Targeting the Warburg Effect in Cancer Cells: A Mechanistic Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2017, 18, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Warrier, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Arfuso, F. Potential Role of Natural Compounds as Anti-Angiogenic Agents in Cancer. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sethi, G.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Krishnan, S.; Shishodia, S. Targeting cell signaling pathways for drug discovery: An old lock needs a new key. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Hwang, S.T.; Sethi, G.; Fan, L.; Arfuso, F.; Ahn, K.S. Potential Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Cancer Properties of Farnesol. Molecules 2018, 23, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merarchi, M.; Sethi, G.; Fan, L.; Mishra, S.; Arfuso, F.; Ahn, K.S. Molecular Targets Modulated by Fangchinoline in Tumor Cells and Preclinical Models. Molecules 2018, 23, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Warrier, S.; Merarchi, M.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A. Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-Cancer Properties of Diosgenin: A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Um, J.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Bishayee, A.; Ahn, K.S. The Role of Resveratrol in Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, D.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M.; Sureda, A.; Farooqi, A.A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Vacca, R.A.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting activator protein 1 signaling pathway by bioactive natural agents: Possible therapeutic strategy for cancer prevention and intervention. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Lee, J.H.; Chai, E.Z.; Kanchi, M.M.; Kar, S.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ramar, P.S.; Looi, C.Y.; et al. Cancer prevention and therapy through the modulation of transcription factors by bioactive natural compounds. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Nguyen, A.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G. Targeted inhibition of tumor proliferation, survival, and metastasis by pentacyclic triterpenoids: Potential role in prevention and therapy of cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012, 320, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimali, D.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Zhang, J.; Tan, B.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. Targeted abrogation of diverse signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 341, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, K.; Harsha, C.; Bordoloi, D.; Lalduhsaki Sailo, B.; Sethi, G.; Leong, H.C.; Arfuso, F.; Mishra, S.; Wang, L.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Therapeutic potential of gambogic acid, a caged xanthone, to target cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, D.H.J.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Tran, T. Molecular targets and anti-cancer potential of escin. Cancer Lett. 2018, 422, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.; Um, J.Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Arctiin is a pharmacological inhibitor of STAT3 phosphorylation at tyrosine 705 residue and potentiates bortezomib-induced apoptotic and anti-angiogenic effects in human multiple myeloma cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 55, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deorukhkar, A.; Krishnan, S.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Back to basics: How natural products can provide the basis for new therapeutics. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1753–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xing, Z.; Wang, F.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y. Fangchinoline inhibits migration and causes apoptosis of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5307–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Verma, S.S.; Rai, V.; Awasthee, N.; Chava, S.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Challagundla, K.B.; Sethi, G.; Gupta, S.C. Long non-coding RNAs are emerging targets of phytochemicals for cancer and other chronic diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 1947–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Jung, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Pleiotropic Pharmacological Actions of Capsazepine, a Synthetic Analogue of Capsaicin, against Various Cancers and Inflammatory Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Um, J.Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Casticin-Induced Inhibition of Cell Growth and Survival Are Mediated through the Dual Modulation of Akt/mTOR Signaling Cascade. Cancers 2019, 11, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girisa, S.; Shabnam, B.; Monisha, J.; Fan, L.; Halim, C.E.; Arfuso, F.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Potential of Zerumbone as an Anti-Cancer Agent. Molecules 2019, 24, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Yap, C.T.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting autophagy using natural compounds for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer 2019, 125, 1228–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.; Kashyap, D.; Sak, K.; Tuli, H.S.; Jain, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Garg, V.K.; Sethi, G.; Yerer, M.B. Molecular Mechanisms of Action of Tocotrienols in Cancer: Recent Trends and Advancements. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S. World Cancer Report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloni, D.; Martinelli, G.; Messa, F.; Baccarani, M.; Saglio, G. Nuclear factor kB as a target for new drug development in myeloid malignancies. Haematologica 2007, 92, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, R.; Grabow, S.; Davids, M.S. The rise of apoptosis: Targeting apoptosis in hematologic malignancies. Blood 2018, 132, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Stahl, M.; Zeidan, A.M. Immunotherapy in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes: The dawn of a new era? Blood Rev. 2018, 34, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tergaonkar, V.; Krishna, S.; Androphy, E.J. Human papillomavirus type 16 E6-enhanced susceptibility of L929 cells to tumor necrosis factor alpha correlates with increased accumulation of reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24819–24827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akincilar, S.C.; Khattar, E.; Boon, P.L.; Unal, B.; Fullwood, M.