NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
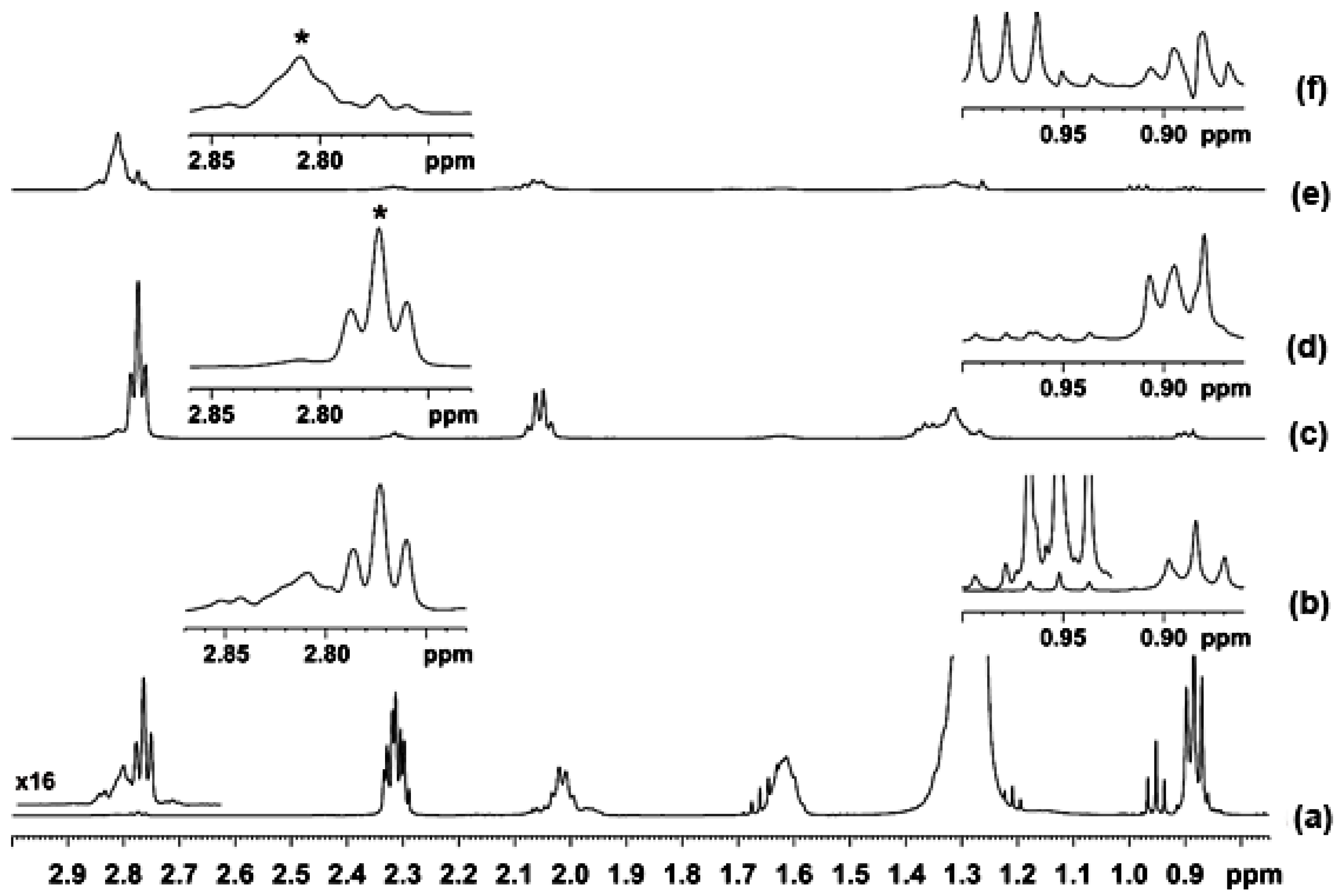
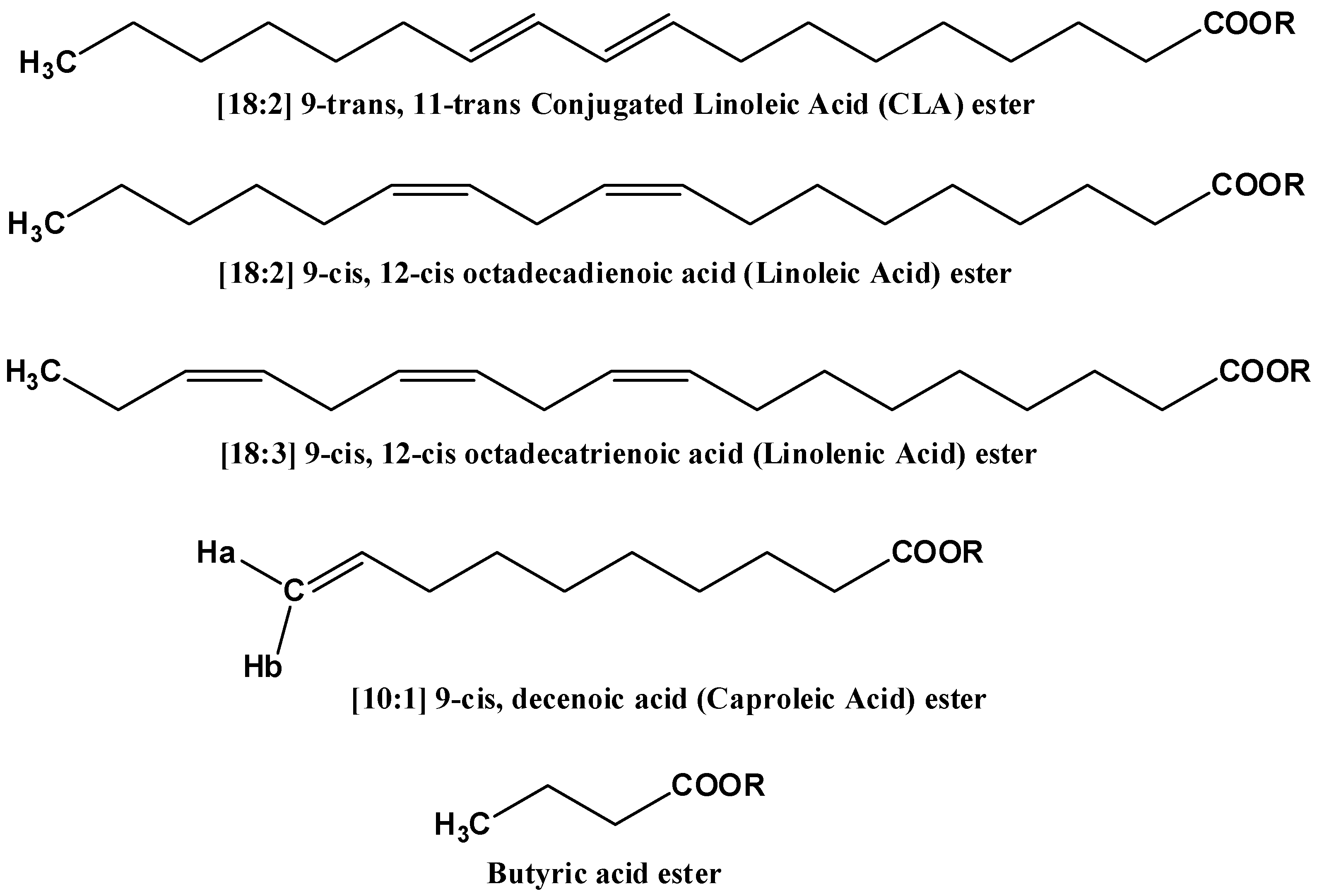
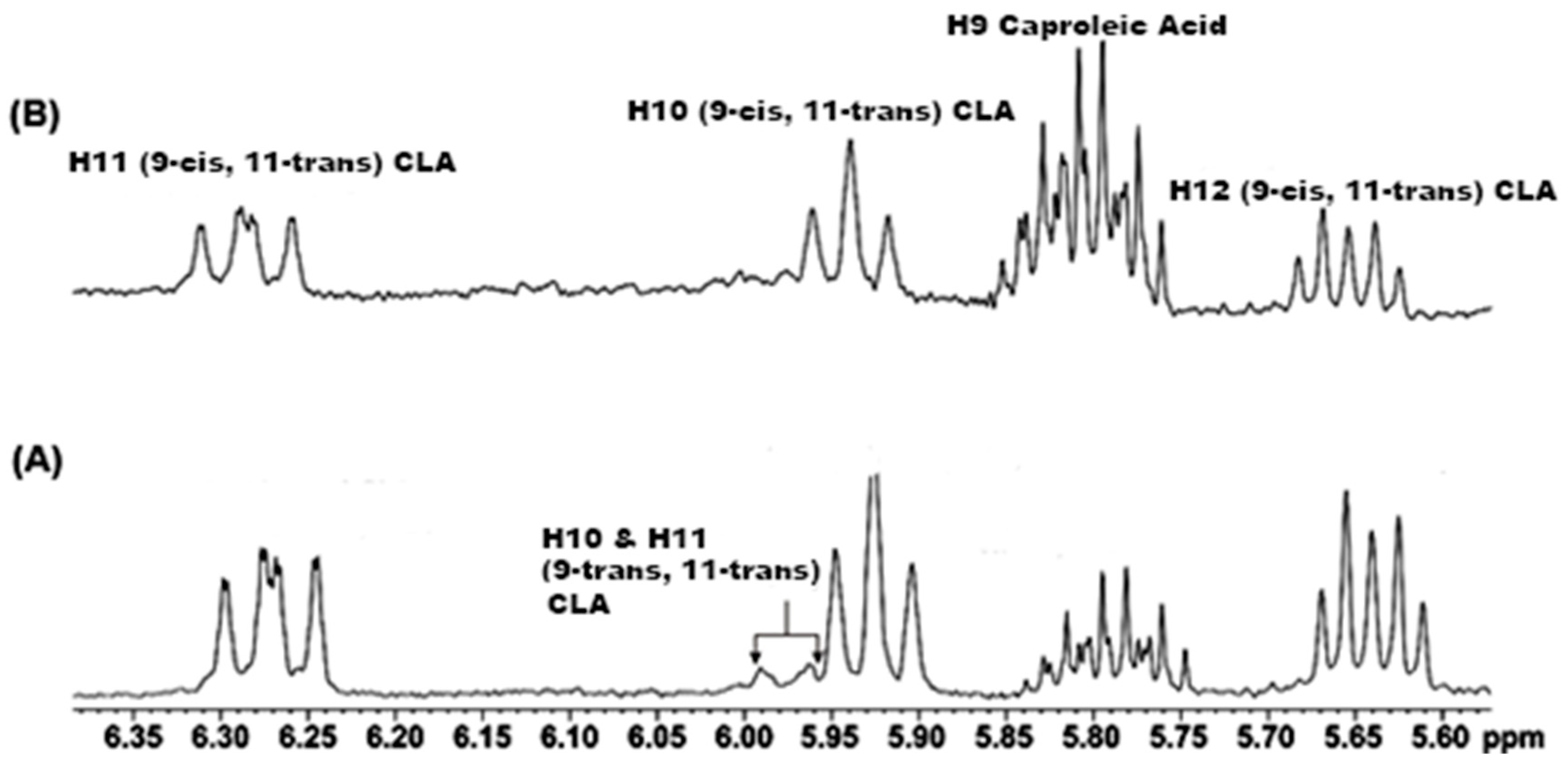
2.1. Spectral Analysis of Minor Components Using 1D 1H and 1D 1H TOCSY NMR
2.2. Quantification Using 1D NMR
2.3. Analytical Performance Characteristics
2.3.1. Robustness
2.3.2. Precision
2.4. Metabolomic Study of Organic and Conventional Milk Samples
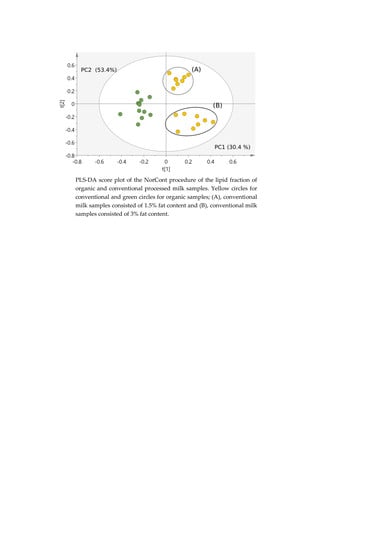
2.4.1. Classification of Milk Samples
2.4.2. Marker Identification and Quantification
2.4.3. Nutritive Value of Organic Versus Conventional Milk Regarding Their Lipid Composition
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Milk Sample Collection
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. NMR Analysis
3.4. Multivariate Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karoui, R.; De Baerdemaeker, J. A review of the analytical methods coupled with chemometric tools for the determination of the quality and identity of dairy products. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H.; Van Hekken, D.L. Dairy products and health: Recent insights. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9381–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnould, V.M.-R.; Soyeurt, H. Genetic variability of milk fatty acids. J. Appl. Genet. 2009, 50, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B.; Bertram, H.C. Nuclear magnetic resonance metabonomics reveals strong association between milk metabolites and somatic cell count in bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Larsen, L.B.; Bertram, H.C. NMR-based milk metabolomics. Metabolites 2013, 3, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzamaloukas, O.; Orford, M.; Miltiadou, D.; Papachristoforou, C. Partial suckling of lambs reduced the linoleic and conjugated linoleic acid contents of marketable milk in Chios ewes. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.P.; Dunshea, F.R.; Doyle, P.T. Effects of nutrition and management on the production and composition of milk fat and protein: A review. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2004, 55, 1009–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.; Zemel, M.B. Functional properties of whey, whey components, and essential amino acids: Mechanisms underlying health benefits for active people. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2003, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, P.J.; DiRienzo, D.B.; Miller, G.D. Major scientific advances with dairy foods in nutrition and health. