Customizable Ceramic Nanocomposites Using Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Yan, H.; Jayaseelan, D.D.; Pejis, T.; Reece, M.J. Electrically conductive alumina–carbon nanocomposites prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.D.; Kuntz, J.D.; Wan, J.; Mukherjee, A.K. Single-wall carbon nanotubes as attractive toughening agents in alumina-based nanocomposites. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estili, M.; Sakka, Y. Recent advances in understanding the reinforcing ability and mechanism of carbon nanotubes in ceramic matrix composites. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2014, 15, 064902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maensiri, S.; Laokul, P.; Klinkaewnarong, J.; Amornkitbamrung, V. Carbon nanofiber-reinforced alumina nanocomposites: Fabrication and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 447, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, L.; Zhang, T.; Du, G.H.; Li, W.Z.; Wang, Q.W.; Datye, A.; Wu, K.H. Thermal properties of CNT-Alumina nanocomposites. Compos. Sci Technol. 2008, 68, 2178–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Yan, H.; Pejis, T.; Reece, M.J. The sintering and grain growth behaviour of ceramic–carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Bindal, R.C.; Prabhakar, S.; Tewari, P.K.; Dasgupta, K.; Sathiyamoorthy, D. Potential of carbon nanotubes in water purification: An approach towards the development of an integrated membrane system. Int. J. Nucl. Desalin. 2008, 3, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady-Estévez, A.S.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M. A single-walled-carbon-nanotube filter for removal of viral and bacterial pathogens. Small 2008, 4, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2010, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Srivastava, O.N.; Talapatra, S.