Natural Occurrence, Bioactivity and Biosynthesis of Elaiophylin Analogues
Abstract
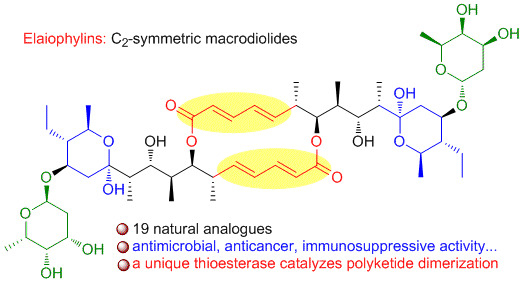
:1. Introduction
2. Natural Occurrence
3. Biological Activities
3.1. Antimicrobial and Anthelmintic Activity
3.2. Anticancer Effect
3.2.1. Cytotoxicity.
3.2.2. Autophagy Inhibitory Activity.
3.2.3. Inducing Apoptosis and Proliferation Activity.
3.2.4. Antiangiogenic Activity.
3.3. Immunosuppressive and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.4. Antiviral Activity and α-glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
3.5. Other Activity
4. Biosynthesis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hertweck, C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ōmura, S. Macrolide Antibiotics: Chemistry, Biology, and Practice, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arcamone, F.; Bertazzoli, C.; Ghione, M.; Scotti, T. Melanosporin and elaiophylin, new antibiotics from Streptomyces melanosporus (sive melonsporofaciens) n. sp. G. Microbiol. 1959, 7, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Westley, J.W.; Liu, C.M.; Evans, R.H.; Blount, J.F. Conglobatin, a novel macrolide dilactone from Streptomyces conglobatus ATCC 31005. J. Antibiot. 1979, 32, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dramae, A.; Nithithanasilp, S.; Choowong, W.; Rachtawee, P.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Antimalarial 20-membered macrolides from Streptomyces sp. BCC33756. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 8205–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okujo, N.; Iinuma, H.; George, A.; Eim, K.S.; Li, T.L.; Ting, N.S.; Jye, T.C.; Hotta, K.; Hatsu, M.; Fukagawa, Y.; et al. Bispolides, novel 20-membered ring macrodiolide antibiotics from microbispora. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuska, J.; Nemec, P.; Kuhr, I. Vermiculine, a new antiprotozoal antibiotic from Penicillium vermiculatum. J. Antibiot. 1972, 25, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebach, D.; Seuring, B.; Kalinowski, H.-O.; Lubosch, W.; Renger, B. Synthesis and determination of the absolute configuration of pyrenophorin and vermiculin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1977, 16, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, H.; Keller-Schierlein, W. Stoffwechselprodukte von mikroorganismen. 202. mitteilung. Strukturaufklärung von elaiophylin: Spektroskopische untersuchungen und abbau. Helv. Chim. Acta 1981, 64, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert-Laves, K.; Dobler, M. Stoffwechselprodukte von mikroorganismen. 211. milteilung. röntgenstrukturanalyse von elaiophylin. Helv. Chim. Acta 1982, 65, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, E.F.; Vertesy, L.; Sheldrick, G. Structure of salbomycin, C54H88O18. 2H2O. Acta Crystallogr. C 1984, 40, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M. Azalomycins B and F, two new antibiotics. II. Properties of azalomycins B and F. J Antibiot. 1960, 13, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Arai, M.; Oki, E. Chemical studies on azalomycins. I. Preliminary study of azalomycin-B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1967, 15, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Oki, E. Chemical studies on azalomycins. 3. Alkaline degradation of azalomycin-B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1967, 15, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.V.; Neuhaus, D.; Williams, D.J. A conformational study of elaiophylin by X-ray crystallography and difference 1H NMR methods; observation of a selective sign reversal of the nuclear overhauser effect. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, H.; Bischoff, E.; Fugmann, B.; Weber, K.; Frobel, K.; Rosen, B.; Grutzmann, R.; Karmann, G.; Kohlsdorfer, C. Efomycins a, e and g as Antiinflammatory Agents. U.S. Patent 5,185,326A, 9 February 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, M.G.; Chandra, A.; Thorogood, D.L.; Ammermann, E.; Walker, N.; Kiehs, K. Gopalamicin, an antifungal macrodiolide produced by soil actinomycetes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2308–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.M.; Melo, J.G.; Militao, G.C.; Lima, G.M.; do Carmo, A.L.M.; Aguiar, J.S.; Araujo, R.M.; Braz-Filho, R.; Marchand, P.; Araujo, J.M.; et al. Characterization of the biochemical, physiological, and medicinal properties of Streptomyces hygroscopicus ACTMS-9H isolated from the Amazon (Brazil). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikosova, M.; Blazsek, M.; Kubis, M.; Gajdosikova, J.; Borosova, G. Biotechnological preparation of the elaiophylin. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 2004, 49, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzau, M.; Heinze, S.; Fleck, W.F.; Dahse, H.M.; Grafe, U. New macrodiolide antibiotics, 11-O-monomethyl- and 11, 11’-O-dimethylelaiophylins, from Streptomyces sp. HKI-0113 and HKI-0114. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Lam, P.W.; Shahab, S.; Santosa, D.A.; Proteau, P.J.; Zabriskie, T.M.; Mahmud, T. Identification of elaiophylin skeletal variants from the Indonesian Streptomyces sp. ICBB 9297. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frobel, K.; Bischoff, E.; Muller, H.; Salcher, O.; De Jong, A.; Berschauer, F.; Scheer, M. Efomycins as Performance Promoters in Animals. U.S. Patent 5,073,369, 17 December 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Frobel, K.; Muller, H.; Bischoff, E.; Salcher, O.; De Jong, A.; Berschauer, F.; Scheer, M. Efomycin G and It’s Use as Yield Promoter in Animals. U.S. Patent 4,927,810, 22 May 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Tan, Y.; Gan, M.