Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Platelet-Activating Factor
2. The Discovery and Structural Elucidation of the Platelet-Activating Factor
2.1. The Discovery of the Platelet-Activating Factor
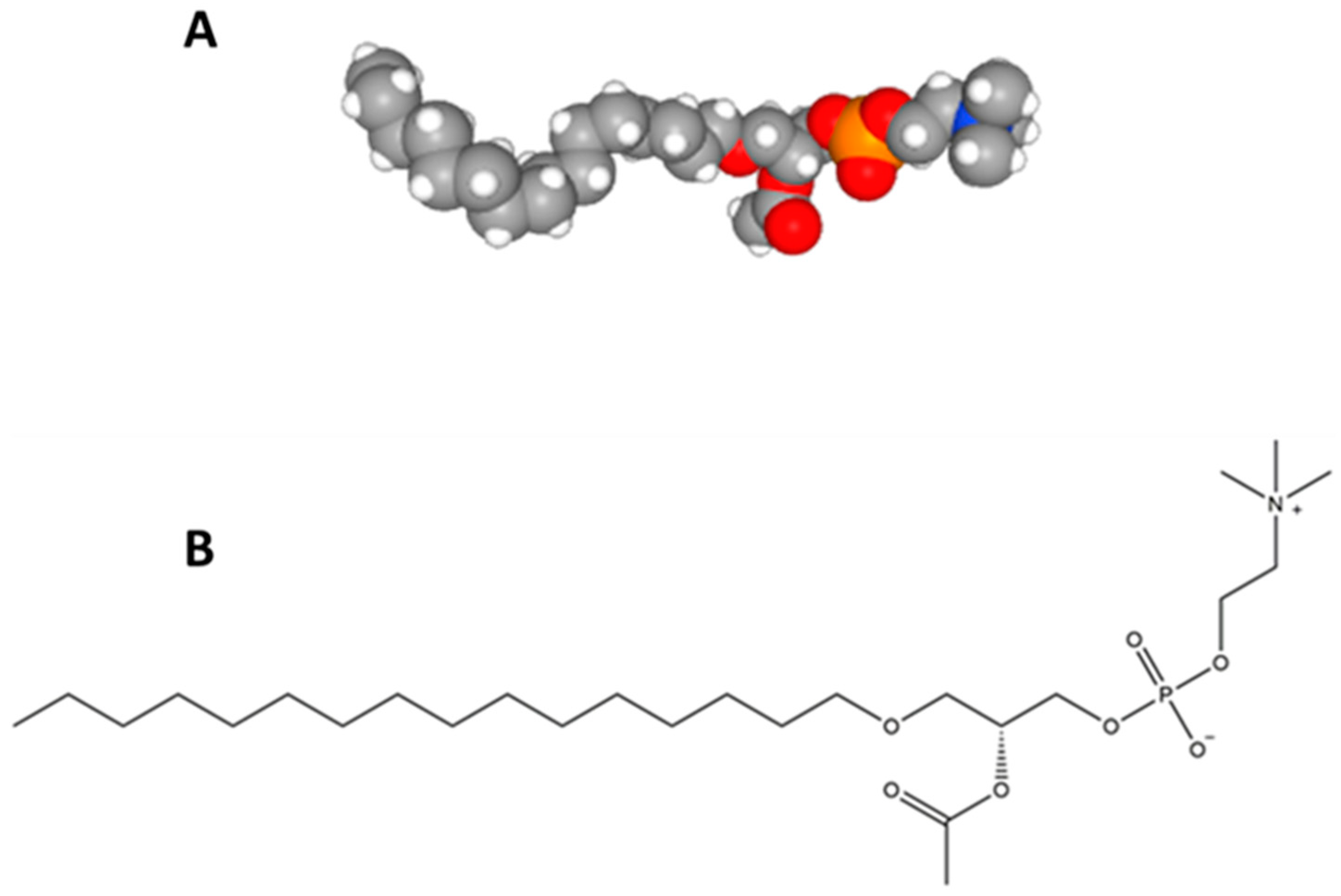
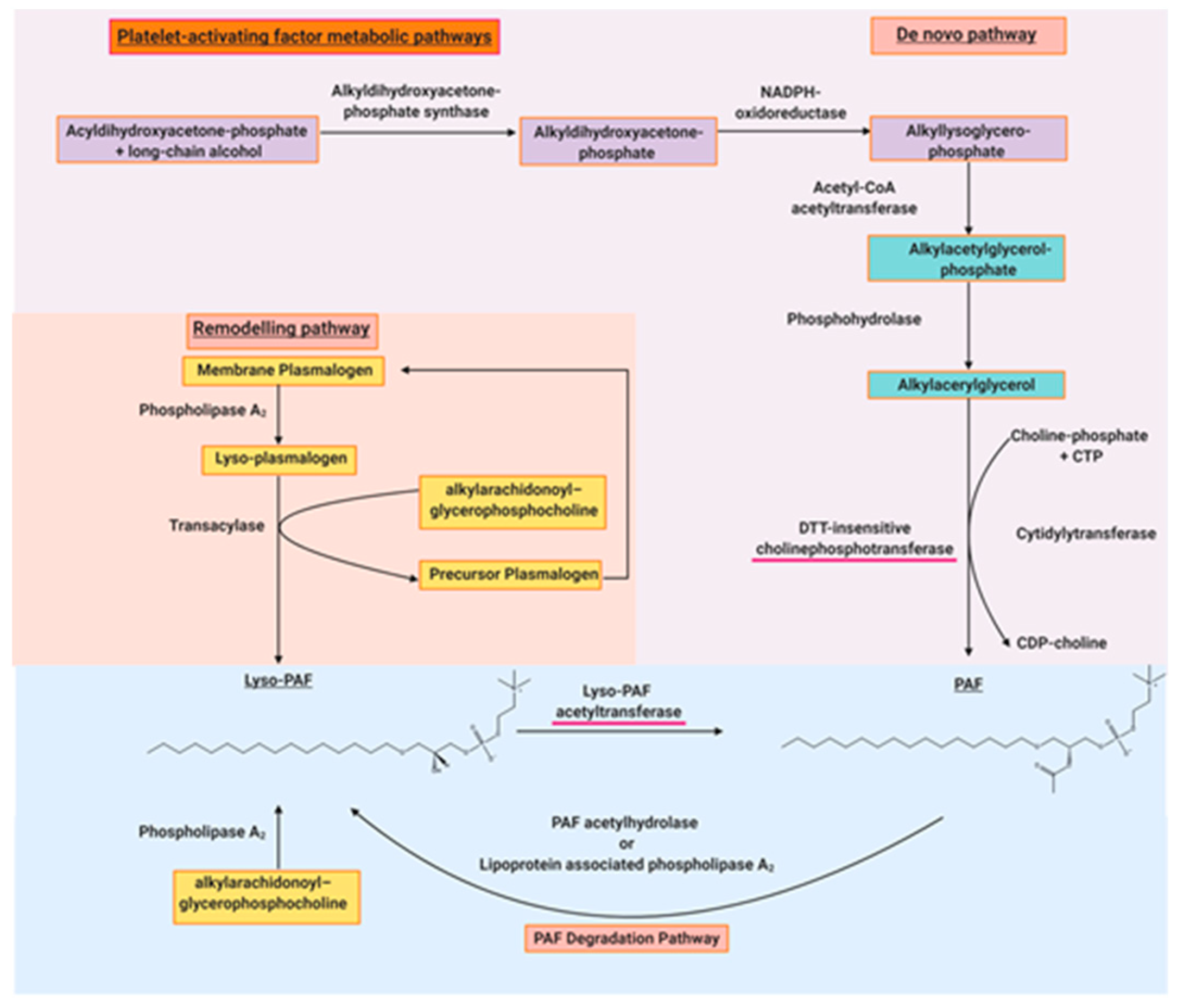
2.2. Structural Elucidation of the Platelet-Activating Factor
3. The Importance of Platelet-Activating Factor Research
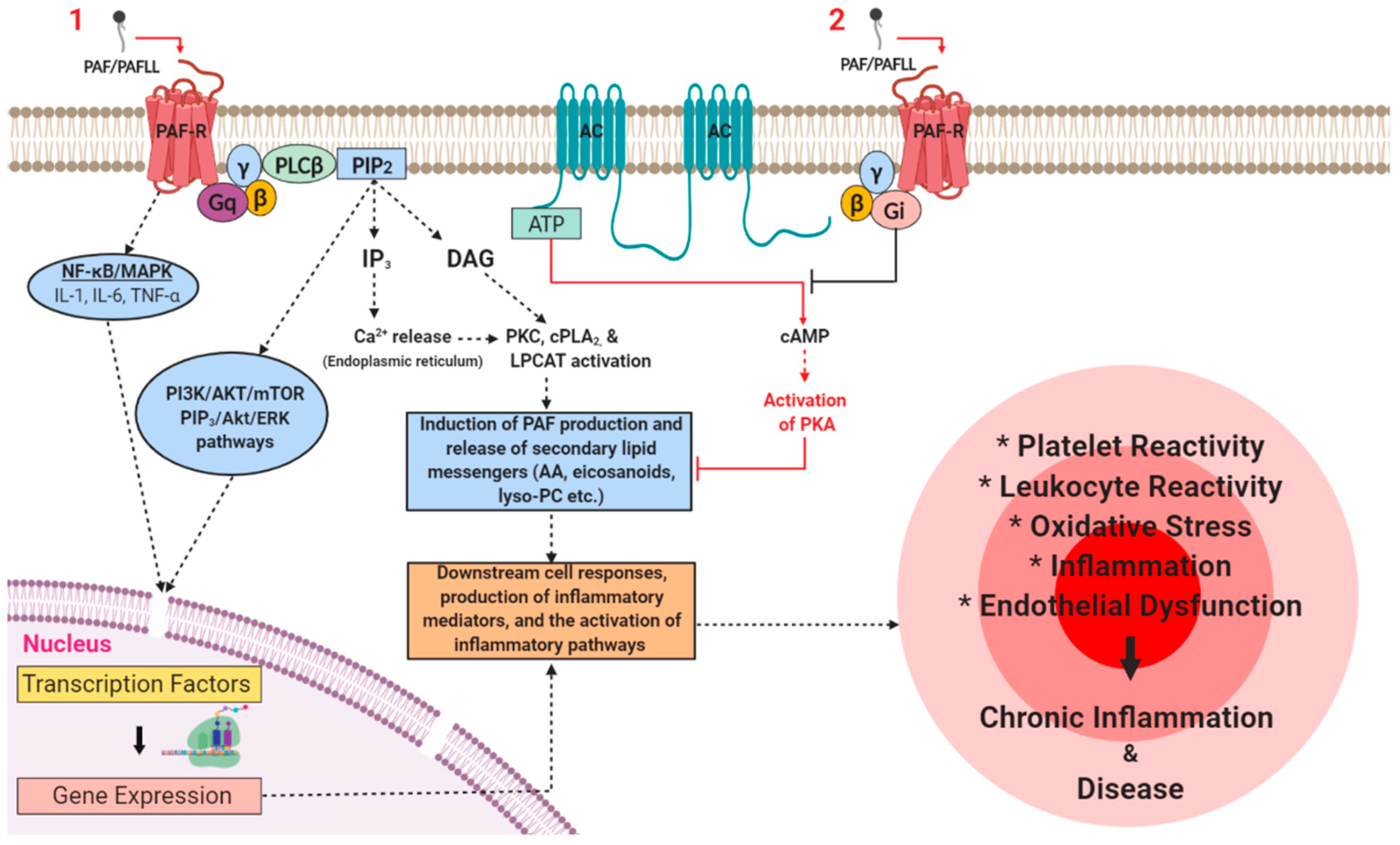
3.1. PAF Signalling in Physiology
3.2. PAF Signalling in Pathophysiology
4. The Potential Use of Platelet-Activating Factor Inhibitors as Therapeutics and Preventatives of Disease
4.1. PAF Inhibitors of Synthetic Origin
4.2. PAF Inhibitors of Natural Origin
5. Current Trends in Platelet-Activating Factor Research
5.1. A Potential Anti-Inflammatory Role of PAF
5.2. PAF and Cancer
5.3. Current Research Trends on PAF and PAFLL in Cardiovascular Disease
5.4. Current Research Trends on PAF in Neurological Disorders
5.5. Current Research Trends on PAF in Renal and Urinary System Disorders
6. New Frontiers in PAF Research
6.1. PAF-R Strucutral Elucidation
6.2. Induction of Inflammatory Pathways Independent of the PAF-R
7. Conclusions and Future Research Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demopoulos, C.A. State of lipid research in greece. Euro. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2000, 102, 665–666. [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos, C.A. Biological activity of lipids of pine pollen on platelet aggregation in correlation with the platelet activating factor. In Proceedings of the second international conference on platelet-activating factor and structurally related alkyl ether lipids, Gatlinburg, TN, USA, 26–29 October 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Stafforini, D.M.; McIntyre, T.M. Platelet-activating factor and related lipid mediators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclennan, K.M.; Smith, P.F.; Darlington, C.L. Platelet-activating factor in the cns. Prog. Neurobiol. 1996, 50, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Inflammation, not cholesterol, is a cause of chronic disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suvarna, Y.; Maity, N.; Shivamurthy, M.C. Emerging trends in retrograde signaling. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkl, D.; Quiros, M.; García-Hernández, V.; Zhou, D.W.; Brazil, J.C.; Hilgarth, R.; Keeney, J.; Yulis, M.; Bruewer, M.; García, A.J.; et al. TNF-α promotes mucosal wound repair through enhanced platelet activating factor receptor signaling in the epithelium. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. The potential role of dietary platelet-activating factor inhibitors in cancer prevention and treatment. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva-Jr, I.; Chammas, R.; Lepique, A.; Jancar, S. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor as a promising target for cancer cell repopulation after radiotherapy. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demopoulos, C.A.; Karantonis, H.C.; Antonopoulou, S. Platelet-activating factor — a molecular link between atherosclerosis theories. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2003, 105, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palur Ramakrishnan, A.V.K.; Varghese, T.P.; Vanapalli, S.; Nair, N.K.; Mingate, M.D. Platelet activating factor: A potential biomarker in acute coronary syndrome? Cardiovasc. Ther. 2017, 35, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, C.C.; Weyrich, A.S.; Zimmerman, G.A. The platelet activating factor (PAF) signaling cascade in systemic inflammatory responses. Biochimie 2010, 92, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Tsogas, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Lioni, A.; Mangafas, N.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Antonopoulou, S.; Lazanas, M.C. Anti-platelet-activating factor effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART): A new insight in the drug therapy of hiv infection? Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2008, 24, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Nomikos, T.; Karantonis, H.; Fragopoulou, E.; Demopoulos, C.A. PAF, a potent lipid mediator. In Bioactive phospholipids: Role in inflammation and atherosclerosis; Tselepis, A.D., Ed.; Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2008; pp. 85–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikov, V.; Muzya, G. Ether lipids and platelet-activating factor: Evolution and cellular function. Biochem. Biokhimiia 1997, 62, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaro, J.F.; Zvaifler, N.J. Antigen induced histamine release from platelets of rabbits producing homologous PGA antibody. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 122, 1245–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siraganian, R.P.; Osler, A.G. Destruction of rabbit platelets in the allergic response of sensitized leukocytes: I. Demonstration of a fluid phase intermediate. J. Immunol. 1971, 106, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, J.; Henson, P.M.; Cochrane, C.G. Leukocyte-dependent histamine release from rabbit platelets: The role of IGE, basophils, and a platelet-activating factor. J. Exp. Med. 1972, 136, 1356–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, J. Platelet-activating factor, a new mediator of anaphylaxis and immune complex deposition from rabbit and human basophils. Nature 1974, 249, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chap, H. Forty five years with membrane phospholipids, phospholipases and lipid mediators: A historical perspective. Biochimie 2016, 125, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotboom, A.J.; de Haas, G.H.; Bonsen, P.P.M.; Burbach-Westerhuis, G.J.; van Deenen, L.L.M. Hydrolysis of phosphoglycerides by purified lipase preparations i. Substrate-, positional- and stereo-specificity. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1970, 4, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, P.M.; Pinckard, R.N. Basophil-derived platelet-activating factor (PAF) as an in vivo mediator of acute allergic reactions: Demonstration of specific desensitization of platelets to PAF during IGE-induced anaphylaxis in the rabbit. J. Immunol. 