L-765,314 Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Activity
Abstract
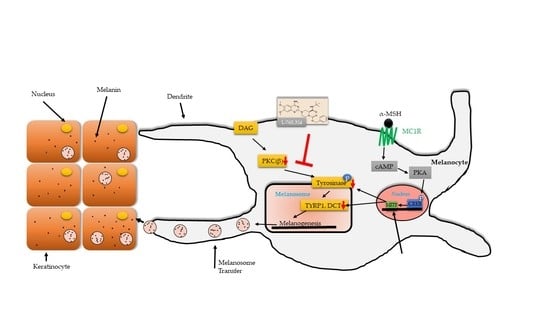
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. L-765,314 Reduces Melanin Production
2.2. The Anti-Melanogenic Effect of L-765,314 Is not Associated with α1B-Adrenoceptor Signaling
2.3. L-765,314 Downregulates Tyrosinase Activity via Disruption of the PKC Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Screening
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. Tyrosinase Activity
4.6. Antibodies and Western Blots
4.7. RNA and qRT-PCR
4.8. Promoter Activity Assay
4.9. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UVR | Ultraviolet Radiation |
| FSK | Forskolin |
| MEFs | Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts |
| MITF | Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor |
| Tyr | Tyrosinase |
| Tyrp1 | Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 |
| DCT | Dopachrome Tautomerase |
| l-DOPA | l-Dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| TPA | 12-O-Tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate |
References
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The protective role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alba, L.; Shawkey, M.D. Melanosomes: Biogenesis, Properties, and Evolution of an Ancient Organelle. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, I.; Kinst-Hori, I.; Yokokawa, Y. Tyrosinase inhibitors from Anacardium occidentale fruits. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, H.; Takekoshi, S.; Takeyama, R.; Homma, T.; Yoshiyuki Osamura, R. Quercetin enhances melanogenesis by increasing the activity and synthesis of tyrosinase in human melanoma cells and in normal human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2004, 17, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeyama, R.; Takekoshi, S.; Nagata, H.; Osamura, R.Y.; Kawana, S. Quercetin-induced melanogenesis in a reconstituted three-dimensional human epidermal model. J. Mol. Histol. 2004, 35, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patane, M.A.; Scott, A.L.; Broten, T.P.; Chang, R.S.; Ransom, R.W.; DiSalvo, J.; Forray, C.; Bock, M.G. 4-Amino-2-[4-[1-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-2(S)- [[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-piperazinyl]-6, 7-dimethoxyquinazoline (L-765,314): A potent and selective alpha1b adrenergic receptor antagonist. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.P.; Chiba, S. Effects of L-765,314, a selective and potent alpha 1B-adrenoceptor antagonist, on periarterial nerve electrical stimulation-induced double-peaked constrictor responses in isolated dog splenic arteries. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 89, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.P.; Daniels, D.V.; Chang, D.J.; Gever, J.R.; Jasper, J.R.; Lesnick, J.D.; Clarke, D.E. Pharmacological pleiotropism of the human recombinant alpha1A-adrenoceptor: Implications for alpha1-adrenoceptor classification. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minneman, K.P.; Theroux, T.L.; Hollinger, S.; Han, C.; Esbenshade, T.A. Selectivity of agonists for cloned alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 929–936. [Google Scholar]
- Langer, S.Z.; Hicks, P.E. Alpha-adrenoreceptor subtypes in blood vessels: Physiology and pharmacology. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1984, 6 (Suppl. 4), 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, K.; Obika, K.; Foglar, R.; Tsujimoto, G. Selectivity of the imidazoline alpha-adrenoceptor agonists (oxymetazoline and cirazoline) for human cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Gilchrest, B.A. Signaling pathways mediating melanogenesis. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 45, 919–930. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.Y.; Noh, M. The regulation of epidermal melanogenesis via cAMP and/or PKC signaling pathways: Insights for the development of hypopigmenting agents. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2013, 36, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Perez, J.M.; Laursen, R.; Hara, M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Protein kinase C-beta activates tyrosinase by phosphorylating serine residues in its cytoplasmic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 16470–16478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Industry Analysts, Inc. Obsession with lighter skin tones in Asia, the Middle East & Africa drives opportunities in the global skin lighteners market. Available online: https://www.strategyr.com/blog/blog-post.asp?bcode=MCP-6140 (accessed on 19 February 2019).
