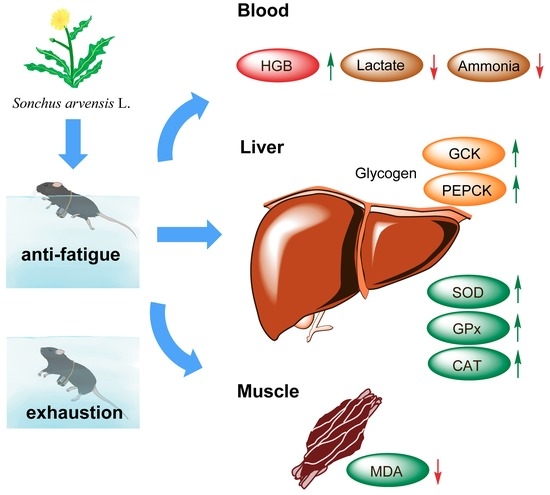
Anti-Fatigue Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. in Exercise Trained Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of SA on Exhaustive Swimming Test in Exercise Trained Mice
2.2. Histological Examination on Mice Hind Leg Muscle Structure in Exercise Trained Mice
2.3. Effects of SA on Blood-Oxygen Related Parameters in Exercise Trained Mice
2.4. Effects of SA on Liver and Muscle Glycogen Levels
2.5. Effects of SA on the Glycogen Synthesis Related Gene Expressions in Mice Liver and Muscle
2.6. SA Ameliorated Oxidative Stress in Mice Liver and Muscle
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Preparation of SA and Determination of Major Components
3.2. Animal Experimental Design
3.3. Swimming Training Exercise and Exhaustion Exercise Test
3.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and MRI
3.5. Routine Blood Tests
3.6. Analyses of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of Mice Liver and Muscle
3.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Analyses
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chi, A.; Li, H.; Kang, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Tang, L. Anti-fatigue activity of a novel polysaccharide conjugates from Ziyang green tea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, T.H.; Nielsen, O.B.; Lamb, G.D.; Stephenson, D.G. Intracellular acidosis enhances the excitability of working muscle. Science 2004, 305, 1144–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Shieh, M.-J.; Kuo, S.-L.; Lee, C.-L.; Pan, T.-M. Effect of red mold rice on antifatigue and exercise-related changes in lipid peroxidation in endurance exercise. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Lv, J.; Lo, Y.M.; Cui, S.W.; Hu, X.; Fan, M. Effects of oat β-glucan on endurance exercise and its anti-fatigue properties in trained rats. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.L.; Ren, F.; Huang, W.; Ding, R.T.; Zhou, Q.S.; Liu, X.W. Anti-fatigue activity of extracts of stem bark from Acanthopanax senticosus. Molecules 2010, 16, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Huang, W.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Wang, M.-F.; Ho, C.-S.; Huang, W.-P.; Hou, C.-C.; Chuang, H.-L.; Huang, C.-C. Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) fruit extract improves physical fatigue and exercise performance in mice. Molecules 2012, 17, 11864–11876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamou, B.; Taiwe, G.S.; Hamadou, A.; Houlray, J.; Atour, M.M.; Tan, P.V. Antioxidant and antifatigue properties of the aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera in rats subjected to forced swimming endurance test. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, D.-Z.; Yu, X.-F.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Zou, Z.-D. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of six edible wild plants (Sonchus spp.) in China. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkreathy, H.M.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.R.; Sahreen, S. CCl4 induced genotoxicity and DNA oxidative damages in rats: Hepatoprotective effect of Sonchus arvensis. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-González, L.; Cienfuegos-Pecina, E.; Perales-Quintana, M.M.; Alarcon-Galvan, G.; Muñoz-Espinosa, L.E.; Pérez-Rodríguez, E.; Cordero-Pérez, P. Nephroprotective effect of sonchus oleraceus extract against kidney injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion in wistar rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.A. Evaluation of flavonoids and diverse antioxidant activities of Sonchus arvensis. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Song, G.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Chicoric acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress via promoting the Keap1/Nrf2 transcriptional signaling pathway in BV-2 microglial cells and mouse brain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Chicoric acid supplementation prevents systemic inflammation-induced memory impairment and amyloidogenesis via inhibition of NF-κB. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.P.; Jang, S.; Sung, Y.Y.; Sun, D.P.; Kim, H.K. Akebia quinata Decaisne aqueous extract acts as a novel anti fatigue agent in mice exposed to chronic restraint stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Gelabert-Rebato, M.; Wiebe, J.C.; Martin-Rincon, M.; Gericke, N.; Perez-Valera, M.; Curtelin, D.; Galvan-Alvarez, V.; Lopez-Rios, L.; Morales-Alamo, D.; Jal, C. Mangifera indica L. Leaf extract in combination with luteolin or quercetin enhances VO2 peak and peak power output, and preserves skeletal muscle function during ischemia-reperfusion in humans. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, A.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Shen, Z. Metabolic mechanism of a polysaccharide from Schisandra chinensis to relieve chronic fatigue syndrome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Hui, A.; Du, B.; Wang, T.; Meng, L.; Bian, H.; Wu, Z. Purification, characterization and anti-fatigue activity of polysaccharide fractions from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench). Food Funct. 2018, 9, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, X.; Yan, L.; Li, J.; He, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wei, B.; Ye, Z.; Jie, W. Extraction, purification and anti-fatigue activity of γ-aminobutyric acid from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, T.-H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-P.; Hung, S.-W.; Wu, C.-P.; Chuang, H.-L. Supplementation with beef extract improves exercise performance and reduces post-exercise fatigue independent of gut microbiota. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Di, W.; Lv, S.; Tang, L.; Ding, G. Targeted molecular magnetic resonance imaging detects brown adipose tissue with ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3619548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, B.; Rehman, H.J.; Minn, H. Interpretation of hemoglobin A1C in primary care setting. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2019, 9, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.-H.; Paik, I.-Y.; Jacobs, K. Regulation of blood glucose homeostasis during prolonged. Mol. Cells 2007, 23, 272–279. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, H.; Ma, H.; Lin, H.; Putheti, R. Antifatigue activity of water extracts of Toona sinensis Roemor leaf and exercise-related changes in lipid peroxidation in endurance exercise. J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Bingquan, C.; Weiqiao, H.; Yuanzao, L. Experimental study of the anti-fatigue and anti-hypoxia function of phyllanthus emblica L. in Mice. Mod. Chin. Med. 2008, 6, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian, P. Molecular physiology of mammalian glucokinase. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Lucas, A.; Duarte, J.A.G.; Sunny, N.E.; Satapati, S.; He, T.; Fu, X.; Bermúdez, J.; Burgess, S.C.; Perales, J.C. PEPCK-M expression in mouse liver potentiates, not replaces, PEPCK-C mediated gluconeogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Kalhan, S.C.; Hanson, R.W. What is the metabolic role of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase? J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27025–27029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadda, A.A.; Sallam, R.M. Reactive oxygen species in health and disease. BioMed. Res. Int. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Liu, Z.; Cadenas, E. Mitochondrial function in ageing: Coordination with signalling and transcriptional pathways. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 2025–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R. Initial events in exercise-induced muscular injury. Med. Sci. Sport. Exer. 1990, 22, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Ren, B.; Guo, R.; Zhang, W.; Ma, S.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Supplementation of lycopene attenuates oxidative stress induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via Nrf2/NF-κB transcriptional pathway. Food Chem. Toxico. 2017, 109, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giera, M.; Lingeman, H.; Niessen, W.M. Recent advancements in the LC-and GC-based analysis of malondialdehyde (MDA): A brief overview. Chromatographia 2012, 75, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Kitts, D. Role of chlorogenic acids in controlling oxidative and inflammatory stress conditions. Nutrients 2016, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-S.; Lii, C.-K.; Lin, A.-H.; Yeh, Y.-W.; Yao, H.-T.; Li, C.-C.; Wang, T.-S.; Chen, H.