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Long-Range Chromatin Interactions Drive Mutant TERT Promoter Activation. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnott, C.H.; Scott, K.A.; Moore, R.J.; Hewer, A.; Phillips, D.H.; Parker, P.; Balkwill, F.R.; Owens, D.M. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha mediates tumour promotion via a PKC alpha- and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Um, J.Y.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Ophiopogonin D modulates multiple oncogenic signaling pathways, leading to suppression of proliferation and chemosensitization of human lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 40, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ong, T.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Lun, C.K.; Ho, P.C.; Wong, P.T.; Hui, K.M.; Sethi, G. Ursolic acid inhibits the initiation, progression of prostate cancer and prolongs the survival of TRAMP mice by modulating pro-inflammatory pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, H.S.; Chng, W.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Activation of mutant TERT promoter by RAS-ERK signaling is a key step in malignant progression of BRAF-mutant human melanomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14402–14407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tergaonkar, V. Telomerase reactivation in cancers: Mechanisms that govern transcriptional activation of the wild-type vs. mutant TERT promoters. Transcription 2016, 7, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattar, E.; Kumar, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Akincilar, S.C.; Raju, A.; Lakshmanan, M.; Maury, J.J.; Qiang, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, E.Y.; et al. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promotes cancer cell proliferation by augmenting tRNA expression. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4045–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Kumar, A.P.; Tergaonkar, V. Multifaceted link between cancer and inflammation. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. Potential pharmacological control of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB activation: From bench to bedside. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2008, 233, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.H.; Sethi, G. Role of NF-κB in Tumorigenesis. Forum Immunopathol. Dis. Ther. 2013, 4, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappa B: From clone to clinic. Curr. Mol. Med. 2007, 7, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Zayed, M.E.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G. NF-kappaB in cancer therapy. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 711–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Li, F.; Fong, C.W.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, P.; Sethi, G. First evidence that gamma-tocotrienol inhibits the growth of human gastric cancer and chemosensitizes it to capecitabine in a xenograft mouse model through the modulation of NF-kappaB pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sethi, G. Targeting transcription factor NF-kappaB to overcome chemoresistance and radioresistance in cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1805, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ahn, K.S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Wang, H.; Shen, H.; Arfuso, F.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Chang, Y.; Sethi, G.; et al. Oleuropein induces apoptosis via abrogating NF-kappaB activation cascade in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 4504–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puar, Y.R.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Fan, L.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. Evidence for the Involvement of the Master Transcription Factor NF-kappaB in Cancer Initiation and Progression. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, E.Z.; Siveen, K.S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G. Analysis of the intricate relationship between chronic inflammation and cancer. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kannaiyan, R.; Mustafa, N.; Manu, K.A.; Siveen, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Chng, W.J.; Kumar, A.P. Celastrol Attenuates the Invasion and Migration and Augments the Anticancer Effects of Bortezomib in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Multiple Myeloma. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ramachandran, L.; Li, F.; Siveen, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Zayed, M.E.; Alharbi, S.A.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Isorhamnetin augments the anti-tumor effect of capeciatbine through the negative regulation of NF-kappaB signaling cascade in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 363, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Siveen, K.S.; Wang, F.; Ong, T.H.; Loo, S.Y.; Swamy, M.M.; Mandal, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Garcinol sensitizes human head and neck carcinoma to cisplatin in a xenograft mouse model despite downregulation of proliferative biomarkers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5147–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gehlot, P. Inflammation and cancer: How friendly is the relationship for cancer patients? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S.; Sandur, S.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Sethi, G. Inflammation and cancer: How hot is the link? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.M.; Sung, B.; Yadav, V.R.; Kannappan, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. NF-kappaB addiction and its role in cancer: ‘one size does not fit all’. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Embelin, an inhibitor of X chromosome-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein, blocks nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway leading to suppression of NF-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene products. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Rajendran, P.; Li, F.; Nema, T.; Vali, S.; Abbasi, T.; Kapoor, S.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.P.; Ho, P.C.; et al. Ursolic acid inhibits multiple cell survival pathways leading to suppression of growth of prostate cancer xenograft in nude mice. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 2011, 89, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Manu, K.A.; Ong, T.H.; Ramachandran, L.; Surana, R.; Bist, P.; Lim, L.H.; Kumar, A.P.; Hui, K.M.; Sethi, G. Inhibition of CXCR4/CXCL12 signaling axis by ursolic acid leads to suppression of metastasis in transgenic adenocarcinoma of mouse prostate model. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manu, K.A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Chen, L.; Siveen, K.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G. Simvastatin sensitizes human gastric cancer xenograft in nude mice to capecitabine by suppressing nuclear factor-kappa B-regulated gene products. J. Mol. Med. (Berl) 2014, 92, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chen, L.; Chatterjee, S.; Basha, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Kundu, T.K.; Sethi, G. Garcinol, a polyisoprenylated benzophenone modulates multiple proinflammatory signaling cascades leading to the suppression of growth and survival of head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 2013, 6, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ningegowda, R.; Shivananju, N.S.; Rajendran, P.; Rangappa, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Li, F.; Achar, R.R.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Bist, P.; Alharbi, S.A.; et al. A novel 4,6-disubstituted-1,2,4-triazolo-1,3,4-thiadiazole derivative inhibits tumor cell invasion and potentiates the apoptotic effect of TNFalpha by abrogating NF-kappaB activation cascade. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keerthy, H.K.; Mohan, C.D.; Siveen, K.S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Rangappa, S.; Sundaram, M.S.; Li, F.; Girish, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Bender, A.; et al. Novel synthetic biscoumarins target tumor necrosis factor-alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 31879–31890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirvanappa, A.C.; Mohan, C.D.; Rangappa, S.; Ananda, H.; Sukhorukov, A.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Sundaram, M.S.; Nayaka, S.C.; Girish, K.S.; Chinnathambi, A.; et al. Novel Synthetic Oxazines Target NF-kappaB in Colon Cancer In Vitro and Inflammatory Bowel Disease In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Targeting TNF for Treatment of Cancer and Autoimmunity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 647, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, G.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. TNF: A master switch for inflammation to cancer. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5094–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.D.; Bharathkumar, H.; Dukanya, D.; Rangappa, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Lobie, P.E.; et al. N-Substituted Pyrido-1,4-Oxazin-3-Ones Induce Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.D.; Anilkumar, N.C.; Rangappa, S.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Mishra, S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Novel 1,3,4-Oxadiazole Induces Anticancer Activity by Targeting NF-kappaB in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Liu, Z.; Zandi, E. AP-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaulian, E. AP-1—The Jun proteins: Oncogenes or tumor suppressors in disguise? Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, T.J.; Margiotta, P.; Bush, L.; Wasilenko, W. Enhanced cell motility and invasion of chicken embryo fibroblasts in response to Jun over-expression. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.; Chamboredon, S.; Castellazzi, M.; Kerry, J.A.; Bos, T.J. Transcriptional upregulation of SPARC, in response to c-Jun overexpression, contributes to increased motility and invasion of MCF7 breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7077–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Waha, A.; Gelman, I.H.; Vogt, P.K. Expression of a down-regulated target, SSeCKS, reverses v-Jun-induced transformation of 10T1/2 murine fibroblasts. Oncogene 2001, 20, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Targeting nuclear factor-kappa B activation pathway by thymoquinone: Role in suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and enhancement of apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trop-Steinberg, S.; Azar, Y. AP-1 Expression and its Clinical Relevance in Immune Disorders and Cancer. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 353, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. The value of plants used in traditional medicine for drug discovery. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.D.; Yuan, C.F.; Bu, Y.Q.; Wu, X.M.; Wan, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, N.; Liu, X.J.; Zu, Y.; Liu, G.L.; et al. Fangchinoline inhibits cell proliferation via Akt/GSK-3beta/cyclin D1 signaling and induces apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kar, S.; Lai, X.; Cai, W.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Lobie, P.E.; Goh, B.C.; Lim, L.H.K.; Hartman, M.; et al. Triple negative breast cancer in Asia: An insider’s view. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 62, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pang, D. Fangchinoline induces G1 arrest in breast cancer cells through cell-cycle regulation. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1790–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Han, W.; Lu, X.; Jin, S.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; He, W.; Qian, Y. Fangchinoline suppresses the proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma cells through the inhibition of PI3K and downstream signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Su, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, K.; Li, X. Fangchinoline as a kinase inhibitor targets FAK and suppresses FAK-mediated signaling pathway in A549. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Guo, B.; Hui, Q.; Chang, P.; Tao, K. Fangchinoline suppresses growth and metastasis of melanoma cells by inhibiting the phosphorylation of FAK. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Xie, P.; Su, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Liang, G. Fangchinoline suppresses the growth and invasion of human glioblastoma cells by inhibiting the kinase activity of Akt and Akt-mediated signaling cascades. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.D.; Huang, J.G.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, S.Y.; Yan, X.; Zou, A.; Chang, J.