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwood, P.C.; Pickering, J.E.; Givens, D.; Gallacher, J.E. The consumption of milk and dairy foods and the incidence of vascular disease and diabetes: An overview of the evidence. Lipids 2010, 45, 925–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonthuis, M.; Hughes, M.C.B.; Ibiebele, T.I.; Green, A.C.; van der Pols, J.C. Dairy consumption and patterns of mortality of Australian adults. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Hakansson, N.N.; Wolk, A. Association between dairy food consumption and weight change over 9 y in 19,352 perimenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Bergkvist, L.; Wolk, A. High-fat dairy food and conjugated linoleic acid intakes in relation to colorectal cancer incidence in the Swedish mammography cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendel, B.H.; Wester, T.J.; Morel, P.C.H.; Tavendale, M.H.; Deadman, C.; Shadbolt, N.M.; Otter, D.E. Organic and conventionally produced milk-an evaluation of factors influencing milk composition. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 9, 721–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Spangler, C.; Brandeau, M.L.; Hunter, G.E.; Bavinger, J.C.; Pearson, M.; Eschbach, P.J.; Sundaram, V.; Liu, H.; Schirmer, P.; Stave, C.; et al. Are organic foods safer or healthier than conventional alternatives?: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummer, R.R. Effect of feed on the composition of milk fat. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3244–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilzer, A.; Park, Y. Implication of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2012, 52, 488–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riediger, N.D.; Othman, R.A.; Suh, M.; Moghadasian, M.H. A systemic review of the roles of n-3 fatty acids in health and disease. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2009, 109, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Lu, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, G. A data preprocessing strategy for metabolomics to reduce the mask effect in data analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2015, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudonck, K.J.; Mitchell, M.W.; Wulff, J.; Rayals, J.A. Characterization of the biochemical variability of bovine milk using metabolomics. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Wanasundara, P.K.J.P.D. Food Lipids: Chemistry, Nutrition and Biotechnology. In Food Lipids, Chemistry, Nutrition and Biotechnology; Akoh, D.B., Min, C.C., Eds.; Marcel Decker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, T.W.; Brown, S.H.O.; Blanksby, S.J. Structural lipidomics. In Lipidomics: Technologies and Applications; Ekroos, K., Ed.; Wiley VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 99–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hancock, S.E.; Poad, B.J.; Batarseh, A.; Abbott, S.K.; Mitchell, T.D. Advances and unresolved challenges in the structural characterization of isomeric lipids. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, I.; Aubourg, S.; Gallardo, J.M.; Pérez-Martín, R. Comparison of six methylation methods for analysis of the fatty acid composition of albacore lipid. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1992, 27, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Aursand, M.; Hirata, Y.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Wada, S.; Nonaka, M. Nondestructive quantitative determination of docosahexaenoic acid and n−3 fatty acids in fish oils by high-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuente, A.M.; Luna, P.; Juárez, M. Chromatographic techniques to determine conjugated linoleic acid isomers. Trends Anal. Chem. 2006, 25, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, L. NMR-based metabolomics: From sample preparation to applications in nutrition research. Progr. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2014, 83, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghi, L.; Picone, G.; Capozzi, F. Nuclear magnetic resonance for foodomics beyond food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimigno, A.; Marincola, F.C.; Dellarosa, N.; Picone, G.; Laghi, L. Definition of food quality by NMR-based foodomics. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.S.; Almstetter, M.F.; Schlamberger, G.; Nürnberger, N.; Dettmer, K.; Oefner, P.J.; Meyer, H.H.; Wiedemann, S.; Gronwald, W. Nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry-based milk metabolomics in dairy cows during early and late lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.S.; Buttchereit, N.; Miemczyk, S.P.; Immervoll, A.-K.; Louis, C.; Wiedemann, S.; Junge, W.; Thaller, G.; Oefner, P.J.; Gronwald, W. NMR metabolomic analysis of dairy cows reveals milk glycerophosphocholine to phosphocholine ratio as prognostic biomarker for risk of ketosis. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincola, F.C.; Noto, A.; Caboni, P.; Reali, A.; Barberini, L.; Lussu, M.; Santoru, M.L.; Atzori, L.; Fanos, V. A metabolomic study of preterm human and formula milk by high resolution NMR and GC/MS analysis: Preliminary results. J. Matern. Fetal Neon. Med. 2012, 25 (Suppl. 5), 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundekilde, U.K.; Frederiksen, P.D.; Clausen, M.R.; Larsen, L.B.; Bertram, H.C. Relationship between the metabolite profile and technological properties of bovine milk from two dairy breeds elucidated by NMR-based metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7360–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandri, E.; Ahmed, R.; Siddiqui, H.; Choudhary, I.M.; Tsiafoulis, G.C.; Gerothanassis, P.I. High resolution NMR spectroscopy as a structural and analytical tool for unsaturated lipids in solution. Molecules 2017, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, M.A.; Mazzilli, V.; Sgaramella, A.; Ghelli, S.; Paolo Fanizzi, F.; Sacco, A. 1H NMR characterization of milk lipids: A comparison between cow and buffalo milk. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2004, 81, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, G.; Lamanna, R.; Trivellone, E.; Motta, A. 13C NMR Spectra of TAG: An easy way to distinguish milks from different animal species. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2002, 79, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievano, E.; Pasini, G.; Cozzi, G.; Mammi, S. Identification of the production chain of Asiago d’Allevo cheese by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and principal component analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7208–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erich, S.; Schill, S.; Annweiler, E.; Waiblinger, H.-U.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W.; Monakhova, Y.B. Combined chemometric analysis of 1H NMR, 13C NMR and stable isotope data to differentiate organic and conventional milk. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scano, P.; Anedda, R.; Melis, M.P.; Dessi, M.A.; Lai, A.; Roggio, T. 1H- and 13C-NMR characterization of the molecular components of the lipid fraction of Pecorino Sardo cheese. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, H.L. Fatty acids in bovine milk fat. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 52, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanouil, C.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Alivertis, D.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Miltiadou, D.; Tzakos, A.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Selective One-dimensional total correlation spectroscopy nuclear magnetic resonance experiments for a rapid identification of minor components in the lipid fraction of milk and dairy products: Toward spin chromatography? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5381–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, D.; Turner, T.D.; Jensen, J.; Pilfold, J.L.; Church, J.S.; Donkor, K.K.; Cinel, B. Rapid determination of total conjugated linoleic acid concentrations in beef by 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeou, S.; Papaemmanouil, C.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Miltiadou, D.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. NMR in dairy lipid research: Improving the fatty acid profile of sheep milk by olive cake supplementation. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Modern Trends and Applications, Kalamata, Greece, 20–24 September 2015; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Skarlas, T.