Black Sorghum Phenolic Extract Regulates Expression of Genes Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxicity of Phenolic-Rich Black Sorghum Extract (BSE) on HUVECs
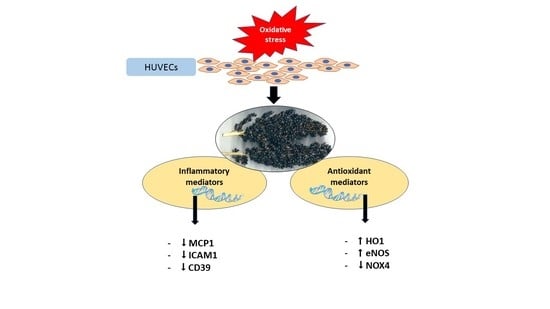
2.2. Phenolic-Rich BSE Regulates the Expression of Oxidative Stress-Induced Antioxidant Pathway-Related Genes
2.3. Phenolic-Rich BSE Regulates the Expression of Oxidative Stress-Induced Inflammatory Pathway Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sorghum Samples and Phenolic Extraction
4.2. Cells and Culture Conditions
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Experimental Design and Oxidative Stress Induction
4.5. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription
4.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3DXA | 3-deoxyanthocyanidin |
| BSE | black sorghum extract |
| CD | cluster differentiation |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| HO 1 | heme oxygenase |
| HUVECs | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| ICAM 1 | intercellular adhesion molecule |
| MCP) 1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein |
| NOX) 4 | NADPH oxidase |
| NQO 1 | NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
References
- Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Rengarajan, T.; Thangavel, J.; Nishigaki, Y.; Sakthisekaran, D.; Sethi, G.; Nishigaki, I. The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craige, S.M.; Kant, S.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Reactive Oxygen Species in Endothelial Function–From Disease to Adaptation. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, J. The role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress-induced endothelial injuries. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 225, R83–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vendrov, A.E.; Vendrov, K.C.; Smith, A.; Yuan, J.; Sumida, A.; Robidoux, J.; Runge, M.S.; Madamanchi, N.R. NOX4 NADPH oxidase-dependent mitochondrial oxidative stress in aging-associated cardiovascular disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 23, 1389–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorescu, D.; Weiss, D.; Lassègue, B.; Clempus, R.E.; Szöcs, K.; Sorescu, G.P.; Valppu, L.; Quinn, M.T.; Lambeth, J.D.; Vega, J.D. Superoxide production and expression of nox family proteins in human atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U. Nitric oxide and oxidative stress in vascular disease. Pflügers Archiv-Eur. J. Physiol. 2010, 459, 923–939. [Google Scholar]
- Bernot, D.; Peiretti, F.; Canault, M.; Juhan-Vague, I.; Nalbone, G. Upregulation of TNF-α-induced ICAM-1 surface expression by adenylate cyclase-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 202, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook-Mills, J.M.; Marchese, M.E.; Abdala-Valencia, H. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and signaling during disease: Regulation by reactive oxygen species and antioxidants. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1607–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Jing, G.; Wang, J.J.; Sheibani, N.; Zhang, S.X. ATF4 is a novel regulator of MCP-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. J. Inflamm. 2015, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaglio, S.; Robson, S.C. Ectonucleotidases as regulators of purinergic signaling in thrombosis, inflammation, and immunity. In Advances in Pharmacology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 61, pp. 301–332. [Google Scholar]
- Antonioli, L.; Pacher, P.; Vizi, E.S.; Haskó, G. CD39 and CD73 in immunity and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dykes, L.; Rooney, L.W.; Waniska, R.D.; Rooney, W.L. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of sorghum grains of varying genotypes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6813–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Santhakumar, A.B.; Chinkwo, K.A.; Wu, G.; Johnson, S.K.; Blanchard, C.L. Characterization of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity in sorghum grains. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Johnson, S.K.; Bornman, J.F.; Bennett, S.J.; Clarke, M.W.; Singh, V.; Fang, Z. Growth temperature and genotype both play important roles in sorghum grain phenolic composition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganyadevi, P.; Saravanakumar, K.; Mohandas, S. The antiproliferative activity of 3-deoxyanthocyanins extracted from red sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) bran through P53-dependent and Bcl-2 gene expression in breast cancer cell line. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, S.; Kim, H.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U.; Awika, J.M. Complementary cereals and legumes for health: Synergistic interaction of sorghum flavones and cowpea flavonols against LPS-induced inflammation in colonic myofibroblasts. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callcott, E.T.; Blanchard, C.L.; Oli, P.; Santhakumar, A.B. Pigmented Rice-Derived Phenolic Compounds Reduce Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, L.; Vinayak, M. Long term effect of curcumin in restoration of tumour suppressor p53 and phase-II antioxidant enzymes via activation of Nrf2 signalling and modulation of inflammation in prevention of cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.R.; Monteiro, E.B.; Graziele, F.; Inada, K.O.; Torres, A.G.; Perrone, D.; Soulage, C.O.; Monteiro, M.C.; Resende, A.C.; Moura-Nunes, N. Up-regulation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling by Açaí (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) extract prevents oxidative stress in human endothelial cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Liu, W.