The Removal of Brilliant Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Nano Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite as a Sorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural and Surface Characterization of the Adsorbent
2.1.1. FTIR Study
2.1.2. X-ray Diffraction Studies
2.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.1.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.1.5. Zeta Potential Distribution Study
2.2. Effect of pH
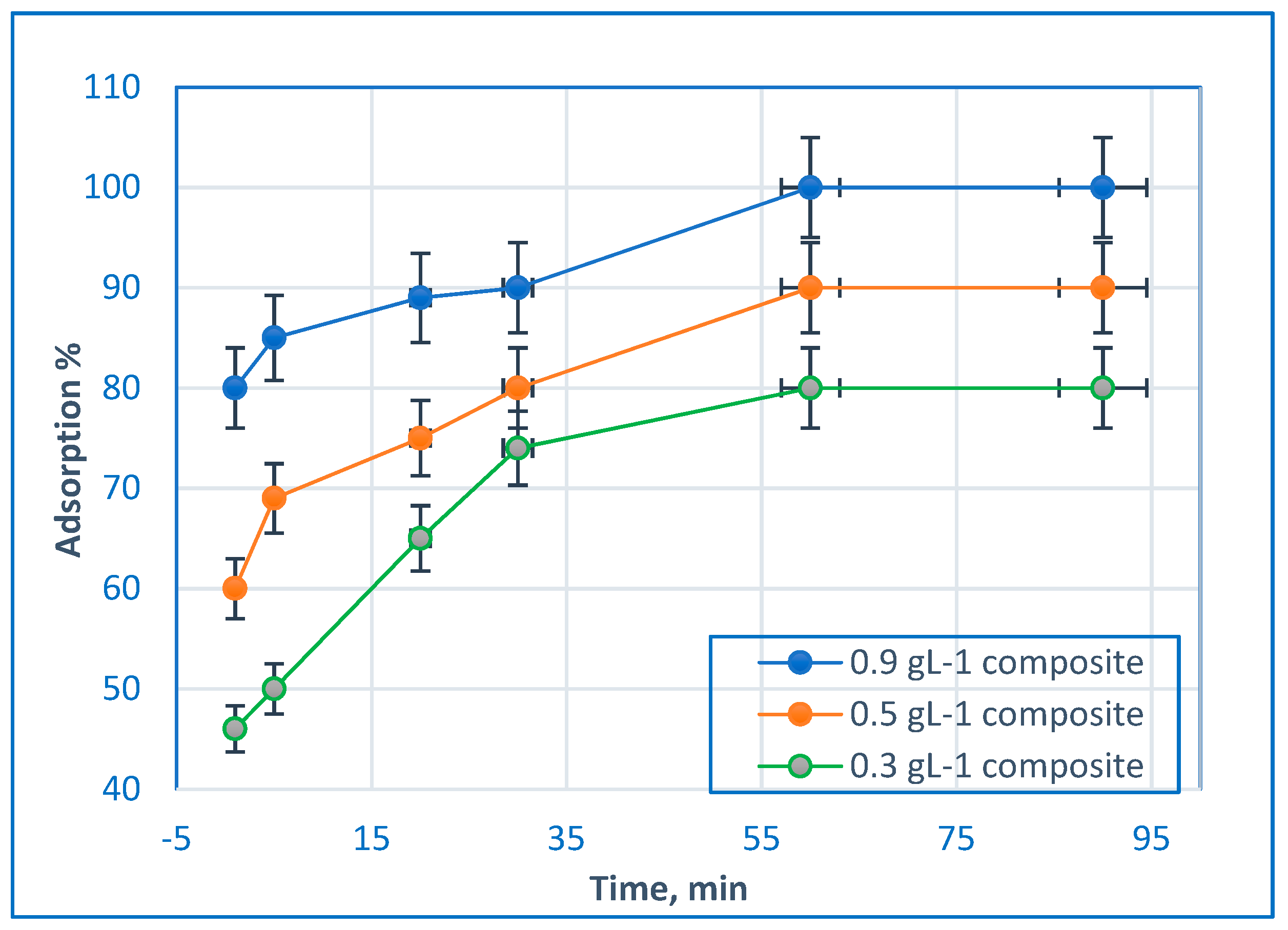
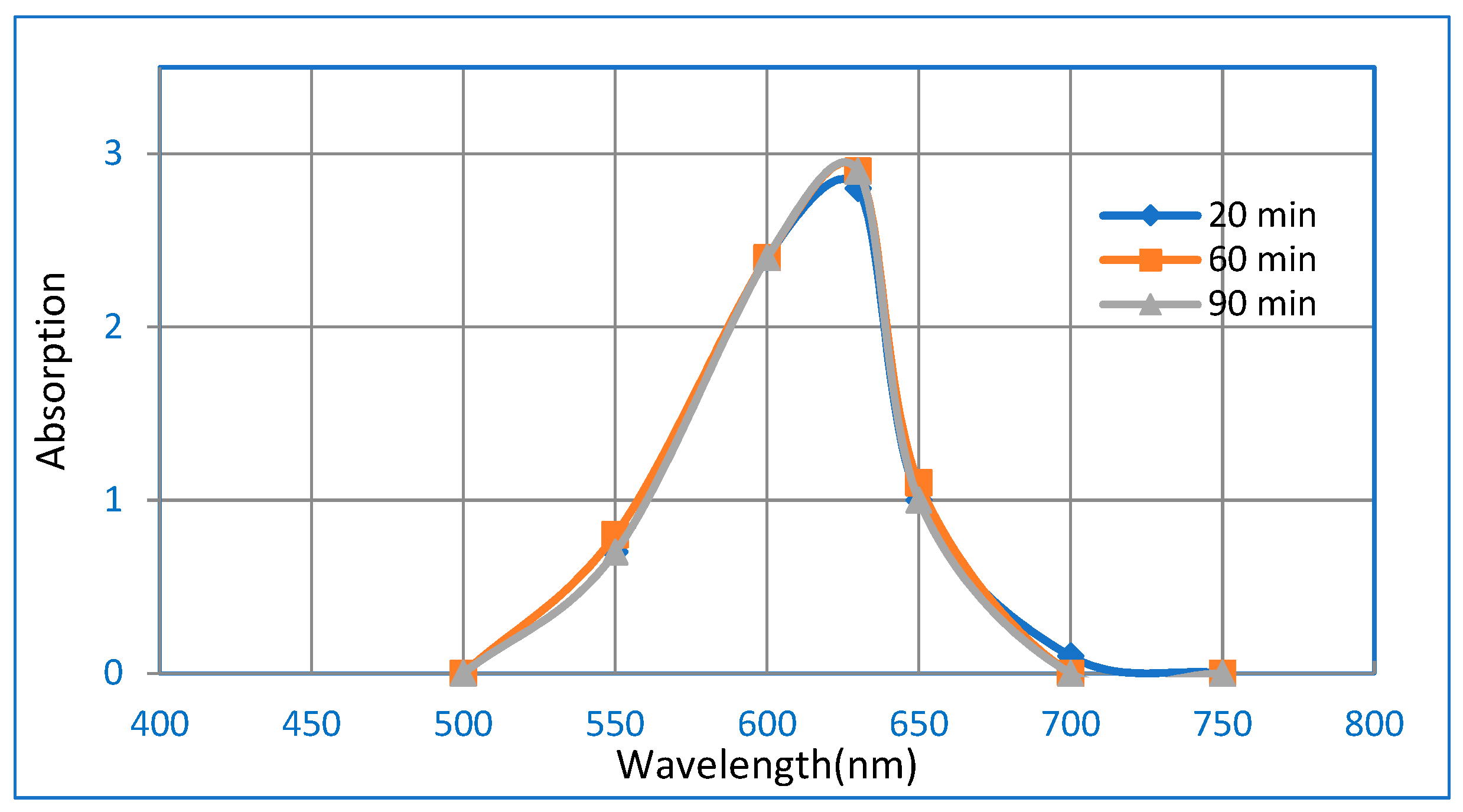
2.3. Effect of Contact Time and Initial BG Dye Concentration
2.4. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage on BG dye Removal
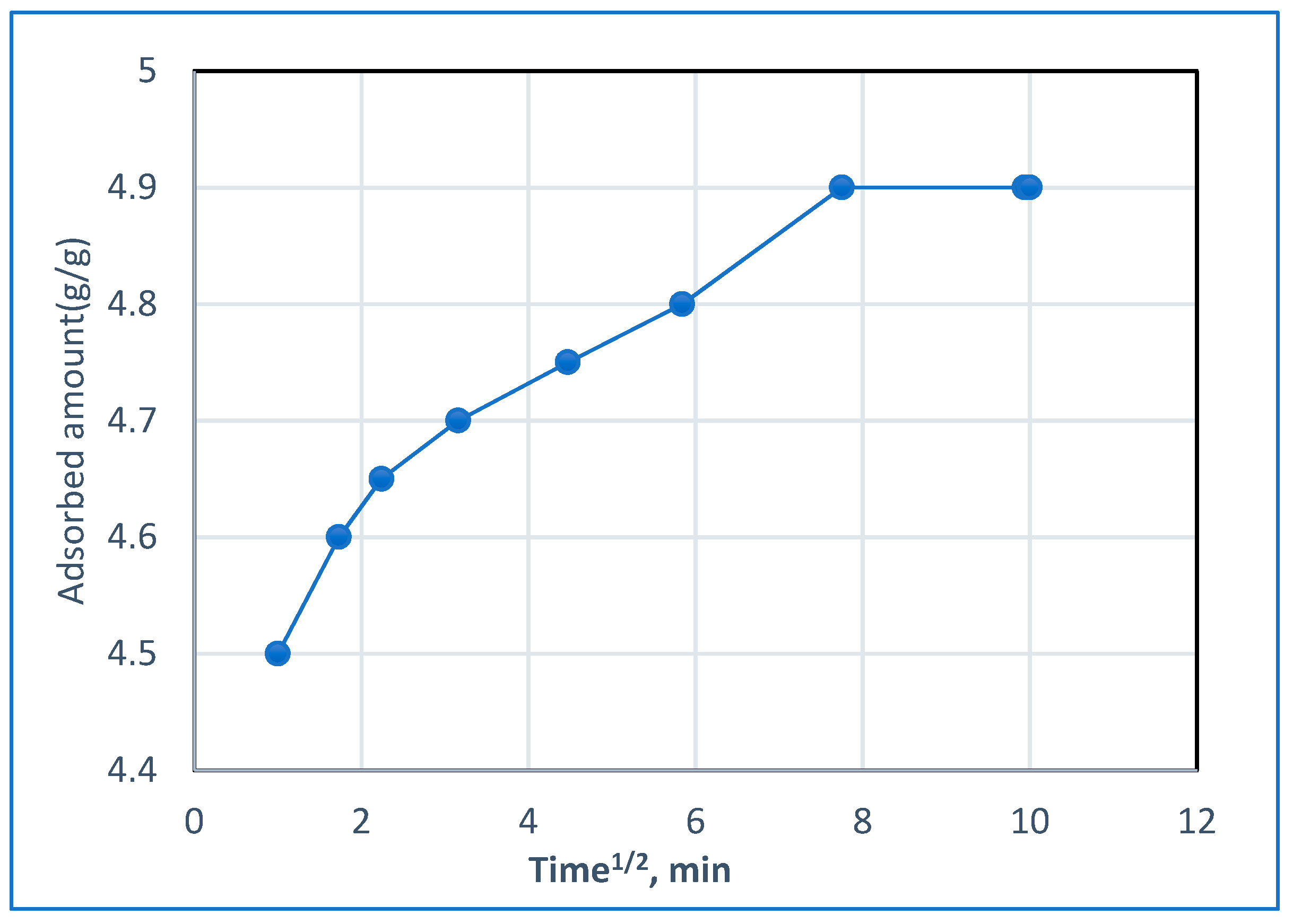
2.5. Sorption Model
2.6. Isotherm Model
2.6.1. Langmuir Isotherm
2.6.2. Freundlich Isotherm
2.6.3. Dubinin-Radusekevisch-Kanager Isotherm
2.7. Thermodynamic Parameters
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Synthesis of the Hap/CS Nanocomposite
3.2. Structural and Surface Characterization of the Hap/CS Nanocomposite
Analytical Instruments
3.3. Adsorption Studies of BG Dye
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravi, M. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandy, T.; Sharma, C.P. Chitosan-as a biomaterial. Biomater. Artif. Cells Artif. Organs 1990, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randy, C.; Jack, C. Chitosan: An Update on Potential Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5156–5186. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, S.; Bardhan, R.; Mondal, B.; Dey, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Roy, S.; Guha, R.; Roy, G.; Bull, K. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity assessment of hydroxyapatite from different bioresources for tissue engineering application. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriela, C.; Simona, B.; Maria, H. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on adsorption of Reactive Blue 19 dye from aqueous solutions by nanohydroxyapatite adsorbent. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, L. Water-soluble Fe3O4 nanoparticles with high solubility for removal of heavy-metal ions from waste water. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhermendra, K.T.; Behari, J.; Prasenjit, S. Application of Nanoparticles in Waste Water Treatment. World Appl. Sci. J. 2008, 3, 417–433. [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose, N.; Ozaki, Y.; Kashu, S. Superfine Particle Technology; Springer: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Poursaberi, T.; Hassanisadi, M.; Torkestani, K.; Zare, M. Development of zirconium (IV)-metalloporphyrin grafted Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient fluoride removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 117, 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Stoimenov, P.; Klinger, R.; Marchin, G.; Klabunde, K. Metal oxide nanoparticles as bactericidal agents. Langmuir 2002, 18, 6679–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kamel, R.; Hind, A. Preparation of Sustainable Nanocomposite as New Adsorbent for Dyes Removal. Fiber. Polym. 2017, 18, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger, H. Color Chemistry Synthesis, Properties and Applications of Organic, Dyes and Pigments; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Barun, N.; Sunil, P. Effects of operational parameters on the removal of brilliant green dye from aqueous solutions by electrocoagulation. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2961–S2968. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Shukla, P.; Prasad, G.; Singh, N. China clay as an adsorbent for dye house wastewaters. Environ. Technol. 1992, 13, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anmoldeep, S.; Anshumaan, S.; Anirudhha, T.; Narendra, D. Optimization of Brilliant Green Dye Removal Efficiency by Electrocoagulation Using Response Surface Methodology. World J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, M.; Munira, M.; Ashfaqa, M.; Rashid, N.; Faizan, M.; Danish, M.; Han, J. Adsorption of Brilliant Green dye from aqueous solution onto red clay. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, S.; Salleh, M. Hydroxyapatite/ Chitosan Biocomposite for Remazol Blue Dyes Removal. AMM 2015, 695, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijuan, H.; Ronghui, Z.; Peng, W.; Lan, W. Removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution with hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211, 336–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.M.; Elliott, J.C.; Dowker, S.E.P.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Rietveld refinements and spectroscopic studies of the structure of Ca-deficient apatite. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaozhi, F.; Gang, G.; Xinlong, W.; Liangxue, Z.; Tingting, L.; Pengwei, D.; Feng, L.; Yingchun, G.; Xingyu, S.; Xia, Z.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of n-Hydroxyapatite/PCL-Pluronic-PCL Nanocomposites for Tissue Engineering.Nanosci. Nanotechnol 2010, 10, 711. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, B.O. Infrared studies of apatites. I. Vibrational assignments for calcium, strontium, and barium hydroxyapatite utilizing isotopic substitution. Inorg. Chem. 1974, 13, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalia, D.; Raúl, G.; Carlos, P.; Yaimara, S.; Ruth, E. Chitosan/apatite composite beads prepared by in situ generation of apatiteor Si-apatite nanocrystals. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 466–476. [Google Scholar]
- Manjubala, I.; Scheler, S.; Bossert, J.; Jandt, K.D. Mineralisation of chitosan scaffolds with nano-apatite formation by double diffusion technique. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilchenko, S.N.; Kalinkevich, O.V.; Pogorelov, M.V.; Kalinkevich, A.N.; Sklyar, A.M.; Kalinichenko, T.G.; Ilyashenko, V.Y.; Starikov, V.V.; Bumeyster, V.I.; Sikora, V.Z.; et al. Chitosan–hydroxyapatite composite biomaterials made by a one step co-precipitation method: Preparation, characterization and in vivo tests. J. Biol. Phys. 2009, 9, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mande, Q.; Aimei, D.; Pan, Y.; Miao, N.; Yidan, W.; Guoyi, B. Preparation, Microanalysis and Performance of Hap/Cs-Cmc Composite Materials. Am. J. Mater. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.C.; Po, Q.H. Preparation of chitosan coated magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and application for adsorption of reactive Blue 19 and Ni2+ ions. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 273082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapuan, S.M.; Pua, F.L.; El-Shekeil, Y.A.; Al-Oqla, F.M. Mechanical properties of soil buried kenaf fibre reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, P.; Shikha, S.; Pardeep, S. Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1445–S1451. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, M.; Alkan, M.; Türkyilmaz, A.; Özdemir, Y.J. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto perlite.hazard. Materials 2004, 109, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Aljeboree, M.; Alshirifi, N.; Alkaim, F. Kinetics and equilibrium study for the adsorption of textile dyes on coconut shell activated carbon. Arab. J. chem. 2017, 10, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, W.; Plazinski, W. Studies of the Kinetics of Solute Adsorption at Solid/Solution Interfaces: On the Possibility of Distinguishing between the Diffusional and the Surface Reaction Kinetic Models by Studying the Pseudo-First-order Kinetics. J. Physic. Chem. C. 2007, 111, 15100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.; Mohamed, S. Adsorption of copper ions and alizarin red S from aqueous solutions onto a polymeric nanocomposite in single and binary systems. Turk. J. Chem. 2017, 41, 967–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V. Modeling of batch sorber system: Kinetic, mechanistic, and thermodynamic modelling. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, A.; Öncü, M.; Özcan, S. Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite. Colloid Surf. A 2006, 277, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jlil, A. Adsorption of cobalt ions from waste water on activated Saudi clays. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Chen, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, X. Sorption of Ni2+ on Na–rectorite studied by batch and spectroscopy methods. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Tuzen, M.; Soylak, M. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(III) from aqueous solution onCeltek clay. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, S.S.; Rauf, N. Thermodynamics studies of Nickel (II) adsorptions onto bentonite from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2003, 35, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S. Selection of Optimum Sorption Isotherm. Carbon 2004, 42, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naruporn, M. Nano-size Hydroxyapatite Powders Preparation by Wet-Chemical Precipitation RouteJournal of Metals. Mater. Miner. 2008, 18, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, D. Sonochemically Synthesized Beta-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Graphene Oxide and its Efficient Role in Adsorption of Water Soluble Brilliant Green Dye. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds and composite all are available from the authors. |