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Carbon nanotube filters. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafavi, S.; Ehrnia, M.; Rashidi, A. Preparation of nanofilter from carbon nanotubes for application in virus removal from water. Desalination 2009, 238, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, N.; Rautio, A.; Leino, A.R.; Kyllönen, T.; Tóth, G.; Lappalainen, J.; Kordás, K.; Huuhtanen, M.; Keiski, R.L.; Sápi, A.; et al. Three-dimensional carbon nanotube scaffolds as particulate filters and catalyst support membranes. ACS Nano. 2010, 4, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, K.Y.; Na, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.H. Fabrication of a multi-walled carbon nanotube-deposited glass fiber air filter for the enhancement of nano and submicron aerosol particle filtration and additional antibacterial efficacy. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4132–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermisoglou, E.; Pilatos, G.; Romanos, G.E.; Karanikolos, G.; Nikos, B.; Merits, K.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Synthesis and characterisation of carbon nanotube modified anodised alumina membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 110, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, H.; Bates, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y. A highly efficient and versatile carbon nanotube/ceramic composite filter. Carbon 2013, 54, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parham, H.; Kennedy, A.; Zhu, Y. Preparation of porous alumina–carbon nanotube composites via direct growth of carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci Technol. 2011, 71, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Yan, H.; Reece, M.J.; Peijs, T. Dimethylformamide: An effective dispersant for making ceramic–carbon nanotube composites. Nanotechnology. 