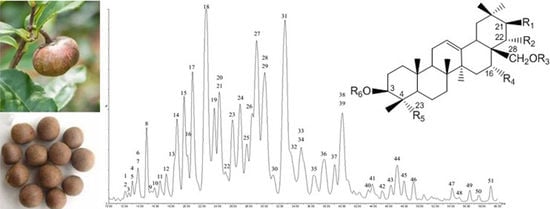
Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Triterpene Saponins from Camellia sinensis Seeds Using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
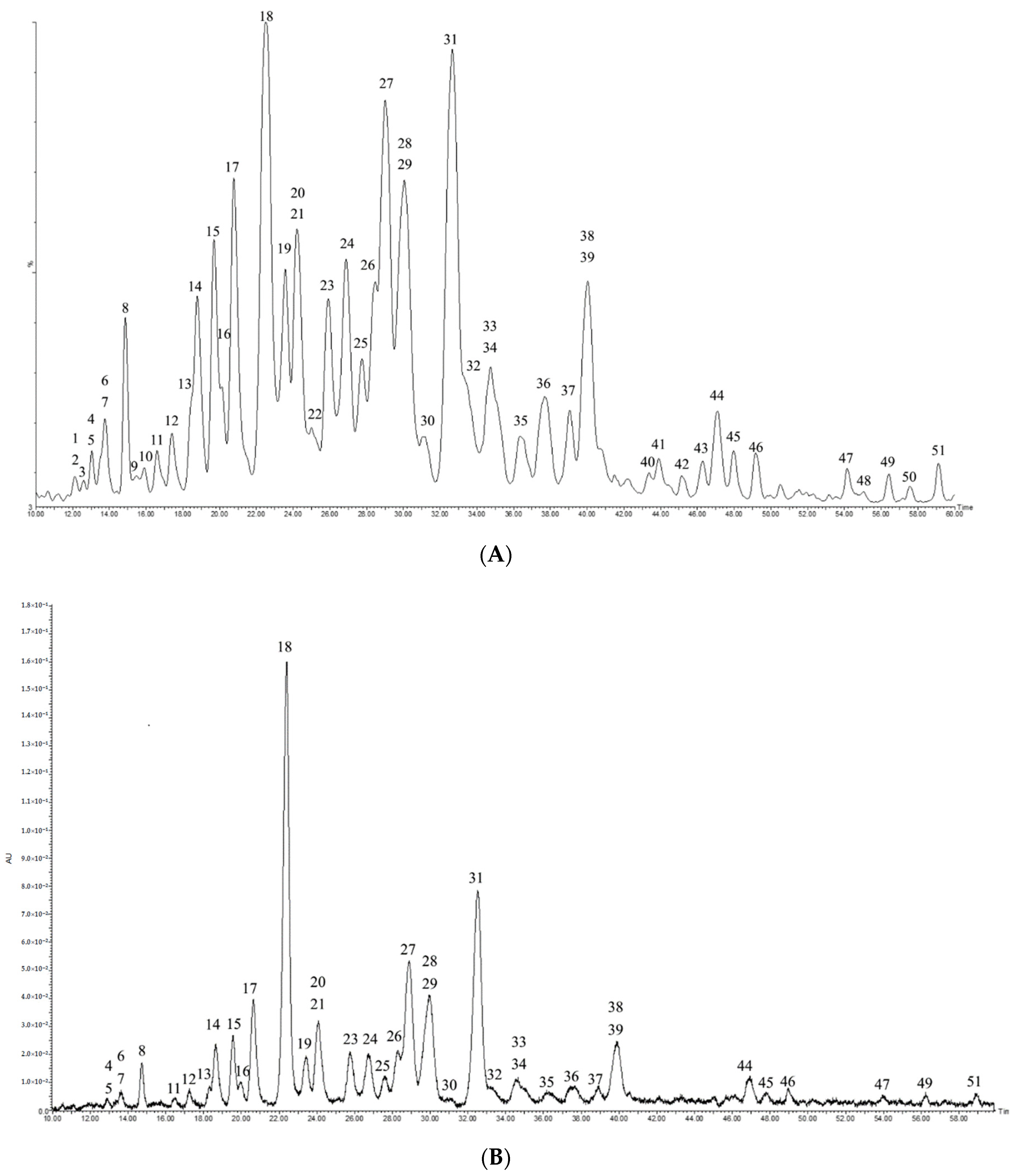
2.1. Optimization of UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS Chromatography
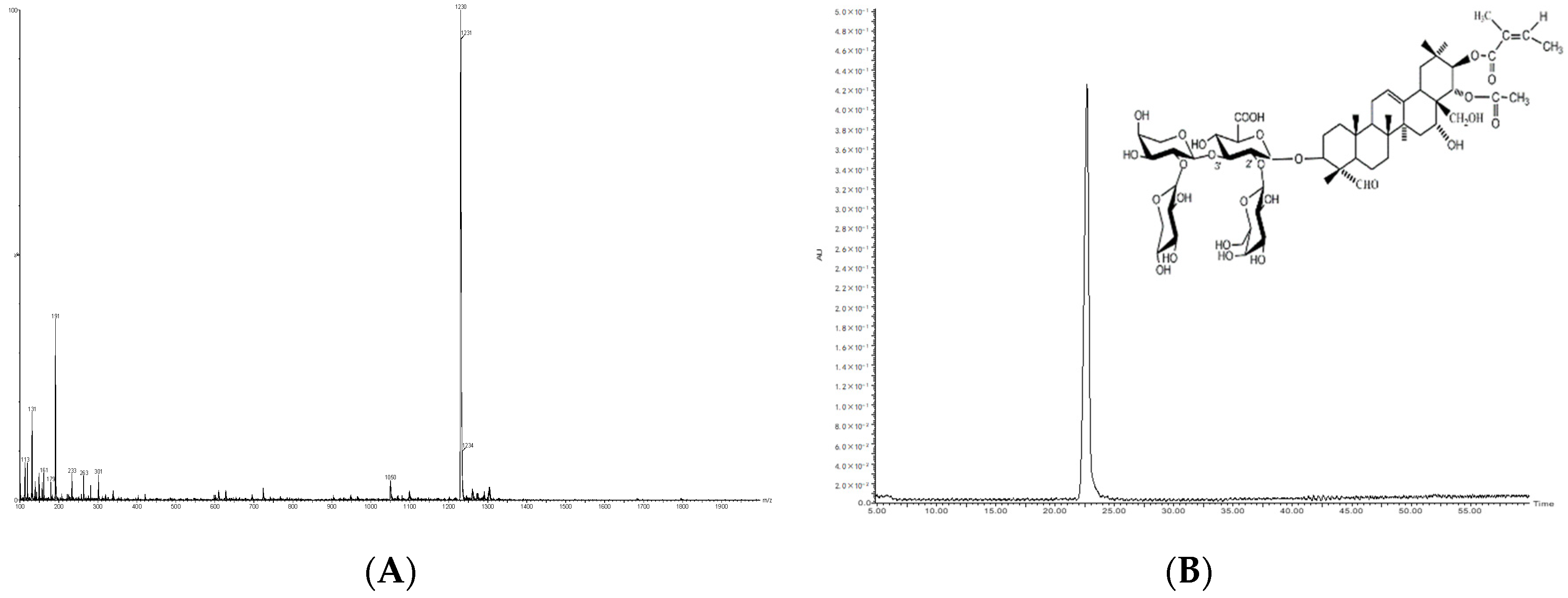
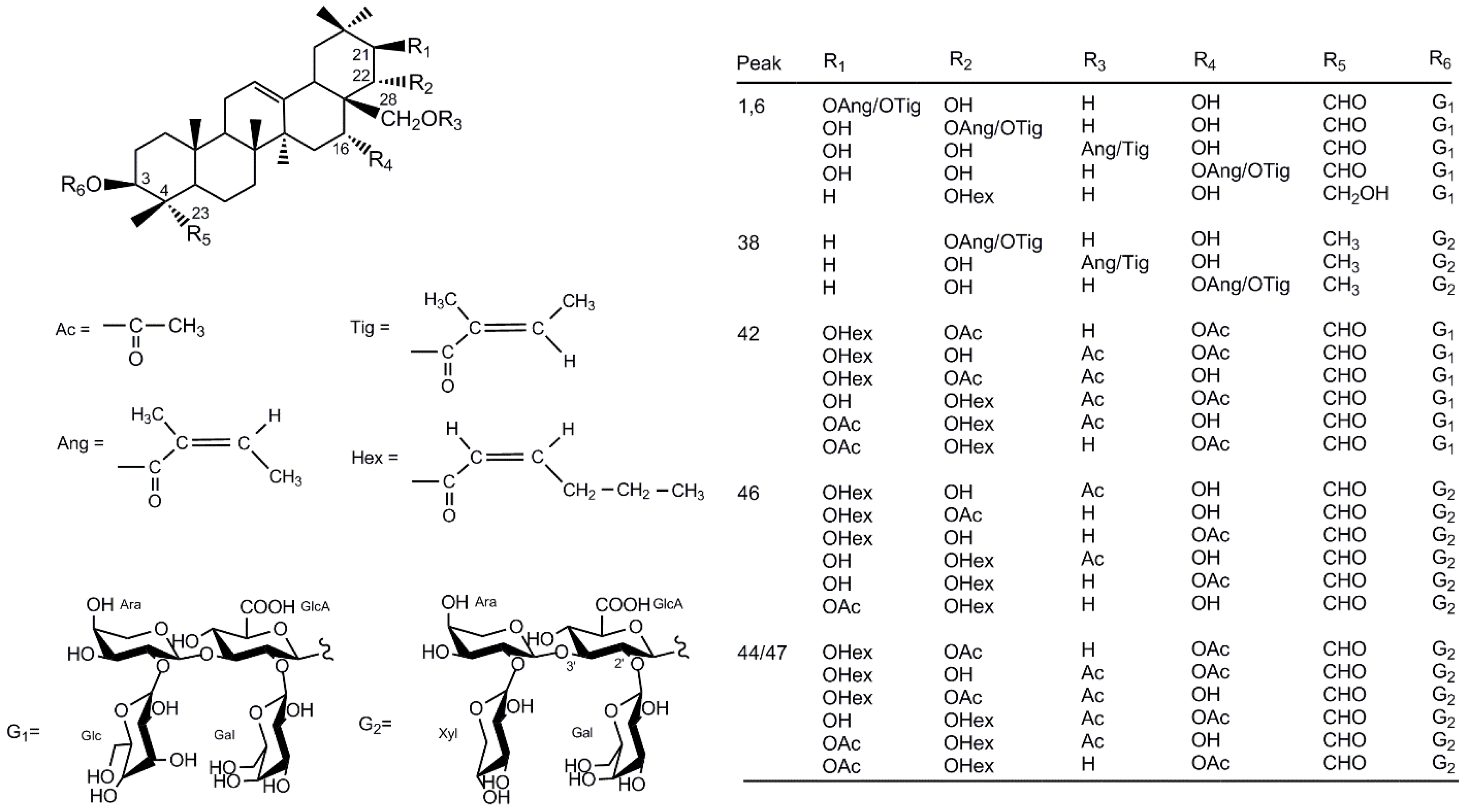
2.2. Compound Characterization of Saponins by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS
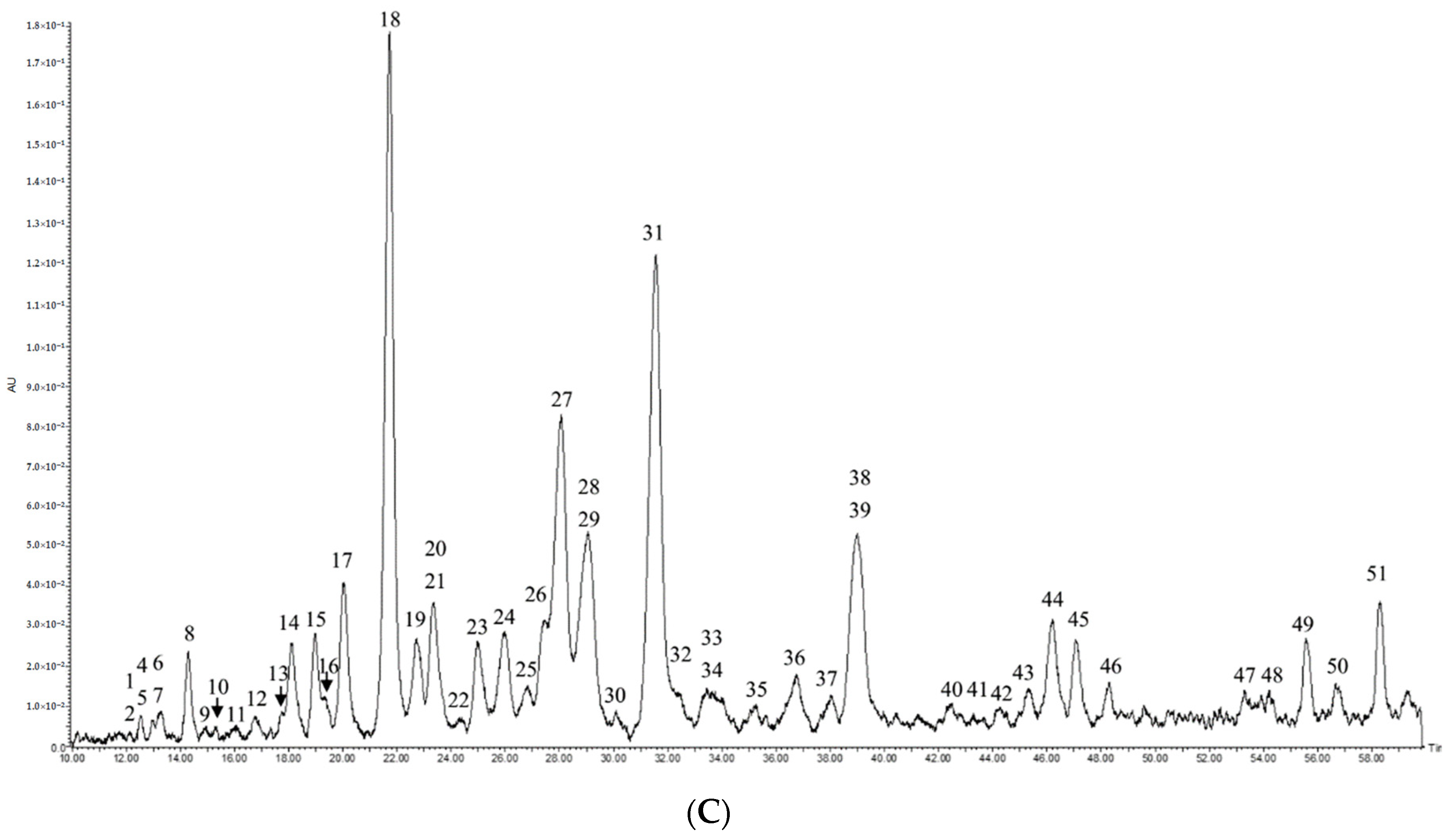
2.3. Quantitation of Saponins by UPLC-PDA
2.4. Comparison between Vanillin-Sulfuric Acid Assay and UPLC-PDA
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plant Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Tea Seed Extract, Total Saponin Fraction and Standard Substance (Theasaponin E1)
3.3. Separation and Identification of Saponins by UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS
3.4. Quantification of Saponins by UPLC-PDA
3.5. Vanillin-Sulfuric Acid Assay
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Carbon | 13C-NMR δ (ppm) | 1H-NMR δ (ppm), Multiplicity, JHH (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| C-1 | 37.91 | |
| C-2 | 25.00 | |
| C-3 | 84.28 | |
| C-4 | 54.91 | |
| C-5 | 48.08 | |
| C-6 | 20.12 | |
| C-7 | 32.15 | |
| C-8 | 40.03 | |
| C-9 | 46.51 | |
| C-10 | 35.78 | |
| C-11 | 23.52 | |
| C-12 | 122.75 | 5.38 (1H), br s |
| C-13 | 142.67 | |
| C-14 | 41.44 | |
| C-15 | 34.30 | |
| C-16 | 67.67 | |
| C-17 | 47.75 | |
| C-18 | 39.84 | |
| C-19 | 46.90 | |
| C-20 | 36.02 | |
| C-21 | 78.63 | 6.62 (1H), d, 10.1 |
| C-22 | 74.11 | 6.21 (1H), d, 10.1 |
| C-23 | 209.74 | 9.93 (1H), s |
| C-24 | 10.82 | 1.48 (3H), s |
| C-25 | 15.53 | 0.81 (3H), s |
| C-26 | 16.54 | 0.87 (3H), s |
| C-27 | 27.14 | 1.78 (3H), s |
| C-28 | 63.57 | |
| C-29 | 29.22 | 1.10 (3H), s |
| C-30 | 20.02 | 1.22 (3H), s |
| GlcA-1′ | 103.91 | 4.86 (1H), d, 7.3 |
| 2′ | 78.02 | |
| 3′ | 83.78 | |
| 4′ | 70.58 | |
| 5′ | 77.04 | |
| 6′ | 171.89 | |
| Gal-1′′ | 103.02 | 5.79 (1H), d, 7.6 |
| 2′′ | 73.47 | |
| 3′′ | 75.15 | |
| 4′′ | 70.27 | |
| 5′′ | 76.32 | |
| 6′′ | 61.82 | |
| Ara-1′′′ | 101.39 | 5.77 (1H), d, 6.5 |
| 2′′′ | 82.08 | |
| 3′′′ | 73.12 | |
| 4′′′ | 68.09 | |
| 5′′′ | 65.75 | |
| Xyl-1′′′′ | 106.82 | 5.02 (1H), d, 7.6 |
| 2′′′′ | 75.70 | |
| 3′′′′ | 77.99 | |
| 4′′′′ | 70.51 | |
| 5′′′′ | 67.27 | |
| Ang-1′′′′′ | 167.61 | |
| 2′′′′′ | 128.73 | |
| 3′′′′′ | 136.78 | 6.00 (1H), dq-like |
| 4′′′′′ | 15.65 | 2.11 (3H), d, 7.0 |
| 5′′′′′ | 20.76 | 2.03 (3H), s |
| Ac-1′′′′′′ | 170.72 | |
| 2′′′′′′ | 20.62 | 1.93 (3H), s |
References
- Mukhopadhyay, M.; Mondal, T.K.; Chand, P.K. Biotechnological advances in tea (Camellia sinensis [L.] O. Kuntze): A review. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 255–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Vik, S.B.; Tu, Y.Y. Theaflavins inhibit the ATP synthase and the respiratory chain without increasing superoxide production. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirbas, A. Tea seed upgrading facilities and economic assessment of biodiesel production from tea seed oil. Energy Convers. Manage. 