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, H.; Shang, X.; You, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Identification of elaiophylin derivatives from the marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. 7-145 using PCR-based screening. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2153–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakakoshi, M.; Kimura, K.; Nakajima, N.; Yoshihama, M.; Uramoto, M. SNA-4606-1, a new member of elaiophylins with enzyme inhibition activity against testosterone 5α-reductase. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Halichoblelide, a potent cytotoxic macrolide from a Streptomyces species separated from a marine fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R.; Numata, A. Halichoblelides B and C, potent cytotoxic macrolides from a Streptomyces species separated from a marine fish. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2842–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tian, E.; Xu, D.; Ma, M.; Deng, Z.; Hong, K. Halichoblelide D, a new elaiophylin derivative with potent cytotoxic activity from mangrove-derived Streptomyces sp. 219807. Molecules 2016, 21, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schon, M.P.; Krahn, T.; Schon, M.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Antonicek, H.; Schultz, J.E.; Ludwig, R.J.; Zollner, T.M.; Bischoff, E.; Bremm, K.D.; et al. A new specific inhibitor of selectin, impairs leukocyte adhesion and alleviates cutaneous inflammation. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supong, K.; Thawai, C.; Choowong, W.; Kittiwongwattana, C.; Thanaboripat, D.; Laosinwattana, C.; Koohakan, P.; Parinthawong, N.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Antimicrobial compounds from endophytic Streptomyces sp. BCC72023 isolated from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Res. Microbiol. 2016, 167, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klassen, J.L.; Lee, S.R.; Poulsen, M.; Beemelmanns, C.; Kim, K.H. Efomycins K and L from a termite-associated Streptomyces sp. M56 and their putative biosynthetic origin. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J. Extracting value: Mechanistic insights into the formation of natural product artifacts–case studies in marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Hong, S.-D.; Lee, J.-J. Structure determination and biological activities of elaiophylin produced by Streptomyces sp. MCY-846. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 6, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, A.; Wong, G.K.; Demain, A.L. Enhancement of the antifungal activity of rapamycin by the coproduced elaiophylin and nigericin. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, P.A.; Schlegel, R.; Gräfe, U. Cation selective ion channels formed by macrodiolide antibiotic elaiophylin in lipid bilayer membranes. Bioelectrochemistry 2001, 54, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Han, S.-B.; Kim, H.-M.; Hong, S.-D.; Lee, J.-J. Immunosuppressive activity of elaiophylins. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 7, 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Hammann, P.; Kretzschmar, G.; Seibert, G. Secondary metabolites by chemical screening. 7. I. Elaiophylin derivatives and their biological activities. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, T.; Lai, H.; Meng, L.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Elaiophylin, a novel autophagy inhibitor, exerts antitumor activity as a single agent in ovarian cancer cells. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1849–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, P.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Tan, J.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, J. The novel autophagy inhibitor elaiophylin exerts antitumor activity against multiple myeloma with mutant TP53 in part through endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.N.; Jang, J.P.; Han, J.M.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, H.J. Antiangiogenic potential of microbial metabolite elaiophylin for targeting tumor angiogenesis. Molecules 2018, 23, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonicek, H.-P.; Bischoff, E.; Gondol, D.; Gutbrod, O.; Krahn, T.; Rodriguez, M.-L.; Schütz, H. Use of Efomycins. U.S. Patent 6,291515 B1, 18 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Oostingh, G.J.; Pozgajova, M.; Ludwig, R.J.; Krahn, T.; Boehncke, W.H.; Nieswandt, B.; Schon, M.P. Diminished thrombus formation and alleviation of myocardial infarction and reperfusion injury through antibody- or small-molecule-mediated inhibition of selectin-dependent platelet functions. Haematologica 2007, 92, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostingh, G.J.; Ludwig, R.J.; Enders, S.; Gruner, S.; Harms, G.; Boehncke, W.H.; Nieswandt, B.; Tauber, R.; Schon, M.P. Diminished lymphocyte adhesion and alleviation of allergic responses by small-molecule- or antibody-mediated inhibition of L-selectin functions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, B.; Constantin, G. Anti-selectin therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Woo, J.-K.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.; Cho, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Riu, K.Z.; Lee, D.-S. Antiviral activity of methylelaiophylin, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 263–266. [Google Scholar]