1977, 119, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard, R.N.; Farr, R.S.; Hanahan, D.J. Physicochemical and functional identity of rabbit platelet-activating factor (PAF) released in vivo during IGE anaphylaxis with PAF released in vitro from IGE sensitized basophils. J. Immunol. 1979, 123, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chignard, M.; Le Couedic, J.; Tence, M.; Vargaftig, B.; Benveniste, J. The role of platelet-activating factor in platelet aggregation. Nature 1979, 279, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benveniste, J.; Le Couedic, J.P.; Polonsky, J.; Tence, M. Structural analysis of purified platelet-activating factor by lipases. Nature 1977, 269, 170–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haas, G.H.; Van Deenen, L.L.M. Structural identification of isomeric lysolecithins. Biochim. Biophys. Lipids Lipid Metab. 1965, 106, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demopoulos, C.; Pinckard, R.; Hanahan, D.J. Platelet-activating factor. Evidence for 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine as the active component (a new class of lipid chemical mediators). J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 9355–9358. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, M.L.; Snyder, F.; Byers, L.W.; Brooks, B.; Muirhead, E.E. Antihypertensive activity of an alkyl ether analog of phosphatidylcholine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 90, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, J.; Tence, M.; Varenne, P.; Bidault, J.; Boullet, C.; Polonsky, J. Semi-synthese et structure proposde du facteur activant les plaquettes (PAF): Paf-acether, un alkyl ether analogue de la lysophosphatidylcholine. C R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1979, 289D, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Mcmanus, L.M.; Hanahan, D.; Demopoulos, C.; Pinckard, R. Pathobiology of the intravenous infusion of acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine (AGEPC), a synthetic platelet-activating factor (PAF), in the rabbit. J. Immunol. 1980, 124, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar]
- Halonen, M.; Palmer, J.D.; Lohman, I.C.; McManus, L.M.; Pinckard, R.N. Respiratory and circulatory alterations induced by acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine, a mediator of ige anaphylaxis in the rabbit. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1980, 122, 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard, R.N.; O’Rourke, R.A.; Crawford, M.H.; Grover, F.S.; McManus, L.M.; Ghidoni, J.J.; Storrs, S.B.; Olson, M.S. Complement localization and mediation of ischemic injury in baboon myocardium. J. Clin. Investig. 1980, 66, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halonen, M.; Palmer, J.D.; Lohman, I.C.; McManus, L.M.; Pinckard, R.N. Differential effects of platelet depletion on the physiologic alterations of ige anaphylaxis and acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine infusion in the rabbit. Am. Rev. Resp. Dis. 1981, 124, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.J.; Demopoulos, C.; Liehr, J.; Pinckard, R. Identification of platelet activating factor isolated from rabbit basophils as acetyl glyceryl ether phosphorylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 5514–5516. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polonsky, J.; Tencé, M.; Varenne, P.; Das, B.C.; Lunel, J.; Benveniste, J. Release of 1-O-alkylglyceryl 3-phosphorylcholine, O-deacetyl platelet-activating factor, from leukocytes: Chemical ionization mass spectrometry of phospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7019–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valone, F. Quantifying platelet-activating factor in biologic systems. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1993, 91, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chap, H.; Mauco, G.; Simon, M.F.; Benveniste, J.; Douste-Blazy, L. Biosynthetic labelling of platelet activating factor from radioactive acetate by stimulated platelets. Nature 1981, 289, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbes, G.; Ninio, E.; Fontan, P.; Record, M.; Chap, H.; Benveniste, J.; Douste-Blazy, L. Evidence that biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) by human neutrophils occurs in an intracellular membrane. Febs Lett. 1985, 191, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pincock, S. Jacques benveniste. Lancet 2004, 364, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, G. Jacques benveniste. BMJ 2004, 329, 1290. [Google Scholar]
- Cusack, N.J. Platelet-activating factor. Nature 1980, 285, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Pubchem Database, Platelet-Activating Factor, cid = 108156. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Platelet-activating-factor (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Argyrou, C.; Vlachogianni, I.; Stamatakis, G.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Antonopoulou, S.; Fragopoulou, E. Postprandial effects of wine consumption on platelet-activating factor metabolic enzymes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 130, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, G.K.; Johnson, C.; Billings, S.D.; Southall, M.D.; Pei, Y.; Spandau, D.; Murphy, R.C.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M.; Travers, J.B. Ultraviolet B radiation generates platelet-activating factor-like phospholipids underlying cutaneous damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35448–35457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A. The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases, 1st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; 348p. [Google Scholar]
- Platelet-Activating Factor as an Effector for Environmental Stressors. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/164_2019_218. (accessed on 17 October 2019).
