Abstract
In this study, four malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides (MIGs), a type of isoflavonoid with poor structural stability, were efficiently isolated and purified from Astragali Radix by a medium pressure ODS C18 column chromatography. The structures of the four compounds were determined on the basis of NMR and literature analysis. Their major diagnostic fragment ions and fragmentation pathways were proposed in ESI/Q-TOF/MS positive mode. Using a target precursor ions scan, a total of 26 isoflavonoid compounds, including eleven malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides coupled with eight related isoflavonoid glycosides and seven aglycones were characterized from the methanolic extract of Astragali Radix. To clarify the relationship of MIGs and the ratio of transformation in Astragali Radix under different extraction conditions, two MIGs (calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate and formononetin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate) coupled with related glycosides (calycosin-7-O-glycoside and formononetin-7-O-glycoside) and aglycones (calycosin and formononetin) were detected by a comprehensive HPLC-UV method. Results showed that MIGs could convert into related glycosides under elevated temperature conditions, which was further confirmed by the conversion experiment of MIGs reference compounds. Moreover, the total contents of MIGs and related glycosides displayed no obvious change during the long-duration extraction. These findings indicated that the quality of Astragali Radix could be evaluated efficiently and accurately by using the total content of MIGs and related glycosides as the quality index.
1. Introduction
Astragali Radix, named “huangqi” in Traditional Chinese Medicine, is the dried root of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. or A. membranaceus var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao (family Leguminosae) [1]. As a commonly used natural herb, Astragali Radix has been listed in the Pharmacopoeia of many countries, including the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, the United States Pharmacopoeia, and Japanese Pharmacopoeia. It exhibits many biological functions, such as antioxidative [2,3], anticarcinogenic [4], immunomodulation [5], and anti-inflammatory activities [6], so it is frequently used to treat diabetes and related complications [7].
Chemical investigations have shown that isoflavonoids, triterpene saponins, and polysaccharides are the main active components in Astragali Radix [8,9]. Among them, isoflavonoids, as natural compounds that promote human health, were established to be important active components [10]. When the quality of Astragali Radix and its products are evaluated, the inherent isoflavonoids were generally selected as “marker compounds” since their chromophores are suitable for UV detection [11]. However, the criteria and quality assessment methods of isoflavonoids for Astragali Radix are obviously different among the pharmacopoeias and publications. For example, in the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, the active constituent calycosin 7-O-β-D-glycoside is used for the quality control of Astragali Radix, while in the United States Pharmacopoeia, the total content of four isoflavonoids (calycosin 7-O-β-D-glycoside, ononin, calycosin and formononetin) should be no less than 0.03%. Of note, Astragali Radix contains a group of malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides (MIGs) [12,13,14]. Although MIGs are in relatively high abundance in the raw materials of Astragali Radix, they are seldom investigated for quality evaluation owing to their poor structural stability and unavailability of reference compounds.
To determine the profiles of MIGs in Astragali Radix, the first step of this study was to isolate MIGs using a medium pressure ODS C18 column chromatography (MPLC). Their structures were then elucidated by MS and NMR analysis. Coupling HPLC with Quadrupole Time of Flight Mass Spectrometers (Q-TOF/MS), which shows great advantages in providing accurate mass measurements, resolving power, and high sensitivity [15,16,17], allows unequivocal structural identification of low levels of ingredients and non-target compounds in complicated analysis of herbs. Therefore, a comprehensive HPLC coupled with Q-TOF/MS was developed to characterize MIGs, related glycosides and aglycones in Astragali Radix. Finally, in order to clarify the stability and conversion of MIGs, six major isoflavonoids, including two MIGs, two related glycosides, and two aglycones, were analyzed and compared under different extraction techniques and times.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Compound Separation and Structural Identification
Medium pressure ODS C18 column chromatography (MPLC) has been widely used in isolation and purification of natural compounds, organic synthetic molecules, and biological macromolecules [18]. The MPLC column used was packed with 45–60 μm ODS silica gelto provide a short separation time and high separation efficiency of isoflavonoids [19]. The method was primarily based on the selection of experimental conditions in sample adjustment and elution steps. With simple pretreatment procedures and a short separation time, a phytochemical investigation of Astragali Radix by MPLC led to the isolation of our MIG compounds. The structures and the key HMBC correlation of compounds AR-1 to AR-4 are illustrated in Figure 1. The 13C-NMR and 1H- NMR data of the four compounds are shown in Table 1.
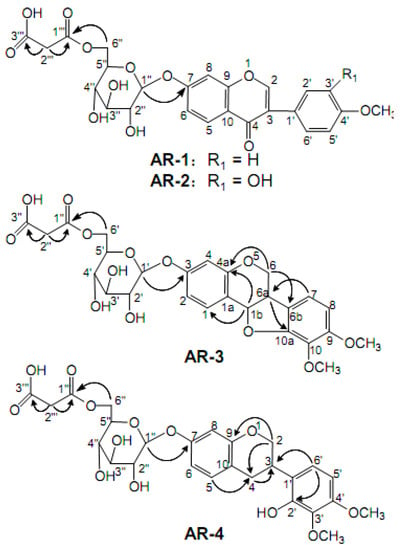
Figure 1.
Chemical structures and key HMBC correlations of four malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides isolated from Astragali Radix.

Table 1.
13C-NMR (125 MHz) and 1H-NMR (500 MHz) data of compound AR-1~AR-4 in DMSO-d6 (δ in ppm).
