Large Pore Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles for Pepstatin A Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
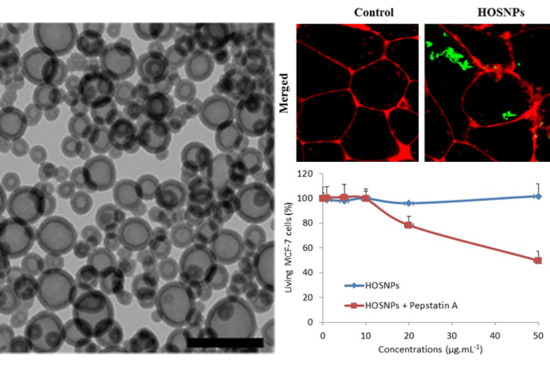
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of HOSNPs
3.2. Synthesis of LPMSNs
3.3. Loading of Nanoparticles with Pepstatin A
3.4. Loading of HOSNPs with Protected RGD Peptide
3.5. Loading of HOSNPs with Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)
3.6. Cell Culture
3.7. Fluorescence Imaging of Cell Uptake of NPs
3.8. Cytotoxic Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruehle, B.; Saint-Cricq, P.; Zink, J.I. Externally controlled nanomachines on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, R.R.; Colilla, M.; Vallet-Regi, M. Advances in mesoporous silica-based nanocarriers for co-delivery and combination therapy against cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, C. Advances in silica based nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqua, L.; Leggio, A.; Sisci, D.; Ando, S.; Morelli, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Relevance of the targeting function. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.F.; Dias, D.R.; Correia, I.J. Stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 236, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Panwar, N.; Tng, D.J.H.; Tjin, S.C.; Wang, K.; Yong, K.-T. The application of mesoporous silica nanoparticle family in cancer theranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 319, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Han, N.; Bai, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Che, E.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, T.; et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giret, S.; Man, M.W.C.; Carcel, C. Mesoporous-silica-functionalized nanoparticles for drug delivery. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 13850–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, C.; Nagaich, U.; Pal, A.K.; Gulati, N. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadrah, P.; Planinsek, O.; Gaberscek, M. Stimulus-responsive mesoporous silica particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, P.N.; Chopda, L.V. A review on application of multifunctional mesoporous nanoparticles in controlled release of drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 781, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyo, C.; Weiss, V.; Bräuchle, C.; Bein, T. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a universal platform for drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 435–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamaeva, V.; Sahlgren, C.; Linden, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in medicine-recent advances. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.-T.; Cheng, S.-H.; Souris, J.S.; Chen, C.-T.; Mou, C.-Y.; Lo, L.-W. Theranostic applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and their organic/inorganic hybrids. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, E.; Mori, S.; Shimojima, A.; Wada, H.; Kuroda, K. Fabrication of colloidal crystals composed of pore-expanded mesoporous silica nanoparticles prepared by a controlled growth method. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, E.; Kuroda, K. Colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 501–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knezevic, N.Z.; Durand, J.-O. Large pore mesoporous silica nanomaterials for application in delivery of biomolecules. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.; Pochert, A.; Gerber, M.; Raber, H.F.; Linden, M. Influence of mesopore size and peptide aggregation on the adsorption and release of a model antimicrobial peptide onto/from mesoporous silica nanoparticles in vitro. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2017, 2, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, K.; Pochert, A.; Lindén, M.; Davoudi, M.; Schmidtchen, A.; Nordström, R.; Malmsten, M. Membrane interactions of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers of antimicrobial peptides. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2016, 475, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, R.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Shezad, K.; et al. Encapsulation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic peptides into hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhancement of antitumor immune response. Small 2017, 13, 1701741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Xing, G.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J. A pH-dependent antibacterial peptide release nano-system blocks tumor growth in vivo without toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre, C.; Domínguez-Berrocal, L.; Murguía, J.R.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Bravo, J.; Sancenón, F. ϵ-polylysine-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carrier of the c9h peptide to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 1890–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Cattoen, X.; Durand, J.-O.; Wong Chi Man, M.; Khashab, N.M. Organosilica hybrid nanomaterials with a high organic content: Syntheses and applications of silsesquioxanes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 19945–19972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M. Biomedical applications of organosilica nanoparticles toward theranostics. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2012, 1, 469–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; Zhang, X.; Kleitz, F.; Qiao, S.Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with organo-bridged silsesquioxane framework as innovative platforms for bioimaging and therapeutic agent delivery. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 90–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Chemistry of mesoporous organosilica in nanotechnology: Molecularly organic-inorganic hybridization into frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3235–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Cattoen, X.; Man, M.W.C.; Durand, J.-O.; Khashab, N.M. Syntheses and applications of periodic mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20318–20334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urata, C.; Yamada, H.; Wakabayashi, R.; Aoyama, Y.; Hirosawa, S.; Arai, S.; Takeoka, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Aqueous colloidal mesoporous nanoparticles with ethenylene-bridged silsesquioxane frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8102–8105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datz, S.; Engelke, H.; Schirnding, C.V.; Nguyen, L.; Bein, T. Lipid bilayer-coated curcumin-based mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for cellular delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 225, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meka, A.K.; Zhang, H.; Xu, C.; Lin, C.X.C.; Yu, M.; Yu, C. Biphasic synthesis of large-pore and well-dispersed benzene bridged mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles for intracellular protein delivery. Small 2015, 11, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynadier, M.; Vezenkov, L.L.; Amblard, M.; Martin, V.; Gandreuil, C.; Vaillant, O.; Gary-Bobo, M.; Basile, I.; Hernandez, J.-F.; Garcia, M.; et al. Dipeptide mimic oligomer transporter mediates intracellular delivery of cathepsin D inhibitors: A potential target for cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2013, 171, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, S.; Cao, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhou, S.; Pang, Z.; Geng, D.; Zhang, J. A multimodal pepstatin A peptide-based nanoagent for the molecular imaging of p-glycoprotein in the brains of epilepsy rats. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981; pp. 59–124. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmani, S.; Budimir, J.; Sejalon, M.; Daurat, M.; Aggad, D.; Vives, E.; Raehm, L.; Garcia, M.; Lichon, L.; Gary-Bobo, M.; et al. Large Pore Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles for Pepstatin A Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020332
Rahmani S, Budimir J, Sejalon M, Daurat M, Aggad D, Vives E, Raehm L, Garcia M, Lichon L, Gary-Bobo M, et al. Large Pore Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles for Pepstatin A Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules. 2019; 24(2):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020332
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmani, Saher, Jelena Budimir, Mylene Sejalon, Morgane Daurat, Dina Aggad, Eric Vives, Laurence Raehm, Marcel Garcia, Laure Lichon, Magali Gary-Bobo, and et al. 2019. "Large Pore Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles for Pepstatin A Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells" Molecules 24, no. 2: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020332
APA StyleRahmani, S., Budimir, J., Sejalon, M., Daurat, M., Aggad, D., Vives, E., Raehm, L., Garcia, M., Lichon, L., Gary-Bobo, M., Durand, J.-O., & Charnay, C. (2019). Large Pore Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles for Pepstatin A Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells. Molecules, 24(2), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24020332