2008, 19, 195710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurst, J.; Nelson, J. Lineal intercept technique for measuring grain size in two-phase polycrystalline ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1972, 55, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengisu, M. Properties of Ceramic Materials and Their Evaluation, in Engineering Ceramics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 209–362. [Google Scholar]
- Inam, F.; Peijs, T.; Reece, M.J. The production of advanced fine-grained alumina by carbon nanotube addition. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2853–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inam, F.; Reece, M.J.; Peijs, T. Shortened carbon nanotubes and their influence on the electrical properties of polymer nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojny, F.H.; Wichmann, M.H.; Fiedler, B.; Kinloch, I.A.; Bauhofer, W.; Windle, A.H.; Schulte, K. Evaluation and identification of electrical and thermal conduction mechanisms in carbon nanotube/epoxy composites. Polymer 2006, 47, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Mo, C.B.; Park, S.B.; Hong, S.H. Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Multiwalled CNT-Alumina Nanocomposites Prepared by a Sequential Two-Step Processing of Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis and Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 3774–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.; Lezec, H.J.; Hiura, H.; Bennett, J.W.; Ghaemi, H.F.; Thio, T. Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes. Nature 1996, 382, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 7th ed.; John wiley & sons: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Menchavez, R.L.; Fuji, M.; Takahashi, M. Electrically conductive dense and porous alumina with in-situ-synthesized nanoscale carbon networks. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2345–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, R. Handbook of Properties of Technical and Engineering Ceramics; Hmso: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs, R.; Brissette, L. Expressions for shear modulus and Poisson’s ratio of porous refractory oxides. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1962, 45, 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Curtin, W.; Sheldon, B. Fracture toughness of highly ordered carbon nanotube/alumina nanocomposites. J. Eng Mater. Technol. 2004, 126, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigney, A.; Flahaut, E.; Laurent, C.; Chastel, F.; Rousset, A. Aligned carbon nanotubes in ceramic-matrix nanocomposites prepared by high-temperature extrusion. Chem Phys. Lett. 2002, 352, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inam, F.; Peijs, Y. Transmission light microscopy of carbon nanotubes-epoxy nanocomposites involving different dispersion methids. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2006, 15, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Vo, T.; Jones, J.P.; Lee, X. Effect of carbon nanotube lengths on the mechanical properties of epoxy resin: An experimental study. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah. Carbon nanotube membranes for water purification: Developments, challenges, and prospects for the future. Sep. Purif. Techol. 2019, 209, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Vo, T.; Bhat, B.R. Structural stability studies of graphene in sintered ceramic nanocomposite. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16227–16233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, F.; Yan, H.; Reece, M.J.; Peijs, T. Structural and chemical stability of multiwall carbon nanotubes in sintered ceramic nanocomposite. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2010, 109, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |

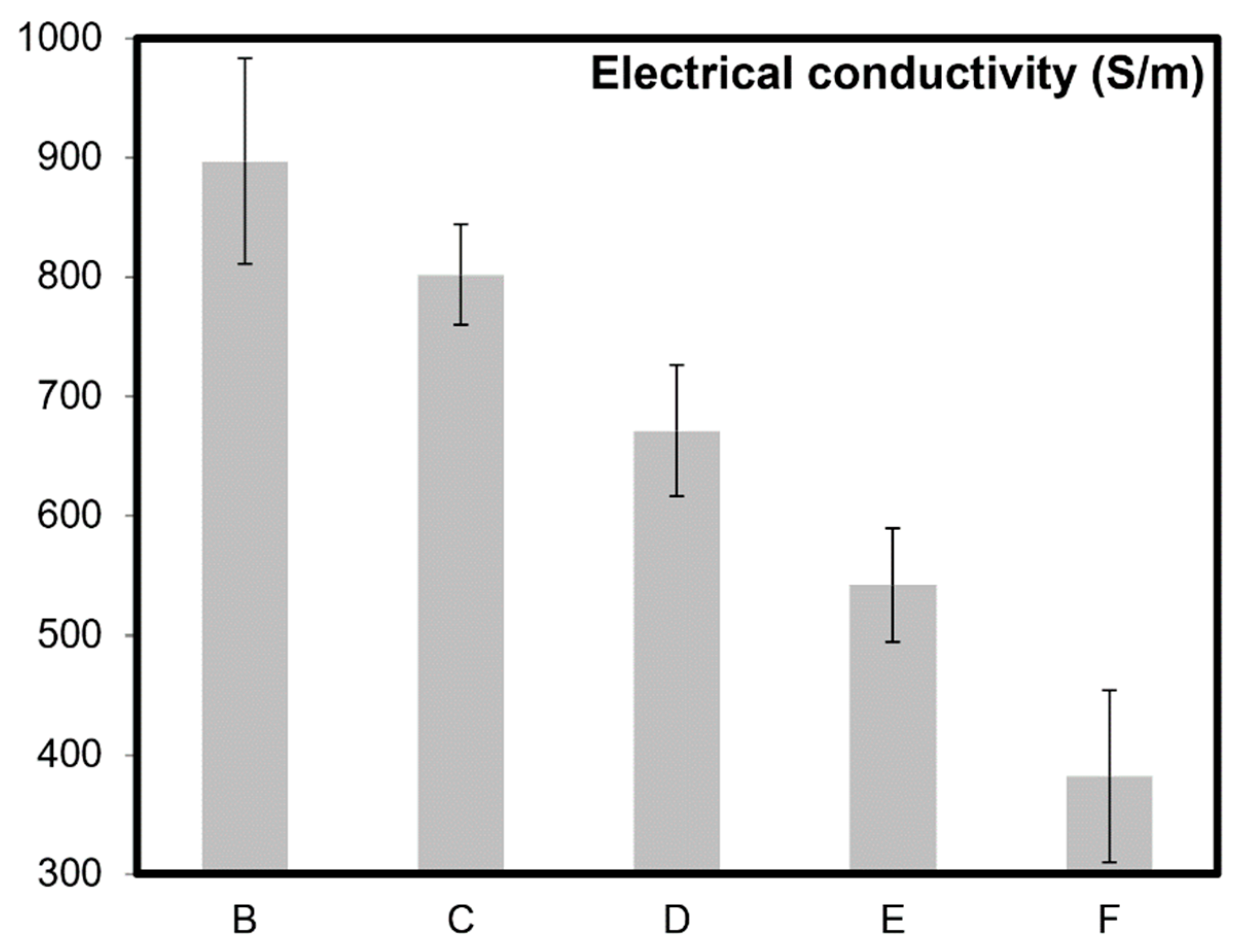
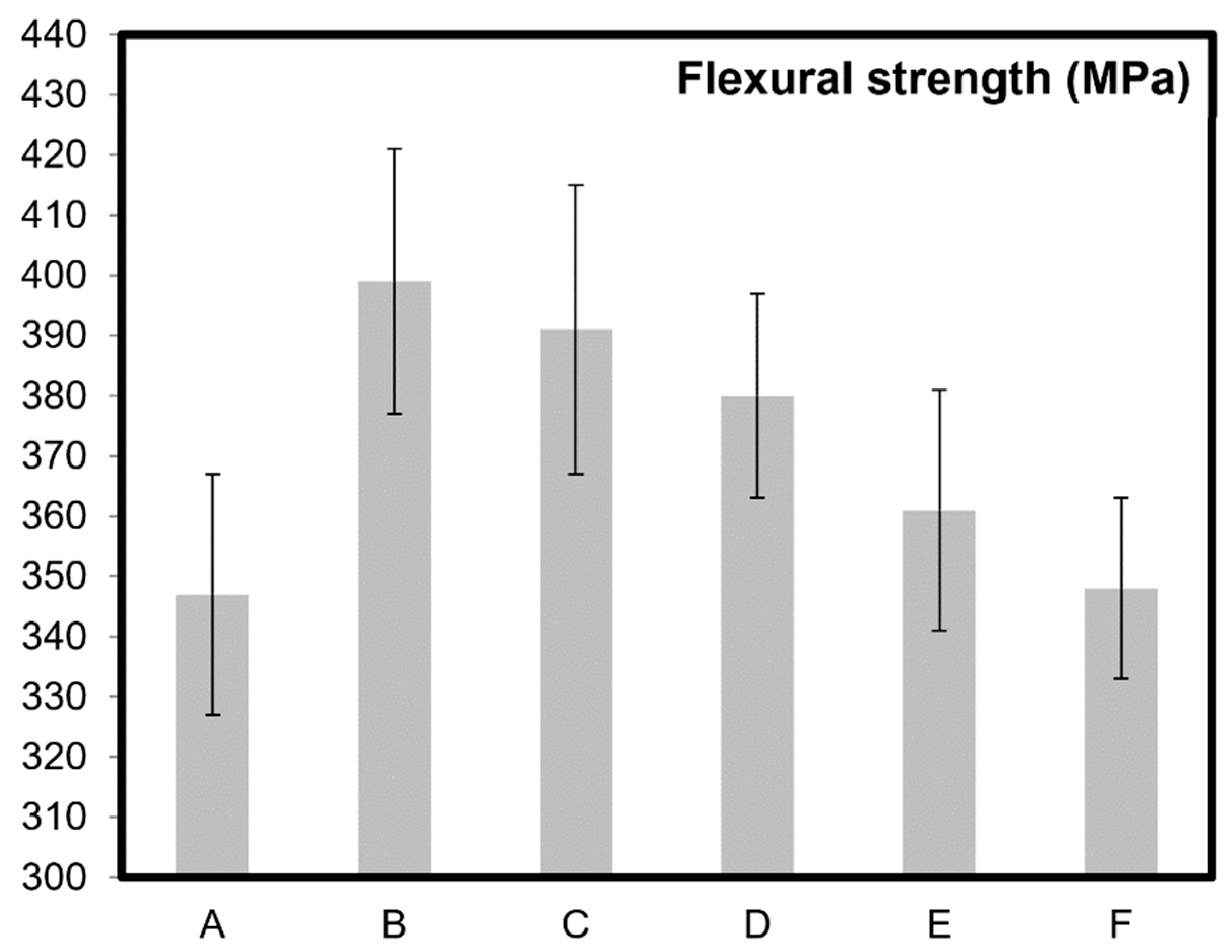

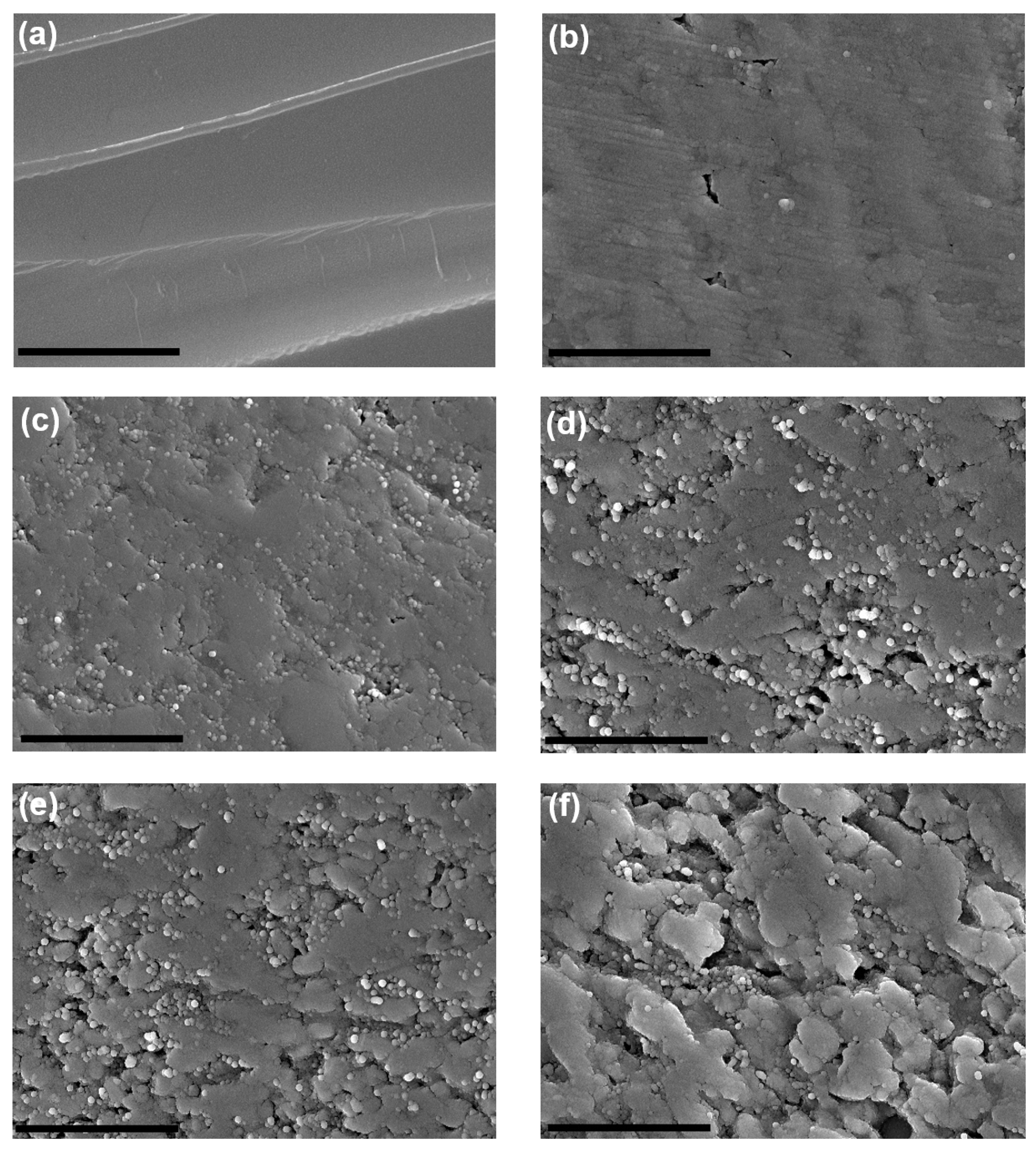
| Sample Name | wt% of CNTs | Grain Size, Before Oxidation | Oxidation Time (mins) After Sintering | Relative Color Intensity After Oxidation (%) | Theoretical Density (%), After Oxidation | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0 | 5.3 ± 1.7 µm | NA | 0 | NA | 1.9 ± 0.2 |
| B | 5 | 78 ± 36 nm | 0 | 100 | 99.9 | 4.9 ± 0.5 |
| C | 5 | 84 ± 32 nm | 5 | 92 | 99.5 | 15.3 ± 0.2 |
| D | 5 | 90 ± 43 nm | 10 | 80 | 99.0 | 22.9 ± 0.3 |
| E | 5 | 85 ± 65 nm | 15 | 72 | 98.7 | 26.3 ± 0.6 |
| F | 5 | 89 ± 46 nm | 20 | 61 | 98.5 | 37.9 ± 0.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okolo, C.; Rafique, R.; Iqbal, S.S.; Subhani, T.; Saharudin, M.S.; Bhat, B.R.; Inam, F. Customizable Ceramic Nanocomposites Using Carbon Nanotubes. Molecules 2019, 24, 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173176
Okolo C, Rafique R, Iqbal SS, Subhani T, Saharudin MS, Bhat BR, Inam F. Customizable Ceramic Nanocomposites Using Carbon Nanotubes. Molecules. 2019; 24(17):3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173176
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkolo, Chinyere, Rafaila Rafique, Sadia Sagar Iqbal, Tayyab Subhani, Mohd Shahneel Saharudin, Badekai Ramachandra Bhat, and Fawad Inam. 2019. "Customizable Ceramic Nanocomposites Using Carbon Nanotubes" Molecules 24, no. 17: 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173176
APA StyleOkolo, C., Rafique, R., Iqbal, S. S., Subhani, T., Saharudin, M. S., Bhat, B. R., & Inam, F. (2019). Customizable Ceramic Nanocomposites Using Carbon Nanotubes. Molecules, 24(17), 3176. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24173176








