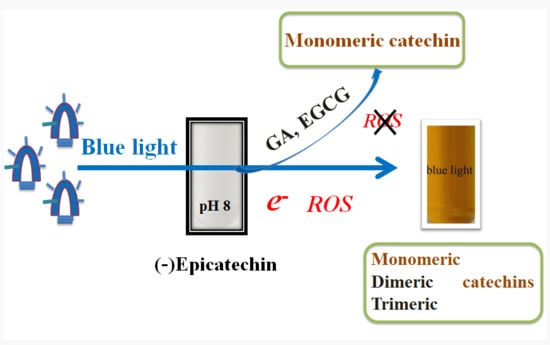
Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Stability of Epicatechin in a Photolytic Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Blue, Green, and Red Lights on EC Photolysis
2.2. Detection of O2•− in EC Photolysis
2.3. Effects of Blue Light on EC, EGCG, GA, and PG Photolysis
2.4. Effects of EGCG and GA on the EC Photolysis
2.5. Molecular Identification by LC–MS/MS Analysis
2.6. HPLC–DAD Analysis of EGCG Under Blue Light Illumination
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Illumination System
4.3. Effects of Blue, Green, and Red Lights on EC Photolysis
4.4. O2•− Determination
4.5. Effects of Blue Light on the Photolysis of EC, EGCG, GA, and PG
4.6. Effects of EGCG or GA on EC Under Blue Light Illumination
4.7. LC–MS/MS Analysis of EC Treated with GA Under Blue Light Illumination
4.8. HPLC–DAD Analysis of EGCG Under Blue Light Illumination
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balasundram, N.; Sundram, K.; Samman, S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Liang, J.Y. Effect of esterification condensation on the Folin-Ciocalteu method for the quantitative measurement of total phenols. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Wu, C.C.; Tzen, J.T. Catechin content and the degree of its galloylation in oolong tea are inversely correlated with cultivation altitude. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dube, A.; Ng, K.; Nicolazzo, J.A.; Larson, I. Effective use of reducing agents and nanoparticle encapsulation in stabilizing catechins in alkaline solution. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeiro, P.; Oliveira Brett, A.M. Catechin electrochemical oxidation mechanisms. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 518, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Kinetic analysis and mechanistic aspects of autoxidation of catechins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1569, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, V.; Huber, C.; Trettenhahn, G.; Hadacek, F. (+/−)-catechin: Chemical weapon, antioxidant, or stress regulator? J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Liang, J.Y. Using chromatography and mass spectrometry to monitor isomerization of catechin in alkaline aqueous with thermal processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Nie, Y.; Zheng, X.Q.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.R.; Ye, J.H. Ultraviolet B (UVB) photosensitivities of tea catechins and the relevant chemical conversions. Molecules 2016, 21, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forest, K.; Wan, P.; Preston, C.M. Catechin and hydroxybenzhydrols as models for the environmental photochemistry of tannins and lignins. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm-Mouton, A.; Bonnet, S.L.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.C.; Ferreira, D.; van der Westhuizen, J.H. Photochemistry synthesis. Part 2: Enantiomerically pure polyhydroxy-1, 1, 3-triarylpropan-2-ols. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2012, 227, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Hu, A.; Chen, L.Y. Photo-catalytic polymerization of catechin molecules in alkaline aqueous. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 165, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.J.; Hung, Y.A.; Wong, T.W.; Lee, N.Y.; Yuann, J.P.; Huang, S.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, I.Z.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of blue-light-induced free radical formation from catechin hydrate on the inactivation of Acinetobacter baumannii, including a carbapenem-resistant strain. Molecules 2018, 23, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Shi, Y.L.; Li, X.M.; Yang, R.; Cai, Z.Y.; Li, Q.S.; Ma, S.C.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; Liang, Y.R.; et al. Food-grade encapsulation systems for (−)-epigallocatechin gallate. Molecules 2018, 23, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braicu, C.; Pilecki, V.; Balacescu, O.; Irimie, A.; Neagoe, I.B. The relationships between biological activities and structure of flavan-3-ols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 9342–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuann, J.M.P.; Wang, J.S.; Jian, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of Clinacanthus nutans (Burm. f) Lindau leaf extracts on protection of plasmid DNA from riboflavin photoreaction. MC-Trans. Biotech. 2012, 4, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B.; Gutteridge, J.M. Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: An overview. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 186, 1–85. [Google Scholar]
- Juen, J.W.; Jian, H.L.; Liang, J.Y. The effect of illuminance on light induced reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium. MC-Trans. Biotech. 2010, 2, e2. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.Y.; Yuann, J.M.; Cheng, C.W.; Jian, H.L.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, L.Y. Blue light induced free radicals from riboflavin on E. coli DNA damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 119, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Yu, C.H.; Chen, L.Y. Investigations of blue light-induced reactive oxygen species from flavin mononucleotide on inactivation of E. coli. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 143, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.W.; Cheng, C.W.; Hsieh, Z.J.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of blue or violet light on the inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus by riboflavin-5′-phosphate photolysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Lee, N.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Yang, M.J.; Hung, Y.A.; Wong, T.W.; Liang, J.Y. Effects of 462 nm light-emitting diode on the inactivation of Escherichia coli and a multidrug-resistant by tetracycline photoreaction. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourie, T.G.; Ferreira, D.; Roux, D.G. Flavonoid synthesis based on photolysis of flavan-3-ols, 3-hydroxyflavanones, and 2-benzylbenzofuranones. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1977, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.; Steenken, S. Photoionization (lambda.= 248 or 308 nm) of triphenylmethyl radical in aqueous solution. Formation of triphenylmethyl carbocation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 1277–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A.; Xie, D.Y.; Sharma, S.B. Proanthocyanidins-a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol. 2005, 165, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tan, H.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Qian, Y.; et al. Analysis of accumulation patterns and preliminary study on the condensation mechanism of proanthocyanidins in the tea plant [Camellia sinensis]. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojwang, L.O.; Yang, L.; Dykes, L.; Awika, J. Proanthocyanidin profile of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) reveals catechin-O-glucoside as the dominant compound. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huvaere, K.; Sinnaeve, B.; Van Bocxlaer, J.; Skibsted, L.H. Flavonoid deactivation of excited state flavins: Reaction monitoring by mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9261–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.F.; Kolodziej, H.; Hemingway, R.W.; Steynberg, J.P.; Young, D.A.; Ferreira, D. Oligomeric flavanoids. Part W. base-catalyzed pyran rearrangements of procyanidin B-2, and evidence for the oxidative transformation of B-to A-type procyanidins. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 5733–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Pan, Q.H.; Shi, Y.; Duan, C.Q. Chemical synthesis of proanthocyanidins in vitro and their reactions in aging wines. Molecules 2008, 13, 3007–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.M.; Cipriani, T.R.; Iacomini, M.; Gorin, P.A.; Sassaki, G.L. HPLC/ESI-MS and NMR analysis of flavonoids and tannins in bioactive extract from leaves of Maytenus ilicifolia. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Vervoort, L.; Moalin, M.; Mommers, A.; Douny, C.; den Hartog, G.J.M.; Haenen, G. The chemical reactivity of (−)-epicatechin quinone mainly resides in its B-ring. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dettlaff, K.; Stawny, M.; Ogrodowczyk, M.; Jelinska, A.; Bednarski, W.; Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Keck, R.W.; Khan, O.A.; Mostafa, I.H.; Jankun, J. Formulation and characterization of EGCG for the treatment of superficial bladder cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wyganowska-Swiatkowska, M.; Matthews-Kozanecka, M.; Matthews-Brzozowska, T.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Jankun, J. Can EGCG alleviate symptoms of Down syndrome by altering proteolytic activity? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Khaskheli, A.R.; Aljabour, A.; Kara, H.; Talpur, F.N.; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Khaskheli, A.A.; Jawaid, S. Synthesis of highly stable cobalt nanomaterial using gallic acid and its application in catalysis. Adv. Chem. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhani, B.; Sharma, N.; Kakkar, R. Gallic acid: A versatile antioxidant with promising therapeutic and industrial applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27540–27557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.C.; Pasanphan, W.; Wagner, B.A.; Buettner, G.R. Free radicals produced by the oxidation of gallic acid: An electron paramagnetic resonance study. Chem. Cent. J. 2010, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunckel, S.; Santander, P.; Cordano, G.; Ferreira, J.; Munoz, S.; Nunez-Vergara, L.J.; Squella, J.A. Antioxidant activity of gallates: An electrochemical study in aqueous media. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1998, 114, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zou, T.; Gao, J.M.; Gu, L. Depolymerization of cranberry procyanidins using (+)-catechin, (−)-epicatechin, and (−)-epigallocatechin gallate as chain breakers. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Chen, L.Y.; Chou, C.W.; Liang, J.Y. Investigations of riboflavin photolysis via coloured light in the nitro blue tetrazolium assay for superoxide dismutase activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 148, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds (epicatechin) are available from the authors. |









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, S.-T.; Hung, Y.-A.; Yang, M.-J.; Chen, I.-Z.; Yuann, J.-M.P.; Liang, J.-Y. Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Stability of Epicatechin in a Photolytic Process. Molecules 2019, 24, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040787
Huang S-T, Hung Y-A, Yang M-J, Chen I-Z, Yuann J-MP, Liang J-Y. Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Stability of Epicatechin in a Photolytic Process. Molecules. 2019; 24(4):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040787
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Shiuh-Tsuen, Yi-An Hung, Meei-Ju Yang, Iou-Zen Chen, Jeu-Ming P. Yuann, and Ji-Yuan Liang. 2019. "Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Stability of Epicatechin in a Photolytic Process" Molecules 24, no. 4: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040787
APA StyleHuang, S. -T., Hung, Y. -A., Yang, M. -J., Chen, I. -Z., Yuann, J. -M. P., & Liang, J. -Y. (2019). Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on the Stability of Epicatechin in a Photolytic Process. Molecules, 24(4), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040787