- Proceeding of the PAF communications, 6th International Conference on Phospholipase A2 and Lipid Mediators, Tokyo, Japan, 10–12 February 2015; Available online: https://www.bioweb.ne.jp/mid_meeting/stg_info/id_16774/ (accessed on 2 December 2019).
- Demopoulos, C.A.; Antonopoulou, S. A discovery trip to compounds with PAF-like activity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 416, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of animal and marine origin: Structure, function, and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snyder, F. The ether lipid trail: A historical perspective1. Biochim. Biophys. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1999, 1436, 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, F. Metabolic processing of paf. Clin. Rev. Allergy 1995, 12, 309–327. [Google Scholar]
- Blank, M.L.; Lee, T.-c.; Fitzgerald, V.; Snyder, F. A specific acetylhydrolase for 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (a hypotensive and platelet-activating lipid). J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Renooij, W.; Snyder, F. Biosynthesis of 1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor and a hypotensive lipid) by cholinephosphotransferase in various rat tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Lipids Lipid Metab. 1981, 663, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Iatrou, C.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Characterization of the de novo biosynthetic enzyme of platelet activating factor, ddt-insensitive cholinephosphotransferase, of human mesangial cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007, 27683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Chini, M.; Mangafas, N.; Tsogas, N.; Stamatakis, G.; Tsantila, N.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Gargalianos, P.; Demopoulos, C.A. Platelet-activating factor and its basic metabolic enzymes in blood of naive hiv-infected patients. Angiology 2012, 63, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verouti, S.N.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Alevizopoulou, F.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Iatrou, C. Paricalcitol effects on activities and metabolism of platelet activating factor and on inflammatory cytokines in hemodialysis patients. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2013, 36, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Nomikos, T.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Kotroyiannis, I.; Vassiliadou, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Chrysohoou, C.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Platelet activating factor (PAF) and activity of its biosynthetic and catabolic enzymes in blood and leukocytes of male patients with newly diagnosed heart failure. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida-Sakazume, T.; Endo-Sakamoto, Y.; Unozawa, M.; Fukumoto, C.; Shimada, K.; Kasamatsu, A.; Ogawara, K.; Yokoe, H.; Shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase1 overexpression promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression via enhanced biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hackler, P.C.; Reuss, S.; Konger, R.L.; Travers, J.B.; Sahu, R.P. Systemic platelet-activating factor receptor activation augments experimental lung tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Growth Metastasis 2014, 7, CGM.S14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathonnet, M.; Descottes, B.; Valleix, D.; Truffinet, V.; Labrousse, F.; Denizot, Y. Platelet-activating factor in cirrhotic liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2773–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafforini, D.M. Biology of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (PAF-AH, lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2). Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2009, 23, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindou, H.; Hishikawa, D.; Harayama, T.; Eto, M.; Shimizu, T. Generation of membrane diversity by lysophospholipid acyltransferases. J. Biochem. 2013, 154, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarui, M.; Shindou, H.; Kumagai, K.; Morimoto, R.; Harayama, T.; Hashidate, T.; Kojima, H.; Okabe, T.; Nagano, T.; Nagase, T.; et al. Selective inhibitors of a paf biosynthetic enzyme lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 2. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marathe, G.K.; Pandit, C.; Lakshmikanth, C.L.; Chaithra, V.H.; Jacob, S.P.; D’Souza, C.J.M. To hydrolyze or not to hydrolyze: The dilemma of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafforini, D.M.; Zimmerman, G.A. Unraveling the paf-ah/lp-pla2 controversy. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1811–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Ito, M.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. Acyltransferases and transacylases that determine the fatty acid composition of glycerolipids and the metabolism of bioactive lipid mediators in mammalian cells and model organisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 18–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, G.A.; Mcintyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M. Production of platelet-activating factor by human vascular endothelial cells: Evidence for a requirement for specific agonists and modulation by prostacyclin. Circulation 1985, 72, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M. Human endothelial cells in culture produce platelet-activating factor (1-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine) when stimulated with thrombin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3534–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, E.S.; McIntyre, T.M.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A. The leukocyte integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23409–23412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weyrich, A.S.; Elstad, M.R.; McEver, R.P.; McIntyre, T.M.; Moore, K.L.; Morrissey, J.H.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A. Activated platelets signal chemokine synthesis by human monocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angle, M.J.; Tom, R.; Jarvi, K.; McClure, R.D. Effect of platelet-activating factor (PAF) on human spermatozoa–oocyte interactions. Reproduction 1993, 98, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, B.S.; Kumar, R.; Ricker, D.D.; Roudebush, W.E.; Dodson, M.G.; Fortunato, S.J. Effects of platelet activating factor on mouse oocyte fertilization in vitro. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 1714–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, A. Platelet activating factor improves the in vitro penetration of zona free hamster eggs by buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) spermatozoa. Theriogenology 2005, 63, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou, M.; Drakakis, P.; Antonopoulou, S.; Anagnostou, E.; Loutradis, D.; Patargias, T. Intravenous infusion of PAF affects ovulation, fertilization and preimplantation embryonic development in nzb x nzw f1 hybrid mice. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2008, 85, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecewicz, M.; Kordan, W.; Majewska, A.; Kamiński, S.; Dziekońska, A.; Mietelska, K. Effects of the platelet-activating factor (paf) on selected quality parameters of cryopreserved bull semen (AI) with reduced sperm motility. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 19, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, C. The role of paf in embryo physiology. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senanayake, V.; Goodenowe, D.B. Plasmalogen deficiency and neuropathology in alzheimer’s disease: Causation or coincidence? Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2019, 5, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Farooqui, T.; Horrocks, L.A. Roles of platelet-activating factor in brain. In Metabolism and functions of bioactive ether lipids in the brain; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 171–195. [Google Scholar]
- Sogos, V.; Bussolino, F.; Pilia, E.; Torelli, S.; Gremo, F. Acetylcholine-induced production of platelet-activating factor by human fetal brain cells in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 27, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, M.T.; Spinnewyn, B.; Chabrier, P.E.; Braquet, P. Presence of specific binding sites for platelet-activating factor (PAF) in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 151, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.L.; Stadel, J.M.; Sarau, H.M.; Friedman, E.; Gu, J.L.; Powers, D.A.; Gleason, M.M.; Feuerstein, G.; Wang, H.Y. Platelet-activating factor stimulates phosphoinositide turnover in neurohybrid ncb-20 cells: Involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and inhibition by protein kinase c. Mol. Pharm. 1992, 41, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shields, L.B.E.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Chu, T.; Zhu, Q.; Shields, C.B.; Cai, J. Current understanding of platelet-activating factor signaling in central nervous system diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5563–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; DeCoster, M.A.; Bazan, N.G. Interplay among platelet-activating factor, oxidative stress, and group i metabotropic glutamate receptors modulates neuronal survival. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 77, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, K.; Hirashima, Y.; Endo, S.; Takaku, A. Involvement of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in glutamate neurotoxicity in rat neuronal cultures. Brain Res. 1997, 754, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, A.M. Platelet-activating factor (PAF): Implications for coronary heart and vascular diseases. ProstaglandinsLeukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 1994, 50, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montrucchio, G.; Alloatti, G.; Camussi, G. Role of platelet-activating factor in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1669–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselepis, A.D.; Evangelou, A.; Tsoukatos, D.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Kapoulas, V.M. Electrocardiographic alterations induced by agepc in wistar rats in relation to its hypotensive and hematologic effects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharm. 1987, 87, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, R.P.; Claussen, K.A.; Kuersteiner, K.A. State of the heart: An overview of the disease burden of cardiovascular disease from an epidemiologic perspective. Prim. Care. 2018, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokes, K.Y.; Granger, D.N. Platelets: A critical link between inflammation and microvascular dysfunction. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, G.K.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Prescott, S.M.; McIntyre, T.M. Activation of vascular cells by PAF-like lipids in oxidized ldl. Vasc. Pharm. 2002, 38, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainger, E.G.; Chimen, M.; Harrison, M.J.; Yates, C.M.; Harrison, P.; Watson, S.P.; Lordkipanidzé, M.; Nash, G.B. The role of platelets in the recruitment of leukocytes during vascular disease. Platelets 2015, 26, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, D.S.; Ostrom, K.K.; McManus, L.M. Lipid inhibitors of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in normal human plasma. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal. 1995, 12, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouis, M.; Nigon, F.; John Chapman, M. Platelet activating factor is a potent stimulant of the production of active oxygen species by human monocyte-derived macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1988, 156, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Naito, Y.; Tanigawa, T.; Yoshida, N.; Kondo, M. Role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) in superoxide production by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lipids 1991, 26, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaut, J.P.; Heinecke, J.W. Mechanisms for oxidizing low-density lipoprotein: Insights from patterns of oxidation products in the artery wall and from mouse models of atherosclerosis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 11, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liapikos, T.A.; Antonopoulou, S.; Karabina, S.-A.P.; Tsoukatos, D.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Tselepis, A.D. Platelet-activating factor formation during oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein when PAF-acetylhydrolase has been inactivated. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipid. Lipid Metab. 1994, 1212, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, G.K.; Prescott, S.M.; Zimmerman, G.A.; McIntyre, T.M. Oxidized LDL contains inflammatory PAF-like phospholipids. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2001, 11, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Salomon, R.G.; McIntyre, T.M. Platelet activation by low concentrations of intact oxidized LDL particles involves the PAF receptor. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tjoelker, L.W.; Wilder, C.; Eberhardt, C.; Stafforinit, D.M.; Dietsch, G.; Schimpf, B.; Hooper, S.; Trong, H.L.; Cousens, L.S.; Zimmerman, G.A.; et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature 1995, 374, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafforini, D.; McIntyre, T.; Carter, M.; Prescott, S. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Association with lipoprotein particles and role in the degradation of platelet-activating factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 4215–4222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stremler, K.E.; Stafforini, D.M.; Prescott, S.M.; McIntyre, T.M. Human plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Oxidatively fragmented phospholipids as substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11095–11103. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio, G.; Oriente, A.; Napoli, C.; Palumbo, G.; Chiariello, P.; Marone, G.; Condorelli, M.; Chiariello, M.; Triggiani, M. Oxygen radicals inhibit human plasma acetylhydrolase, the enzyme that catabolizes platelet-activating factor. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detopoulou, P.; Nomikos, T.; Fragopoulou, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Antonopoulou, S. Platelet activating factor in heart failure: Potential role in disease progression and novel target for therapy. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2013, 10, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselepis, A.D.; Chapman, M.J. Inflammation, bioactive lipids and atherosclerosis: Potential roles of a lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, platelet activating factor-acetylhydrolase. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2002, 3, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Iatrou, C.; Frangia, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. The implication of platelet-activating factor in cancer growth and metastasis: Potent beneficial role of PAF-inhibitors and antioxidants. Infect. Dis. Drug Targets 2009, 9, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salajegheh, A. Platelet-activating factor. In Angiogenesis in Health, Disease and Malignancy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Montrucchio, G.; Sapino, A.; Bussolati, B.; Ghisolfi, G.; Rizea-Savu, S.; Silvestro, L.; Lupia, E.; Camussi, G. Potential angiogenic role of platelet-activating factor in human breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnikova, V.; Bar-Eli, M. Inflammation and melanoma growth and metastasis: The role of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and its receptor. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2007, 26, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizzi, M.F.; Battaglia, E.; Montrucchio, G.; Dentelli, P.; Del Sorbo, L.; Garbarino, G.; Pegoraro, L.; Camussi, G. Thrombopoietin stimulates endothelial cell motility and neoangiogenesis by a platelet-activating factor–dependent mechanism. Circ. Res. 1999, 84, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bussolati, B.; Biancone, L.; Cassoni, P.; Russo, S.; Rola-Pleszczynski, M.; Montrucchio, G.; Camussi, G. Paf produced by human breast cancer cells promotes migration and proliferation of tumor cells and neo-angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anandi, L.; Lahiri, M. Platelet-activating factor leads to initiation and promotion of breast cancer. Cancer Cell Microenviron. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denizot, Y.; Truffinet, V.; Bouvier, S.; Gainant, A.; Cubertafond, P.; Mathonnet, M. Elevated plasma phospholipase A2 and platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase activity in colorectal cancer. Mediat. Inflamm. 2004, 13, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karandish, F.; Mallik, S. Biomarkers and targeted therapy in pancreatic cancer. Biomark. Cancer 2016, 8s1, BIC.S34414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuchic, A.C.; Machado, C.M.; Saito, R.F.; Rios, F.J.; Jancar, S.; Chammas, R. Expression of pafr as part of a prosurvival response to chemotherapy: A novel target for combination therapy in melanoma. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyland, I.K.; O’Toole, R.F.; Smith, J.A.; Bissember, A.C. Progress in the development of platelet-activating factor receptor (PAFR) antagonists and applications in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Chem. Med. Chem. 2018, 13, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, C.; Williams, A. A-synuclein-induced synapse damage in cultured neurons is mediated by cholesterol-sensitive activation of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pałgan, K.; Bartuzi, Z. Platelet activating factor in allergies. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2015, 28, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cano, R.M.; Casas-Saucedo, R.; Valero Santiago, A.; Bobolea, I.; Ribó, P.; Mullol, J. Platelet-activating factor (paf) in allergic rhinitis: Clinical and therapeutic implications. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vadas, P.; Perelman, B.; Liss, G. Platelet-activating factor, histamine, and tryptase levels in human anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelesidis, T.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Detopoulou, P.; Fragopoulou, E.; Chini, M.; Lazanas, M.C.; Antonopoulou, S. The role of platelet-activating factor in chronic inflammation, immune activation, and comorbidities associated with hiv infection. Aids Rev. 2015, 17, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bounes, F.V.; Mujalli, A.; Cenac, C.; Severin, S.; Le Faouder, P.; Chicanne, G.; Gaits-Iacovoni, F.; Minville, V.; Gratacap, M.P.; Payrastre, B. The importance of blood platelet lipid signaling in thrombosis and in sepsis. Adv. Biol. Reg. 2018, 67, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.D.; Muller, H.K.; Latham, R.; Sohal, S.S.; Walters, E.H. Platelet-activating factor receptor (pafr) is upregulated in small airways and alveoli of smokers and copd patients. Respirology 2016, 21, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, R.; Shukla, S.D.; Walters, E.H.; O’Toole, R.F. Temporal upregulation of host surface receptors provides a window of opportunity for bacterial adhesion and disease. Microbiology 2017, 163, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, J.; Walters, H.; Sohal, S.S.; Wood-Baker, R.; Reid, D.W.; Xu, C.-B.; Edvinsson, L.; Morissette, M.C.; Stämpfli, M.R.; Kirwan, M.; et al. Cigarette smoke and platelet-activating factor receptor dependent adhesion of Streptococcus pneumoniae to lower airway cells. Thorax 2012, 67, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbier, M.; Oliver, A.; Rao, J.; Hanna, S.L.; Goldberg, J.B.; Albertí, S. Novel phosphorylcholine-containing protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic infection isolates interacts with airway epithelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Toole, R.F.; Shukla, S.D.; Walters, E.H. Does upregulated host cell receptor expression provide a link between bacterial adhesion and chronic respiratory disease? J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigg, J. The platelet activating factor receptor: A new anti-infective target in respiratory disease? Thorax 2012, 67, 840–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasperska-Zajac, A.; Brzoza, Z.; Rogala, B. Platelet-activating factor (PAF): A review of its role in asthma and clinical efficacy of paf antagonists in the disease therapy. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2008, 2, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasperska-Zajac, A.; Brzoza, Z.; Rogala, B. Platelet activating factor as a mediator and therapeutic approach in bronchial asthma. Inflammation 2008, 31, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Tsoupras, A.; Baltas, G.; Kotsifaki, H.; Mantzavinos, Z.; Demopoulos, C.A. Hydroxyl-platelet-activating factor exists in blood of healthy volunteers and periodontal patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2003, 12, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reznichenko, A.; Korstanje, R. The role of platelet-activating factor in mesangial pathophysiology. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macpherson, J.L.; Kemp, A.; Rogers, M.; Mallet, A.I.; Toia, R.F.; Spur, B.; Earl, J.W.; Chesterman, C.N.; Krilis, S.A. Occurrence of platelet-activating factor (PAF) and an endogenous inhibitor of platelet aggregation in diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1989, 77, 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Iatrou, C. Blood cardiolipin in haemodialysis patients. Its implication in the biological action of platelet-activating factor. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 28, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukatos, D.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Tselepis, A.D.; Moschidis, M.C.; Donos, A.; Evangelou, A.; Benveniste, J. Inhibition by cardiolipins of platelet-activating factor-induced rabbit platelet activation. Lipids 1993, 28, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussolino, F.; Benveniste, J. Pharmacological modulation of platelet-activating factor (paf) release from rabbit leucocytes. I. Role of camp. Immunology 1980, 40, 367–376. [Google Scholar]
