Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of the IC50 for Bacopasides I and II Individually and Combined
2.2. Bacopasides I and II Combined Reduced the Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.3. Higher Combination Doses of Bacopasides I and II Induced G2/M Arrest
2.4. Bacopasides I and II Combined Altered the Morphology of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.5. Combination Doses of Bacopasides I and II Increased Annexin-V Staining
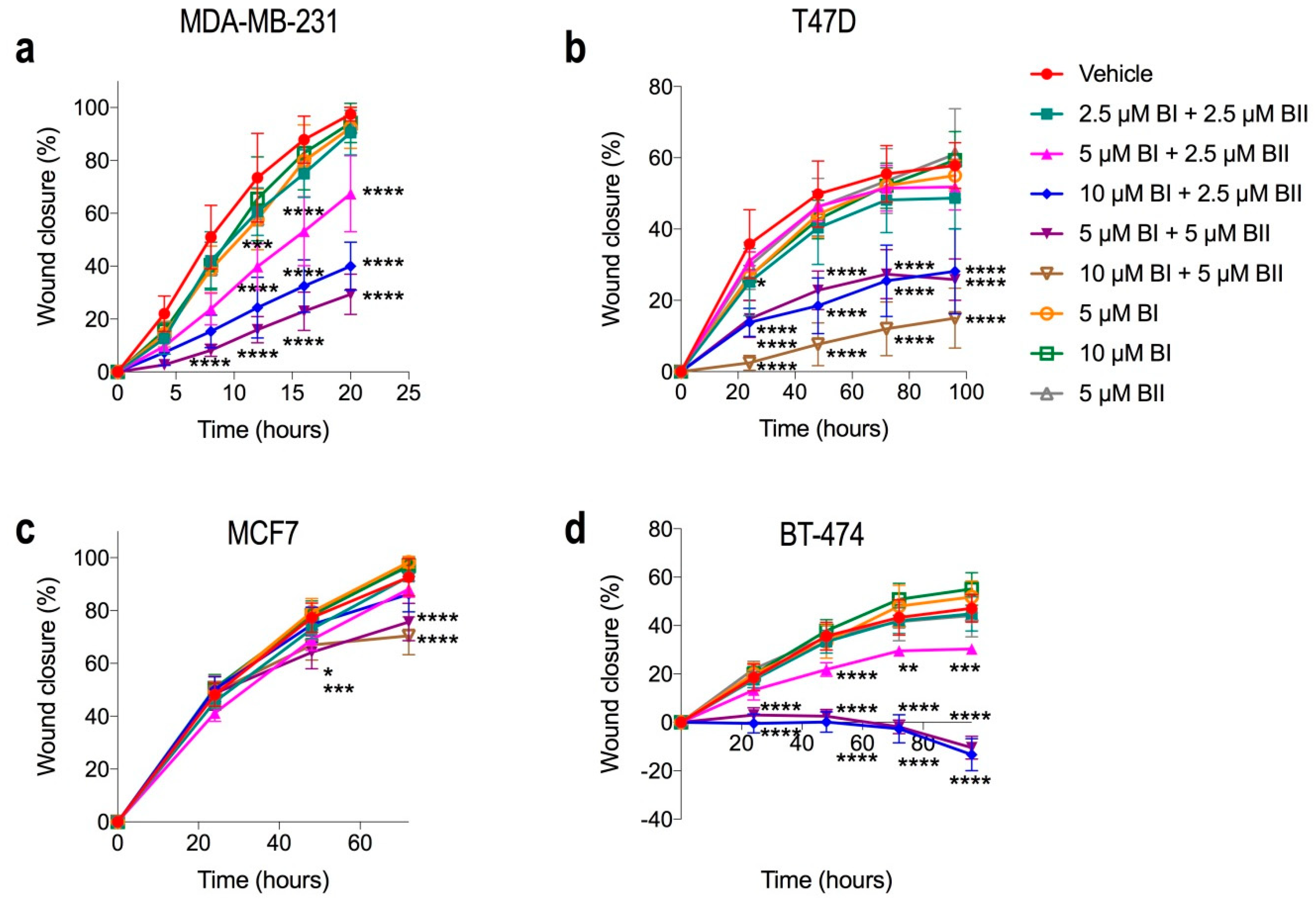
2.6. Combination Doses of Bacopasides I and II Reduced Migration of Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.7. Combination Doses of Bacopasides I and II Reduced Invasion of MDA-MB-231
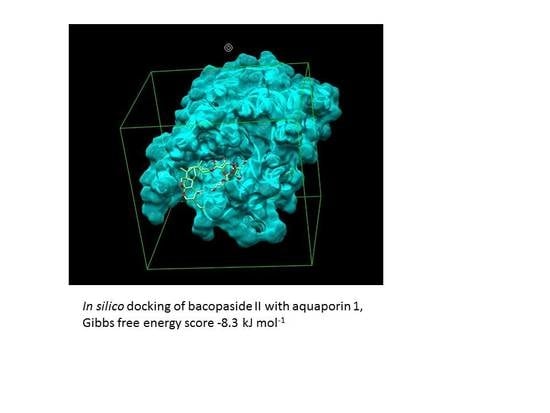
2.8. Combination Doses of Bacopasides I and II Reduced Transcript Expression of AQP1 in MDA-MB-231 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Cell Lines
4.2. Cell Viability Assay for Determining IC50 and Drug Synergy
4.3. Cell Proliferation
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Apoptosis Assay
4.6. Scratch Wound (Wound Closure) Migration Assay
4.7. Spheroid Invasion Assay
4.8. Analysis of Aquaporin-1 Expression by Quantitative PCR
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yersal, O.; Barutca, S. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMichele, A.; Yee, D.; Esserman, L. Mechanisms of Resistance to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2287–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Cabal, M.; García-Teijido, P.; Fernández-Pérez, Y.; Sánchez-Lorenzo, L.; Palacio-Vázquez, I. Mechanisms behind the Resistance to Trastuzumab in HER2-Amplified Breast Cancer and Strategies to Overcome It. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2016, 10, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebert, J.; Lester, R.; Powell, E.; Seal, M.; McCarthy, J. Advances in the systemic treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S142–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.C. Production and engineering of terpenoids in plant cell culture. Nat. Methods 2007, 3, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghersi, D.; Willson, M.L.; Chan, M.M.K.; Simes, J.; Donoghue, E.; Wilcken, N. Taxane-containing regimens for metastatic breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD003366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marupudi, N.I.; Han, J.E.; Li, K.W.; Renard, V.M.; Tyler, B.M.; Brem, H. Paclitaxel: A review of adverse toxicities and novel delivery strategies. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2007, 6, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němcová-Fürstová, V.; Kopperová, D.; Balušíková, K.; Ehrlichová, M.; Brynychová, V.; Václavíková, R.; Daniel, P.; Souček, P.; Kovář, J. Characterization of acquired paclitaxel resistance of breast cancer cells and involvement of ABC transporters. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 310, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.-R.; Long, F.-Y.; Chen, C. Research Progress on Natural Triterpenoid Saponins in the Chemoprevention and Chemotherapy of Cancer. DNA Replication Across Taxa 2014, 36, 95–130. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Kong de, Y.; Zhang, W.D. Antitumor activities of dammarane triterpene saponins from bacopa monniera. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 864–868. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.V.; Kourghi, M.; De Ieso, M.L.; Campbell, E.M.; Dorward, H.S.; Hardingham, J.E.; Yool, A.J. Differential Inhibition of Water and Ion Channel Activities of Mammalian Aquaporin-1 by Two Structurally Related Bacopaside Compounds Derived from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The Aquaporin 1 Inhibitor Bacopaside II Reduces Endothelial Cell Migration and Tubulogenesis and Induces Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Pei, J.V.; Townsend, A.R.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. The Purified Extract from the Medicinal Plant Bacopa monnieri, Bacopaside II, Inhibits Growth of Colon Cancer Cells In Vitro by Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis. Cells 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Borrelli, F. Bacopa monniera, a reputed nootropic plant: An overview. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, S.; Borowski, T. Neuropharmacological Review of the Nootropic Herb Bacopa monnieri. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Anderson, M.O.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins: Important but elusive drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A.S. Impairment of angiogenesis and cell migration by targeted aquaporin-1 gene disruption. Nature 2005, 434, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva-Font, C.; Jin, B.J.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-1 gene deletion reduces breast tumor growth and lung metastasis in tumor-producing mmtv-pyvt mice. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Verkman, A.S. Increased migration and metastatic potential of tumor cells expressing aquaporin water channels. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorward, H.S.; Du, A.; Bruhn, M.A.; Wrin, J.; Pei, J.V.; Evdokiou, A.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Hardingham, J.E. Pharmacological blockade of aquaporin-1 water channel by aqb013 restricts migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells and prevents endothelial tube formation in vitro. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourghi, M.; Pei, J.V.; De Ieso, M.L.; Flynn, G.; Yool, A.J. Bumetanide derivatives aqb007 and aqb011 selectively block the aquaporin-1 ion channel conductance and slow cancer cell migration. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Luo, L.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhao, C. Aquaporins in human breast cancer: Identification and involvement in carcinogenesis of breast cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 106, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zhang, H.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Fu, L.; Gu, F.; Ma, Y. Expression of aquaporin1, a water channel protein, in cytoplasm is negatively correlated with prognosis of breast cancer patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8143–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.-B.; Shi, S.; Zhang, R.-J.; Wang, T.-T.; Tan, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Fei, X.-Y.; Ding, G.-L.; Gao, Q.; Chen, C.; et al. Aquaporin-1 Plays a Crucial Role in Estrogen-Induced Tubulogenesis of Vascular Endothelial Cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E672–E682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otterbach, F.; Callies, R.; Adamzik, M.; Kimmig, R.; Siffert, W.; Schmid, K.W.; Bankfalvi, A. Aquaporin 1 (aqp1) expression is a novel characteristic feature of a particularly aggressive subgroup of basal-like breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 120, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczurkiewicz, P.; Łojewski, M.; Piska, K.; Michalik, M.