AR-1 was obtained as a light yellow powder and its molecular formula was determined as C25H24O12 based on the HR-ESI-MS at m/z 517.1341 [M + H]+ (calcd 517.1321). Based on the 1H-NMR spectra, three aromatic proton signals at δH 8.08 (1H, d, J = 8.8 Hz), δH 7.15 (1H, dd, J = 8.8 Hz, J = 2.2 Hz), and δH 7.23 (1H, d, J = 2.2 Hz) represented the structure containing the AMX spin-coupling. The signal at δH 8.40 (1H, s) was an obvious isoflavonoid signal at the H-2 position. In addition, the AA′BB′ spin-coupling system, with signals at δH 7.53 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz) and δH 7.00 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz), was attributed to the four protons of the B-ring. These characteristic features implied that A was a typical isoflavonoid compound. The carbohydrate chain of A consisted of one monosaccharide residue ascribing the signals of an anomeric carbon at δC 99.7, which was deduced from the 13C NMR spectra. This carbohydrate chain was correlated with the corresponding signals of anomeric proton at δH 5.15 (1H, d, J = 7.5 Hz) in the HSQC spectrum. The coupling constant of the anomeric protons indicated that the glycosidic bond had a β-configuration. The positive ESI-TOF/MS of AR-1 produced a protonated ion at m/z 517.1341 [M + H]+, as well as the secondary dissociation mass fragment ion at m/z 269.0801 [M-C6H10O5-C3H2O3 + H]+, indicating that the carbohydrate chain consisted of one glucoside and malonyl, which was confirmed by the signals of two carboxyl carbons at 168.0 and 166.9 ppm, one anomeric carbon at 99.7 ppm, four tertiary carbons at 69.7–76.0 ppm, and two secondary carbons at 41.5 and 64.1 ppm. The determination of the linkage sites was obtained from the HMBC correlations between δH 5.15 (H-1′) and δC 161.2 (C-7), as well as δH 4.12 (H-6′) and δC 166.9 (C-1′). Comparing the data with the literature [20,21], the compound AR-1 was identified as formononetin-7-O-β-D-glycoside-6″-O-malonate.
The compound AR-2 was obtained as a light yellow powder. It produced a protonated ion at 533.1267 [M + H]+ (calcd 533.1290) in the HR-ESI-MS, corresponding to the molecular formula of C25H24O13, thus it had only one oxygen atom more than AR-1. When comparing the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectral data of AR-2 with the data from AR-1, the spectral data were very similar; further spectroscopic analysis revealed that the only difference was in the region of the B-ring. In the 1H-NMR spectrum, an ABX spin coupling system in AR-2 rather than AA′ BB′ in AR-1 were observed, indicating the presence of a hydroxyl moiety at C-3′ in the B-ring of aglycone. Thus, the compound was clarified as calycosin-7-O-β-D-glycoside-6″-O-malonate, which was further verified by comparison with the literatures [20,21].
AR-3, a white powder, generated a [M + NH4]+ ion at m/z 566.1839 and a [M + H]+ at m/z 549.1581, which is in agreement with the molecular formula of C26H28O13. The fragment ion peaks at m/z 301.1063 [M-C6H10O5-C3H2O3 + H]+, as well as two secondary carbons at δC 64.3 and 43.1, four tertiary carbons at δC 69.8–76.3, two carboxyl carbons at δC 166.8 and 167.9, and one anomeric carbons δC 100.1 suggested the presence of malonyl glucoside moiety. The 13C NMR spectrum of compound AR-3 exhibited 17 carbon resonances assigned to the aglycone moiety consisting of two OCH3, one CH2, seven CH (five aromatic, two aliphatic), and seven quaternary carbons (all aliphatic).
The comparative analysis between the 13C-NMR spectrum of AR-3 and AR-2 showed that the main difference was in the C-ring region. The signals of two methines (δC 39.5, δC 78.2) and one methylene (δC 65.8) in AR-3, rather than two unsaturated quaternary carbons (δC 123.6, δC 174.7) and one unsaturated methylene (δC 153.5) in AR-2 were observed, indicating that AR-3 was a type of pterocarpan compound. The correlations in the HMBC spectrum from δH 4.28, 3.65 (H-6) to δC 156.1 (C-4a) and 121.6 (C-6a), from δH 6.99 (H-7) to δC 39.5 (C-6a), and from δH 3.65 (H-6a) to δC 150.9 (C-10a) confirmed the compound type of AR-3. From these spectroscopic data and the literature information [12,22], compound AR-3 was identified to be astraperocarpan-3-O-β-D-glycoside-6′-O-malonate.
AR-4 was obtained as a white powderwith a molecular formula of C26H30O13 as determined by HR-ESI-MS at m/z 568.1991 [M + NH4]+ ion and m/z 551.1736 [M + H]+ (calculated 365.1759), two more hydrogens than AR-3. The 13C-NMR spectrum of AR-4 was similar to the spectrum of AR-3, and detail spectroscopic analysis revealed the signal of one methylene at δC 29.7 (C-4) in AR-4 rather than one oxygenated methane (δC 78.2) as in AR-3. These data suggested that AR-4 was derived from AR-3 with the ring-opening of its furan ring. This structure was further confirmed by the HSQC correlations between δH 2.92, 2.81(2H, m, H-4) and δC 29.7 (C-4), together with HMBC correlations from δH 4.19 (H-2α) and δH 7.01 (H-5) to δC 29.7 (C-4). Based on the above discussion and the literature [22], AR-4 was identified as astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-malonate.
