Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
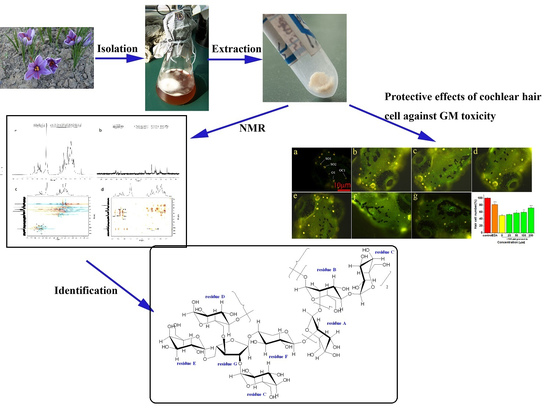
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Exopolysaccharide
2.2. Fourier Transformed Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. Methylation Analysis
2.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy Analysis
2.5. Effects of EPS-2 on the Viability of House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 (HEI-OC1) Cells Treated with GM
2.6. Protective Effect of EPS-2 on Hair Cells in Neuromasts
3. Experimental
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Fungal Material Microbial Strain and Culture Conditions
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Zebrafish Husbandry
3.5. Isolation and Purification of EPS-2
3.6. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics
3.7. FT-IR Analysis
3.8. Methylation Analysis
3.9. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.10. Protection Assay
3.10.1. Cell Viability Assay
3.10.2. Assay of Zebrafish Neuromast Hair Cell Protection
3.10.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Media centre. Deafness and hearing loss. World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs300/en/ (accessed on 15 March 2018).
- Thomas, A.J.; Wu, P.; Raible, D.W.; Rubel, E.W.; Simon, J.A.; Ou, H.C. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of cisplatin-induced hair cell death: Results of a 10,000 compound screen in the zebrafish lateral line. Otol. Neurotol. 2015, 36, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, M.; Boney, R.; Ordoobadi, A.J.; Sommers, T.F.; Trapani, J.G.; Coffin, A.B. Natural bizbenzoquinoline derivatives protect zebrafish lateral line sensory hair cells from aminoglycoside toxicity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterberg, R.; Coffin, A.B.; Ou, H.; Simon, J.A.; Raible, D.W.; Rubel, E.W. Fish in a dish: drug discovery for hearing habilitation. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 10, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fausti, S.A.; Henry, J.A.; Schaffer, H.I.; Olson, D.J.; Frey, R.H.; McDonald, W.J. High-frequency audiometric monitoring for early detection of aminoglycoside ototoxicity. J. Infect. Dis. 1992, 165, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noack, V.; Pak, K.; Jalota, R.; Kurabi, A.; Ryan, A.F. An antioxidant screen identifies candidates for protection of cochlear hair cells from gentamicin toxicity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, E.I.; Abdin, A.A.; Sarhan, N.I.; Gabr, T.A. Neurotrophic and antioxidant effects of silymarin comparable to 4-methylcatechol in protection against gentamicin-induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, N.; Kendall, A.; Schacht, J. Metformin protects against gentamicin-induced hair cell death in vitro but not ototoxicity in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 583, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Ojano-Dirain, C.; Rudnick, E.W.; Nelson, M.A.; DeRemer, S.J.; Prieskorn, D.M.; Miller, J.M. Assessment of nutrient supplement to reduce gentamicin-induced ototoxicity. J. Assoc. Res. Oto. 2014, 15, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, M.; Yu, Z.; Qi, R.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Self-stabilized hyaluronate nanogel for intracellular codelivery of doxorubicin and cisplatin to osteosarcoma. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Xu, W.; Sun, T.; Xiao, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Receptor and microenvironment dual-recognizable nanogel for targeted chemotherapy of highly metastatic malignancy. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 4526–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Han, J.; Ding, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Acid-sensitive dextran prodrug: A higher molecular weight makes a better efficacy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 161, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.J.; White, J.F., Jr.; Arnold, A.E.; Redman, R.S. Fungal endophytes: diversity and functional roles. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.H.; Chung, J.Y.; Ahn, D.J.; Kwon, T.R.; Lee, S.K.; Bae, I.; Yun, H.K.; Bae, H. Screening and characterization of endophytic fungi of Panax ginseng Meyer for biocontrol activity against Ginseng pathogens. Biol. Control 2015, 91, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.X.; Mao, W.J.