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Szewczyk, A.; Hałaszuk, P.; Pękala, E.; Muszyńska, B. Chemopreventive and Anticancer Activities of Bacopa Monnieri Extracted from Artificial Digestive Juices. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, M.; Sangli, G.K.; Arun, P.C.; Amit, A. Quantitative determination of the major saponin mixture bacoside A inBacopa monnieri by HPLC. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.N.; Khan, W.; Parveen, R.; Ahmad, S.; Sadaf; Najm, M.; Ahmad, I.; Husain, S. Exploring the cytotoxic potential of triterpenoids-enriched fraction of Bacopa monnieri by implementing In vitro, In vivo, and In silico approaches. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, 595. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, M.N.; Akhtar, M.S.; Najm, M.Z.; Tamboli, E.T.; Ahmad, S.; Husain, S.A. Evaluation of anticancer potential of Bacopa monnieri L. against MCF-7 and MDA-MB 231 cell line. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 325–328. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.; Vadera, K.; Patil, D.; Phatak, A.; Juvekar, A.; Chandra, N. In vitro anticancer activity and phytochemical analysis of bacopa monnieri (l.) wettst. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 4432–4438. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, N.S.; Sundaram, R.; Mitra, S.K. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of bacoside a from whole plant of bacopa monnieiri (linn). Am. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 6, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Sivakumar, K.C.; Mishra, R. Bacoside A Induces Tumor Cell Death in Human Glioblastoma Cell Lines through Catastrophic Macropinocytosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, P.; Sivakumari, K.; Geetha, A.; Ravisankar, B.; Parthasarathy, C. Chemopreventive effect of bacoside a on n-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnoi, S.; Agarwal, R.C. Chemopreventive action of bacopa monnieri (brahmi) hydromethanolic extract on dmba-induced skin carcinogenesis in swiss albino mice. J. Pharmacog. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Shilki, V.; Agrawal, N. Modulation of carcinogenicity and mutagenicity by herbal medicinal plant Bacopa monnieri extract in swiss albino mice. J. Mol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rébé, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy on cancer and immune cells: How can it be modulated to generate novel therapeutic strategies? Futur. Oncol. 2015, 11, 2645–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murthy, P.B.S.; Raju, V.R.; Ramakrisana, T.; Chakravarthy, M.S.; Kumar, K.V.; Kannababu, S.; Subbaraju, G.V. Estimation of twelve bacopa saponins in Bacopa monnieri extracts and formulations by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phrompittayarat, W.; Putalun, W.; Tanaka, H.; Jetiyanon, K.; Wittaya-areekul, S.; Ingkaninan, K. Comparison of various extraction methods of bacopa monnieri. Naresuan Univ. J. 2007, 15, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sireeratawong, S.; Jaijoy, K.; Khonsung, P.; Lertprasertsuk, N.; Ingkaninan, K. Acute and chronic toxicities of Bacopa monnieri extract in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhateria, M.; Ramakrishna, R.; Puttrevu, S.K.; Singh, R.; Bhatta, R.S. Analysis of bacopaside I in biomatrices using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Pharmacokinetics and brain