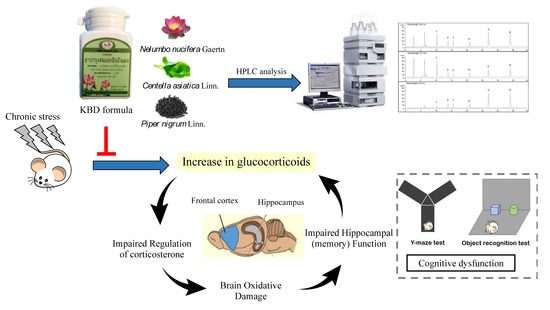
Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of KBD on UCMS-Induced Cognitive Deficits
2.2. Effect of KBD on the UCMS-Induced Hypersecretion of the Serum Corticosterone (CORT)
2.3. Effect of KBD on the UCMS-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in the Brain
2.4. Effect of KBD on UCMS-Reduced Brain Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT) Activities
2.5. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents
2.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of the Constituents of the KBD Extract and the Validation Method
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Preparation of the KBD Extract
4.2. Animal
4.3. Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress (UCMS)
4.4. Drug Administration
4.5. Behavioral Analysis
4.5.1. Y-Maze Test
4.5.2. Novel Object Recognition Test (NORT)
4.6. Determination of Serum CORT Levels
4.7. Determination of MDA Contents by the Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) Assay
4.8. Determination of Catalase (CAT) and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activities
4.9. Determination of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents
4.10. HPLC Analysis and Validation of the Analytical Method
4.11. Statistic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radley, J.; Morilak, D.; Viau, V.; Campeau, S. Chronic stress and brain plasticity: mechanisms underlying adaptive and maladaptive changes and implications for stress-related CNS disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 58, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, C.; McGlade, E.; Yurgelun-Todd, D. Chronic stress in adolescents and its neurobiological and psychopathological consequences: An RDoC perspective. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks) 2017, 1, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuki, D.; Matsumoto, K.; Tanaka, K.; Thi Le, X.; Fujiwara, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Higuchi, Y. Antidepressant-like effect of Butea superba in mice exposed to chronic mild stress and its possible mechanism of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 156, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and physical activity: Making the neuroplastic connection. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 7260130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Notaras, M.; Du, X.; Hill, R.A. On the developmental timing of stress: Delineating sex-specific effects of stress across development on adult behavior. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, S.; Jaquet, V.; Trabace, L.; Krause, K.-H. Severe life stress and oxidative stress in the brain: From animal models to human pathology. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 1475–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Liew, W.-P.-P.; Sulaiman Rahman, H. Antioxidant and oxidative stress: A mutual interplay in age-related diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Wen, Z.; Song, H.; Christian, K.M.; Ming, G. Adult neurogenesis and psychiatric disorders. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, K.; Xian, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z. Resveratrol prevents ompaired cognition induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in rRats. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 49, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress. 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritcu, L.; Noumedem, J.A.; Cioanca, O.; Hancianu, M.; Kuete, V.; Mihasan, M. Methanolic extract of Piper nigrum fruits improves memory impairment by decreasing brain oxidative stress in amyloid beta (1–42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, N.E.; Alcazar Magana, A.; Lak, P.; Wright, K.M.; Quinn, J.; Stevens, J.F.; Maier, C.S.; Soumyanath, A. Centella asiatica—Phytochemistry and mechanisms of neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 161–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.P.; Khanum, F. Neuroprotective potential of phytochemicals. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Weon, J.B.; Yun, B.-R.; Lee, J.; Eom, M.R.; Oh, K.-H.; Ma, C.J. Cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective effect of the embryo of the Nelumbo nucifera seed. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014, 214, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.M.; Shim, K.J.; Choi, M.J.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, B.-J.; Chang, M.S.; Park, S.K. Novel effects of Nelumbo nucifera rhizome extract on memory and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 443, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.Y.; Kim, W.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, I.-J.; Yoon, Y.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Won, M.-H.; Hwang, I.K. Effects of Nelumbo nucifera rhizome extract on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in a scopolamine-induced amnesia animal model. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiratmatrakul, S.; Yenjai, C.; Waiwut, P.; Vajragupta, O.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Tohda, M.; Boonyarat, C. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling study of novel tacrine-carbazole hybrids as potential multifunctional agents for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 75, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajragupta, O.; Boonyarat, C.; Olson, A.J.; Murakami, Y.; Tohda, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. A novel neuroprotective agent with antioxidant and nitric oxide synthase inhibitory action. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, C.D.; Galea, L.A.; Kuroda, Y.; McEwen, B.S. Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y Maze, and this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav. Neurosci. 1996, 110, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monthakantirat, O.; Sukano, W.; Umehara, K.; Noguchi, H.; Chulikhit, Y.; Matsumoto, K. Effect of miroestrol on ovariectomy-induced cognitive impairment and lipid peroxidation in mouse brain. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesing, A.; Bilang-Bleuel, A.; Droste, S.K.; Linthorst, A.C.; Holsboer, F.; Reul, J.M. Psychological stress increases hippocampal mineralocorticoid receptor levels: Involvement of corticotropin-releasing hormone. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 4822–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takahashi, T.; Sumitani, K.; Takatsu, H.; Urano, S. Glucocorticoid generates ROS to induce oxidative injury in the hippocampus, leading to impairment of cognitive function of rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 47, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, A.; Rabiei, Z.; Setorki, M. Effect of gallic acid on chronic restraint stress-induced anxiety and memory loss in male BALB/c mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontella, F.U.; Siqueira, I.R.; Vasconcellos, A.P.; Tabajara, A.S.; Netto, C.A.; Dalmaz, C. Repeated restraint stress induces oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, N.; Saleem, A.; Yasmin, F.; Shehzad, M.A. Quercetin protects against stress-induced anxiety- and depression-like behavior and improves memory in male mice. Physiol. Res. 2018, 67, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafir, A.; Banu, N. Modulation of in vivo oxidative status by exogenous corticosterone and restraint stress in rats. Stress Amst. Neth. 2009, 12, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Cuesta, L.A.; Márquez-Valadez, B.; Cruz, V.P.-D.L.; Escobar-Briones, C.; Galván-Arzate, S.; Alvarez-Ruiz, Y.; Maldonado, P.D.; Santana, R.A.; Santamaría, A.; Carrillo-Mora, P. Diazepam blocks striatal lipid peroxidation and improves stereotyped activity in a rat model of acute stress. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 109, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alexandria J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.-M.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Chemical and molecular mechanisms of antioxidants: Experimental approaches and model systems. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 840–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.-M.; Yun, S.-J.; Nam, K.N.; Kang, C.; Won, R.; Lee, E.H. Mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced oxidative stress in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 87, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritcu, L.; Noumedem, J.A.; Cioanca, O.; Hancianu, M.; Postu, P.; Mihasan, M. Anxiolytic and antidepressant profile of the methanolic extract of Piper nigrum fruits in beta-amyloid (1-42) rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Funct. 2015, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceremuga, T.E.; Valdivieso, D.; Kenner, C.; Lucia, A.; Lathrop, K.; Stailey, O.; Bailey, H.; Criss, J.; Linton, J.; Fried, J.; et al. Evaluation of the anxiolytic and antidepressant effects of asiatic acid, a compound from Gotu kola or Centella asiatica, in the male Sprague Dawley rat. AANA J. 2015, 83, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rajput, M.A.; Khan, R.A. Phytochemical screening, acute toxicity, anxiolytic and antidepressant activities of the Nelumbo nucifera fruit. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouhestani, S.; Jafari, A.; Babaei, P. Kaempferol attenuates cognitive deficit via regulating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in an ovariectomized rat model of sporadic dementia. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1827–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, D.