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Yang, G.X.; et al. Fangchinoline induced G1/S arrest by modulating expression of p27, PCNA, and cyclin D in human prostate carcinoma cancer PC3 cells and tumor xenograft. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Peng, J.M.; Su, L.D.; Wang, D.Y.; Yu, Y.J. Fangchinoline inhibits the proliferation of SPC-A-1 lung cancer cells by blocking cell cycle progression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Leng, Y.; Wang, G. Fangchinoline induces G0/G1 arrest by modulating the expression of CDKN1A and CCND2 in K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, A. Fangchinoline Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy and Energetic Impairment in Bladder Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Pan, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, M.; Hao, X.; Liang, G.; Feng, Y. Fangchinoline induces autophagic cell death via p53/sestrin2/AMPK signalling in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Safe, S.; Lee, S.O. Inactivation of the orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 contributes to apoptosis induction by fangchinoline in pancreatic cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 332, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, E.Z.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Arfuso, F.; Dharmarajan, A.; Wang, C.; Kumar, A.P.; Samy, R.P.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Targeting transcription factor STAT3 for cancer prevention and therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Hong, M.; Zhu, H.; Qian, S.; Li, J. Effects of chidamide and its combination with decitabine on proliferation and apoptosis of leukemia cell lines. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 2567–2578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Artesunate suppresses tumor growth and induces apoptosis through the modulation of multiple oncogenic cascades in a chronic myeloid leukemia xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4020–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S.; Sethi, G.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. A synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO-Me, inhibits IkappaBalpha kinase and enhances apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents through down-regulation of expression of nuclear factor kappaB-regulated gene products in human leukemic cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Sandur, S.K.; Lin, X.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Indirubin enhances tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis through modulation of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23425–23435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Pandey, M.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Blood 2007, 109, 2727–2735. [Google Scholar]
- Hanada, T.; Yoshimura, A. Regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002, 13, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Mustafa, N.; Li, F.; Kannaiyan, R.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Chng, W.J.; Sethi, G. Thymoquinone overcomes chemoresistance and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib through abrogation of NF-kappaB regulated gene products in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 634–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannaiyan, R.; Hay, H.S.; Rajendran, P.; Li, F.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Vali, S.; Abbasi, T.; Kapoor, S.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Celastrol inhibits proliferation and induces chemosensitization through down-regulation of NF-kappaB and STAT3 regulated gene products in multiple myeloma cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 1506–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, B.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Sethi, G.; Anand, P.; Guha, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin circumvents chemoresistance in vitro and potentiates the effect of thalidomide and bortezomib against human multiple myeloma in nude mice model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Sethi, G.; Vadhan-Raj, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Takada, Y.; Gaur, U.; Nair, A.S.; Shishodia, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and overcomes chemoresistance through down-regulation of STAT3 and nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated antiapoptotic and cell survival gene products in human multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-kappaB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadjavi, A.; Valente, E.; Giribaldi, G.; Prato, M. Involvement of p38 MAPK in haemozoin-dependent MMP-9 enhancement in human monocytes. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2014, 32, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Lin, C.W.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Cheng, H.L.; Lue, K.H.; Yang, S.F.; Lu, K.H. Selaginella tamariscina (Beauv.) possesses antimetastatic effects on human osteosarcoma cells by decreasing MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretions via p38 and Akt signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B. Simvastatin potentiates TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis through the down-regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent antiapoptotic gene products: Role of IkappaBalpha kinase and TGF-beta-activated kinase-1. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates nuclear factor-kappaB through IkappaBalpha kinase-independent but EGF receptor-kinase dependent tyrosine 42 phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Ahn, K.S.; Hsu, A.; Woo, C.C.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, K.H.B.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Koh, A.P.F.; et al. Thymoquinone Inhibits Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer Cells Through Abrogation of the CXCR4 Signaling Axis. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Narula, A.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Oxymatrine Attenuates Tumor Growth and Deactivates STAT5 Signaling in a Lung Cancer Xenograft Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Bian, J.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Formononetin-induced oxidative stress abrogates the activation of STAT3/5 signaling axis and suppresses the tumor growth in multiple myeloma preclinical model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).