- Gerlitz, M.; Hammann, P.; Thiericke, R.; Rohr, J. The biogenetic origin of the carbon skeleton and the oxygen atoms of elaiophylin, a symmetric macrodiolide antibiotic. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4030–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydock, S.F.; Mironenko, T.; Ghoorahoo, H.I.; Leadlay, P.F. The putative elaiophylin biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces sp. DSM4137 is adjacent to genes encoding adenosylcobalamin-dependent methylmalonyl CoA mutase and to genes for synthesis of cobalamin. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 113, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haltli, B.A. Elaiophylin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster. U.S. Patent 7,595,187B2, 29 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.; Jiang, M.; Ren, Z.; Dong, Y.; Lu, T. The complete genome sequence of Streptomyces autolyticus CGMCC 0516, the producer of geldanamycin, autolytimycin, reblastatin and elaiophylin. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 252, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Yin, M.; Wu, S.; Han, X.; Ji, K.; Wen, M.; Lu, T. GdmRIII, a TetR family transcriptional regulator, controls geldanamycin and elaiophylin biosynthesis in Streptomyces autolyticus CGMCC0516. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Prediger, P.; Dias, L.C.; Murphy, A.C.; Leadlay, P.F. Macrodiolide formation by the thioesterase of a modular polyketide synthase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 5232–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Strains | Phenotype | 1 | 2 | 3 | 9 | 10 | 11 | Azithromycin | Erythromycin | Oxacillin | Vancomycin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC 29213 | MSSA | 1 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 32 | 2 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| S. aureus 09-6 | MSSA | 1 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 32 | 2 | 2 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| S. aureus ATCC 33591 | MRSA | 1 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 32 | 2 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 0.5 |
| S. aureus 09-13 | MRSA | 1 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 32 | 2 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 0.5 |
| S. aureus R6101 | MRSA | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 16 | >64 | >256 | NT | >256 | NT |
| S. aureus ATCC 6538P | Thios-R | 0.5 | 2 | 16 | 2 | >128 | 4 | >256 | NT | NT | NT |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 | MSSE | 1 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 64 | >64 | >256 | 16 | >256 | 0.5 |
| S. epidermidis 09-9 | MSSE | 2 | 2 | 16 | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | NT | 0.5 |
| S. epidermidis 09-3 | MRSE | 2 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 64 | >64 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 4 |
| Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 | VSE | 1 | 32 | 16 | 2 | 64 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 4 | 1 |
| E. faecalis 09-8 | VSE | 1 | 2 | 16 | 16 | 64 | 2 | >256 | 32 | >256 | 1 |
| E. faecalis ATCC 51299 | VRE | 1 | 1 | 16 | 2 | 64 | 2 | >256 | 8 | >256 | 4 |
| E. faecalis W4138 | VRE | 1 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 64 | 4 | >256 | NT | NT | 4 |
| E. faecalis R6512 | VRE | 1 | 1 | 8 | 2 | >128 | 4 | >256 | NT | NT | >256 |
| Enterococcus faecium 09-10 | VSE | 2 | 2 | 32 | >64 | 64 | >64 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 1 |
| E. faecium ATCC 700221 | VRE | 1 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 64 | 4 | >256 | 64 | >256 | 128 |
| Micrococcus faecium ATCC 10240 | Apram-R | 0.5 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 128 | 2 | 2 | NT | NT | NT |
| Escherichia coli 09-1 | ESBL-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | 64 | >256 | >256 | >256 |
| E. coli 09-20 | BL-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | >256 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 | ESBL-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | 64 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| K. pneumoniae ATCC BAA-2146 | NDM-1-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | 64 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | BL-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | 256 | >256 | >256 | >128 |
| Morganella morganii ATCC 25830 | BL-prod | >256 | >256 | >256 | >64 | >128 | >64 | 64 | >256 | 256 | 128 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gui, M.; Zhang, M.-x.; Wu, W.-h.; Sun, P. Natural Occurrence, Bioactivity and Biosynthesis of Elaiophylin Analogues. Molecules 2019, 24, 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213840
Gui M, Zhang M-x, Wu W-h, Sun P. Natural Occurrence, Bioactivity and Biosynthesis of Elaiophylin Analogues. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213840
Chicago/Turabian StyleGui, Min, Meng-xue Zhang, Wen-hui Wu, and Peng Sun. 2019. "Natural Occurrence, Bioactivity and Biosynthesis of Elaiophylin Analogues" Molecules 24, no. 21: 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213840
APA StyleGui, M., Zhang, M. -x., Wu, W. -h., & Sun, P. (2019). Natural Occurrence, Bioactivity and Biosynthesis of Elaiophylin Analogues. Molecules, 24(21), 3840. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213840