Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel 2H-Benzo[e]-[1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide Derivatives as PI3Kδ Inhibitors
Abstract
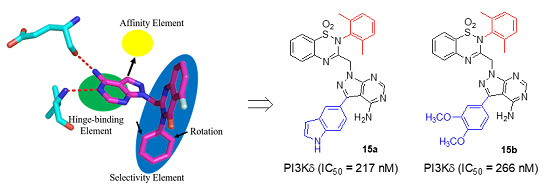
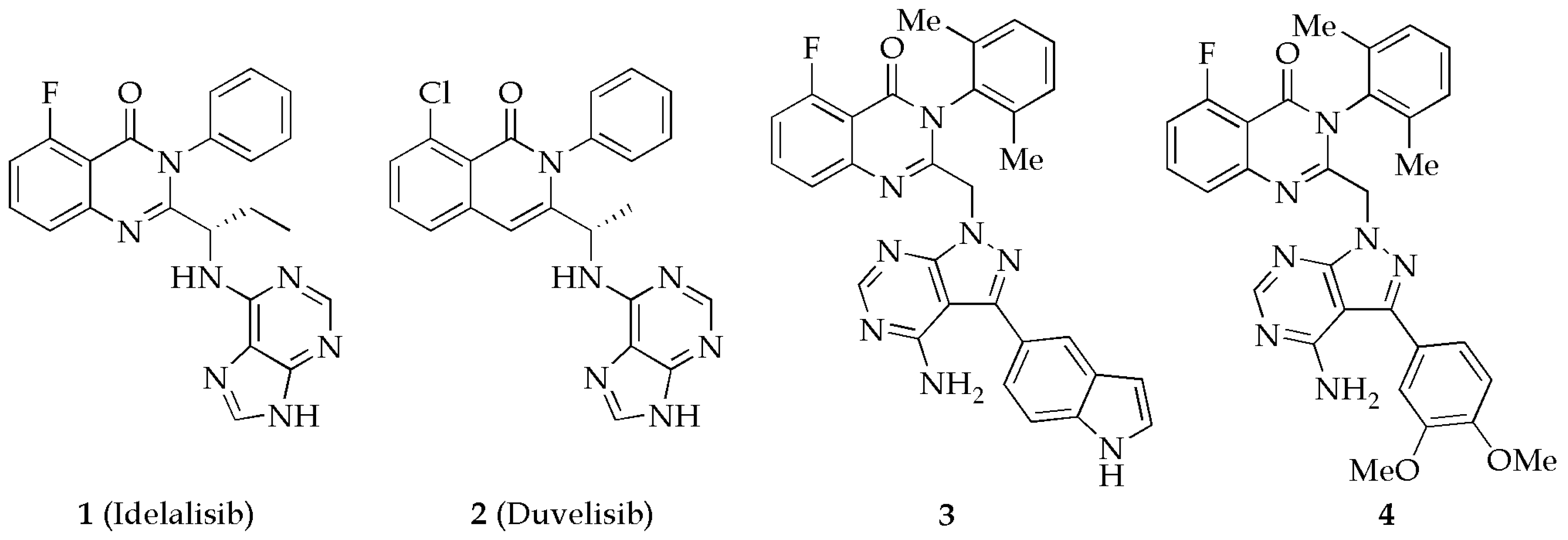
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
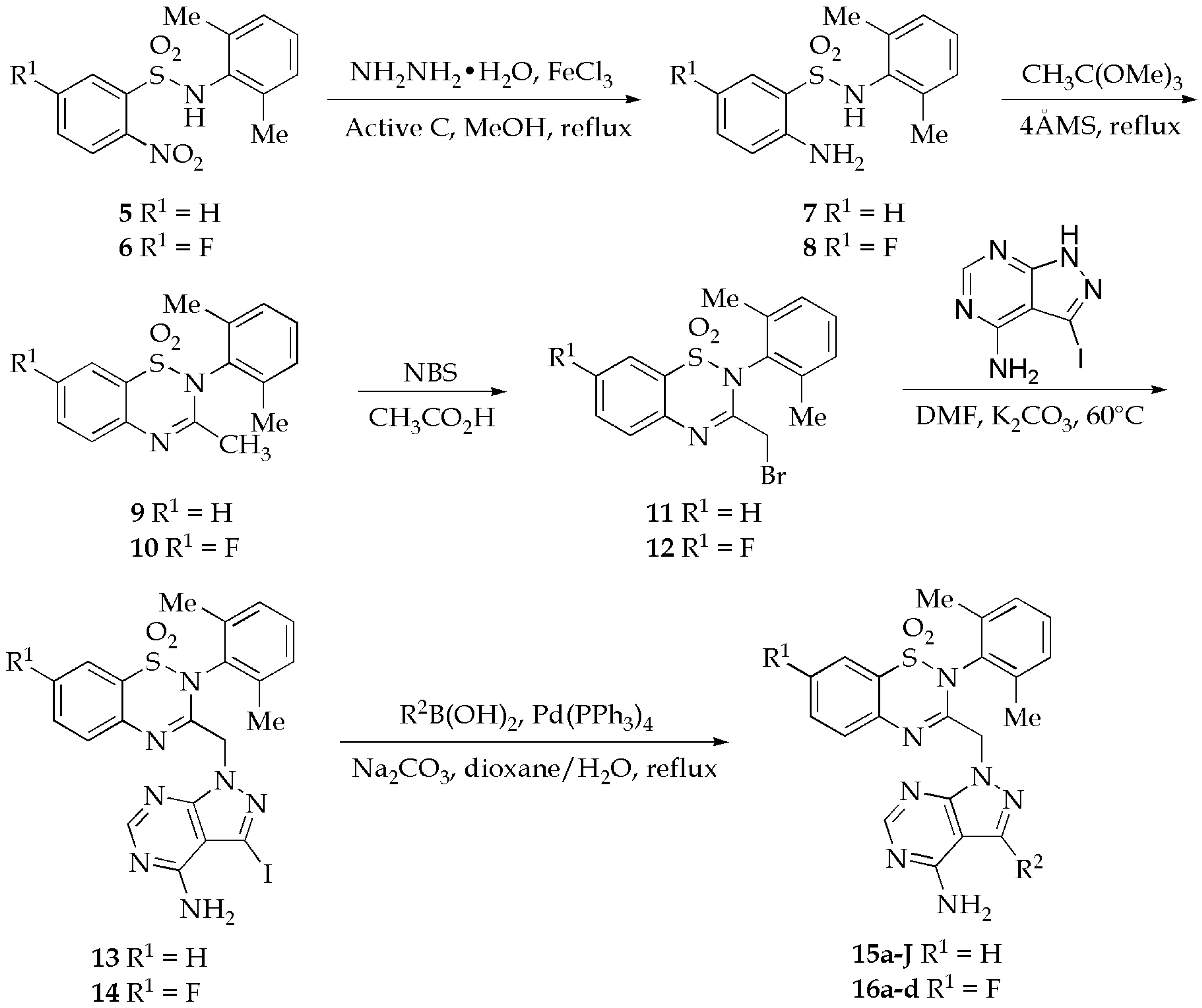
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. PI3Kδ Inhibitory Activity and Isoform Selectivity
2.3. SU-DHL-6 Cell Growth Inhibitory Activity
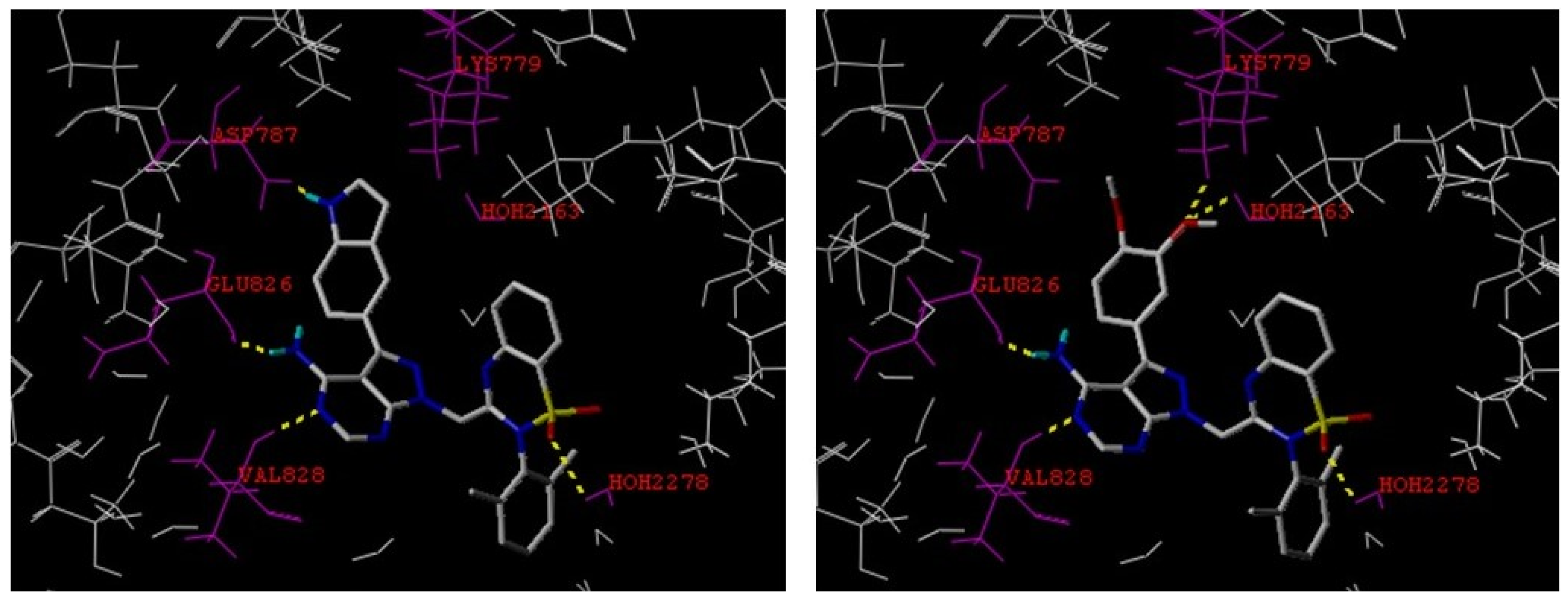
2.4. Molecular Modeling Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Chemical Experimental Procedures
3.2. PI3K Kinase Assay
3.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
3.4. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PI3Ks | Phosphoinositide 3-kinases |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| NBS | N-Bromosuccinimide |
| ADP | Adenosine diphosphate |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| APDS | PI3Kδ syndrome |
| FL | Follicular lymphoma |
| SLL | Small lymphocytic lymphoma |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
References
- Toker, A.; Cantley, L.C. Signalling through the lipid products of phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase. Nature 1997, 387, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantley, L.C. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 2002, 296, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, S.M.; Yballe, C.M.; Innocenti, M.; Deane, J.A.; Fruman, D.A.; Thomas, S.M.; Cantley, L.C. Role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulatory isoforms in development and actin rearrangement. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2593–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform specific PI3K signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606−619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, C.; Hernandez, C.; Pimentel, B.; Carrera, A.C. The p85 regulatory subunit controls sequential activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase by tyr kinases and ras. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41556–41562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, C.; Schaefer, M.; Reusch, H.P.; Czupalla, C.; Michalke, M.; Spicher, K.; Schultz, G.; Nurnberg, B. Roles of Gβγ in membrane recruitment and activation of p110γ/p101 phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K in lymphocyte development, differentiation and activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Puri, K.D.; Penninger, J.M.; Kubes, P. Leukocyte PI3Kγ and PI3Kδ have temporally distinct roles for leukocyte recruitment in vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.J.; Smith, A.; Head, D.H.; Milne, L.; Nicholls, A.; Pearce, W.