2010, 51, 2595–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Morikawa, T.; Matsuda, H.; Ninomiya, K.; Li, X.A.; Yoshikawa, M. New flavanone oligoglycosides, theaflavanosides I, II, III, and IV, with hepatoprotective activity from the seeds of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Heterocycles 2007, 71, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tu, Y. Response surface optimization of supercritical fluid extraction of kaempferol glycosides from tea seed cake. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 32, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T.T.; Sun, P.L. Isolation, antioxidant and antitumor in vitro activities of cold pressed green tea seed cake polysaccharide. Curr. Top Nutraceut. R 2015, 13, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, D.F.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.G.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.R.; Zhang, Y.J. Triterpenoid saponins from the genus Camellia. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Tong, T.T.; Ren, N.; Tu, Y.Y.; Li, B. Saponins from seeds of Genus Camellia: Phytochemistry and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 2018, 149, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Nakamura, J.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XV. Saponin constituents with gastroprotective effect from the seeds of tea plant, Camellia sinensis L. var. assamica Pierre, cultivated in Sri Lanka: Structures of assamsaponins A, B, C, D, and E. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1999, 47, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Nakamura, J.; Kageura, T.; Matsuda, H.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XVII. Inhibitory effect on gastric emptying and accelerating effect on gastrointestinal transit of tea saponins: Structures of assamsaponins F, G, H, I, and J from the seeds and leaves of the tea plant. Chem Pharm Bull. 2000, 48, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Gao, Y.; Rankin, G.O.; Pigliacampi, A.; Bucur, H.; Li, B.; Tu, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Inhibitory effects of total triterpenoid saponins isolated from the seeds of the tea plant (Camellia sinensis) on human ovarian cancer cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Ma, Z.J.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Phytochemical analysis of the triterpenoids with cytotoxicity and QR inducing properties from the total tea seed saponin of Camellia sinensis. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Ko, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.G.; Sung, N.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Yang, S.; Rho, H.S.; Hong, Y.D.; et al. 21-O-Angeloyltheasapogenol E3, a Novel triterpenoid saponin from the seeds of tea plants, inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses in a NF-kappa B-dependent manner. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 658351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boran, H.; Ciftci, C.; Er, A.; Kose, O.; Kurtoglu, I.Z.; Kayis, S. Evaluation of antibacterial activity of green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) seeds against some fish pathogens in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum). Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 15, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, R.; Sood, S.; Dogra, P.; Mahendru, M.; Kumar, D.; Bhangalia, S.; Pal, H.C.; Kumar, N.; Bhushan, S.; Gulati, A.; et al. In vitro cytotoxicity, antimicrobial, and metal-chelating activity of triterpene saponins from tea seed grown in Kangra valley, India. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 4030–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.D.; Khan, M.I.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, M.G.; Seo, H.J.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, M.Y. HPLC fractionation and pharmacological assessment of green tea seed saponins for antimicrobial, anti-angiogenic and hemolytic activities. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2015, 20, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cay, S. Enhancement of cadmium uptake by Amaranthus caudatus, an ornamental plant, using tea saponin. Environ. Monit Assess. 2016, 188, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, C.Y.; Salman, H.A.K.; Sulaiman, R. Extraction and quantification of saponins: A review. Food Res. Int. 2014, 59, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, C.H.; Chang, M.S.; Ciou, Y.P.; Huang, Y.C. Foam properties and detergent abilities of the saponins from Camellia oleifera. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4417–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.E. Screening of antioxidant and antitumor activities of major ingredients from defatted Camellia oleifera seeds. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, W.A. Chromatographic determination of plant saponins. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 967, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszek, W.; Bialy, Z. Chromatographic determination of plant saponins—An update (2002–2005). J. Chromatogr. A. 2006, 1112, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Wang, Q.; Jin, J.; Qiu, M.S.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.H.; Li, H.; Zhao, ZX. Simultaneous qualitative and quantitative analyses of triterpenoids in Ilex pubescens by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foubert, K.; Cuyckens, F.; Vleeschouwer, K.; Theunis, M.; Vlietinck, A.; Pieters, L.; Apers, S. Rapid quantification of 14 saponins of Maesa lanceolata by UPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 2010, 81, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, R.C.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.H.; An, R.; Ma, Y.M. Quantitative analysis of flavonoids, alkaloids and saponins of Banxia Xiexin decoction using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2014, 88, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Hori, K.; Motozawa, T.; Murakami, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Structures of new acylated oleanene-type triterpene oligoglycosides, theasaponins E1 and E2, from the seeds of tea plant, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze. Chem. Pharm. Bull 1998, 46, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Service, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Center for Veterinary Medicine. Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry; Center for Drug Evaluation and Research: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2018.
