In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
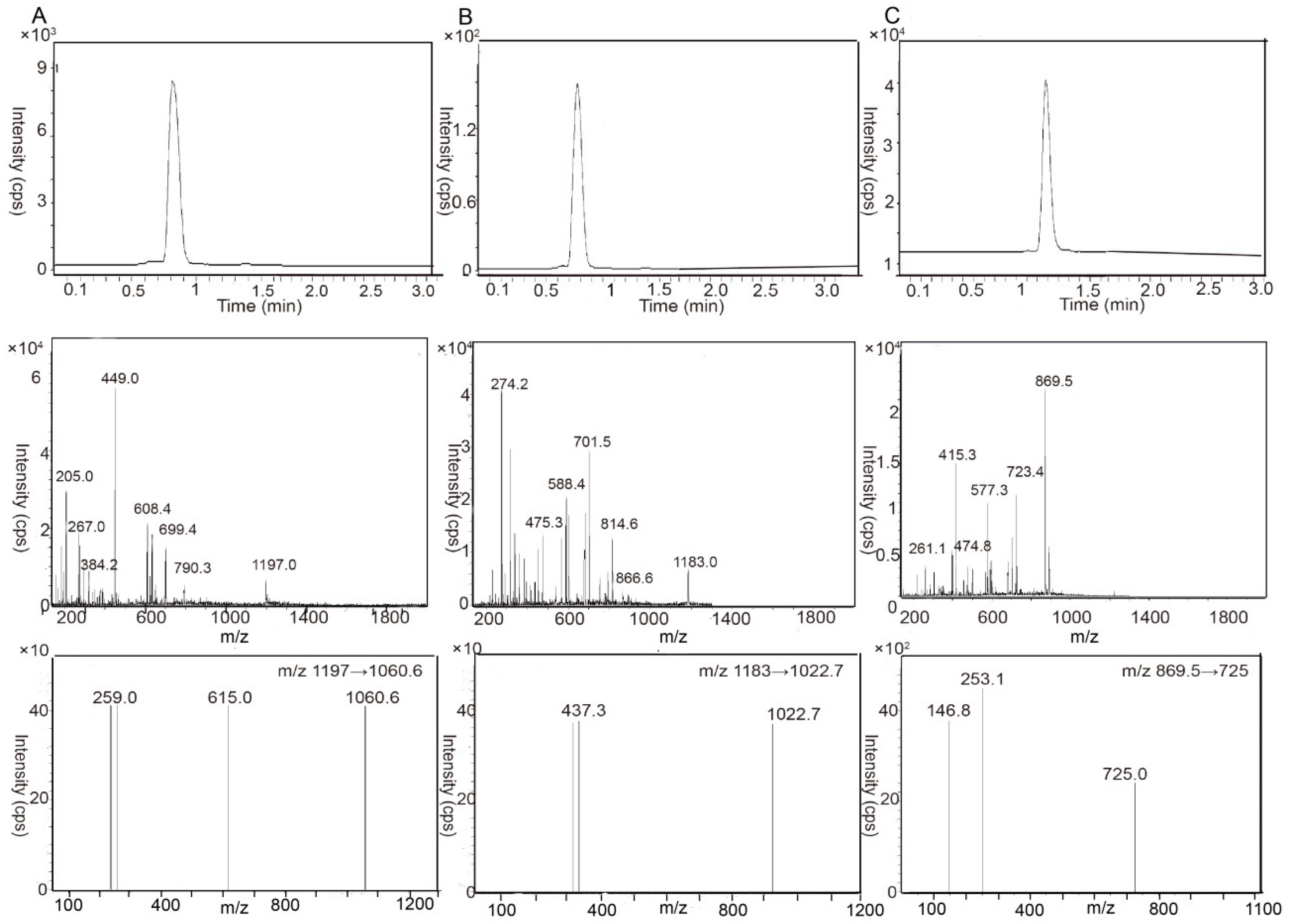
2.1. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis Method Validation
2.2. The Characterization of Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
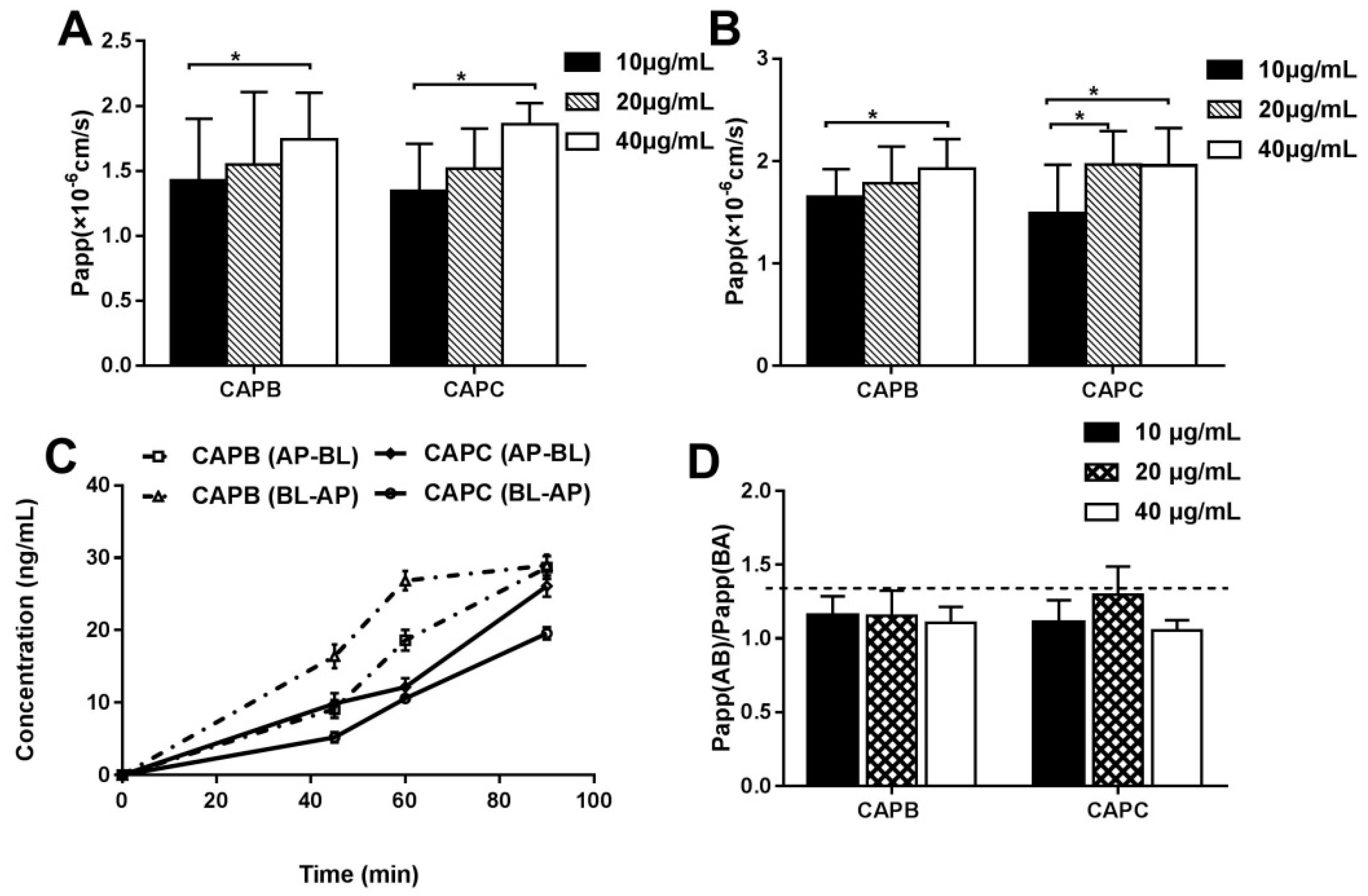
2.3. The Characterization of the Intestinal Permeability Features of CAPB and CAPC In a Caco-2 Cell monolayer
2.4. The Role of P-gp, MRP2 and CYP3A4 on CAPB and CAPC Transport Across Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
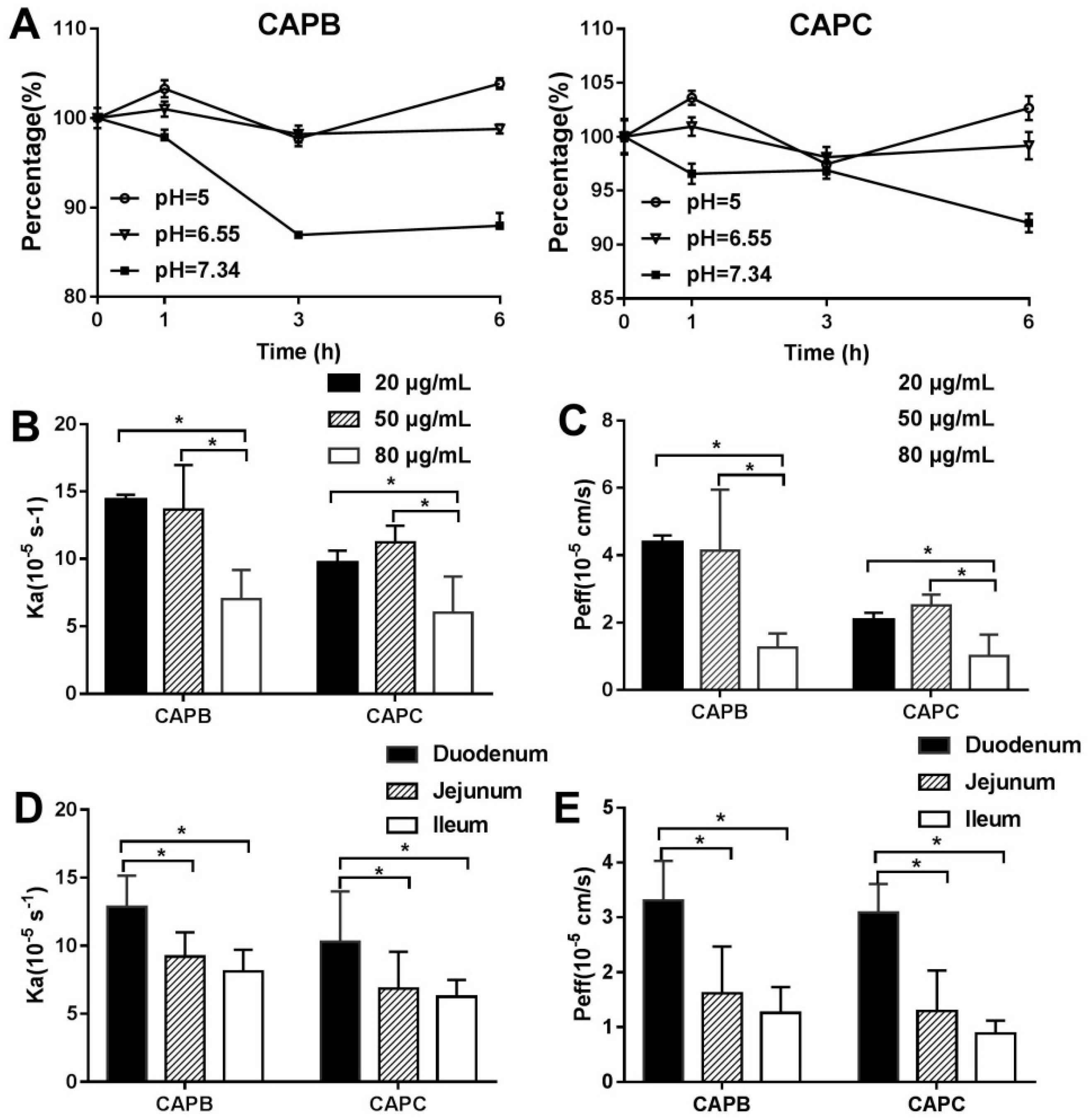
2.5. The Characterization of the Intestinal Permeability of CAPB and CAPC In Rats
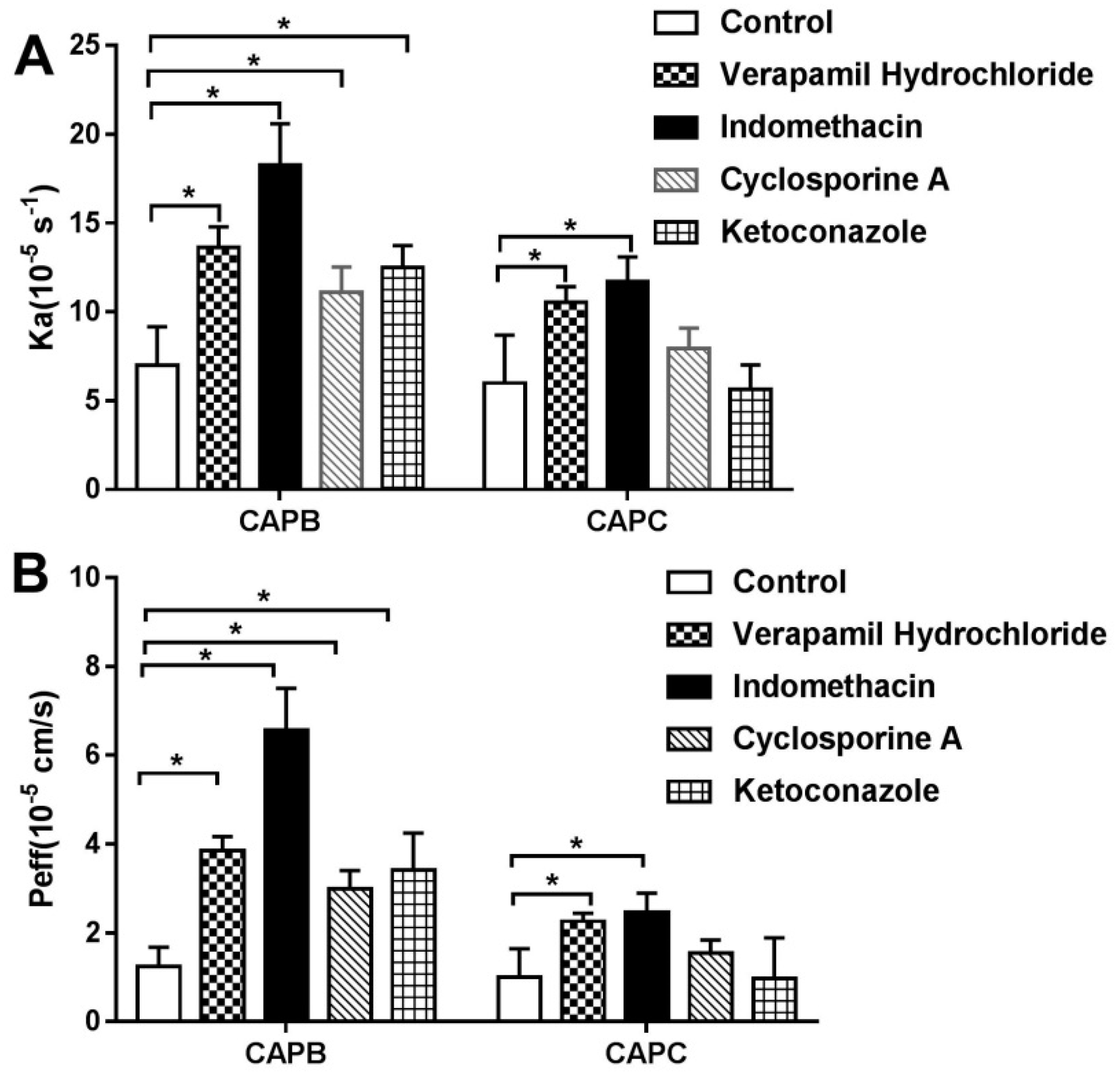
2.6. The Role of P-gp, MRP2, and CYP3A4 on Intestinal Permeability of CAPB and CAPC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) Analysis
4.3. Caco-2 Cell Culture
4.4. Permeability Studies Using Caco-2 Cells
4.5. In Situ Single-Pass Intestinal Perfusion (SPIP) Studies In Rats
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, L.; Fu, L.L.; Zhu, Z.F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.X.; Shan, W.G.; Zhang, Z.H. Modified mixed nanomicelles with collagen peptides enhanced oral absorption of Cucurbitacin B: preparation and evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, K. Nanoparticles for oral delivery: Targeted nanoparticles with peptidic ligands for oral protein delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat, D.; Dahan, A. Active intestinal drug absorption and the solubility-permeability interplay. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estudante, M.; Morais, J.G.; Soveral, G.; Benet, L.Z. Intestinal drug transporters: An overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1340–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; de Graaf, I.A.M.; van de Steeg, E.; de Jager, M.H.; Groothuis, G.M.M. The consequence of regional gradients of P-gp and CYP3A4 for drug-drug interactions by P-gp inhibitors and the P-gp/CYP3A4 interplay in the human intestine ex vivo. Toxicol. In Vitro 2017, 40, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hierro, J.N.; Herrera, T.