2.2. LC-QTOF/MS Analysis of the Extract of Astragali Radix
The total ion chromatograms (TICs) of stock solution with eight reference standards and the extract of Astragali Radix in positive mode are shown in Figure 2. The eight references were divided into three groups based on the structural characteristics: isoflavones including calycosin-7-O-glycoside (1), calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (6), formononetin-7-O-glycoside (8), formononetin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (14), calycosin (15), and formononetin (22); isoflavans consisting of astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-malonate (18); and pterocarpans comprising astraperocarpan-3-O-glycoside-6′-O-malonate (16). A total of 26 isoflavonoids were identified, and their structures are presented in Figure 3. As shown in Table 2, each authentic compound had a significant and distinctive [M + H]+ or [M + NH4]+ ion, MS fragment ions, and quite different retention times. Therefore, they could be unambiguously identified in the extract of Astragali Radix. Other isoflavonoids could be characterized by the developed strategy [23]: First, the molecular formulas of unknown compounds could be obtained by accurate mass measurement and screened in chemical databases such as SciFinder Scholar. Second, typical dissociations of the skeleton were helpful for predicting chemical groups and substituent numbers, and diagnostic ions from [M + H]+ were useful for determining substituent moieties. Finally, the number of candidates was sharply reduced after their substructures were identified by the structurally summarized diagnostic ions. If a compound had been reported in plants, especially in the genus Astragalus, it was the most proper candidate.
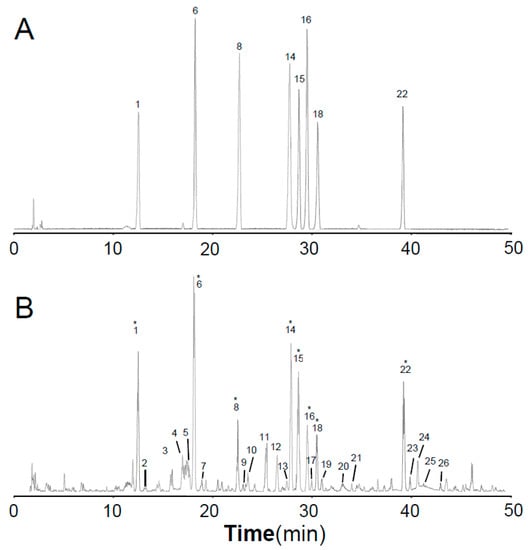
Figure 2.
LC-QTOF/MS total ion current (TIC) profile of eight isoflavonoid references (A) and the extract of Astragali Radix (B) operated in positive mode. * These compounds were identified by their corresponding references.
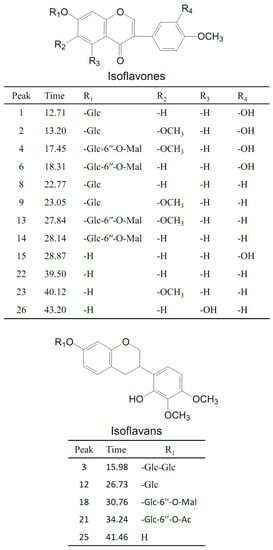
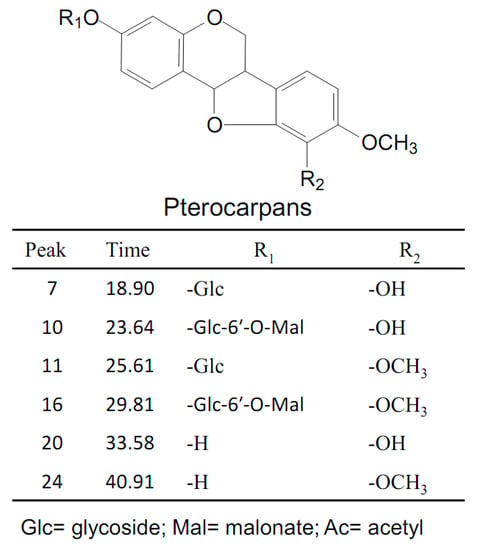
Figure 3.
Chemical structures of the isoflavonoid compounds identified in Astragali Radix.

Table 2.
MS data for identification of isoflavonoids in Astragali Radix by (+) HPLC-Q TOF/MS.
2.2.1. Identification of Malonyl Isoflavone Glycosides and Related Aglycones
Peaks 6 and 14 were unambiguously identified as calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate and formononetin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate, respectively, which were confirmed by comparing their tR values and mass spectra with those of the references. In the positive mode (supplementary materials Figure S1), the [M + H]+ ion of calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (6) at m/z 533.1260 (C25H24O13) first lost the 248 Da free radical at the carbohydrate chain, yielding the aglycone ion at m/z 285.0740 [M + H-C6H10O5-C3H2O3]+ (named[Aglycone + H]+) as its predominant fragmentation, which further produced ions at m/z 137.1 corresponding to the RDA cleavage of a C-ring. From the isoflavone aglycone ion at m/z 285.0740 [Aglycone + H]+, the MS2 spectra revealed that the loss of 15 Da (a methyl radical), 16 Da (CH4), or 32 Da (CH3OH) led to the formation of the fragmentation ions at m/z 270.1 [Aglycone + H-CH3]+, m/z 269.1 [Aglycone + H-CH4]+, or m/z 253.1 [Aglycone + H-CH3OH]+, respectively, representing the characteristic fragmentation pathway of 4′-methoxylisoflavones [24]. In addition, the base peak at m/z 285.0740 [Aglycone + H]+ also showed a concurrent loss of CH3· and CO or 2CO, concurrent loss of CH4 and 2CO, and concurrent loss of CH3OH and CO or 2CO, forming the significant ions of [Aglycone + H-CH3-CO]+, [Aglycone + H-CH3-2CO]+, [Aglycone + H-CH4-2CO]+, [Aglycone + H-CH3OH-CO]+, and [Aglycone + H-CH3OH-2CO]+, respectively. These product ions allowed us to propose a fragmentation pathway for the [M + H]+ ion of calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (Figure 4A and Table 1).