- Lecrubier, C.; Conard, J.; Horellou, M.H.; Samama, M. Study of platelet aggregation induced by platelet activating factor (PAF) after administration of ticlopidine or aspirin. Agents Actions 1983, 13, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.V. Calmodulin antagonist w-7 inhibits aggregation of human platelets induced by platelet activating factor. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1983, 172, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apitz-Castro, R.; Cabrera, S.; Cruz, M.R.; Ledezma, E.; Jain, M.K. Effects of garlic extract and of three pure components isolated from it on human platelet aggregation, arachidonate metabolism, release reaction and platelet ultrastructure. Thromb. Res. 1983, 32, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Rethinking ginkgo biloba l.: Medicinal uses and conservation. Pharm. Rev. 2015, 9, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Lagopati, N.; Tsilibary, E.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Philippopoulos, A.I. A review on platelet activating factor inhibitors: Could a new class of potent metal-based anti-inflammatory drugs induce anticancer properties? Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Nasopoulou, C.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. The anti-inflammatory properties of food polar lipids. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sioriki, E.; Lordan, R.; Nahra, F.; van hecke, K.; Zabetakis, I.; Nolan, S.P. In vitro anti-atherogenic properties of n-heterocyclic carbene aurate(I) compounds. ChemMedChem 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, Z.-I.; Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T. Platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Biochem. 2002, 131, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) receptor and genetically engineered paf receptor mutant mice. Prog. Lipid Res. 2000, 39, 41–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.; Olson, M.S. Platelet-activating factor: Receptors and signal transduction. Biochem. J. 1993, 292 Pt 3, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, S.B. Specific receptors of platelet-activating factor, receptor heterogeneity, and signal transduction mechanisms. J. Lipid Mediat. 1990, 2, 123–158. [Google Scholar]
- Terashita, Z.-I.; Tsushima, S.; Yoshioka, Y.; Nomura, H.; Inada, Y.; Nishikawa, K. Cv-3988 - a specific antagonist of platelet activating factor (PAF). Life Sci. 1983, 32, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valone, F.H. Inhibition of binding of the platelet-activating factor agepc to platelets by the AGEPC analog rac-3-(n-n-octadecylcarbamoyloxy)-2-methoxypropyl 2-thiazolioethyl phosphate (CV-3988). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985, 126, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashita, Z.; Imura, Y.; Takatani, M.; Tsushima, S.; Nishikawa, K. CV-6209, a highly potent antagonist of platelet activating factor in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharm. Exp. 1987, 242, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- D’Humières, S.; Russo-Marie, F.; Boris Vargaftig, B. PAF-acether-induced synthesis of prostacyclin by human endothelial cells. Eur. J. Pharm. 1986, 131, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyofuku, T.; Kubo, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kusama, S. Effects of ONO-6240, a platelet-activating factor antagonist, on endotoxin shock in unanesthetized sheep. Prostaglandins 1986, 31, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, D.A.; Tomesch, J.C.; Saunders, R.N. Inhibition of PAF-induced systemic responses in the rat, guinea pig, dog and primate by the receptor antagonist SRI 63–441. Thromb. Haemost. 1986, 55, 040–044. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, R.N.; Handley, D.A. Platelet-activating factor antagonists. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 1987, 27, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlos, M.; Gómez, L.A.; Giral, M.; Vericat, M.L.; García-Rafanell, J.; Forn, J. Effects of paf-antagonists in mouse ear oedema induced by several inflammatory agents. Br. J. Pharm. 1991, 104, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wissner, A.; Carroll, M.L.; Green, K.E.; Kerwar, S.S.; Pickett, W.C.; Schaub, R.E.; Torley, L.W.; Wrenn, S.; Kohler, C.A. Analogues of platelet activating factor. 6. Mono-and bis-aryl phosphate antagonists of platelet activating factor. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsnorth, A.N.; Galloway, S.W.; Formela, L.J. Randomized, double-blind phase II trial of lexipafant, a platelet-activating factor antagonist, in human acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 1995, 82, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuitert, L.M.; Angus, R.M.; Barnes, N.C.; Barnes, P.J.; Bone, M.F.; Chung, K.F.; Fairfax, A.J.; Higenbotham, T.W.; O’Connor, B.J.; Piotrowska, B. Effect of a novel potent platelet-activating factor antagonist, modipafant, in clinical asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komuro, Y.; Imanishi, N.; Uchida, M.; Morooka, S. Biological effect of orally active platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist SM-10661. Mol. Pharm. 1990, 38, 378–384. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hair, D.P.; Roza, A.M.; Komorowski, R.; Moore, G.; McManus, R.P.; Johnson, C.P.; Adams, M.B.; Pieper, G.M. Tulopafant, a paf receptor antagonist, increases capillary patency and prolongs survival in discordant cardiac xenotransplants. J. Lipid Mediat. 1993, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Casals-Stenzel, J.; Heuer, H.O. Use of WEB 2086 and WEB 2170 as platelet-activating factor antagonists. In Methods Enzymol; Murphy, R.C., Fitzpatrick, F.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; Volume 187, pp. 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Kornecki, E.; Ehrlich, Y.; Lenox, R. Platelet-activating factor-induced aggregation of human platelets specifically inhibited by triazolobenzodiazepines. Science 1984, 226, 1454–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.B.; Lam, M.H.; Biftu, T.; Beattie, T.R.; Shen, T.Y. Trans-2,5-bis-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl) tetrahydrofuran. An orally active specific and competitive receptor antagonist of platelet activating factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 15639–15645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Papakyriakou, A.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Synthesis, biochemical evaluation and molecular modeling studies of novel rhodium complexes with nanomolar activity against platelet activating factor. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 120, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnout, J.; van Hecken, A.; De Lepeleire, I.; Miyamoto, Y.; Holmes, I.; De Schepper, P.; Vermylen, J. Effectiveness and tolerability of CV-3988, a selective paf antagonist, after intravenous administration to man. Br. J. Clin. Pharm. 1988, 25, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, K.H. Effects of PAF antagonist, bn52021, on the PAF-, methacholine-, and allergen-induced bronchoconstriction in asthmatic children. Chest 1991, 99, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, F.P.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Platelet-activating factor antagonists. Biodrugs 2000, 14, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, D.P.; Browne, S.M.; Wade, D.T.; Halligan, P.W. Neuroprotection during cardiac surgery: A randomised trial of a platelet activating factor antagonist. Heart 2003, 89, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.; Fatovich, D.; Hitchcock, T.; Morrison, C.; Curtis, L. Platelet-activating factor antagonism and streptokinase-induced hypotension in clinical acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Sci. 2001, 100, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suputtamongkol, Y.; Intaranongpai, S.; Smith, M.D.; Angus, B.; Chaowagul, W.; Permpikul, C.; Simpson, J.A.; Leelarasamee, A.; Curtis, L.; White, N.J. A double-blind placebo-controlled study of an infusion of lexipafant (platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist) in patients with severe sepsis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, C.D.; Kingsnorth, A.N.; Imrie, C.W.; McMahon, M.J.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; McKay, C.; Toh, S.K.C.; Skaife, P.; Leeder, P.C.; Wilson, P.; et al. Double blind, randomised, placebo controlled study of a platelet activating factor antagonist, lexipafant, in the treatment and prevention of organ failure in predicted severe acute pancreatitis. Gut 2001, 48, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuitert, L.M.; Hui, K.P.; Uthayarkumar, S.; Burke, W.; Newland, A.C.; Uden, S.; Barnes, N.S. Effect of the platelet-activating factor antagonist UK-74,505 on the early and late response to allergen. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, B.J.; SUden, S.; Carty, T.J.; Eskra, J.D.; Barnes, P.J.; Chung, K.J. Inhibitory effect of uk,74505, a potent and specific oral platelet activating factor (PAF) receptor antagonist, on airway and systemic responses to inhaled paf in humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.J.; Barnes, P.J.; Cluzel, M.; O’Connor, B.J. Effects of a potent platelet-activating factor antagonist, SR27417a, on allergen-induced asthmatic responses. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, F.; Roca, J.; Barbera, J.; Chung, K.; Peinado, V.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Effect of a platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonist, SR27417a, on paf-induced gas exchange abnormalities in mild asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stack, W.A.; Jenkins‡, D.; Vivet§, P.; Hawkey*, C.J. Lack of effectiveness of the platelet-activating factor antagonist SR27417a in patients with active ulcerative colitis: A randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, A.; Watson, R.M.; Matsos, G.; Eastwood, C.; O’Byrne, P.M. Effect of a platelet activating factor antagonist, WEB 2086, on allergen induced asthmatic responses. Thorax 1993, 48, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baltás, E.; Trach, V.; Dobozy, A.; Kemény, L. Platelet-activating factor antagonist WEB 2086 inhibits ultraviolet-B radiation-induced dermatitis in the human skin. Ski. Pharm. Physiol. 2003, 16, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliquin, P.; Chermat-Izard, V.; Menkes, C.J. A double blind, placebo controlled study of a platelet activating factor antagonist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer, T.; Grote, M.; Oppelt, P.; Franke, U.; Schaefers, H.-J.; Wahlers, T. Impact of PAF antagonist BN 52021 (ginkolide b) on post-ischemic graft function in clinical lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2001, 20, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elders, M.E.; Gerritsen, M.J.P.; Van De Kerkhof, P.C.M. The effect of topical application of the platelet-activating factor-antagonist, RO 24–0238, in psoriasis vulgaris—a clinical and immunohistochemical study. Clin. Exp. Derm. 1994, 19, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poeze, M.; Froon, A.H.; Ramsay, G.; Buurman, W.A.; Greve, J.W. Decreased organ failure in patients with severe sirs and septic shock treated with the platelet-activating factor antagonist TCV-309: A prospective, multicenter, double-blind, randomized phase II trial. TCV-309 septic shock study group. Shock 2000, 14, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Kwatra, G.; Badyal, D.K.; Thomas, E.A. Levocetirizine and rupatadine in chronic idiopathic urticaria. Int. J. Derm. 2015, 54, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullol, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, W.G.; Gimenez-Arnau, A.; Kowalski, M.L.; Marti-Guadano, E.; Maurer, M.; Picado, C.; Scadding, G.; et al. Rupatadine in allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. Allergy 2008, 63 (Suppl. 