distribution in Swiss-albino mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Yue, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Shan, L.; Zhang, W. The antidepressant-like effect of bacopaside I: Possible involvement of the oxidative stress system and the noradrenergic system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 110, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollala, V.R.; Upadhya, S.; Nayak, S. Learning and memory-enhancing effect of Bacopa monniera in neonatal rats. Bratisl Lek List. 2011, 112, 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Roodenrys, S.; Booth, D.; Bulzomi, S.; Phipps, A.; Micallef, C.; Smoker, J. Chronic Effects of Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) on Human Memory. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2002, 27, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Abichandani, L.G.; Thawani, V.; Gharpure, K.J.; Naidu, M.U.; Venkat Ramana, G. Efficacy of standardized extract of bacopa monnieri (bacognize(r)) on cognitive functions of medical students: A six-week, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 4103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.K.; Dhawan, B.N. Neuropsychopharmacologial effects of the ayurvedic nootropic bacopa monniera linn. (brahmi). Ind. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 29, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Estimating the maximum safe starting dose in initial clinical trials for therapeutics in adult healthy volunteers. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/estimating-maximum-safe-starting-dose-initial-clinical-trials-therapeutics-adult-healthy-volunteers (accessed on 20 May 2019).
- Janani, P.; Sivakumari, K.; Geetha, A.; Yuvaraj, S.; Parthasarathy, C. Bacoside A downregulates matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in DEN-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2010, 28, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wientjes, M.G.; Zhao, L. Comparison of methods for evaluating drug-drug interaction. Front. Biosci. 2010, 2, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palethorpe, H.M.; Drew, P.A.; Smith, E. Androgen Signaling in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ieso, M.L.; Pei, J.V. An accurate and cost-effective alternative method for measuring cell migration with the circular wound closure assay. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palethorpe, H.M.; Smith, E.; Tomita, Y.; Nakhjavani, M.; Yool, A.J.; Price, T.J.; Young, J.P.; Townsend, A.R.; Hardingham, J.E. Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193539
Palethorpe HM, Smith E, Tomita Y, Nakhjavani M, Yool AJ, Price TJ, Young JP, Townsend AR, Hardingham JE. Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules. 2019; 24(19):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193539
Chicago/Turabian StylePalethorpe, Helen M., Eric Smith, Yoko Tomita, Maryam Nakhjavani, Andrea J. Yool, Timothy J. Price, Joanne P. Young, Amanda R. Townsend, and Jennifer E. Hardingham. 2019. "Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines" Molecules 24, no. 19: 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193539
APA StylePalethorpe, H. M., Smith, E., Tomita, Y., Nakhjavani, M., Yool, A. J., Price, T. J., Young, J. P., Townsend, A. R., & Hardingham, J. E. (2019). Bacopasides I and II Act in Synergy to Inhibit the Growth, Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules, 24(19), 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24193539