| Lagrange (Pseudo-First-Order) | Kads (min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BG dye | 0.02 | 30.2 | 0.998 |
| (pseudo-second-order) | |||
| k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| BG dye | 2.05 | 30.2 | 0.995 |
| Bangham | |||
| A | Ko | R2 | |
| BG dye | 0.02 | 9.2 | 0.985 |
| Langmuir | |||
| b (L·mg−1) | Qmax (mg·g−1) | R2 | |
| BG dye | 10.3 | 49.1 | 0.987 |
| Freundlich | |||
| Kf (moln−1 Ln g−1) | n | R2 | |
| BG dye | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.980 |
| D-R model | |||
| E (kJ mol−1) | q(D-R) (mg·g−1) | R2 | |
| BG dye | 8.2 | 29.9 | 0.985 |
| BG Dye | T (K) | lnKd | ∆Go (kJ·mol−1) | ∆Ho (J·mol−1) | ∆So (J·mol−1·K−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 mg∙L−1 | 288 | 6.7 | −16.2 | 20.1 | 29.9 | 0.998 |
| 298 | 6.9 | −17.1 | 0.997 | |||
| 313 | 7.1 | −8.51 | 0.988 | |||
| 323 | 7.3 | −19.6 | 0.989 | |||
| 80 mg∙L−1 | 288 | 5.9 | −14.1 | 19.8 | 29.5 | 0.995 |
| 298 | 6.3 | −15.6 | 0.985 | |||
| 313 | 6.9 | −17.9 | 0.958 | |||
| 323 | 7.1 | −19.0 | 0.997 |
| Chemical Formula | Molecular Weight | Color Index | λmax |
|---|---|---|---|
| C27H33N2.HO4S | 482.64 g/mol | 42040 | 626 nm |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragab, A.; Ahmed, I.; Bader, D. The Removal of Brilliant Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Nano Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite as a Sorbent. Molecules 2019, 24, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050847
Ragab A, Ahmed I, Bader D. The Removal of Brilliant Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Nano Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite as a Sorbent. Molecules. 2019; 24(5):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050847
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagab, Ahmed, Inas Ahmed, and Dina Bader. 2019. "The Removal of Brilliant Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Nano Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite as a Sorbent" Molecules 24, no. 5: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050847
APA StyleRagab, A., Ahmed, I., & Bader, D. (2019). The Removal of Brilliant Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Nano Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Composite as a Sorbent. Molecules, 24(5), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050847