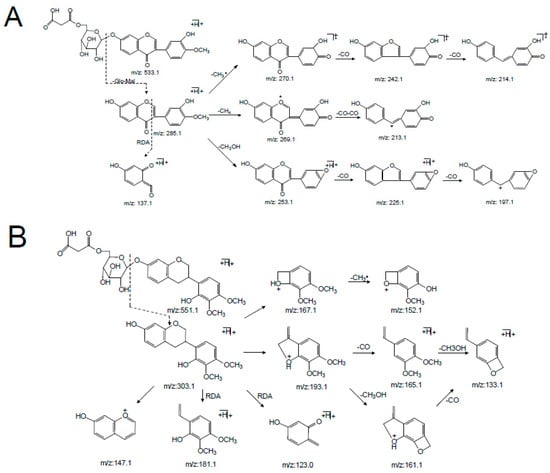
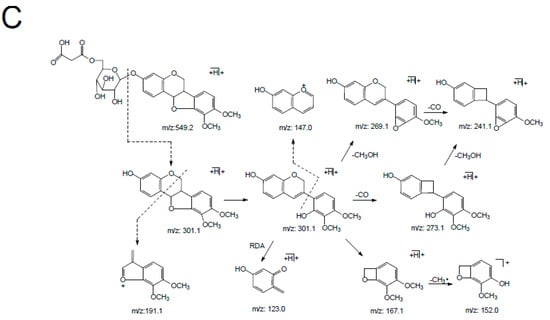
Figure 4.
The main MSn fragmentation pathway for three malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides from Astragali Radix. (A) Calycosin-7-O-Glc-6″-O-Mal. (B) Astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-Mal. (C) Astraperocarpan-3-O-Glc-6′-O-Mal.
Peak 4 showed an intense ion at m/z 563.1323 [M + H]+ (C26H26O14), which produced an aglycone ion at m/z 315.0867 by losing 248 Da (162 + 86 Da), corresponding to a malonyl glucose residue. In the MS2 spectrum, peak 4 was different from peak 6 by an increase of 30 Da (CH2O) by the base ion at m/z 315.1 [Aglycone + H]+ and characteristic RDA fragmentation ion at m/z 167.1, indicating that the difference between peak 4 and 6 was the substituted group at the A-ring. With the comparison with the literature [21], peak 4 was tentatively identified as odoratin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate. Peak 13 showed an intense ion at m/z 547.1421 [M + H]+, corresponding to the molecular formula C26H26O13. In LC-MS2spectrum, the characteristic fragment ion at m/z 167.1 produced in the RDA cleavage was the same as that of 4, indicating that the difference between peak 13 and 4 was the substituted group at the B-ring. In addition, other fragmented ions at m/z 284.1, 283.1, 267.1, and 239.1 visible the m/z 299.1 indicated one less hydroxyl in the aglycone structure than peak 4. According to the literature [24], peak 13 could be considered as afrormosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate.
Peaks 1, 2, 8, and 9 each indicated aglycone ions at m/z 285.1, 315.1, 269.1, and 299.1, originating from the loss of 162 Da, respectively, which indicated they were isoflavone glycosides consisting of one glucose residue. Among them, peaks 1 and 2 were unambiguously identified as calycosin-7-O-glycoside and formononetin-7-O-glycoside, respectively, by comparing the peaks with reference compounds. Peaks 8 and 9 could be tentatively characterized asodoratin-7-O-glycoside and 6, 4′-dimethoxyisoflavone-7-O-Glc by the MS2 spectrum where the product ions were identical with those of peaks 4 and 13, respectively. Moreover, peaks 15, 22, and 23 were considered aglycone of peaks 1, 8, and 9, respectively, because their MS2 characteristic ions were identical with the MS3 spectrum of peaks 1, 8, and 9.
2.2.2. Analysis of Malonyl Isoflavan Glycosides and Related Aglycones
The retention time of astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-malonate (peak 18) was determined to be 30.76 min by comparison with the reference compound. The [M + NH4]+ and [M + H]+ of peak 18 were at m/z 551.1738 and 568.2004, respectively. In the positive ion mode of the LC-MSn spectrum (supplementary materials Figure S2), the product ions at m/z 515.1 and 497.1 were from [M + H]+ by the successive eliminations of 2 × 18 Da (2H2O) and 3 × 18 Da (3H2O). In addition, the typical loss of 86 Da (m/z 497.1→411.1) and 248 Da (m/z 551.1→303.1) were observed in the MS2 spectrum, corresponding to the malonyl and malonyl glucose residue. The other product ions at m/z 193.1, 181.1, 167.1, 165.1, 161.1, 152.1, 147.1, 133.1, and 123.0 were produced from aglycone ion m/z 303.1 due to C-ring RDA cleavage, as well as arrangement at and successive loss of CH3, CO, and CH3OH (Figure 4B). These characteristic ions were identical with the MS2 spectra of peak 25, leading to the identification of peak 25 as isomucronulatol.
Peaks 3, 12 and 21 all showed a distinctive aglycone ion at m/z 303.1, resulting from the loss of carbohydrate units (two glucoses (2 × 162 Da), one glucose (162 Da), and an acetylglucose (42 + 162 Da), respectively). According to their identical characteristic aglycone product ions with isomucronulatol and typical neutral losses, peaks 3 and 12 were tentatively deduced as isomucronulatol-7-O-glycoside-glycoside and astraisoflavanglycoside, respectively, while peak 21 was tentatively characterized as isomucronulatol-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-acetyl.