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.Y.; Xia, Z.; Cao, S.J.; Li, J.; Qin, L.; Xian, H.L. Extracellular polysaccharide with novel structure and antioxidant property produced by the deep-sea fungus Aspergillus versicolor N2bc. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitake, D.; Devi, P.B.; Singh, S.P.; Shetty, P.H. Characterization of a novel galactan produced by Weissella confusa KR780676 from an acidic fermented food. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatziagapiou, K.; Kakouri, E.; Lambrou, G.I.; Bethanis, K.; Tarantilis, P.A. Antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus L. and its constituents and relevance to neurodegenerative diseases; focus on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopresti, A.L.; Drummond, P.D.; Inarejos-García, A.M.; Prodanov, M. Affron®, a standardised extract from saffron (Crocus sativus L.) for the treatment of youth anxiety and depressive symptoms: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Affect Disorders 2018, 232, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, E.; Kadoglou, N.P.E.; Stasinopoulou, M.; Konstandi, O.A.; Kenoutis, C.; Kakazanis, Z.I.; Rizakou, A.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Valsami, G. Crocus sativus L. aqueous extract reduces atherogenesis, increases atherosclerotic plaque stability and improves glucose control in diabetic atherosclerotic animals. Atherosclerosis 2018, 268, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Xu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Modeling and optimum extraction of multiple bioactive exopolysaccharide from an endophytic fungus of Crocus sativus L. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Yang, N.; Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, G. Structural characterization of water-soluble polysaccharides from Opuntia monacantha cladodes in relation to their anti-glycated activities. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1480–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayabaskar, P.; Babinastarlin, S.; Shankar, T.; Sivakumar, T.; Anandapandian, K.T.K. Quantification and characterization of exopolysaccharides from Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 121). Adv. Biol. Res. 2011, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.M.; Joo, J.H.; Kim, H.O.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, S.W.; Hwang, H.J.; Yun, J.W. Structural analysis and molecular characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by submerged mycelial culture of Collybia maculata TG-1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 61, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H.; Cui, Z.; Cheng, F.; Wang, K.P. Structural characterization and in vitro, antitumor activity of an acidic polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis, (Oliv.) Diels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeff, I.B.; Li, S.; Peng, X.; Kassim, R.M.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y. Purification, structural elucidation and antitumor activity of a novel mannogalactoglucan from the fruiting bodies of Lentinus edodes. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.G.; Liang, J.; Yang, B.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Kuang, H.X. Structural studies of an arabinan from the stems of Ephedra sinica by methylation analysis and 1D and 2D-NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, I.K.; Mandal, A.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Behera, B.; Yadav, K.K.; Maiti, T.K.; Islam, S.S. Structural and immunological studies of an exopolysaccharide from Acinetobacter junii BB1A. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeff, I.B.; Yuan, X.; Sun, L.; Kassim, R.M.; Foday, A.D.; Zhou, Y. Purification and in vitro anti-proliferative effect of novel neutral polysaccharides from Lentinus edodes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 52, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Zhou, J.W.; Xiang, Z.N.; Zhou, C.G.; Wan, L.S.; Chen, J.C. Structure features and in vitro hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from different species of Maidong. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.T.; Zirrolli, J.; Bendiak, B. Differentiation of the anomeric configuration and ring form of glucosyl-glycolaldehyde anions in the gas phase by mass spectrometry: isomeric discrimination between m/z 221 anions derived from disaccharides and chemical synthesis of m/z 221 standards. Carbohydr Res. 2007, 342, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, A.B.; Rubel, E.W.; Raible, D.W. Bax, Bcl2, and P53 differentially regulate neomycin- and gentamicin-induced hair cell death in the zebrafish lateral line. J. Assoc. Res. Oto. 2013, 14, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.F.; Dudman, W.F.; Aspinall, G.O. The extracellular polysaccharide of Aerobacter aerogenes A3 (S1) (Klebsiella type 54). Biochem. J. 1955, 59, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, W.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L.; Gu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Shan, J.; et al. Preparation and characterization of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by the deep-sea fungus Penicillium griseofulvum. Bioresource Technol. 2013, 132, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedevi, P.; Moovendhan, M.; Viramani, S.; Shanmugam, A. Bioactive potential and structural chracterization of sulfated polysaccharide from seaweed (Gracilaria corticata). Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, H.C.; Santos, F.; Raible, D.W.; Simon, J.A.; Rubel, E.W. Drug screening for hearing loss: using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for drugs that prevent and cause hearing loss. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinec, G.M.; Webster, P.; Lim, D.J.; Kalinec, F. A cochlear cell line as an in vitro system for drug ototoxicity screening. Audiol. Neurootol. 2003, 8, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.J.; Lee, J.D.; Lee, B.D.; Chae, S.W.; Park, M.K. Effect of diesel exhaust particles on human middle ear epithelial cells. J. Assoc. Res. Oto. 2012, 76, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rah, Y.C.; Choi, J.; Yoo, M.H.; Yum, G.; Park, S.; Oh, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Kims, S.; et al. Ecabet sodium alleviates neomycin-induced hair cell damage. Free Radical Bio. Med. 2015, 89, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; et al. Meclofenamic acid reduces reactive oxygen species accumulation and apoptosis, inhibits excessive autophagy, and protects hair cell-like HEI-OC1 cells from cisplatin-induced damage. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |





| PMAA | Mass Fragments (m/z) | Molar Ratio | Linkage Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3,4,6-Me3-Manp a | 87, 101, 117, 129, 161, 189, 233 | 7.2 | →2)-d-Manp-(1→ |
| 3,6-Me2-Manp | 43, 71, 87, 129, 173, 189, 233 | 2.3 | →2, 4)-d-Manp-(1→ |
| 2,3,4,6-Me4-Glcp | 45, 71, 87, 101, 117, 129, 145, 161, 205 | 3.3 | d-Glcp-(1→ |
| 2,3,4-Me3-Glcp | 58, 71, 87, 99, 101, 117, 129, 161, 189, 233 | 1.2 | →6)-d-Glcp-(1→ |
| 2,3,4,6-Me4-Galp | 87, 101, 117, 129, 189, 233 | 1.0 | d-Galp-(1→ |
| 2,3-Me2-Xylp | 43, 87, 101, 117, 129, 189 | 1.1 | →4)-d-Xylp-(1→ |
| Araf | 73, 85, 115, 145, 158, 187, 217 | 1.1 | →2, 3, 5)-d-Araf-(1→ |
| No. | Glycosyl Residues | Chemical Shifts, δ (ppm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1/H1 | C2/H2 | C3/H3 | C4/H4 | C5/H5 | C6/H6 | ||
| A | →2)–α-d-Manp-(1→ | 100.5 5.30 | 78.5 4.11 | 70.6 3.97 | 66.8 3.65 | 73.9 3.80 | 63.4 3.91 |
| B | →2, 4)–α-d-Manp-(1→ | 98.2 5.16 | 78.3 3.96 | 70.1 4.07 | 70.3 3.89 | 73.6 3.76 | 66.9 3.85, 3.77 |
| C | α-d-Glcp-(1→ | 98.3 5.07 | 70.4 3.80 | 73.3 3.85 | 76.7 4.08 | 70.1 3.90 | 61.0 3.81, 3.75 |
| D | →6)-α-d-Glcp-(1→ | 102.4 5.10 | 73.3 3.36 | 73.5 3.60 | 70.4 3.62 | 76.8 4.08 | 66.2 3.75 |
| E | α-d-Galp-(1→ | 102.1 5.06 | 70.2 3.82 | 73.2 4.13 | 71.2 4.02 | 73.3 4.04 | 61.1 3.72 |
| F | →4)–α-d-Xylp-(1→ | 102.0 5.03 | 75.3 3.82 | 76.3 3.95 | 78.4 3.73 | 65.5 3.65 | |
| G | →2, 3, 5)–β-d-Araf-(1→ | 102.3 5.07 | 81.1 4.25 | 82.8 4.02 | 81.1 4.23 | 66.6 3.96, 3.88 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wu, G.; Qin, C.; Chen, W.; Chen, G.; Wen, L. Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron. Molecules 2019, 24, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040749
Li J, Wu G, Qin C, Chen W, Chen G, Wen L. Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040749
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Juan, Guimei Wu, Cuiying Qin, Wuhai Chen, Gang Chen, and Lu Wen. 2019. "Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron" Molecules 24, no. 4: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040749
APA StyleLi, J., Wu, G., Qin, C., Chen, W., Chen, G., & Wen, L. (2019). Structure Characterization and Otoprotective Effects of a New Endophytic Exopolysaccharide from Saffron. Molecules, 24(4), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040749