- Chang, T.S. Natural Melanogenesis Inhibitors Acting Through the Down-Regulation of Tyrosinase Activity. Materials 2012, 5, 1661–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, A.A. Current contact news. Hydroquinone uses and abnormal reactions. Cutis 1983, 31, 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Kepa, J.K.; Siegel, D.; Miura, S.; Hiraki, Y.; Ross, D. Benzene metabolite hydroquinone up-regulates chondromodulin-I and inhibits tube formation in human bone marrow endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, N.; Onodera, H.; Mitsumori, K.; Tamura, T.; Maruyama, S.; Ito, A. Changes in thyroid function during development of thyroid hyperplasia induced by kojic acid in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, A.E.; Archambault, M.; Messana, E.; Gilchrest, B.A. Topically applied diacylglycerols increase pigmentation in guinea pig skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 105, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P.R.; Gilchrest, B.A. Human melanogenesis is stimulated by diacylglycerol. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 93, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Russakovsky, V.; Ohno, S.; Gilchrest, B.A. The beta isoform of protein kinase C stimulates human melanogenesis by activating tyrosinase in pigment cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11742–11749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Russakovsky, V.; Ao, Y.; Fernandez, E.; Gilchrest, B.A. Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced pigmentation is blocked by depletion of protein kinase C. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 227, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Apgar, J.; Russakovsky, V.; Gilchrest, B.A. Cell-Specific and Age-Dependent Expression of Protein-Kinase-C in Human Skin-Derived Cells. Clin. Res. 1991, 39, A148. [Google Scholar]
- Racchi, M.; Bergamaschi, S.; Govoni, S.; Wetsel, W.C.; Bianchetti, A.; Binetti, G.; Battaini, F.; Trabucchi, M. Characterization and Distribution of Protein-Kinase-C Isoforms in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 314, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiki, H.; Uwada, J.; Anisuzzaman, A.S.; Umada, H.; Hayashi, R.; Kainoh, M.; Masuoka, T.; Nishio, M.; Muramatsu, I. Pharmacologically distinct phenotypes of alpha1B -adrenoceptors: Variation in binding and functional affinities for antagonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4890–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Gillespie, S.K.; Hersey, P. Staurosporine induces apoptosis of melanoma by both caspase-dependent and -independent apoptotic pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2004, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toullec, D.; Pianetti, P.; Coste, H.; Bellevergue, P.; Grand-Perret, T.; Ajakane, M.; Baudet, V.; Boissin, P.; Boursier, E.; Loriolle, F.; et al. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15771–15781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.P.; Reddy, H.; Caivano, M.; Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Gonzalez, S.; Middelkamp-Hup, M.A.; Kapasi, S.; Peterson, S.; Gilchrest, B.A. Topical application of a protein kinase C inhibitor reduces skin and hair pigmentation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwahn, D.J.; Xu, W.; Herrin, A.B.; Bales, E.S.; Medrano, E.E. Tyrosine levels regulate the melanogenic response to alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone in human melanocytes: Implications for pigmentation and proliferation. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, C.; Ito, S.; Takeuchi, T. Enhancement of pheomelanogenesis by l-dopa in the mouse melanocyte cell line, TM10, in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 1987, 87, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Pawelek, J. L-tyrosine and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.; Won, K.H.; Moon, H.R.; Yoo, H.; Hong, A.; Song, Y.; Chang, S.E. Novel regulation of melanogenesis by adiponectin via the AMPK/CRTC pathway. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2017, 30, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Bang, S.; Yoo, H.; Kim, I.; Chang, S.E.; Song, Y. L-765,314 Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Activity. Molecules 2019, 24, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040773
Kim J, Kim Y-H, Bang S, Yoo H, Kim I, Chang SE, Song Y. L-765,314 Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Activity. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040773
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jinhwan, Yo-Han Kim, Seunghyun Bang, Hanju Yoo, InKi Kim, Sung Eun Chang, and Youngsup Song. 2019. "L-765,314 Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Activity" Molecules 24, no. 4: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040773
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, Y.-H., Bang, S., Yoo, H., Kim, I., Chang, S. E., & Song, Y. (2019). L-765,314 Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Activity. Molecules, 24(4), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040773