2.2.3. Characterization of Malonyl Pterocarpan Glycosides and Related Aglycones
Peak 16 was unambiguously identified as astraperocarpan-3-O-glycoside-6′-O-malonate, which was confirmed by the comparison of its tR and mass spectra with the reference standard. The intense [M + NH4]+ and weak ion [M + H]+ of peak 16 was at m/z 549.1584 and 566.1846, respectively. In the LC-MSn spectrum (supplementary materials Figure S3), successive losses of several H2O and malonyl molecules from the m/z 549.1 [M + H]+ produced m/z 513.1 [M + H-2H2O]+, 495.1 [M + H-3H2O]+, and 409.1 [M + H-3H2O-C3H2O3]+. The distinctive aglycone fragment at m/z 301.1 was formed due to the neutral loss of 248 Da (malonyl glucose moiety) from [M + H]+. The product ions at m/z 273.1, 269.1, and 241.1 arose from the aglycone ion by concurrent loss of CH3OH (32Da) and CO (28Da) fragments; the ion at m/z 123.0 was produced from the RDA cleavage of the aglycone ion. In addition, the other product ions were at m/z 191.1, 167.1, 152.1 and 147.0 due to the losses of the B-ring and C-ring arrangement (Figure 4C). This result indicated that peak 16 (pterocarpans) exhibited similar MS/MS fragmentation features to that of peak 18 (isoflavans). The main difference between peaks 16 and 18 was that pterocarpans yielded the typical ions by the concurrent loss of CH3OH and CO from [Aglycone + H]+ ion, where asisoflavans did not show the same characteristic losses.
Peak 11 produced precursor ions at m/z 463.1579 [M + H]+ and m/z 480.1841 [M + NH4]+, indicating the molecular formula of C23H26O10. The MS2 spectra yielded the aglycone ion at m/z 301.1 by the loss of 162 Da (glucose), and their characteristic product ions at m/z 273.1, 269.1, 241.1, 191.1, 167.1, 152.0, 147.0 and 123.0, identical to MS2 spectra of peak 16, leading to the identification of peak 11 as astraperocarpan-3-O-glycoside (9,10-dimethoxypterocarpan-3-O-Glc). The protonated molecular ion at m/z 301.1064 and fragmentation pattern of peak 24 coincided with the aglycone ion of peaks 11 and 16, demonstrating that this compound was 3-hydroxy-9, 10-dimethoxypterocarpan.
Peak 7 generated a [M + H]+ ion at m/z 449.1424 and a [M + NH4]+ at m/z 466.1697 corresponding to the molecular formula of C22H24O10. In the MS2 data, the typical ions m/z 287.0924, 259.0976 and 255.0675 generated from [M + H]+ by the concurrent loss of C6H10O5, CH3OH and CO ion, respectively, indicated peak 7 was a pterocarpan glycoside. After comparing with the literature [26], peak 7 was proposed as licoagroside D (10-dihydroxy-9-methoxypterocarpan-3-O-Glc). Peak 20 displayed a precursor ion at m/z 287.0911 [M + H]+ and the characteristic ions at m/z 259.1, 255.1, 227.1, 177.1, 153.1, 147.0, 138.1 and 123.0 were consistent with the MS3 of the aglycone ion of peaks 7. Thus, peak 20 was tentatively identified as 3, 10-dihydroxy-9-methoxypterocarpan.
Peak 10 gave the precursor ions at m/z 535.1428 [M + H]+ and m/z 552.1690 [M + NH4]+ (molecular formula of C25H26O13), which were 86 Da (malonyl residue) more than that of licoagroside D (peak 7), giving the same aglycone ion at m/z 287.1. In addition, peak 10 had a similar fragmentation pattern as the astraperocarpan-3-O-glycoside-6′-O-malonate (16) with a decrease of 14 Da (H instead of CH3) for the precursor and some fragment ions, confirmed the presence of OH at C-10 in peak 10. Thus, the structure of peak 10 was presumed to 10-dihydroxy-9-methoxypterocarpan-3-O-glycoside-6′-O-malonate.
2.3. Conversion Analysis of MIGs in Astragali Radix under Different Extract Conditions
The LC-TOF/MS revealed that Astragali Radix contained abundant isoflavonoids, among which MIGs had higher relative peak area. However, a previous study has reported that MIGs were unstable [13]. To clarify the content of MIGs and its possible conversion, six major isoflavonoid components, including two MIGs (calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (CYM) and formononetin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate (FMM)) couple with related glycosides (calycosin-7-O-glycoside (CYG) and formononetin-7-O-glycoside(FMG)) and aglycones (calycosin (CY)and formononetin (FM)), were quantified in different extracts of Astragali Radix using a comprehensive HPLC-PDA method.
2.3.1. Calibration Curves, Linearity, Limits of Detection, and Quantification
Under the optimized chromatographic conditions, all six references calibration curves showed good linear regressions in the range of 1.298–811.4, 0.672–420.0, 0.383–239.1, 0.464–290.1, 0.576–360.0, and 0.470–294.0 μg·mL−1, respectively, with the correlation coefficients of 0.9983–0.9995. The analysis of LOD and LOQ showed efficient quantification, which ranged from 0.026–0.047 μg·mL−1 and 0.085–0.280 μg·mL−1, respectively. The RSD values of inter- and intra-day accuracy of six reference compounds were less than 2.21% and 5.63%, respectively (Table 3). Stability of the Astragali Radix sample was tested at room temperature and analyzed at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 and 24 h. The results, however, showed that CYM, FMM, CYG and FMG were unstable at room temperature within 24 h; therefore, the references and sample solution should be stored at 4 °C until analysis.