-W. Protection by chrysin, apigenin, and luteolin against oxidative stress is mediated by the Nrf2-dependent up-regulation of heme oxygenase 1 and glutamate cysteine ligase in rat primary hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro Smiderle, F.; Morales, D.; Gil-Ramírez, A.; Inara de Jesus, L.; Gilbert-López, B.; Iacomini, M.; Soler-Rivas, C. Evaluation of microwave-assisted and pressurized liquid extractions to obtain β-d-glucans from mushrooms. Carbohydr Polym. 2017, 156, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, A.; Lamien, C.E.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O.G. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Luo, S.; Chu, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Extract of sesame cake and sesamol alleviate chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and memory deficits. J. Funct Foods 2018, 42, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. are available from the authors. |





| Routine Blood Test | Control | EC | EC + LSA | EC + HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White blood cell (109/L) | 3.72 ± 0.74 1 | 3.02 ± 1.04 | 2.72 ± 0.87 | 2.56 ± 1.30 |
| Lymphocyte (109/L) | 2.54 ± 0.54 | 2.35 ± 0.64 | 2.03 ± 0.68 | 2.00 ± 1.01 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 69.54 ± 7.69 | 79.7 ± 8.42 | 74.14 ± 4.82 | 78.26 ± 5.71 |
| Monocyte (109/L) | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.062 ± 0.02 |
| Monocyte (%) | 2.62 ± 0.52 | 2.06 ± 0.92 | 2.04 ± 1.06 | 2.84 ± 1.55 |
| Red blood cell (g/L) | 7.74 ± 0.21 | 8.06 ± 0.83 | 8.54 ± 0.56 | 8.21 ± 0.48 |
| Hemoglobin (109/L) | 112.50 ± 2.65 | 111.33 ± 8.08 | 129.67 ± 6.51 | 124.33 ± 4.16 * |
| Hematocrit (%) | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 834.40 ± 154.77 | 842.50 ± 83.24 | 807.60 ± 75.48 | 749.75 ± 77.48 |
| Antioxidant Enzymes | Control | EC | EC + LSA | EC + HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| liver | ||||
| SOD (U/g prot) 1 | 193.76 ± 3.67 2 | 193.66 ± 22.41 | 203.64 ± 27.92 | 248.09 ± 13.89 * |
| CAT (U/mL) | 45.29 ± 8.99 | 61.58 ± 0.80 | 86.37 ± 13.90 | 82.28 ± 5.25 |
| MDA (nmol/g prot) | 30.53 ± 6.62 | 26.42 ± 4.99 | 22.21 ± 3.14 | 20.09 ± 8.48 |
| muscle | ||||
| SOD (U/g prot) | 94.73 ± 13.43 | 104.49 ± 12.29 | 102.11 ± 15.59 | 97.98 ± 5.83 |
| CAT (U/mL) | 2.46 ± 1.64 | 2.71 ± 0.79 | 2.63 ± 0.19 | 2.67 ± 1.98 |
| MDA (nmol/g prot) | 36.85 ± 1.48 | 42.42 ± 9.11 | 36.17 ± 8.21 | 25.36 ± 0.69 * |
| Major Components | Contents (mg/g) |
|---|---|
| Total polysaccharide | 64.8 ± 0.74 1 |
| Total polyphenols | 82.17 ± 2.15 |
| Total flavonoids | 139.18 ± 7.06 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 5.35 ± 3.24 |
| Luteolin | 24.92 ± 5.85 |
| Chicoric acid | 19.84 ± 1.77 |
| Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | |
|---|---|---|
| Gck | AGTATGACCGGATGGTGGATGAA | CCAGCTTAAGCAGCACAAGTCGTA |
| Pepck | ACTGTTGGCTGGCTCTCACTG | GGGAACCTGGCGTTGAATGC |
| Cat | CGTTCGATTCTCCACAGTCA | CCCACAAGATCCCAGTTACC |
| Gpx-1 | AAGGCTCACCCGCTCTTTAC | ACACCGGAGACCAAATGATG |
| Gapdh | TGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATGA | TGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCTGT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, T.; Wu, D.; Sun, K.; Tan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Ren, B.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Anti-Fatigue Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. in Exercise Trained Mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061168
Yuan T, Wu D, Sun K, Tan X, Wang J, Zhao T, Ren B, Zhao B, Liu Z, Liu X. Anti-Fatigue Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. in Exercise Trained Mice. Molecules. 2019; 24(6):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061168
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Tian, Di Wu, Keyu Sun, Xintong Tan, Jia Wang, Tong Zhao, Bo Ren, Beita Zhao, Zhigang Liu, and Xuebo Liu. 2019. "Anti-Fatigue Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. in Exercise Trained Mice" Molecules 24, no. 6: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061168
APA StyleYuan, T., Wu, D., Sun, K., Tan, X., Wang, J., Zhao, T., Ren, B., Zhao, B., Liu, Z., & Liu, X. (2019). Anti-Fatigue Activity of Aqueous Extracts of Sonchus arvensis L. in Exercise Trained Mice. Molecules, 24(6), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24061168