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Wymann, M.P.; Hirsch, E.; Trifilieff, A.; et al. Airway inflammation: Chemokine-induced neutrophilia and the class I phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Rommel, C. PI3K and cancer: Lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Yuzugullu, H.; Zhao, J.J. PI3K in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janku, F. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway inhibitors in solid tumors: From laboratory to patients. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 59, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K pathway in human disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, D. Class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garces, A.E.; Stocks, M.J. Class 1 PI3K clinical candidates and recent inhibitor design strategies: A medicinal chemistry perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4815–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, Z.A.; Gonzalez, B.; Feldman, M.E.; Zunder, E.R.; Goldenberg, D.D.; Williams, O.; Loewith, R.; Stokoe, D.; Balla, A.; Toth, B.; et al. A pharmacological map of the PI3-K family defines a role for P110α in insulin signaling. Cell 2006, 125, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, G.; Guo, J.; Su, Z. The PI3K/AKT Pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1483–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Schoenwaelder, S.M.; Goncalves, I.; Nesbitt, W.S.; Yap, C.L.; Wright, C.E.; Kenche, V.; Anderson, K.E.; Dopheide, S.M.; Yuan, Y.; et al. PI 3-Kinase P110β: A new target for antithrombotic therapy. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Schoenwaelder, S.M. Antithrombotic phosphoinositide 3-kinase β inhibitors in humans: A ‘shear’ delight! J. Thromb. Haemostasis 2012, 10, 2123–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, T.D.; Metz, D.P.; Whittington, D.A.; McGee, L.R. PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ as targets for autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8559–8581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, W.C.; Smith, J.L.; Affleck, K.; Amour, A. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ for allergic asthma. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, E.J.; Ojiaku, C.A.; Sunder, K.; Panettieri, R.A. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in asthma: Novel roles and therapeutic approaches. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 56, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, M.W.D.; Abdulai, R.; Mogemark, M.; Petersen, J.; Thomas, M.J.; Valastro, B.; Eriksson, A.W. Evolution of PI3Kγ and δ Inhibitors for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4783–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracker, S.; Curtis, J.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Sediva, A.; Salisbury, J.; Campr, V.; Debré, M.; Edgar, J.D.M.; Imai, K.; Picard, C.; et al. Occurrence of B-cell lymphomas in patients with activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkaim, E.; Neven, B.; Bruneau, J.; Mitsui-Sekinaka, K.; Stanislas, A.; Heurtier, L.; Lucas, C.L.; Matthews, H.; Deau, M.-C.; Sharapova, S.; et al. Clinical and immunologic phenotype associated with activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ syndrome 2: A cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, T.I.; Chandra, A.; Bacon, C.M.; Babar, J.; Curtis, J.; Screaton, N.; Goodlad, J.R.; Farmer, G.; Steele, C.L.; Leahy, T.R.; et al. Clinical spectrum and features of activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase δ syndrome: A large patient cohort study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.; Gili, E.; Fruciano, M.; Korfei, M.; Fagone, E.; Iemmolo, M.; Lo Furno, D.; Giuffrida, R.; Crimi, N.; Guenther, A.; et al. PI3K P110γ overexpression in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis lung tissue and fibroblast cells: In vitro effects of its inhibition. Lab. Investig. 2013, 93, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, R.R.; Sharman, J.P.; Coutre, S.E.; Cheson, B.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Hillmen, P.; Barrientos, J.C.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Kipps, T.J.; Flinn, I.; et al. Idelalisib and rituximab in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.Y.; Fowler, N.H. Idelalisib in the management of lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangapandu, H.V.; Jain, N.; Gandhi, V. Duvelisib: A phosphoinositide-3 kinase δ,γ inhibitor for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwell, I.B.; Flowers, C.R.; Blumb, K.A.; Cohen, J.B. Clinical use of PI3K inhibitors in B-cell lymphoid malignancies: Today and tomorrow. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.