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Miltiadou, D.; Gerothanassis, I.P. Direct nuclear magnetic resonance identification and quantification of geometric isomers of conjugated linoleic acid in milk lipid fraction without derivatization steps: Overcoming sensitivity and resolution barriers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 821, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danzer, K. Analytical Chemistry. Theoretical and Metrological Fundamentals; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Filzmoser, P.; Walczak, B. What can go wrong at the data normalization step for identification of biomarkers? J. Chromatogr. 2014, 1362, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, T.; Lalande, J.; Ballaysac, S.; Kluza, J.; Gilard, V.; Marchetti, P.; Malet-Martino, M. Identification and Data Processing Methods in Metabolomics; Future Science Book Series Ltd.: London, UK, 2015; pp. 140–153. [Google Scholar]
- Givens, D.I. The role of animal nutrition in improving the nutritive value of animal-derived foods in relation to chronic disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givens, D.I. Dairy products: Good or bad for cardiometabolic disease? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H.; Puniya, A.K.; Singh, K.; Jain, S.; Marotta, F. Conjugated linoleic acid: Sources, synthesis and potential health benefits- an overview. Curr. Top. Nutraceut. Res. 2007, 5, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Smit, L.A.; Baylin, A.; Campos, H. Conjugated linoleic acid in adipose tissue and risk of myocardial infarction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, G.L. Dietary n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: From biochemistry to clinical implications in cardiovascular prevention. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Evolutionary aspects of diet, the omega-6/omega-3 ratio and genetic variation: Nutritional implications for chronic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahreis, G.; Fritsche, J.; Steinhart, H. Monthly variations of milk composition with special regard to fatty acids depending on season and farm management systems - Conventional versus ecological. Lipid/Fett 1996, 98, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, P.; Fedele, E.; Iannibelli, L.; Marzillo, G. Fat-soluble vitamin contents and fatty acid composition in organic and conventional Italian dairy products. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.A.; Innocent, G.; Grove-White, D.; Cripps, P.; McLean, W.G.; Howard, C.V.; Mihm, M. Comparing the fatty acid composition of organic and conventional milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Taylor, D.S.; Yu-Poth, S.; Huth, P.; Moriarty, K.; Fishell, V.; Hargrove, R.L.; Zhao, G.; Etherton, T.D. Polyunsaturated fatty acids in the food chain in the United States. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71 (Suppl. 1), 179S–188S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids: Evolutionary aspects. World Rev. Nutr. Diet. 2003, 92, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio: Health implications. OCL Oleagineux Corps Gras Lipides 2010, 17, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massiera, F.; Barbry, P.; Guesnet, P.; Joly, A.; Luquet, S.; Moreilhon-Brest, C.; Mohsen-Kanson, T.; Amri, E.Z.; Ailhaud, G.A. Western-like fat diet is sufficient to induce a gradual enhancement in fat mass over generations. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2352–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasbalg, T.L.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Ramsden, C.E.; Majchrzak, S.F.; Rawlings, R.R. Changes in consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids in the United States during the 20th century. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 950–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caterina, R. n-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbrook, C.M.; Butler, G.; Latif, M.A.; Leifert, C.; Davis, D.R. Organic production enhances milk nutritional quality by shifting fatty acid composition: A United States-wide, 18-month study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancliffe, R.A.; Thorpe, T.; Zemel, M.B. Dairy attentuates oxidative and inflammatory stress in metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönfeldt, H.C.; Hall, N.G.; Smit, L.E. The need for country specific composition data on milk. Food Res. Intern. 2012, 47, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 889/2008 of 5 September 2008 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007 on organic production and labelling of organic products with regard to organic production, labelling and control. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 250, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh, J.; Rance, M. Suppression of cross-relaxation effects in TOCSY spectra via a modified DIPSI-2 mixing sequence. J. Magn. Reson. 1992, 96, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, R.; Cagliali, L.R. The potentiality of NMR-based metabolomics in food science and food authentication assessment. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ezernieks, V.; Wang, J.; Arachchillage, N.W.; Garne, J.B.; Wales, W.J.; Cocks, B.G.; Rochfort, S. Heat stress in dairy cattle alters lipid composition of milk. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rochfort, S.; Cocks, B. Milk lipidomics: What we know and what we don’t. Prog. Lipid. Res. 2018, 71, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds conjugated (9-cis, 11-trans) 18:2 linoleic acid and conjugated (9-trans, 11-trans) 18:2 linoleic acid are available from the authors. |