Table 3.
Linear relationships, limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantitation (LOQ) and precision of six isoflavoniod references by HPLC-PDA.
2.3.2. Content Variation of MIGs, Related Glycosides and Aglycones in Different Extraction Samples of Astragali Radix
In this study, two factors, the extraction method and time, which affects the efficiency and stability of the target compounds, were investigated. Extraction methods under different extraction times, including methanol reflux extraction (MFE), water reflux extraction (WFE), and methanol ultrasonic extraction (MUE), were conducted using powdered samples. Then, the effects of the three methods on the concentration of six isoflavonoids were compared.
By comparing the contents of individual components, the highest yield of the two MIGs (CYM and FMM) was achieved by MUE among all three extraction methods used; conversely, the contents of related glycosides (CYG and FMG) were lower in MUE than in MFE and WFE. Additionally, the contents of CYM and FMM decreased significantly in MFE and WFE during the 8-h extraction, while CYG and FMG showed a remarkable improvement. Furthermore, the contents of two aglycones (CY and FM) in Astragali Radix were relatively low but stable in the three different extraction methods (Figure 5A). In addition, our data showed that the higher the contents of CYM and FMM were, the lower the contents of CYG and FMG observed, which was consistent with the published articles [13]. It suggested that MIGs in raw materials of Astragali Radix might be converted into related glycosides under the elevated temperature conditions, while the glycosides could not be further decomposed into corresponding aglycones. This hypothesis was further confirmed by literatures [12,13] and conversion experiment of reference compounds of CYM and FMM (See Figure S4 and Figure S5 in supplementary materials). The results showed that CYM and FMM only transformed into related glycosides of CYG and FMG, respectively, under methanol reflux extraction condition. Considering the conversion process, although the contents of individual MIGs or related glycosides had a large fluctuation in the procedures of high temperature extraction, the total contents of MIGs and related glycosides should remain basically unchanged. Indeed, we found that the total contents of matched-constituents CYG-CYM and FMG-FMM displayed no obvious change during the long-duration extraction (Figure 5B). In addition, when comparing the total content of CYG-CYM and FMG-FMM, the extraction efficiency of MFE was found to be equivalent to that of MUE and greater than WFE.
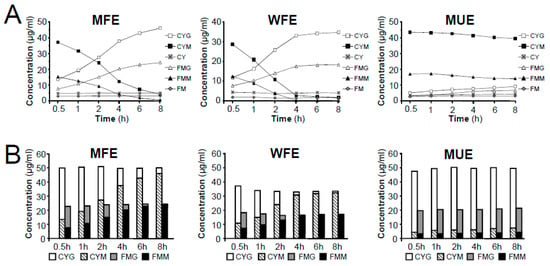
Figure 5.
Comparison of extraction efficiency of different methods on the extraction of MIGs, related glycosides and aglycones in Astragali Radix. (A) Effects of extraction time on the extraction efficiency of six isoflavonoids in three different methods (MFE, WFE and MUE). (B) Effects of extraction method and time on the conversion of the content of matched-constituents (CYG-CYM and FMG–FMM).
As high content of MIGs were found in this study and the literatures [12,13,14], it is indicated that malonate metabolites are widely spread and highly contained in this crude herbal medicine. However, during the extraction conducted under high temperature conditions, MIGs could transform into corresponding glycosides, resulting in a variation in the content and quality evaluation of Astragali Radix. Fortunately, the total content of MIGs and related glycoside in Astragali Radix remained relatively stable, indicating the quality of Astragali Radix could be evaluated efficiently and accurately by determining the total content of MIGs and related glycosides as the quality index.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples, Chemicals and Reagents
Astragali Radix was collected from Baotou County, NeiMenggu Province, China, which is one of the regions in which Astragali Radix is typically cultivated. The samples of Astragali Radix were identified by prof. Xunhong Liuto be the dried roots of A. membranaceus. The samples were stored in a dry, dark room atthe School of Pharmacy, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine.
Reference compounds, including CYG, FMG, CY and FM were purchased from the National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products (Beijing, China). Malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides, including FMM, CYM, astraperocarpan-3-O-β-D-glycoside-6″-O-malonate and astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-malonate were isolated from the dried roots. The structures were confirmed by comparison of their spectral data (UV, MS,1H NMR and 13C NMR) with those published in cited references. The purities of the isolated compounds were above 98.0%, as determined by HPLC-PAD using the peak area normalization method.
HPLC grade ACN and CH3OH were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany); distilled water was further purified by Milli-Q system (Millipore, Milford, MA, USA). HPLC grade formic acid was purchased from the Hanbang Company of Nanjing (Nanjing, China).