- Avula, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Rumalla, C.S.; Ali, Z.; Smillie, T.J.; Khan, I.A. Analytical methods for determination of magnoflorine and saponins from roots of Caulophyllum thalictroides (L.) Michx. Using UPLC, HPLC and HPTLC. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2011, 56, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Nakamura, S.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXV. Acylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins from the seeds of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Li, N.; Nagatomo, A.; Matsuda, H.; Li, X.; Yoshikawa, M. Triterpene saponins with gastroprotective effects from tea seed (the seeds of Camellia sinensis). J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, T.; Matsuda, H.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive Saponins and glycosides. Part 29 Acylated oleanane-type triterpene saponins: Theasaponins A6, A7, and B5, from the seeds of Camellia sinensis. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 2342–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myose, M.; Warashina, T.; Miyase, T. Triterpene saponins with hyaluronidase inhibitory activity from the seeds of Camellia sinensis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Morikawa, T.; Li, N.; Nagatomo, A.; Li, X.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXIII. Triterpene saponins with gastroprotective effect from the seeds of Camellia sinensis - Theasaponins E3, E4, E5, E6, and E7. Chem. Pharm. Bull 2005, 53, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Murakami, T.; Yoshizumi, S.; Murakami, N.; Yamahara, J.; Matsuda, H. Bioactive saponins and glycosides.5. Acylated polyhydroxyolean-12-ene triterpene oligoglycosides, camelliasaponins A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, and C2, from the seeds of Camellia japonica L: Structures and inhibitory activity on alcohol absorption. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 1899–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, X.; Feng, Z. Chemical constituents of tea seed saponins part from Camellia sinensis cultivated in China. J. Shenyang Pharm. Univ. 2008, 25, 544–548. [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa, T.; Matsuda, H.; Li, N.; Nakamura, S.; Li, X.; Yoshikawa, M. Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXVI. New triterpene saponins, theasaponins E10, E11, E12, E13, and G2, from the seeds of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Heterocycles 2006, 68, 1139. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.Z.; Wan, K.H.; Yan, Q.W.; Zhou, G.P.; Feng, T.T.; Dai, M.; Zhong, R.J. Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from the defatted seeds of Camellia oleifera Abel. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 20, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Qiao, J.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Yang, L.L.; Lian, H.Z.; Ge, X.; Chen, H.Y. Determination of n-octanol/water partition coefficient for DDT-related compounds by RP-HPLC with a novel dual-point retention time correction. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Qiao, J.Q.; Lian, H.Z. Determination of reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography based octanol-water partition coefficients for neutral and ionizable compounds: Methodology evaluation. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1528, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, S.K.; Poole, C.F. Separation methods for estimating octanol-water partition coefficients. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 797, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotterbeck, G.; Ceccarelli, S.M. LC-SPE-NMR-MS: A total analysis system for bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Han, J.G.; Mao, P.S. The content and distribution of condensed tannins in different species of the genus sorghum (Sorghum Moench) and their effect on seed protein electrophoresis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Ni, X.Z.; Wang, M. L Structure-reactivity relationships between the fluorescent chromophores and antioxidant activity of grain and sweet sorghum seeds. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; McAllister, T.A.; Xu, Z.J.; Gruber, M.Y.; Skadhauge, B.; Jende-Strid, B.; Cheng, K.J. Effects of proanthocyanidins, dehulling and removal of pericarp on digestion of barley grain by ruminal micro-organisms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.S. Steroids. 223. Color reagent for steroids in thin-layer chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1963, 69, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |

| [M – H]− (m/z) | Peak | Retention Time (min) | Fragments (m/z) | Molecular Formula | Trivial Name | Log P | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1157.5841 | 38 | 39.056 | 1025, 977, 893, 875, 695, 555 | C57H90O24 | New | - | |
| 1171.5630 | 7 | 14.180 | 1039, 1021, 907, 889, 569 | C57H88O25 | Theasaponin G1 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | [9,29,30] |
| 1171.5670 | 28 | 28.314 | 1039, 1021, 907, 889, 569 | C57H88O25 | Theasaponin G2 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | |
| Assamsaponin A | 2.1 ± 0.9 | ||||||
| Assamsaponin E | 3.6 ± 0.9 | ||||||
| 1173.5783 | 15 | 19.949 | 1041, 1023, 909, 891, 711, 571 | C57H90O25 | Theasaponin C1 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | [27,31,32] |
| 1173.5809 | 19 | 23.390 | 1041, 1023, 909, 891, 747, 729, 571 | C57H90O25 | Theasaponin B5 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | |
| 1185.5774 | 45 | 47.343 | 1053, 1035, 921, 903, 759, 741, 583 | C58H90O25 | Teaseedsaponin G | 2.7 ± 0.9 | [32] |
| 1187.5589 | 4 | 13.008 | 1055, 1037, 923, 905, 761, 585 | C57H88O26 | Theasaponin E3 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | [33] |
| 1187.5587 | 8 | 14.812 | 1055, 1037, 923, 905, 761, 585 | C57H88O26 | Theasaponin E6 | 1.0 ± 0.9 | |
| 1187.5953 | 36 | 37.143 | 1025, 1007, 893,875, 554 | C58H92O25 | Camelliasaponin A1/A2 | 3.9 ± 0.9 | [34] |
| 1187.5916 | 40 | 42.869 | 1055, 923, 905, 585 | C58H92O25 | Teaseedsaponin C | 2.6 ± 0.9 | [32] |
| 1189.5742 | 5 | 13.495 | 1057, 1039, 925, 907, 763, 745, 587 | C57H90O26 | Theasaponin A1 | 0.8 ± 0.9 | [30] |
| 1201.5779 | 24 | 26.339 | 1039, 1021, 907, 889, 871, 727, 709, 569 | C58H90O26 | Camelliasaponin B1/B2 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | [34] |
| 1201.5759 | 32 | 32.865 | 1039, 1021, 907, 889, 871, 727, 709, 569 | C58H90O26 | Camelliasaponin B1/B2 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | |
| 1215.5892 | 37 | 38.814 | 1083, 1065, 951, 933, 789, 611 | C59H92O26 | Floratheasaponin A | 3.2 ± 0.9 | [33] |
| 1217.5689 | 1 | 12.071 | 1055, 1037, 905, 887, 761, 585 | C58H90O27 | New | - | |
| 1217.5686 | 6 | 13.628 | 1055, 1037, 923, 905, 761, 585 | C58H90O27 | New | - | |
| 1217.5693 | 10 | 15.835 | 1085, 1067, 953, 935, 791, 615 | C58H90O27 | Theasaponin F1 | 1.4 ± 0.9 | [30] |