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Gong, Z.; Dai, Y. Madecassoside, a triterpenoid saponin isolated from Centella asiatica herbs, protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, P.; Ramanathan, M. Effect of kaempferol on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine induced colorectal carcinoma in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, R.S.; Surya, D.; Nalini, N. Antioxidant efficacy of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) and piperine in rats with high fat diet induced oxidative stress. Redox Rep. 2004, 9, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Q.M.T.; Tran, P.T.; Tran, M.H.; Kim, J.A.; Rho, S.S.; Lim, C.-H.; Kim, J.-C.; Woo, M.H.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, J.-H.; et al. Alkaloids from Piper Nigrum exhibit antiinflammatory activity via activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Phytother. Res. PTR 2017, 31, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, C.L.L.; Guo, Y.; Yang, A.Y.; Paredes-Gonzalez, X.; Ramirez, C.; Pung, D.; Kong, A.-N.T. The berry constituents quercetin, kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive oxygen species: Involvement of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 72, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.S.; Park, C.M. Luteolin and luteolin-7-O-glucoside strengthen antioxidative potential through the modulation of Nrf2/MAPK mediated HO-1 signaling cascade in RAW 264.7 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2014, 65, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, D.K.; Meena, A.; Dubey, V.; Masood, N.; Luqman, S. Rutin protects t-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative impairment via modulating the Nrf2 and iNOS activity. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybertson, B.M.; Gao, B.; Bose, S.K.; McCord, J.M. Oxidative stress in health and disease: The therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. Mol. Aspects Med. 2011, 32, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-G.; Kim, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-B.; Choi, Y.-H.; Son, C.-G. The ethanol extract of Aquilariae lignum ameliorates hippocampal oxidative stress in a repeated restraint stress mouse model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patki, G.; Solanki, N.; Atrooz, F.; Allam, F.; Salim, S. Depression, anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment are associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation in a rat model of social stress. Brain Res. 2013, 1539, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinwa, P.; Kumar, A. Quercetin along with piperine prevents cognitive dysfunction, oxidative stress and neuro-inflammation associated with mouse model of chronic unpredictable stress. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2017, 40, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.W.; Murugan, D.; Leong, X.-F.; Abas, R.; Alias, A.; Mustafa, M.R. Flavonoids as natural anti-inflammatory agents targeting nuclear factor-kappa B (NFκB) signaling in cardiovascular diseases: A mini review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Ruengwinitwong, K.; Gatenakorn, K.; Maneenet, J.; Khamphukdee, C.; Sekeroglu, N.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Effects of the ethanol extract of Dipterocarpus alatus leaf on the unpredictable chronic mild stress-induced depression in ICR mice and its possible mechanism of action. Molecules 2019, 24, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: The samples are available from the authors. |






| Extract | Total Phenolic Content (mg GAE/g extract) | Total Flavonoid Content (mg QE/g Extract) |
|---|---|---|
| Piper nigrum | 95.234 ± 0.008 | 77.837 ± 0.011 |
| Centella asiatica | 51.226 ± 0.015 | 22.709 ± 0.001 |
| Nelumbo nucifera | 207.195 ± 0.022 | 54.612 ± 0.010 |
| KBD | 121.710 ± 3.547 | 70.523 ± 0.007 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maneenet, J.; Daodee, S.; Monthakantirat, O.; Boonyarat, C.; Khamphukdee, C.; Kwankhao, P.; Pitiporn, S.; Awale, S.; Chulikhit, Y.; Kijjoa, A. Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244587
Maneenet J, Daodee S, Monthakantirat O, Boonyarat C, Khamphukdee C, Kwankhao P, Pitiporn S, Awale S, Chulikhit Y, Kijjoa A. Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice. Molecules. 2019; 24(24):4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244587
Chicago/Turabian StyleManeenet, Juthamart, Supawadee Daodee, Orawan Monthakantirat, Chantana Boonyarat, Charinya Khamphukdee, Pakakrong Kwankhao, Supaporn Pitiporn, Suresh Awale, Yaowared Chulikhit, and Anake Kijjoa. 2019. "Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice" Molecules 24, no. 24: 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244587
APA StyleManeenet, J., Daodee, S., Monthakantirat, O., Boonyarat, C., Khamphukdee, C., Kwankhao, P., Pitiporn, S., Awale, S., Chulikhit, Y., & Kijjoa, A. (2019). Kleeb Bua Daeng, a Thai Traditional Herbal Formula, Ameliorated Unpredictable Chronic Mild Stress-Induced Cognitive Impairment in ICR Mice. Molecules, 24(24), 4587. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24244587