-C.; Zhang, C.-M.; Tang, L.-Q.; Liu, Z.-P. Discovery of novel quinazolinone derivatives as high potent and selective PI3Kδ and PI3Kδ/γ inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 151, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Mushtaq, S.; Naz, S.; Farooq, U.; Zaidi, A.; Bukhari, S.M.; Rauf, A.; Mubarak, M.S. Sulfonamides as potential bioactive scaffolds. Curr. Org. Chem. 2018, 22, 818–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, I.; Taslimi, P. Sulfonamide inhibitors: A patent review 2013-present. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Rakesh, K.P.; Ravidar, L.; Fang, W.-Y.; Qin, H.-L. Pharmaceutical and medicinal significance of sulfur (SVI)-Containing motifs for drug discovery: A critical review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 679–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassadin, V.A.; Tomashevskiy, A.A.; Sokolov, V.V.; Ringe, A.; Magull, J.; de Meijere, A. Facile access to bicyclic sultams with methyl-1-sulfonylcyclopropane-1-carboxylate moieties. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2635–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.C.; Ojo, K.K.; Larson, E.T.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Perera, B.G.; Keyloun, K.R.; Kim, J.E.; Bhandari, J.G.; Muller, N.R.; Verlinde, C.L.; et al. Discovery of potent and selective inhibitors of CDPK1 from C. parvum and T. gondii. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koresawa, M.; Okabe, T. High-throughput screening with quantitation of ATP consumption: A universal non-radioisotope, homogeneous assay for protein kinase. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2004, 2, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaud, F.I.; Eccles, S.A.; Patel, S.; Alix, S.; Box, G.; Chuckowree, I.; Folkes, A.; Gowan, S.; De Haven Brandon, A.; Di Stefano, F.; et al. Biological properties of potent inhibitors of class I phosphatidylinositide 3-kinases: From PI-103 through PI-540, PI-620 to the oral agent GDC-0941. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.H.; Wagner, E.C. 3,4-Dihydro-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine. J. Org. Chem. 1951, 16, 815–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, A.; Miller, S.; Williams, O.; Le, D.D.; Houseman, B.T.; Pacold, J.I.; Gorrec, F.; Hon, W.C.; Ren, P.; Liu, Y.; et al. The p110δ structure: Mechanisms for selectivity and potency of new PI(3)K inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 15a–j and 16a–d are available from the authors. |