3.2. Isolation and Identification ofMIGs
Astragali Radix (about 5 kg) was exhaustively extracted with methanol percolation (50 L) at room temperature. The extracts were combined and concentrated to 2000 mL under a vacuum at 40 °C. The supernatant was filtered and concentrated to dryness. The residue (a total of about 135 g) was then separated by silica gel CC (1000 g, 200–300 mesh) to three fractions (Fr. A-C) using a gradient elution of EtOAc-MeOH (100:0; 85:15; 70:30, v/v), respectively. Then, approximately 10.5 g of Fr. C was subjected to middle pressure liquid chromatography (MPLC, BUCHI Chromatography B-688, Flawil, Switzerland) on an RP silica gel column with stepwise solution of MeOH-H2O-HCOOH (30:70:0.1–40:60:0.1, v/v) as the eluent to obtain AR-1 (103 mg) and AR-2(48 mg). Fr. B was then repeatedly separated by MPLC chromatography over an RP-18 silica gel column (400 g, 25–50 μm, 4.5 × 50 cm) eluted with MeOH-H2O-HCOOH (30:70:0.1–40:60:0.1, v/v) to obtain AR-3 (31 mg) and AR-4 (26 mg). The purified compounds were characterized by LC-MS and NMR analyses. The MS spectra were recorded on an AB SCIEX Triple TOFTM 5600 mass spectrometer instrument (AB, SCIEX, Los Angeles, CA, USA) in positive ion mode. 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded with an ASR-400 NMR spectrometer (Bruker, Fällanden, Switzerland). TMS was used as an internal standard and the specimens were dissolved in DMSO-d6 (dimethylsulfoxide).
3.3. Chromatographic Methods
Analyses were performed on a Waters Series 2695 liquid chromatography (Waters Technologies, Milford, MA, USA) with an analytical column of Eclipse XDB-C18 (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The mobile phase consisted of (A) acetonitrile containing 0.1% (v/v) formic acid and (B) distilled water containing 0.1% (v/v) formic acid using a gradient elution: linear from 15 to 32% B (0–25 min), linear from 32 to 62% B (25–50 min). All separations were at 25 °C and a flow-rate of 1.0 mL/min. The injection volume was 5 μL. The HPLC-PDA chromatographic profile was recorded at 260 nm.
3.4. LC-TOF/MS Conditions
The mass spectrometry determination was performed on an aquadrupole time of flight mass spectrometer (TripleTOF 5600 system, AB SCIEX) with an electrospray source in the positive ion mode. The automatic data-dependent information product ion spectra (IDA-MS/MS) without any predefinition of the ions were recorded with mass range m/z 100–2000. The conditions of ESI source were as follows: nitrogen gas for nebulization at 55 psi, heater gas pressure at 55 psi, curtain gas at 35 psi, temperature of 500 °C, and ion spray voltage at 5500 V in positive ion mode. The acquisition of a survey Q-TOF/MS spectrum was operated under high-resolution settings. The optimized declustering potential (DP) and collision energy (CE) were set at 80 eV and 15 eV in positive ion mode. A sweeping collision energy setting at 35 ± 15 eV was applied for collision-induced dissociation (CID).
3.5. Sample Solution Preparation
Methanol ultrasonic extraction (MUE): Approximately 1.0 g dried Astragali Radix powder was weighed and extracted with 20 mL of methanol in an ultrasonic bath for 0.5~8.0 h at room temperature. The supernatant was collected; then stored at a temperature at 4 °C. The extract solution was filtered with 0.45 μm filter membrance before HPLC analysis.
Methanol reflux extraction (MFE): Approximately 1.0 g dried Astragali Radix powder was weighed and extracted with 20 mL of methanol by refluxing in water bath for 0.5~8.0 h at a temperature of 80 °C. After extraction, the glass bottle was kept closed and allowed to cool to room temperature. The supernatant was collected; then stored at a temperature at 4 °C. The extract solution was filtered with 0.45 μm filter membrance before HPLC analysis.
Water reflux extraction (WFE): Approximately 1.0 g dried Astragali Radix powder was weighed and extracted with 20 mL of water by refluxing in water bath for 0.5~8.0 h at a temperature of 100 °C. After extraction, the glass bottle was kept closed and allowed to cool to room temperature. The supernatant was collected; then stored at a temperature at 4 °C. The extract solution was filtered with a 0.45 μm filter membrane before HPLC analysis.
4. Conclusions
This was the first systematic investigation of MIGs in Astragali Radix. In this paper, we isolated and purified four MIGs from Astragali Radix, and their fragmentation pathways in ESI/Q-TOF/MS positive mode were proposed. Further research on the chemical profile of MIGs in Astragali Radix led to identify a total of 26 isoflavonoid compounds, including eleven malonyl isoflavonoid glycosides coupled with eight related isoflavonoid glycosides and seven aglycones. This illustrated that the MIGs were an important type of isoflavonoid in Astragali Radix. The quantitative results verified that MIGs could be converted into related glycosides under the elevated temperature conditions, while the total contentdisplayed no obvious change during the long-duration extraction. Our study has provided some technological support for using MIGs and related glycosides to develop quality evaluation methods for Astragali Radix and its products.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/24/21/3929/s1, Figure S1: ESI-Q-TOF/MS (+) spectrum of calycosin-7-O-Glc-6″-O-Mal (peak 6) and its proposed fragmentations; Figure S2: ESI-Q-TOF/MS (+) spectrum of astraisoflavanglycoside-6″-O-Mal (peak 18) and its proposed fragmentations; Figure S3: ESI-Q-TOF/MS (+) spectrum of astraperocarpan-3-O-Glc-6′-O-Mal (peak 16) and its proposed fragmentations; Figure S4: Conversion analysis of CYM under reflux extraction for 0.5–8.0 h; Figure S5: Conversion analysis of FMM under reflux extraction for 0.5–8.0 h.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. contributed to project design, experimental guidance and paper writing for the study. W.D. and J.S. contributed to finish the experiments and paper writing. Q.C. and C.Z. performed the data analyses. C.L. and G.P. helped to experimental guidance, paper writing and constructive discussions.
Funding
This project is supported by National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1706503) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 81973482).
Conflicts of Interest
None of the authors have any financial or personal relationship with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence or bias this study.