| Metabolite | OR Samples | OP Samples | CR Samples | CP Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (9-cis, 11-trans) 18:2 CLA d | 0.49 ± 0.06 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 0.30 ± 0.08 | 0.31 ± 0.03 |
| p-value b | 3.98 × 10−9 | |||
| p-value c | 2.56 × 10−11 | |||
| Caproleic acid | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.03 |
| p-value b | 3.47 × 10−5 | |||
| p-value c | 4.72 × 10−12 | |||
| α-linolenic acid | 0.92 ± 0.08 | 0.88 ± 0.08 | 0.65 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.05 |
| p-value b | 4.32 × 10−18 | |||
| p-value c | 2.45 × 10−12 | |||
| Linoleic acid | 2.67 ± 0.35 | 2.66 ± 0.22 | 1.72 ± 0.24 | 1.73 ± 0.11 |
| p-value b | 1.12 × 10−15 | |||
| p-value c | 9.23 × 10−15 | |||
| –CH2–CH=CH– | 54.71 ± 2.68 | 54.47 ± 2.47 | 46.79 ± 3.45 | 47.98 ± 1.96 |
| p-value b | 9.38 × 10−9 | |||
| p-value c | 1.61 × 10−9 | |||
| UFA | 28.00 ± 1.19 | 28.07 ± 1.36 | 24.33 ± 1.75 | 24.32 ± 1.22 |
| p-value b | 7.48 × 10−8 | |||
| p-value c | 1.30 × 10−8 |
| Protons | Chemical Shift [δ (ppm)] | Relaxation Time T1 (s) |
|---|---|---|
| CH(12)=CH(11)—CH(10)=CH(9) a | 6.28 | 1.5 |
 | 5.80 (H-9) | 3.2 |
| 4.99 (H-10) b | 3.2 | |
| CH=CH–CH2–CH=CH c | 2.81 | 1.5 |
| CH=CH–CH2–CH=CH d | 2.77 | 1.5 |
| C(2)H2COOR | 2.33 | 2.0 |
| CH2–CH=CH– | 2.02 | 2.0 |
| CH3 e | 0.95 | 1.7 |
| CH3 f | 0.88 | 1.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Papaemmanouil, C.; Alivertis, D.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Miltiadou, D.; Balayssac, S.; Malet-Martino, M.; Gerothanassis, I.P. NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk. Molecules 2019, 24, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061067
Tsiafoulis CG, Papaemmanouil C, Alivertis D, Tzamaloukas O, Miltiadou D, Balayssac S, Malet-Martino M, Gerothanassis IP. NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061067
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsiafoulis, Constantinos G., Christina Papaemmanouil, Dimitrios Alivertis, Ouranios Tzamaloukas, Despoina Miltiadou, Stéphane Balayssac, Myriam Malet-Martino, and Ioannis P. Gerothanassis. 2019. "NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061067
APA StyleTsiafoulis, C. G., Papaemmanouil, C., Alivertis, D., Tzamaloukas, O., Miltiadou, D., Balayssac, S., Malet-Martino, M., & Gerothanassis, I. P. (2019). NMR-Based Μetabolomics of the Lipid Fraction of Organic and Conventional Bovine Milk. Molecules, 24(6), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061067