| 1219.5854 | 3 | 12.675 | 1057, 1039, 925, 587 | C58H92O27 | Theasaponin A4 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | [29] |
| 1229.5697 | 2 | 12.314 | 1097, 965, 947, 627 | C59H90O27 | Theasaponin E1/E7 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | [29,33] |
| 1229.5705 | 13 | 18.593 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C59H90O27 | Theasaponin E1/E7 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | |
| 1229.5699 | 18 | 22.101 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C59H90O27 | Theasaponins E4/E8 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | |
| 1229.5725 | 27 | 27.718 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 803, 785, 627 | C59H90O27 | Theasaponin E4/E8 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | |
| 1229.5719 | 31 | 32.173 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 803, 785, 627 | C59H90O27 | Theasaponin E2 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | |
| 1231.5847 | 11 | 16.616 | 1099, 1081, 967, 949, 931, 629 | C59H92O27 | Assamsaponin D | 1.6 ± 0.9 | [9,30,35] |
| 1231.5838 | 14 | 19.605 | 1099, 967, 949, 931, 629 | C59H92O27 | Theasaponin A9 | 1.8 ± 0.9 | |
| 1231.5873 | 22 | 24.643 | 1099, 1081, 967, 949, 629 | C59H92O27 | Theasaponin A2 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | |
| 1243.5835 | 46 | 48.808 | 1111, 1063, 979, 961, 641 | C60H92O27 | New | - | |
| 1257.5991 | 43 | 45.965 | 1125, 1107, 993, 975, 957, 831, 654 | C61H94O27 | Foliatheasaponin I/III | 3.7 ± 0.9 | [31,35] |
| 1259.5820 | 12 | 17.234 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C60H92O28 | Assamsaponin G | 2.0 ± 1.0 | [10,36] |
| 1259.5807 | 16 | 20.397 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C60H92O28 | Theasaponin E12 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | |
| 1259.5844 | 20 | 23.966 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C60H92O28 | Assamsaponin H | 2.5 ± 1.0 | |
| 1259.5838 | 29 | 29.393 | 1097, 1079, 965, 947, 785, 627 | C60H92O28 | Assamsaponin I | 2.5 ± 1.0 | |
| 1259.5824 | 33 | 34.359 | 1127, 1109, 995, 977, 959, 833, 657 | C60H92O28 C60H92O28 | Theasaponin F2 Theasaponin F3 | 2.1 ± 0.9 2.5 ± 0.9 | [30] |
| 1261.5947 | 9 | 15.604 | 1099, 1081, 967, 949, 805, 629 | C60H94O28 | Theasaponin A6 | 2.1 ± 1.0 | [29,31] |
| 1261.5989 | 25 | 26.645 | 1099, 1081, 967, 949, 805, 769, 629 | C60H94O28 | Theasaponin A5 | 2.3 ± 1.0 | |
| 1269.6005 | 51 | 58.933 | 1137,1119,1005,987,843,807,667 | C62H94O27 | Teaseedsaponin J/K | 2.8 ± 0.9 | [32] |
| 1271.5841 | 30 | 29.634 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 827, 669 | C61H92O28 | Assamsaponin B | 2.3 ± 0.9 | [9,29,32,33] |
| 1271.5805 | 39 | 39.601 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 827, 669 | C61H92O28 | Theasaponin E5/E9 | 2.9 ± 0.9 | |
| 1271.6146 | 49 | 56.398 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 845, 827, 669 | C62H96O27 | Teaseedsaponin E | 2.7 ± 0.9 | |
| 1273.5958 | 17 | 21.009 | 1141, 1009, 991, 811, 671 | C61H94O28 | Theasaponin A3 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | [12,30,32,36] |
| 1273.5993 | 23 | 25.786 | 1141, 1009, 991, 847, 829, 671 | C61H94O28 | Theasaponin E10 | 2.3 ± 0.9 | |
| 1273.5957 | 34 | 36.116 | 1141, 1009, 991, 847, 829, 671 | C61H94O28 | Theasaponin A8 | 2.8 ± 0.9 | |
| 1273.5938 | 41 | 43.580 | 1141, 1009, 991, 847, 829, 671 | C62H98O27 | Teaseedsaponin F | 2.9 ± 0.9 | |