87), 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullol, J.; Bousquet, J.; Bachert, C.; Canonica, G.W.; Giménez-Arnau, A.; Kowalski, M.L.; Simons, F.E.R.; Maurer, M.; Ryan, D.; Scadding, G. Update on rupatadine in the management of allergic disorders. Allergy 2015, 70, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozawa, S.; Haruta, Y.; Ishioka, S.; Yamakido, M. Effects of a PAF antagonist, Y-24180, on bronchial hyperresponsiveness in patients with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint-Martin, F.; Dumur, J.P.; Pérez, I.; Izquierdo, I.; French Rupatadine-Rhinitis Study Group. A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study, comparing the efficacy and safety of rupatadine (20 and 10 mg), a new PAF and H1 receptor-specific histamine antagonist, to loratadine 10 mg in the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 14, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C.; Hwang, S.B.; Libertine-Garahan, L.; Eckman, J.B.; Cai, X.; Scannell, R.T.; Yeh, C.G. Anti-inflammatory activities of LDP-392, a dual paf receptor antagonist and 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. Pharm. Res. 2001, 44, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; D’Souza, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Kavanagh, E.P.; Hynes, N. Chapter 6 - statins: Rationale, mode of action, and side effects. In The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases; Zabetakis, I., Lordan, R., Tsoupras, A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 171–200. [Google Scholar]
- Tsantila, N.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Iatrou, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. In vitro and in vivo effects of statins on platelet-activating factor and its metabolism. Angiology 2011, 62, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Mangafas, N.; Tsogas, N.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Gargalianos, P.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Lazanas, M.C. Effects of haart on platelet-activating factor metabolism in naive HIV-infected patients I: Study of the tenofovir-df/emtricitabine/efavirenz haart regimen. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2012, 28, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, M.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Mangafas, N.; Tsogas, N.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Gargalianos, P.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Lazanas, M.C. Effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy on platelet activating factor metabolism in naive HIV-infected patients: II) study of the abacavir/lamivudine/efavirenz haart regimen. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2012, 25, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussaini, I.M.; Yi-Hua, Z.; Lysiak, J.J.; Shen, T.Y. Dithiolane analogs of lignans inhibit interferon-γ and lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in macrophages. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2000, 21, 897–904. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Seki, T.; Inada, H.; Shimizu, K.; Takahama, A.; Sano, T. Novel agents combining platelet activating factor (PAF) receptor antagonist with thromboxane synthase inhibitor (TXSI). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braquet, P. Treatment and prevention of PAF-acether-induced sickness by a new series of highly specific inhibitors. Gb Pat. 1984, 8, 418–424. [Google Scholar]
- Touvay, C.; Etienne, A.; Braquet, P. Inhibition of antigen-induced lung anaphylaxis in the guinea-pig by BN 52021 a new specific PAF-acether receptor antagonist isolated from ginkgo biloba. Agents Actions 1986, 17, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braquet, P.G.; Spinnewyn, B.; Braquet, M.; Bourgain, R.; Taylor, J.E.; Etienne, A.; Drieu, K. BN 52021 and related compounds: A new series of highly specific PAF-acether receptor antagonists isolated from Ginkgo biloba L. Blood Vessel 1985, 16, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, V.D. Ginkgo biloba and its anti-inflammatory value as a medical tool. Hellenic J. Atherosclerosis 2013, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Braquet, P. Proofs of involvement of PAF-acether in various immune disorders using BN 52021 (ginkgolide b): A powerful PAF-acether antagonist isolated from Ginkgo biloba L. Adv. Prostaglandin. Thromboxane. Leukot. Res. 1986, 16, 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgain, R.H.; Maes, L.; Andries, R.; Braquet, P. Thrombus induction by endogenic PAF-acether and its inhibition by Ginkgo biloba extracts in the guinea pig. Prostaglandins 1986, 32, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.Y.; Hwang, S.B.; Chang, M.N.; Doebber, T.W.; Lam, M.H.; Wu, M.S.; Wang, X.; Han, G.Q.; Li, R.Z. Characterization of a platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist isolated from haifenteng (piper futokadsura): Specific inhibition of in vitro and in vivo platelet-activating factor-induced effects. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koltai, M.; Braquet, P.G. Platelet-activating factor antagonists. Clin. Rev. Allergy 1994, 12, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.S.; Jung, K.Y.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, E.-H.; Cheong, C. Platelet-activating factor antagonistic activity and 13c NMR assignment of pregomisin and chamigrenal fromschisandra chinensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1997, 20, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.-W.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Cai, D.-G.; Bian, J.; Long, K.; Chen, Z.-L. Piperbetol, methylpiperbetol, piperol a and piperol b: A new series of highly specific PAF receptor agonists from piper betle. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantan, I.; Juriyati, J.; Warif, N.A. Inhibitory effects of xanthones on platelet activating factor receptor binding in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 75, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siafaka-Kapadai, A.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Andrikopoulos, N.K. Biological activity of lipids of pine pollen on platelet aggregation in correlation with the platelet activating factor. Biochem. Int. 1986, 12, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Koussissis, S.G.; Semidalas, C.E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Kapoulas, V.M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Kalyvas, V. Paf antagonists in foods: Isolation and identification of paf antagonists in virgin olive oil. Rev. Française Des Corps Gras 1993, 40, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Koussissis, S.G.; Semidalas, C.E.; Hadzistavrou, E.C.; Kalyvas, V.G.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Paf antagonists in foods: Isolation and identification of PAF antagonists in honey and wax. Rev. Française Des Corps Gras 1994, 41, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Semidalas, C.E.; Koussissis, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonists in foods: A study of lipids with paf or anti-paf-like activity in cow’s milk and yogurt. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3047–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rementzis, J.; Antonopoulou, S.; Argyropoulos, D.; Demopoulos, C.A. Biologically active lipids from S. scombrus. In Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators 2: Roles in Health and Disease; Nigam, S., Kunkel, G., Prescott, S.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Nomikos, T.; Antonopoulou, S.; Mitsopoulou, C.A.; Demopoulos, C.A. Separation of biologically active lipids from red wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, A.; Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Chapter 8 - diet and cardiovascular disease: The Mediterranean diet. In The Impact of Nutrition and Statins on Cardiovascular Diseases; Zabetakis, I., Lordan, R., Tsoupras, A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Detopoulou, P.; Demopoulos, C.; Karantonis, H.; Antonopoulou, S. Mediterranean diet and its protective mechanisms against cardiovascular disease: An insight into platelet activating factor (PAF) and diet interplay. Ann. Nutr. Disord. 2015, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tsoupras, A.B.; Fragopoulou, E.; Iatrou, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. In vitro protective effects of olive pomace polar lipids towards platelet activating factor metabolism in human renal cells. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2011, 9, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Tsoupras, A.B.; Karantonis, H.C.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Fish polar lipids retard atherosclerosis in rabbits by down-regulating PAF biosynthesis and up-regulating PAF catabolism. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karantonis, H.C.; Tsantila, N.; Stamatakis, G.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Bioactive polar lipids in olive oil, pomace and waste byproducts. J. Food Biochem. 2008, 32, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantonis, H.C.; Antonopoulou, S.; Perrea, D.N.; Sokolis, D.P.; Theocharis, S.E.; Kavantzas, N.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Demopoulos, C.A. In vivo antiatherogenic properties of olive oil and its constituent lipid classes in hyperlipidemic rabbits. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsantila, N.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Antithrombotic and antiatherosclerotic properties of olive oil and olive pomace polar extracts in rabbits. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsantila, N.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Iatrou, C.; Antonopoulou, S.; Demopoulos, C.A. Atherosclerosis regression study in rabbits upon olive pomace polar lipid extract administration. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Karantonis, H.C.; Perrea, D.N.; Theocharis, S.E.; Iliopoulos, D.G.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. In vivo anti-atherogenic properties of cultured gilthead sea bream (Aparus aurata) polar lipid extracts in hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, M.N.; Kalathara, K.; Melachroinou, S.; Arampatzi-Menenakou, K.; Antonopoulou, S.; Yannakoulia, M.; Fragopoulou, E. Wine consumption reduced postprandial platelet sensitivity against platelet activating factor in healthy men. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Detopoulou, P.; Nomikos, T.; Pliakis, E.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Antonopoulou, S. Mediterranean wild plants reduce postprandial platelet aggregation in patients with metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 2012, 61, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, S.; Fragopoulou, E.; Karantonis, H.C.; Mitsou, E.; Sitara, M.; Rementzis, J.; Mourelatos, A.; Ginis, A.; Phenekos, C. Effect of traditional greek Mediterranean meals on platelet aggregation in normal subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantonis, H.C.; Fragopoulou, E.; Antonopoulou, S.; Rementzis, J.; Phenekos, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. Effect of fast-food Mediterranean-type diet on type 2 diabetics and healthy human subjects’ platelet aggregation. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2006, 72, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavriil, L.; Detopoulou, M.; Petsini, F.; Antonopoulou, S.; Fragopoulou, E. Consumption of plant extract supplement reduces platelet activating factor-induced platelet aggregation and increases platelet activating factor catabolism: A randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Demuru, M.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Structural elucidation of irish organic farmed salmon (Salmo salar) polar lipids with antithrombotic activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsoupras, A.; O’Keeffe, E.; Lordan, R.; Redfern, S.; Zabetakis, I. Bioprospecting for antithrombotic polar lipids from salmon, herring, and boarfish by-products. Foods 2019, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsoupras, A.; Lordan, R.; Shiels, K.; Saha, S.K.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. In vitro antithrombotic properties of salmon (Salmo salar) phospholipids in a novel food-grade extract. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poutzalis, S.; Lordan, R.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Phospholipids of goat and sheep origin: Structural and functional studies. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 167, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megalemou, K.; Sioriki, E.; Lordan, R.; Dermiki, M.; Nasopoulou, C.; Zabetakis, I. Evaluation of sensory and in vitro anti-thrombotic properties of traditional greek yogurts derived from different types of milk. Heliyon 2017, 3, e00227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lordan, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Finnegan, L.; Demuru, M.; Tsoupras, A.; Cotter, P.D.; Zabetakis, I. Caprine milk fermentation enhances the antithrombotic properties of cheese polar lipids. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Finnegan, L.; Cotter, P.D.; Zabetakis, I. The effect of ovine milk fermentation on the antithrombotic properties of polar lipids. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; Zabetakis, I. Invited review: The anti-inflammatory properties of dairy lipids. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R.; O’Keeffe, E.; Dowling, D.; Mullally, M.; Heffernan, H.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. The in vitro antithrombotic properties of ale, lager, and stout beers. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lordan, R.; O’Keeffe, E.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. Total, neutral, and polar lipids of brewing ingredients, by-products and beer: Evaluation of antithrombotic activities. Foods 2019, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darst, M.; Al-Hassani, M.; Li, T.; Yi, Q.; Travers, J.M.; Lewis, D.A.; Travers, J.B. Augmentation of chemotherapy-induced cytokine production by expression of the platelet-activating factor receptor in a human epithelial carcinoma cell line. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6330–6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.R.; Xia, S.H. Role of platelet-activating factor in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-κb: A friend or a foe in cancer? Biochem. Pharm. 2004, 68, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.P.; Kozman, A.A.; Yao, Y.; DaSilva, S.C.; Rezania, S.; Martel, K.C.; Warren, S.J.; Travers, J.B.; Konger, R.L. Loss of the platelet activating factor receptor in mice augments pma-induced inflammation and cutaneous chemical carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnikova, V.O.; Villares, G.J.; Bar-Eli, M. Emerging roles of PAR-1 and PAFR in melanoma metastasis. Cancer Microenviron. 2008, 1, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melnikova, V.O.; Bar-Eli, M. Inflammation and melanoma metastasis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.P.; Harrison, K.A.; Weyerbacher, J.; Murphy, R.C.; Konger, R.L.; Garrett, J.E.; Chin-Sinex, H.J.; Johnston, M.E.; Dynlacht, J.R.; Mendonca, M.; et al. Radiation therapy generates platelet-activating factor agonists. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20788–20800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Travers, J.B.; Berry, D.; Yao, Y.; Yi, Q.; Konger, R.L.; Travers, J.B. Ultraviolet B radiation of human skin generates platelet-activating factor receptor agonists. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva-Junior, I.A.; Dalmaso, B.; Herbster, S.; Lepique, A.P.; Jancar, S. Platelet-activating factor receptor ligands protect tumor cells from radiation-induced cell death. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, S.I.; Andrade, L.N.; Onuchic, A.C.; Nonogaki, S.; Fernandes, P.D.; Pinheiro, M.C.; Rohde, C.B.; Chammas, R.; Jancar, S. Platelet-activating factor receptor (PAF-R)-dependent pathways control tumour growth and tumour response to chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hong, S.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.; Xu, C. The expression of platelet-activating factor receptor modulates the cisplatin sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells: A novel target for combination therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soares, P.M.G.; Lima-Junior, R.C.P.; Mota, J.M.S.C.; Justino, P.F.C.; Brito, G.A.C.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Cunha, F.Q.; Souza, M.H.L.P. Role of platelet-activating factor in the pathogenesis of 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2011, 68, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Stafforini, D.M. Modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and atherosclerosis by lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 1767–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macphee, C.H.; Moores, K.E.; Boyd, H.F.; Dhanak, D.; Ife, R.J.; Leach, C.A.; Leake, D.S.; Milliner, K.J.; Patterson, R.A.; Suckling, K.E.; et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, generates two bioactive products during the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein: Use of a novel inhibitor. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, E.R.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Davidson, M.H.; Hanefeld, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Zalewski, A. The effect of darapladib on plasma lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity and cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with stable coronary heart disease or coronary heart disease risk equivalent: The results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 1632–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Serruys, P.W.; García-García, H.M.; Buszman, P.; Erne, P.; Verheye, S.; Aschermann, M.; Duckers, H.; Bleie, O.; Dudek, D.; Bøtker, H.E.; et al. Effects of the direct lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitor darapladib on human coronary atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation 2008, 118, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The STABILITY Investigators. Darapladib for preventing ischemic events in stable coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, S.-H.; Chan, M.-L.; Marathe, G.K.; Parveen, F.; Chen, C.-H.; Ke, L.-Y. An updated review of lysophosphatidylcholine metabolism in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J. Amelioration of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice by combined rna interference of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase a2 and ykl-40. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkov, V.; Gesslbauer, B.; Mauerhofer, C.; Philippova, M.; Erne, P.; Oskolkova, O.V. Pleiotropic effects of oxidized phospholipids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 111, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Birukov, K.G.; Levonen, A.-L.; Binder, C.J.; Stöckl, J. Generation and biological activities of oxidized phospholipids. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 12, 1009–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, P.; Birukov, K.G. Oxidized phospholipids in control of inflammation and endothelial barrier. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochkov, V.N. Inflammatory profile of oxidized phospholipids. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 97, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarna, C.; Dean, R.T.; May, J.; Stocker, R. Human atherosclerotic plaque contains both oxidized lipids and relatively large amounts of alpha-tocopherol and ascorbate. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1616–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Kadl, A.; Huber, J.; Gruber, F.; Binder, B.R.; Leitinger, N. Protective role of phospholipid oxidation products in endotoxin-induced tissue damage. Nature 2002, 419, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhwirth, G.O.; Loidl, A.; Hermetter, A. Oxidized phospholipids: From molecular properties to disease. Biochim. Biophys. Mol. Basis Dis. 2007, 1772, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.-K.; Binder, C.J.; Torzewski, M.; Witztum, J.L. C-reactive protein binds to both oxidized LDL and apoptotic cells through recognition of a common ligand: Phosphorylcholine of oxidized phospholipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13043–13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salomon, R.G. Structural identification and cardiovascular activities of oxidized phospholipids. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 930–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauerhofer, C.; Philippova, M.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Bochkov, V.N. Hormetic and anti-inflammatory properties of oxidized phospholipids. Mol. Asp. Med. 2016, 49, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakker, A.; Spickett, C.M.; Pitt, A. A targeted mass spectrometry approach to detect and quantify oxidised phospholipids in plasma samples of diabetic patients. bioRxiv 2019, 741132. [Google Scholar]