References
- Pharmacopoeia Commission of PRC. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China: Volume 1; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; p. 302. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Duan, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wei, C.; An, L. Isoflavonoids from Astragalus mongholicus protect PC12 cells from toxicity induced by L-glutamate. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Shen, W.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Sun, Z. The protective effect of total flavonoids Astragalus on DNA strand break in V_(79) cell caused by hydroxyl radicals. Chin. Pharm. Bull 1995, 11, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Lib, J.; Chaic, Q.; Liuc, Z.; Chen, L. Effect of total flavonoid fraction ofAstragalus complanatus R.Brown on angiotensin II-induced portal-vein contraction in hypertensive rats. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.C.; Leung, M.N. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulating and immunorestorative effects of Astragalus membranaceus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, M.; Kim, E.H.; Chun, M.; Kang, S.; Shim, B.; Yu, Y.B.; Jeong, G.; Lee, J.S. Astragali Radix elicits anti-inflammation via activation of MKP-1, concomitant with attenuation of p38 and Erk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoo, R.L.; Wong, J.Y.; Qiao, C.; Xu, A.; Xu, H.; Lam, K.S. The effective fraction isolated from Radix Astragali alleviates glucose intolerance, insulin resistance andhypertriglyceridemia in db/db diabetic mice through its anti-inflammatory activity. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.L.; He, K.; Zhang, L.; Fu, T. Extraction and Fractional Separation of Polysaccharide from Astragalus membranaceus on the Basis of Molecular Weight. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2010, 16, 719–723. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.P.; Zhang, X.P.; Ruan, Y.F.; Ye, S.Y.; Zhao, H.C.; Cheng, Q.H.; Wu, D.J. Protective effect of Radix Astragali injection on immune organs of rats with obstructive jaundice and its mechanism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratkov, V.M.; Shkondrov, A.M.; Zdraveva, P.K.; Krasteva, I.N. Flavonoids from the genus Astragalus: Phytochemistry and biological activity. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.W.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.L.; Huang, L.F.; He, Y.B.; Xie, X.Z. Identification and Determination of Flavonoids in Astragali Radix by High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with DAD and ESI-MS Detection. Molecules 2011, 16, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Z.; He, X.G.; Lindenmaier, M.; Nolan, G.; Yang, J.; Cleary, M.; Qiu, S.X.; Cordell, G.A.; Lindenmaier, M. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry study of the flavonoids of the roots of Astragalus mongholicus and A. J. Chromatogr. A. 2000, 876, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Z.; Mo, S.F.; Yip, Y.K.; Qiao, C.F.; Han, Q.B.; Xu, H.X. Development of microwave assisted extraction for the simultaneous determination of isoflavonoids and saponins in Radix Astragali by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.G.; Bai, Y.J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Huang, L.Q. Analysis of principal isoflavone glycosides and aglycone in Radix Astragali. J. Chin. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 17, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, C.; Cui, X.B.; Shan, C.X.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.Z.; Wen, H.M. Simultaneous Characterization and Quantification of Varied Ingredients from Sojae semen praeparatum inFermentation Using UFLC–Triple TOF MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, L.N.; Zhang, G.; Terry, A.V.; Bartlett, M.G. Comparison of time-of-flight mass spectrometry to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry for quantitative bioanalysis: Application to antipsychotics. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2008, 31, 2737–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, G.L.; Simons, B.L.; Young, J.B.; Hawkridge, A.M.; Muddiman, D.C. Performance characteristics of a new hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometer (tripletof 5600). Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5442–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, C.; Knodler, M.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Carle, R.; Ganzle, M.G.; Schieber, A. Antimicrobial activity of gallotannins isolated from mango (mangiferaindica l.) kernels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7712–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, M.; Peng, G.P.; Dong, T.X.; Xu, L.M.; Tsim, K.W. Prenylated flavonoids from roots of glycyrrhiza uralensis induce differentiation of B16-F10 melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Shen, Y.B.; Wang, Z.H.; He, B.; Xu, Y.H.; Nie, H.; Zhu, Q. Rapid analysis and guided isolation of Astragalus isoflavonoids by UHPLC-DAD-MSn and their cellular antioxidant defense on high glucose induced mesangial cells dysfunction. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.J.; Xu, W.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.Y.; Qiu, X.H. Rapid Characterization and identification of flavonoids in Radix Astragali by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion Trap-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.R.; Liu, Z.Q.; Liu, S.Y. Studies on principal components and antioxidant activity of different Radix Astragali samples using high-performance liquid chromatography/electrosprayionization multiple-stage tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2009, 78, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.Q.; Qu, Q.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Zhong, H.H.; Shan, C.X.; Wang, F.; Li, C.Y.; Peng, G.P. Structural characterization and identification of flavonoid aglycones in three Glycyrrhiza species by liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 39, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, H.B.; Xue, X.Y.; Sun, Y.G.; Liang, X.M. Simultaneous characterization of isoflavonoids and astragalosides in two Astragalus species by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 39, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.Y.; Guan, J.; Bi, Z.M.; Song, Y.; Li, P. Studies on chemical constituents of Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. Var. mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao. Chin. Pharm. J. 2006, 41, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.J.; Liu, H.K.; Hsiao, P.C.; Kuo, L.M.Y.; Lee, I.J.; Wu, T.S.; Chiou, W.F.; Kuo, Y.H. New isoflavonoid glycosides and related constituents from Astragali Radix (Astragalus membranaceus) and their inhibitory activity on nitric oxide production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds calycosin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate and formononetin-7-O-glycoside-6″-O-malonate are available from the authors. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).