| 1285.5945 | 44 | 46.664 | 1153, 1135, 1021, 1003, 683 | C62H94O28 | Teaseedsaponin L | 2.9 ± 0.9 | |
| 1285.5987 | 47 | 53.821 | 1153, 1135, 1021, 1003, 859, 683 | C62H94O28 | New | [32] | |
| 1299.6105 | 50 | 57.373 | 1137, 1119, 1005, 987, 667 | C63H96O28 | Teaseedsaponin I | 3.1 ± 1.0 | [32] |
| 1301.5942 | 26 | 27.364 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 809, 669 | C62H94O29 | Assamsaponin F | 2.6 ± 1.0 | [10,32,36] |
| 1301.5922 | 35 | 36.828 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 845, 809, 669 | C62H94O29 | Theasaponin E11 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | |
| 1301.6239 | 48 | 55.001 | 1139, 1121, 1007, 989, 845, 809, 669 | C63H98O28 | Teaseedsaponin D | 3.0 ± 1.0 | |
| 1303.6111 | 21 | 24.213 | 1141, 1123, 1009, 991, 811, 671 | C62H96O29 | Theasaponin A7 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | [31] |
| 1315.6046 | 42 | 44.765 | 1153, 1135, 1021, 1003, 859, 683 | C63H96O29 | New | - |
| Nominal Concentration (μg/mL) | Calculated Concentration (μg/mL) | Accuracy (DEV, %) | Precision (RSD, %) | 95% Confidence Interval | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |
| 60 | 59.952 ± 0.091 | 59.945 ± 0.012 | 0.080 | 0.092 | 0.152 | 0.020 | 59.726–60.178 | 59.915–59.975 |
| 100 | 100.079 ± 0.095 | 100.046 ± 0.056 | 0.079 | 0.046 | 0.095 | 0.056 | 99.843–100.315 | 99.907–100.185 |
| 500 | 499.960 ± 0.065 | 500.013 ± 0.091 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 0.013 | 0.018 | 499.799–500.122 | 499.787–500.239 |
| Peak | Crude Extract | Total Saponin Fraction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention Time (min) | Content (wt %) | Retention Time (min) | Content (wt %) | |
| 1 | ND | ND | 12.12 | 0.08 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| 4 | 12.95 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 12.59 | 0.31 ± 0.01 |
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | 13.26 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 12.88 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| 7 | 13.72 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 13.29 | 0.46 ± 0.01 |
| 8 | 14.76 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 14.31 | 0.99 ± 0.01 |
| 9 | ND | ND | 14.90 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | 15.77 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 15.34 | 0.16 ± 0.01 |
| 11 | 16.55 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 16.08 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 12 | 17.32 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 16.76 | 0.32 ± 0.01 |
| 13 | 18.34 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 17.77 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| 14 | 18.72 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 18.17 | 1.04 ± 0.02 |
| 15 | 19.60 | 1.02 ± 0.01 | 19.00 | 1.11 ± 0.02 |
| 16 | 19.99 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 19.39 | 0.44 ± 0.02 |
| 17 | 20.72 | 1.07 ± 0.01 | 20.01 | 1.60 ± 0.01 |
| 18 | 22.43 | 5.43 ± 0.02 | 21.82 | 7.62 ± 0.02 |
| 19 | 23.42 | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 22.77 | 0.82 ± 0.02 |
| 20 | 23.95 | 0.76 ± 0.01 | 23.32 | 1.14 ± 0.02 |
| 21 | ||||
| 22 | ND | ND | 24.33 | 0.15 ± 0.01 |
| 23 | 25.81 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 24.97 | 0.96 ± 0.02 |