- Ademowo, O.S.; Dias, H.K.I.; Milic, I.; Devitt, A.; Moran, R.; Mulcahy, R.; Howard, A.N.; Nolan, J.M.; Griffiths, H.R. Phospholipid oxidation and carotenoid supplementation in alzheimer’s disease patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazereeuw, G.; Herrmann, N.; Xu, H.; Blanchard, A.P.; Figeys, D.; Oh, P.I.; Bennett, S.A.; Lanctôt, K.L. Platelet activating factors are associated with depressive symptoms in coronary artery disease patients: A hypothesis-generating study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Philippova, M.; Oskolkova, O.V.; Bicker, W.; Schoenenberger, A.W.; Resink, T.J.; Erne, P.; Bochkov, V.N. Analysis of fragmented oxidized phosphatidylcholines in human plasma using mass spectrometry: Comparison with immune assays. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, D.P.; Hartman, C.L.; Weissler, G.J.; Palladino, E.N.D.; Albert, C.J.; Ford, D.A. Platelet-activating factor quantification using reversed phase liquid chromatography and selected reaction monitoring in negative ion mode. Lipids 2016, 51, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brailoiu, E.; Barlow, C.L.; Ramirez, S.H.; Abood, M.E.; Brailoiu, G.C. Effects of platelet-activating factor on brain microvascular endothelial cells. Neuroscience 2018, 377, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-J.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Zhu, X.-N.; Hu, J.-J. Loss of PAFR prevents neuroinflammation and brain dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellizzi, M.J.; Geathers, J.S.; Allan, K.C.; Gelbard, H.A. Platelet-activating factor receptors mediate excitatory postsynaptic hippocampal injury in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briones, M.R.S.; Snyder, A.M.; Ferreira, R.C.; Neely, E.B.; Connor, J.R.; Broach, J.R. A possible role for platelet-activating factor receptor in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.-Q.; Liu, Y.; Shields, L.B.E.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Q.; Gozal, D.; Shields, C.B.; et al. Attenuated reactive gliosis and enhanced functional recovery following spinal cord injury in null mutant mice of platelet-activating factor receptor. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3448–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Kohro, Y.; Shiratori, M.; Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K. Role of PAF receptor in pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in the dorsal root ganglion and tactile allodynia in a rodent model of neuropathic pain. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuda, M.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Inoue, K. Platelet-activating factor and pain. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bate, C.; Tayebi, M.; Williams, A. Ginkgolides protect against amyloid-β1–42-mediated synapse damage in vitro. Mol. Neurodegener. 2008, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bate, C.; Tayebi, M.; Williams, A. Phospholipase a2inhibitors protect against prion and aβ mediated synapse degeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bate, C.; Ingham, V.; Williams, A. Inhibition of phospholipase a2 increased the removal of the prion derived peptide prp82-146 from cultured neurons. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basran, G.S.; Page, C.P.; Paul, W.; Morley, J. Platelet-activating factor: A possible mediator of the dual response to allergen? Clin. Exp. Allergy 1984, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, N.; Morita, K.; Kitayama, T.; Shiraishi, S.; Uezono, Y.; Nishimura, F.; Kanematsu, T.; Dohi, T. Pain-releasing action of platelet-activating factor (PAF) antagonists in neuropathic pain animal models and the mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Shiraishi, S.; Motoyama, N.; Kitayama, T.; Kanematsu, T.; Uezono, Y.; Dohi, T. Palliation of bone cancer pain by antagonists of platelet-activating factor receptors. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindou, H.; Shiraishi, S.; Tokuoka, S.M.; Takahashi, Y.; Harayama, T.; Abe, T.; Bando, K.; Miyano, K.; Kita, Y.; Uezono, Y.; et al. Relief from neuropathic pain by blocking of the platelet-activating factor–pain loop. Faseb J. 2017, 31, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camussi, G. Potential role of platelet-activating factor in renal pathophysiology. Kidney Int. 1986, 29, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fragopoulou, E.; Iatrou, C.; Demopoulos, C.A. Characterization of acetyl-coa: Lyso-paf acetyltransferase of human mesangial cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plante, G.E.; Hebert, R.L.; Lamoureux, C.; Braquet, P.; Sirois, P. Hemodynamic effects of paf-acether. Pharm. Res. Commun. 1986, 18, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kispert, S.; Marentette, J.; McHowat, J. Cigarette smoking promotes bladder cancer via increased platelet-activating factor. Physiol. Rep. 2019, 7, e13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kullmann, F.A. A new player in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Platelet-activating factor - paf and its connection to smoking. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kispert, S.E.; Marentette, J.O.; McHowat, J. Enhanced breast cancer cell adherence to the lung endothelium via PAF acetylhydrolase inhibition: A potential mechanism for enhanced metastasis in smokers. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 307, C951–C956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McHowat, J.; Lozano, J.C.; Missall, P. PAF expression in skin tumors of smokers and never smokers: A potential role in skin cancer development. Faseb J. 2018, 32, 281.2. [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita, L.; Suri, R.; Dearing, E.; Mudway, I.; Dove, R.E.; Neill, D.R.; Van Zyl-Smit, R.; Kadioglu, A.; Grigg, J. E-cigarette vapour enhances pneumococcal adherence to airway epithelial cells. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1701592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, C.; Tan, Q.; Xu, C.; He, L.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Qiao, A.; Lu, M.; Yi, C.; et al. Structural basis for signal recognition and transduction by platelet-activating-factor receptor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audet, M.; Stevens, R.C. Emerging structural biology of lipid g protein-coupled receptors. Protein Sci. 2019, 28, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, H.; Chen, S.; Yuan, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, H.; Xia, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, B. Structural basis for ligand recognition of the human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Guo, H.; Tam, J.W.; Johnson, B.M.; Brickey, W.J.; New, J.S.; Lenox, A.; Shi, H.; Golenbock, D.T.; Koller, B.H.; et al. Platelet-activating factor (PAF) mediates NLRP3-NEK7 inflammasome induction independently of PAFR. J. Exp. Med. 2019, jem.20190111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Spapen, H.; Bakker, J.; Webster, N.R.; Curtis, L. Phase ii multicenter clinical study of the platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist BB-882 in the treatment of sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, D.P.; Johnston, S.L.; Calverley, P.M.; Dhillon, P.; Higgins, C.; Ramhamadany, E.; Turner, S.; Winning, A.; Winter, J.; Holgate, S.T. The effect of the orally active platelet-activating factor antagonist WEB 2086 in the treatment of asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhainaut, J.-F.A.; Tenaillon, A.; Hemmer, M.; Damas, P.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Radermacher, P.; Schaller, M.-D.; Sollet, J.-P.; Wolff, M.; Holzapfel, L.; et al. Confirmatory platelet-activating factor receptor antagonist trial in patients with severe gram-negative bacterial sepsis: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Mateer, S.W.; Hsu, A.; Goggins, B.J.; Tay, H.; Mathe, A.; Fan, K.; Neal, R.; Bruce, J.; Burns, G.; et al. Platelet activating factor receptor regulates colitis-induced pulmonary inflammation through the NLRP3 inflammasome. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Fu, J. Novel insights into the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Title | Date | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1st International Symposium on Platelet-Activating Factor and Structurally Related Ether-Lipids | 26–29 June 1983 | Paris, France |
| 2nd International Conference on Platelet-Activating Factor and Structurally Related Ether-Lipids | 26–29 October 1986 | Gatlinburg, Tennessee, USA |
| 3rd International Conference on Platelet-Activating Factor and Structurally Related Ether-Lipids | 8–12 May 1989 | Tokyo, Japan |
| 4th International Congress on Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators | 22–25 September 1992 | Snowbird, Utah, USA |
| 5th International Congress on Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators | 12–16 September 1995 | Berlin, Germany |
| 6th International Congress on Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators | 21–24 September 1998 | New Orleans, Louisiana, USA |
| 7th International Congress on Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators | 24–27 September 2001 | Tokyo, Japan |
| 8th International Congress on Platelet-Activating Factor and Related Lipid Mediators | 6–9 October 2004 | Berlin, Germany |
| 6th International Conference on Phospholipase A2 and Lipid Mediators | 10–12 February 2015 | Tokyo, Japan |
| PAF-R Antagonist | Target Disease or Disorder | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lexipafant | Cognitive impairment complications as a result of coronary artery bypass graft | No significant reduction in cognitive impairment | [168] |
| Myocardial infarction | No significant effect on streptokinase-induced hypotension in myocardial infarction patients | [169] | |
| Sepsis | No significant affect in patients with severe sepsis | [170] | |
| Organ failure related to pancreatitis | No significant amelioration of systemic inflammatory response syndrome in pancreatitis-induced organ failure | [171] | |
| Modipafant | Asthma | No significant effect against chronic asthma | [158] |
| Asthma | No significant effect in early or late responses to allergens | [172] | |
| Responses to inhaled PAF | Potent inhibition of airway and neutrophil responses to PAF with a duration of up to 24 h and a reduction of secondary eicosanoid production in response to inhaled PAF | [173] | |
| SR27417A SR27417A | Asthma | Modest inhibitory effects against asthma | [174,175], |
| Ulcerative colitis | No evidence of efficacy in the treatment of acute ulcerative colitis | [176] | |
| WEB 2086 | Asthma | No attenuation of early of late allergen-induced responses or airway hyperresponsiveness | [177] |
| UVB-induced dermatitis | Significant inhibition of UVB light-induced erythema | [178] | |
| BN 50730 | Rheumatoid arthritis | Ineffective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis | [179] |
| BN 52021 | Pulmonary function in the early post ischaemic graft function in clinical lung transplantation | Improvement of alveoloarterial oxygen difference and a reduction of PAF levels | [180] |
| Ro 24-238 | Psoriasis | No significant effects reported | [181] |
| TCV-309 | Septic shock | No significant difference in adverse events or mortality. A substantial reduction of organ dysfunction and morbidity associated with septic shock was reported | [182] |
| Levocetirizine | Chronic idiopathic urticaria | Reduction of urticarial activity score | [183] |
| Rupatadine | Chronic idiopathic urticaria | Reduction of urticarial activity score but not as effective as levocetirizine | [183,184] |
| Allergic rhinitis and allergies | Significant effects against both conditions as demonstrated in the comprehensive review by Mullol et al. | [185] | |
| Y-24180 | Asthma | Improvement of bronchial hyperresponsiveness in patients with asthma | [186] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I.; Demopoulos, C.A. Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives. Molecules 2019, 24, 4414. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234414
Lordan R, Tsoupras A, Zabetakis I, Demopoulos CA. Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives. Molecules. 2019; 24(23):4414. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234414
Chicago/Turabian StyleLordan, Ronan, Alexandros Tsoupras, Ioannis Zabetakis, and Constantinos A. Demopoulos. 2019. "Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives" Molecules 24, no. 23: 4414. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234414
APA StyleLordan, R., Tsoupras, A., Zabetakis, I., & Demopoulos, C. A. (2019). Forty Years Since the Structural Elucidation of Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF): Historical, Current, and Future Research Perspectives. Molecules, 24(23), 4414. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234414









