Composition and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide Extracted from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) Seed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
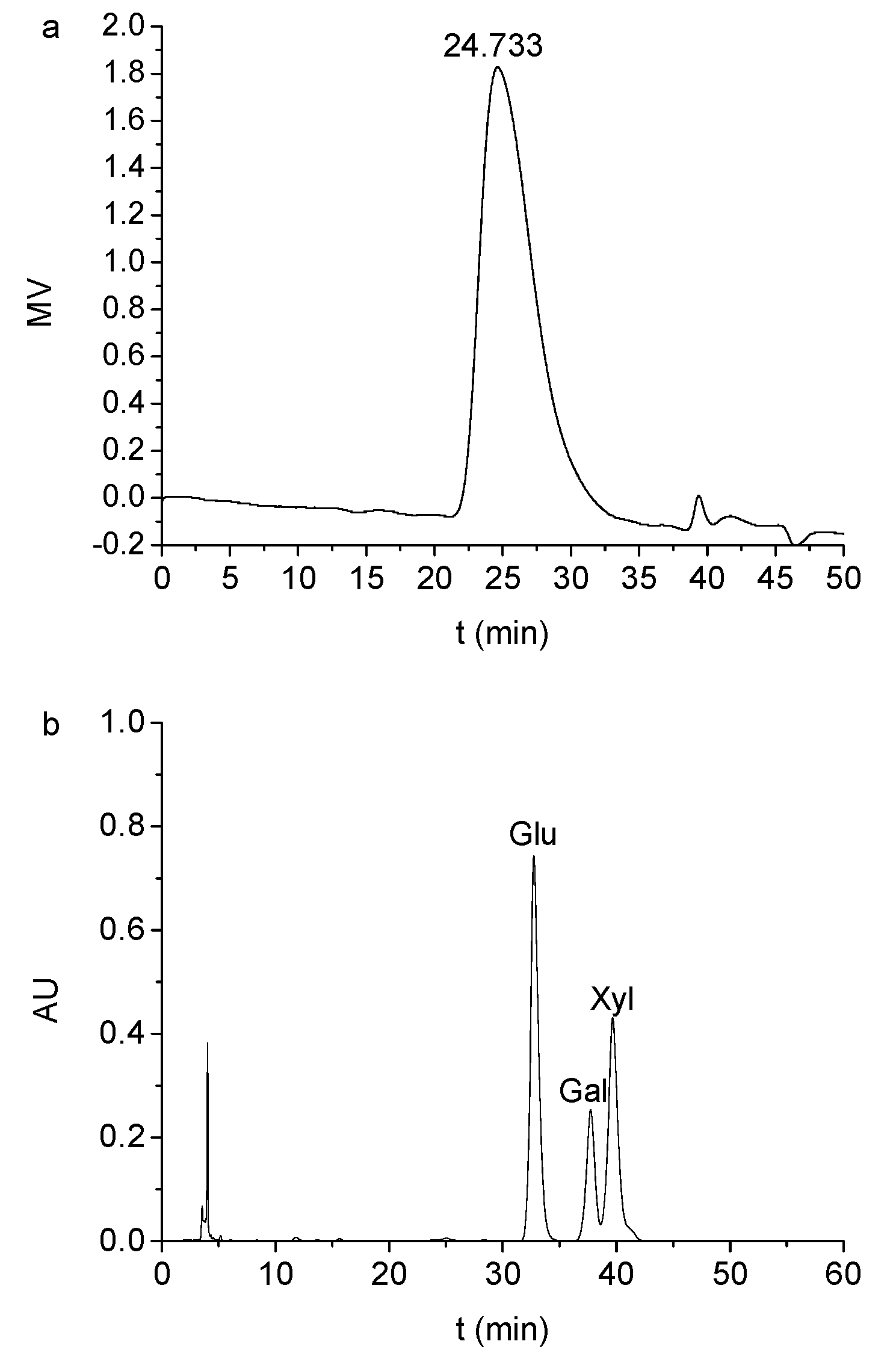
2.1. Chemical Composition and Molecular Weight Analysis of TSP
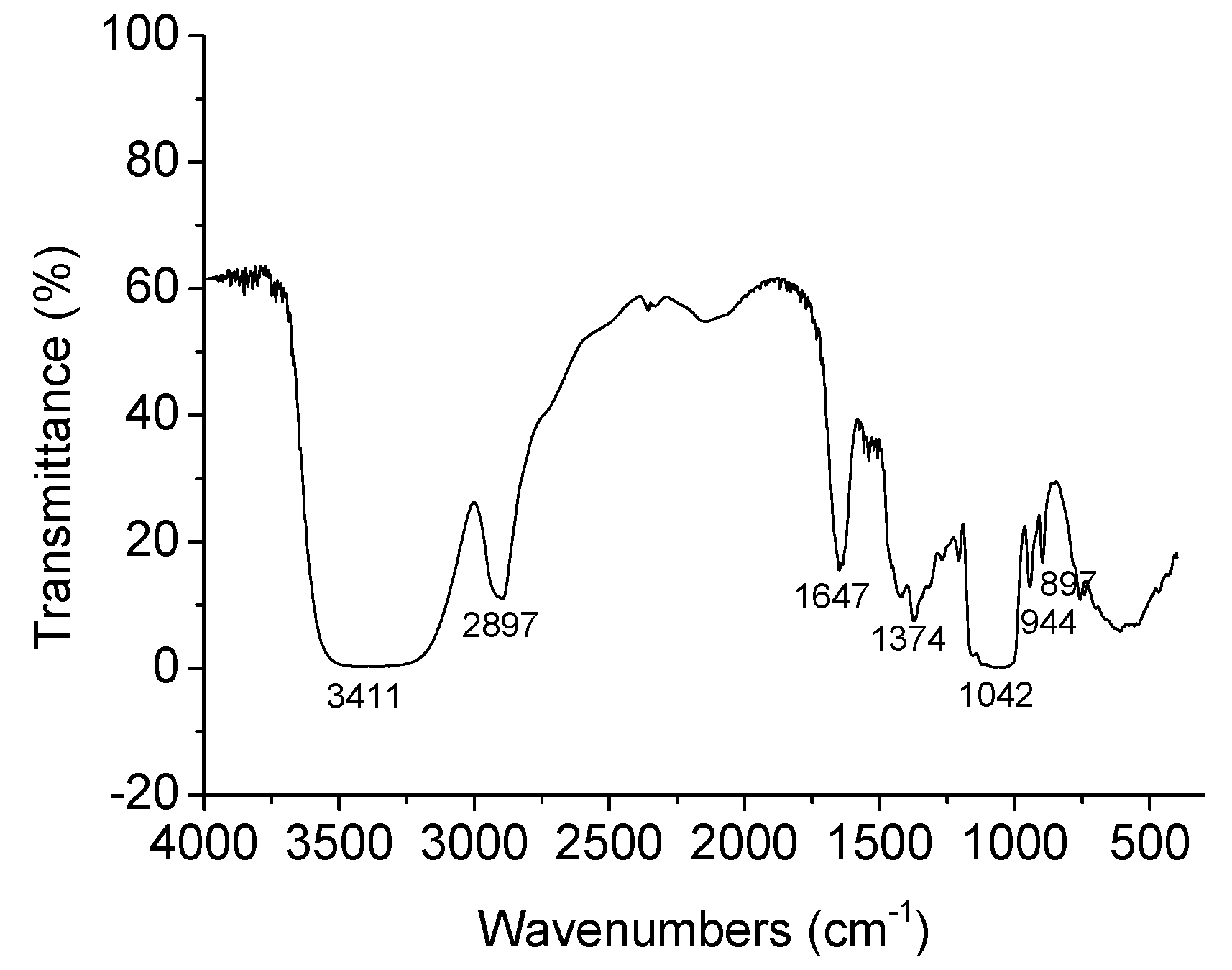
2.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.3. Flow Behaviors of TSP
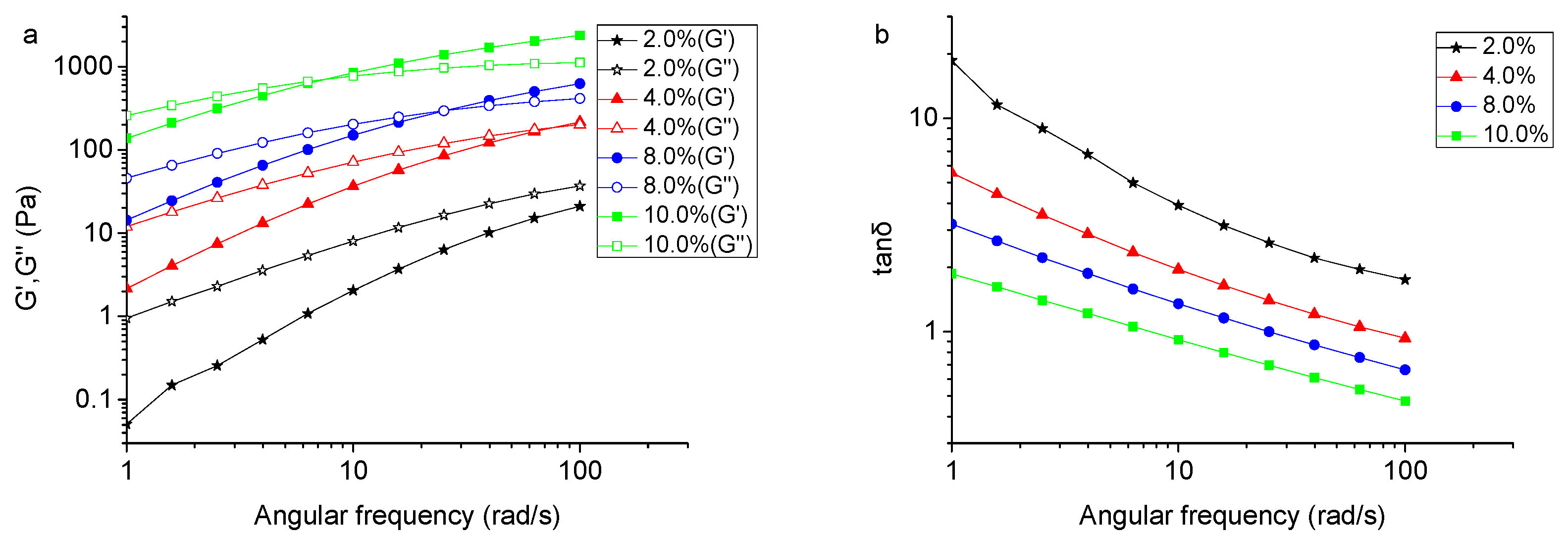
2.4. Viscoelastic Behaviors of TSP
2.5. Effect of pH on the Rheological Property of TSP
2.6. Effect of Temperature on the Rheological Properties of TSP
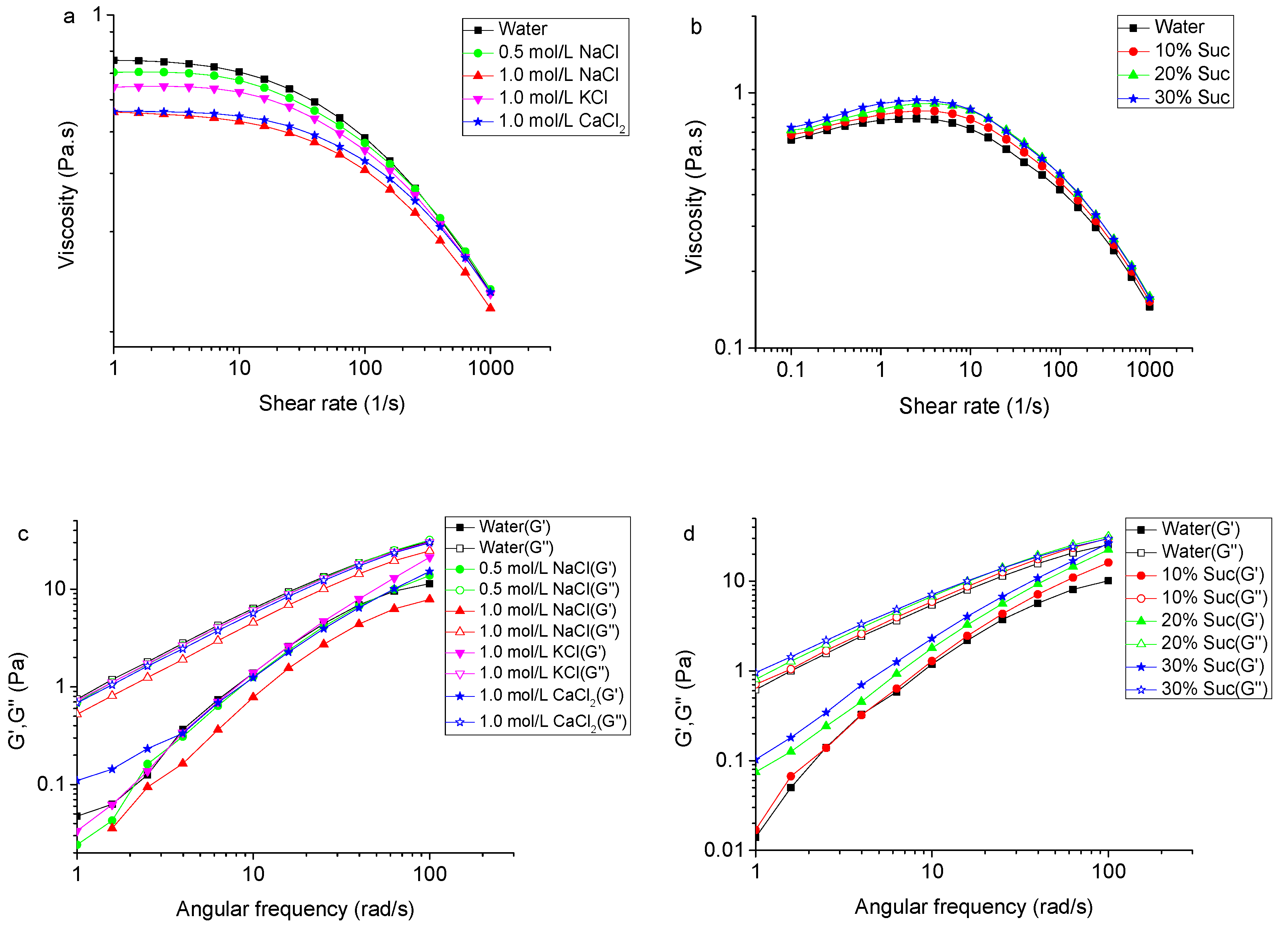
2.7. Effect of Salts and Sucrose on the Rheological Property of TSP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Extraction of TSP
3.3. Chemical Components Analyses
3.4. Determination of Molecular Weight
3.5. Determination of Monosaccharide Compositions
3.6. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.7. Rheological Behavior of TSP
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardoso Lima Reis, P.M.; Dariva, C.; Barroso Vieira, G.Â.; Hense, H. Extraction and evaluation of antioxidant potential of the extracts obtained from tamarind seeds (Tamarindus indica), sweet variety. J. Food Eng. 2016, 173, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Suisha, F.; Kawasaki, N.; Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K.; Attwood, D. Thermally reversible xyloglucan gels as vehicles for rectal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1998, 56, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozioł, A.; Cybulska, J.; Pieczywek, P.M.; Zdunek, A. Evaluation of structure and assembly of xyloglucan from tamarind seed (Tamarindus indica L.) with atomic force microscopy. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Ikeda, I. Antioxidant activity and antitumor activity (in vitro) of xyloglucan selenious ester and sulfated xyloglucan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 45, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Uchida, J.; Ito, S.; Mitsuishi, Y. Structural analysis of the oligosaccharide units of xyloglucan and their effects on growth of COLO 201 human tumor cells. Int. Congr. Ser. 2001, 1223, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Yadav, S.; Ahuja, M.; Dilbaghi, N. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of thiolated tamarind seed polysaccharide as a mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K.; Nishinari, K. Tailoring of xyloglucan properties using an enzyme. Food Hydrocoll. 1998, 12, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, C.K.; Abraham, T.E. Physico chemical properties of aminated tamarind xyloglucan. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 81, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Abo-Shosha, M.H.; Allam, E.A.; El-Zairy, E.M. New thickening agents based on tamarind seed gum and karaya gum polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, I.M.; Gane, A.M.; Dunstan, D.; Allan, G.C.; Boger, D.V.; Melton, L.D.; Bacic, A. Rheological properties of xyloglucans from different plant species. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 37, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busato, A.P.; Reicher, F.; Domingues, R.; Silveira, J.L.M. Rheological properties of thermally xyloglucan gel from the seeds of Hymenaea courbaril. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Yuguchi, Y.; Urakawa, H.; Kajiwara, K.; Shirakawa, M.; Yamatoya, K. Gelation of tamarind seed polysaccharide xyloglucan in the presence of ethanol. Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 14, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Nitta, Y.; Kim, B.S.; Temsiripong, T.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; Nishinari, K. Single-phase mixed gels of xyloglucan and gellan. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Takaya, T.; Nishinari, K. Effects of xyloglucan on the gelatinization and retrogradation of corn starch as studied by rheology and differential scanning calorimetry. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Pal, D.; Santra, K. Screening of polysaccharides from tamarind, fenugreek and jackfruit seeds as pharmaceutical excipients. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.A.; Martin, S.; Santos, G.L.; Valenga, F.; Buckeridge, M.S.; Reicher, F.; Sierakowski, M.R. Physico-chemical properties of seed xyloglucans from different sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, D.U.; Loh, W.; Buckeridge, M.S. Xyloglucan-cellulose interaction depends on the sidechains and molecular weight of xyloglucan. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 42, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, M. Standardization of tamarind seed polyose for pharmaceutical use. Ind. Drugs 1987, 24, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque, P.B.S.; Barros, W.; Santos, G.R.C.; Correia, M.T.S.; Mourao, P.A.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Carneiro-da-Cunha, M.G. Characterization and rheological study of the galactomannan extracted from seeds of Cassia grandis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 104, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, P. Purification and structural characterization of Chinese yam polysaccharide and its activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, G.; Jiang, S.; Mu, J.; Yu, H.; Duan, H.; Deng, X. Antitumor immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharides from Panax japonicus C. A. Mey: Roles of their effects on CD4 + T cells and tumor associated macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.A.; Nunes, C.A.; Pereira, J. Relationship between the chemical components of taro rhizome mucilage and its emulsifying property. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yu, L.; Feng, T.; Yin, X.; Liu, T.; Dong, L. Physicochemical characterization of the polysaccharide from Bletilla striata: Effect of drying method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiro, S.D.; Goes, J.C.; Moreira, R.A.; Sombra, A.S.B. On the physico-chemical and dielectric properties of glutaraldehyde crosslinked galactomannan–collagen films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khounvilay, K.; Sittikijyothin, W. Rheological behaviour of tamarind seed gum in aqueous solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, B.S.; Machado, D.L.P.; Haag, R.B.; Souza, C.R.D.; Lucas, E.F. Evaluation of hydrophobically associated polyacrylamide-containing aqueous fluids and their potential use in petroleum recovery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpizar-Reyes, E.; Roman-Guerrero, A.; Gallardo-Rivera, R.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; Cruz-Olivares, J.; Perez-Alonso, C. Rheological properties of tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) seed mucilage obtained by spray-drying as a novel source of hydrocolloid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, R.V. The flow of pseudoplastic materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1929, 21, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, G.; Xia, Y.; Lai, P.; Ai, L. Structural characterization and rheological properties of beta-D-glucan from hull-less barley (Hordeum vulgare L. var. nudum Hook. f.). Phytochemistry 2018, 155, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Cuadri, A.A.; Berta, M.; Stading, M. Relation between concentration and shear-extensional rheology properties of xanthan and guar gum solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Padilla, L.P.; García-Rivera, J.L.; Romero-Arreola, V.; Casas-Alencáster, N.B. Effects of xanthan gum rheology on the foaming properties of whey protein concentrate. J. Food Eng. 2015, 156, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannopoulos, A.; Sotiropoulos, K.; Pispas, S. Particle tracking microrheology of the power-law viscoelasticity of xanthan solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfak, A.M.; Pass, G.; Phillips, G.O. The effect of shear rate on the viscosity of solutions of sodium carboxymethylcellulose and k-carrageenan. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 30, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Heister, S.D.; Campanella, O.H. Modeling gelled fluid flow with thixotropy and rheological hysteresis effects. Fuel 2014, 128, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Deng, L. The effects of temperature, organic matter and time-dependency on rheological properties of dry anaerobic digested swine manure. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, N.; Mohammadifar, M.A. Role of water soluble and water swellable fractions of gum tragacanth on stability and characteristic of model oil in water emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Tan, G.; Kannan, B.; Liu, X.; Bell, A.E. Rheological properties of polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choppe, E.; Puaud, F.; Nicolai, T.; Benyahia, L. Rheology of xanthan solutions as a function of temperature, concentration and ionic strength. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, N.M.; Santos, P.H.S.; Campanella, O. Mechanically modified xanthan gum: Rheology and polydispersity aspects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 134, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B.; Shatwell, K.P.; Sutherland, I.W.; Dea, I.C.M. Influence of acyl substituents on the interaction of xanthans with plant polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 1996, 10, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsawatmanit, R.; Temsiripong, T.; Ikeda, S.; Nishinari, K. Influence of tamarind seed xyloglucan on rheological properties and thermal stability of tapioca starch. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Chen, W.Y. Rheological properties of the water-soluble mucilage of a green laver, monostroma nitidium. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, J.H.; Yoo, B. Intrinsic viscosity of binary gum mixtures with xanthan gum and guar gum: Effect of NaCl, sucrose, and pH. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; So, J.H.; Yang, S.M. Rheological Evidence for the Silica-Mediated Gelation of Xanthan Gum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 216, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.R.; Singh, R.K.; Handa, A.K.; Rao, M.A. Chemistry and uses of pectin—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 37, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross-Murphy, S.B. Structure-property relationships in food biopolymer gels and solutions. J. Rheol. 1998, 39, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinoso, D.; Martin-Alfonso, M.J.; Luckham, P.F.; Martinez-Boza, F.J. Rheological characterisation of xanthan gum in brine solutions at high temperature. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 203, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Cui, S.W.; Kang, J.; Hu, X.; Xing, X.; Yada, R.Y. Conformational properties of high molecular weight heteropolysaccharide isolated from seeds of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Najafi Kani, E. Rheology and apparent activation energy of alkali activated phosphorous slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, J.; Falzone, G.; Balonis, M.; Bauchy, M.; Sant, G. Anomalous variations in the viscous activation energy of suspensions induced by fractal structuring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 530, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dong, M.; Gong, H.; Sun, M.; Li, Y. Effects of inorganic cations on the rheology of aqueous welan, xanthan, gellan solutions and their mixtures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saggin, R.; Coupland, J.N. Rheology of xanthan/sucrose mixtures at ultrasonic frequencies. J. Food Eng. 2004, 65, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.R.; Powell, D.A.; Gidley, M.J.; Rees, D.A. Conformations and interactions of pectins: I. Polymorphism between gel and solid states of calcium polygalacturonate. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 155, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. AACC Approved Method of the AACC, 10th ed.; Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Strydom, D.J. Chromatographic separation of 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone-derivatized neutral, acidic and basic aldoses. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 678, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



| Concentration (%, w/v) | η0 (Pa·s) | λw (s) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.009 | 0.00003 | 0.659 | 0.9686 |
| 1.0 | 0.057 | 0.0007 | 0.699 | 0.9164 |
| 1.5 | 0.251 | 0.003 | 0.741 | 0.9999 |
| 2.0 | 0.953 | 0.008 | 0.753 | 0.9997 |
| 4.0 | 13.843 | 0.047 | 0.772 | 0.9999 |
| (s−1) | lnη0 (Pa.s) | Ea (kJ/mol) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | −12.778 | 32.208 | 0.9987 |
| 60 | −10.106 | 24.435 | 0.9903 |
| 200 | −8.435 | 19.388 | 0.9814 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, H.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y.; Song, Z.; Lai, P.F.H.; Ai, L. Composition and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide Extracted from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) Seed. Molecules 2019, 24, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071218
Shao H, Zhang H, Tian Y, Song Z, Lai PFH, Ai L. Composition and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide Extracted from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) Seed. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071218
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Huimin, Hui Zhang, Yanjun Tian, Zibo Song, Phoency F. H. Lai, and Lianzhong Ai. 2019. "Composition and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide Extracted from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) Seed" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071218
APA StyleShao, H., Zhang, H., Tian, Y., Song, Z., Lai, P. F. H., & Ai, L. (2019). Composition and Rheological Properties of Polysaccharide Extracted from Tamarind (Tamarindus indica L.) Seed. Molecules, 24(7), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071218