| 24 | 26.80 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 25.99 | 0.98 ± 0.01 |
| 25 | 27.63 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 26.84 | 0.30 ± 0.02 |
| 26 | 28.36 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 27.47 | 0.94 ± 0.01 |
| 27 | 28.84 | 1.65 ± 0.01 | 28.06 | 2.94 ± 0.02 |
| 28 | 30.02 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 29.02 | 2.40 ± 0.01 |
| 29 | ||||
| 30 | 31.19 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 30.10 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 31 | 32.61 | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 31.56 | 4.93 ± 0.01 |
| 32 | 33.26 | 0.12 ± 0.02 | 32.53 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| 33 | 34.58 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 33.47 | 0.81 ± 0.01 |
| 34 | ||||
| 35 | 36.19 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 35.28 | 0.27 ± 0.01 |
| 36 | 37.53 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 36.73 | 0.68 ± 0.02 |
| 37 | 38.85 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 38.01 | 0.34 ± 0.01 |
| 38 | 39.79 | 0.64 ± 0.01 | 38.97 | 2.06 ± 0.02 |
| 39 | ||||
| 40 | ND | ND | 42.49 | 0.28 ± 0.01 |
| 41 | ND | ND | 42.80 | 0.17 ± 0.01 |
| 42 | ND | ND | 44.254 | 0.23 ± 0.01 |
| 43 | ND | ND | 45.39 | 0.37 ± 0.01 |
| 44 | 46.93 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 46.21 | 1.09 ± 0.03 |
| 45 | 47.81 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 47.07 | 0.92 ± 0.02 |
| 46 | 48.94 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 48.30 | 0.40 ± 0.01 |
| 47 | 54.09 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 53.30 | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| 48 | ND | ND | 54.21 | 0.31 ± 0.01 |
| 49 | 56.21 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 55.57 | 0.93 ± 0.01 |
| 50 | ND | ND | 56.68 | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| 51 | 58.82 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 58.29 | 1.28 ± 0.01 |
| Sum | 19.57 ± 0.05 | 41.68 ± 0.09 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Jia, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; Li, B. Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Triterpene Saponins from Camellia sinensis Seeds Using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203794
Wu X, Jia L, Wu J, Liu Y, Kang H, Liu X, Li P, He P, Tu Y, Li B. Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Triterpene Saponins from Camellia sinensis Seeds Using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules. 2019; 24(20):3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203794
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuejin, Lingyan Jia, Jiafan Wu, Yawen Liu, Hyunuk Kang, Xiaobo Liu, Pan Li, Puming He, Youying Tu, and Bo Li. 2019. "Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Triterpene Saponins from Camellia sinensis Seeds Using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS" Molecules 24, no. 20: 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203794
APA StyleWu, X., Jia, L., Wu, J., Liu, Y., Kang, H., Liu, X., Li, P., He, P., Tu, Y., & Li, B. (2019). Simultaneous Determination and Quantification of Triterpene Saponins from Camellia sinensis Seeds Using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules, 24(20), 3794. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24203794