| Compd. | Structure | R | IC50 (nM) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15a |  | 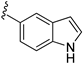 | 217 ± 28 |
| 15b | 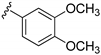 | 266 ± 31 | |
| 15c |  | 980 ± 45 | |
| 15d | 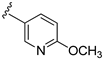 | 498 ± 33 | |
| 15e | 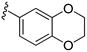 | >1000 | |
| 15f | 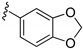 | >1000 | |
| 15g | 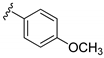 | >1000 | |
| 15h | 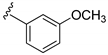 | >1000 | |
| 15i |  | >1000 | |
| 15j | 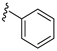 | >1000 | |
| 16a | 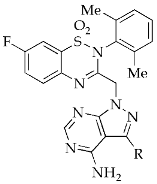 |  | >1000 |
| 16b | 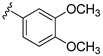 | 518 ± 62 | |
| 16c | 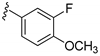 | 824 ± 76 | |
| 16d | 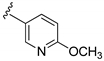 | 823 ± 69 | |
| PI-103 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | ||
| Compound | IC50 (nM) a | GI50 (μM) a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI3Kα | PI3Kβ | PI3Kδ | PI3Kγ | SU-DHL-6 | |
| 15a | >50,000 | 30596 ± 875 | 217 ± 28 | >50,000 | 2.13 ± 0.09 |
| 15b | 16364 ± 768 | 24189 ± 495 | 266 ± 31 | 5838 ± 135 | 2.50 ± 0.11 |
| PI-103 | 6.5 ± 0.7 | 23 ± 1.6 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 78 ± 4.3 | 0.039 ± 0.011 b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.-P.; Tang, L.-Q.; Liu, T.-S.; Liu, Z.-P. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel 2H-Benzo[e]-[1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide Derivatives as PI3Kδ Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234299
Gong Y-P, Tang L-Q, Liu T-S, Liu Z-P. Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel 2H-Benzo[e]-[1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide Derivatives as PI3Kδ Inhibitors. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234299
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Ya-Ping, Long-Qian Tang, Tong-Shen Liu, and Zhao-Peng Liu. 2019. "Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel 2H-Benzo[e]-[1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide Derivatives as PI3Kδ Inhibitors" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234299
APA StyleGong, Y.-P., Tang, L.-Q., Liu, T.-S., & Liu, Z.-P. (2019). Synthesis and Evaluation of Novel 2H-Benzo[e]-[1,2,4]thiadiazine 1,1-Dioxide Derivatives as PI3Kδ Inhibitors. Molecules, 24(23), 4299. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234299