-W.; Shi, A.-W.; Gu, N. Salidroside suppresses HUVECs cell injury induced by oxidative stress through activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Jeong, M.G.; Oh, S.; Jang, E.J.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, E.S. A FoxO1-dependent, but NRF2-independent induction of heme oxygenase-1 during muscle atrophy. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.S.; Park, J.-J.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Yun, S.J.; Lee, J.-B.; Lee, S.-C. Nrf2-dependent and Nrf2-independent induction of phase 2 detoxifying and antioxidant enzymes during keratinocyte differentiation. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ago, T.; Kitazono, T.; Ooboshi, H.; Iyama, T.; Han, Y.H.; Takada, J.; Wakisaka, M.; Ibayashi, S.; Utsumi, H.; Iida, M. Nox4 as the major catalytic component of an endothelial NAD (P) H oxidase. Circulation 2004, 109, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, J.; Wang, C.; Kang, L.; Chang, N.; Sun, H. Rhizoma Dioscoreae Nipponicae polysaccharides protect HUVECs from H2O2-induced injury by regulating PPARγ factor and the NADPH oxidase/ROS–NF-κB signal pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkamp-Fenske, K.; Bollinger, L.; Völler, N.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y.; Bauer, R.; Förstermann, U.; Li, H. Ursolic acid from the Chinese herb danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza L.) upregulates eNOS and downregulates Nox4 expression in human endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e104–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugusman, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Hui, C.K.; Nordin, N.A.M.M. Piper sarmentosum inhibits ICAM-1 and Nox4 gene expression in oxidative stress-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xia, N.; Brausch, I.; Yao, Y.; Förstermann, U. Flavonoids from artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) up-regulate endothelial-type nitric-oxide synthase gene expression in human endothelial cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabart, J.; Schini-Kerth, V.; Pincemail, J.; Kevers, C.; Pirotte, B.; Defraigne, J.-O.; Dommes, J. The leaf extract of Ribes nigrum L. is a potent stimulator of the endothelial formation of NO in cultured endothelial cells and porcine coronary artery rings. J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaki, M.; Kawashima, S.; Yamashita, T.; Hirase, T.; Namiki, M.; Inoue, N.; Hirata, K.-i.; Yasui, H.; Sakurai, H.; Yoshida, Y. Overexpression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase accelerates atherosclerotic lesion formation in apoE-deficient mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remppis, A.; Bea, F.; Greten, H.J.; Buttler, A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Preusch, M.R.; Enk, R.; Ehehalt, R.; Katus, H. Rhizoma coptidis inhibits LPS-induced MCP-1/CCL2 production in murine macrophages via an AP-1 and NFB-dependent pathway. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Latil, A.; Libon, C.; Templier, M.; Junquero, D.; Lantoine-Adam, F.; Nguyen, T. Hexanic lipidosterolic extract of Serenoa repens inhibits the expression of two key inflammatory mediators, MCP-1/CCL2 and VCAM-1, in vitro. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E301–E307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Xia, Y.; Niu, P.; Jiang, L.; Duan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Silica nanoparticles induce oxidative stress, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction in vitro via activation of the MAPK/Nrf2 pathway and nuclear factor-κB signaling. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.; Janovjak, H.; Miserez, A.; Dobbie, Z. Processing of gene expression data generated by quantitative real-time RT PCR (vol 32, pg 1378, 2002). Biotechniques 2002, 33, 514. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |



| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | ATGACAATGAGGTTTCTTCGG | CAATGAAGACTGGGCTCTC |
| NQO1 | ACATCACAGGTAAACTGAAGG | TCAGATGGCCTTCTTTATAAGC |
| HO1 | AACTCCCTGGAGATGACTC | CTCAAAGAGCTGGATGTTGAG |
| NOX4 | TATCCAGTCCTTCCGTTGG | CCAATTATCTTCTGTATCCCATCTG |
| eNOS | GTTACCAGCTAGCCAAAGTC | TCTGCTCATTCTCCAGGTG |
| MCP1 | CCAGATGCAATCAATGCCC | TGGTCTTGAAGATCACAGCT |
| ICAM1 | GATAGCCAACCAATGTGCT | TTCTGGAGTCCAGTACACG |
| CD39 | TCAAATGTAGTGTGAAAGGCTC | TACACTCCTCAAAGGCTCTG |
| CD73 | CATTCCTGAAGATCCAAGCA | AGGAGCCATCCAGATAGAC |
| β-Actin | GAAGATCAAGATCATTGCTCCTC | ATCCACATCTGCTGGAAGG |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francis, N.; Rao, S.; Blanchard, C.; Santhakumar, A. Black Sorghum Phenolic Extract Regulates Expression of Genes Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183321
Francis N, Rao S, Blanchard C, Santhakumar A. Black Sorghum Phenolic Extract Regulates Expression of Genes Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells. Molecules. 2019; 24(18):3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183321
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancis, Nidhish, Shiwangini Rao, Christopher Blanchard, and Abishek Santhakumar. 2019. "Black Sorghum Phenolic Extract Regulates Expression of Genes Associated with Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells" Molecules 24, no. 18: 3321. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24183321