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G.; Martin, D. The gastrointestinal behavior of saponins and its significance for their bioavailability and bioactivities. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.R.; Niu, T.; Gao, S.; Yin, T.J.; You, M.; Jiang, Z.H.; Hu, M. Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein Leads to Improved Oral Bioavailability of Compound K, an Anticancer Metabolite of Red Ginseng Extract Produced by Gut Microflora. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.A.; Ha, S.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Choi, I. Effects of friedelin on the intestinal permeability and bioavailability of apigenin. Pharmacol. Rep. 2017, 69, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, S.; Li, X.H. In vitro Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption Mechanism of Dihydromyricetin in Caco-2 Cell Model. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2018, 37, 908–913. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, G.M.; Sun, B.; Jiang, H.H.; Kong, F.; Yuan, H.Q.; Lou, H.X. Bisbibenzyl derivatives sensitize vincristine-resistant KB/VCR cells to chemotherapeutic agents by retarding P-gp activity. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 6725–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, G.J.; Yi, H.; Zhu, M.J.; Zhou, J.; Shang, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhu, C.C.; Liao, Q.F.; Guan, S.X.; Zhang, L. Study of Absorption Characteristics of the Total Saponins from Radix Ilicis Pubescentis in an In Situ Single-Pass Intestinal Perfusion (SPIP) Rat Model by Using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC). Molecules 2017, 22, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, X.; Qu, D.; Liu, C.Y. Study on the Mechanism of Intestinal Absorption of Epimedins A, B and C in the Caco-2 Cell Model. Molecules 2014, 19, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Y.; Duan, Z.J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.X.; Li, Y.; He, S.C.; Wang, Q.M.; Chang, Q.Y. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 and cytochrome P450 3A4 improves the oral absorption of octreotide in rats with portal hypertension. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3716–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Lv, C.; Zheng, Z.J.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Z.Q. Involvement of CYP3A4/5 and CYP2D6 in the metabolism of aconitine using human liver microsomes and recombinant CYP450 enzymes. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 20, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, D.Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Hu, P. Relative contributions of the major human CYP450 to the metabolism of icotinib and its implication in prediction of drug-drug interaction between icotinib and CYP3A4 inhibitors/inducers using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. Expert. Opin. Drug Met. 2015, 11, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.X.; Liu, G.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Wu, X.W.; Xu, W.; Yang, X.W. Intestinal Absorption of Triterpenoids and Flavonoids from Glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma in the Human Caco-2 Monolayer Cell Model. Molecules 2017, 22, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Ma, T.T.; Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.; Han, J.W.; Hu, T.T.; Li, J. Efficiency of transcellular transport and efflux of flavonoids with different glycosidic units from flavonoids of Litsea coreana L. in a MDCK epithelial cell monolayer model. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 53, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunath, S.; Nanjwade, B.K.; Patila, P.A. Enhanced solubility and intestinal absorption of candesartan cilexetil solid dispersions using everted rat intestinal sacs. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, L.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, J.; Shen, H.Y.; Ji, G.; Shi, X.F.; Xie, Y. The intestinal absorption properties of flavonoids in Hippophae rhamnoides extracts by an in situ single-pass intestinal perfusion model. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappaerts, J.; Brouwers, J.; Annaert, P.; Augustijns, P. In situ perfusion in rodents to explore intestinal drug absorption: challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.D.; Lei, T.L.; Lv, C.N.; Zhao, H.M.; Xu, H.Y.; Lu, J.C. Pharmacokinetic studies of active triterpenoid saponins and the total secondary saponin from Anemone raddeana Regel. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1044, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhai, B.T.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Shi, Y.J.; Guo, D.Y. Intestinal absorption mechanisms of araloside A in situ single-pass intestinal perfusion and in vitro Caco-2 cell model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.K.; Xu, L.Z.; Zou, Z.M.; Yang, S.L. Two new triterpene saponins from Lysimachia capillipes. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, S.A.; Premoli, M.; Tambaro, S.; Kumar, A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Memo, M.; Mastinu, A. Cannabis sativa: A comprehensive ethnopharmacological review of a medicinal plant with a long history. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 227, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.K.; Xu, L.Z.; Zou, Z.M.; Yang, S.L. Three novel triterpenoid saponins from Lysimachia capillipes and their cytotoxic activities. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2006, 54, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, N. Capilliposide C Sensitizes Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cells to Oxaliplatin by Inducing Apoptosis Through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Z.H.; Wu, K.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, S.R.; Ma, S.L. Capilliposide Isolated from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl. Induces ROS Generation, Cell Cycle Arrest, and Apoptosis in Human Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Tian, J.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L. Capilliposide C derived from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl inhibits growth of human prostate cancer PC3 cells by targeting caspase and MAPK pathways. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2014, 46, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Hu, Q.; Piao, Y.; Tang, Q.; Feng, J. Effect of capilliposide for induction apoptosis in human nasopharyngeal cancer CNE-2 cells through up-regulating PUMA expression. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2015, 11, C239–C243. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.R.; Xu, Y.S.; Jin, E.; Zhu, L.C.; Xia, B.; Chen, X.F.; Li, F.Z.; Ma, S.L. Capilliposide from Lysimachia capillipes inhibits AKT activation and restores gefitinib sensitivity in human non-small cell lung cancer cells with acquired gefitinib resistance. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Jiang, H. Simultaneous determination of capilliposide B and capilliposide C in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a PK study. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, B.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Jiang, H. Metabolic Stability and Metabolite Characterization of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C by LC(-)QTRAP(-)MS/MS. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Hu, B.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Jiang, H. Tissue distribution of capilliposide B, capilliposide C and their bioactive metabolite in mice using liquid -tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H. Optimization of solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous determination of capilliposide B and its active metabolite in rat urine and feces: Overcoming nonspecific binding. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.D.; Pang, K.S. Permeability, transport, and metabolism of solutes in caco-2 cell monolayers: A theoretical study. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Sun, D.D.; Sun, S.L.; Sun, C.; Liu, J.G.; Guan, Q.X. Evaluation of the cytotoxicity and intestinal absorption of a self-emulsifying drug delivery system containing sodium taurocholate. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.S. Modeling of intestinal drug absorption: roles of transporters and metabolic enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri-Milani, P.; Valizadeh, H. Intestinal transporters: enhanced absorption through P-glycoprotein-related drug interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Met. 2014, 10, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaessen, S.F.C.; van Lipzig, M.M.H.; Pieters, R.H.H.; Krul, C.A.M.; Wortelboer, H.M.; van de Steeg, E. Regional Expression Levels of Drug Transporters and Metabolizing Enzymes along the Pig and Human Intestinal Tract and Comparison with Caco-2 Cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ye, H.; Zhu, X.M.; Hu, J.N.; Li, H.Y.; Tsao, R.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zheng, Y.N.; Li, W. Esterification enhanced intestinal absorption of ginsenoside Rh2 in Caco-2 cells without impacts on its protective effects against H(2)O(2)-induced cell injury in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Li, W.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Ma, S.W.; Ping, L.; Yang, Z.L. Enhancement of intestinal absorption of akebia saponin D by borneol and probenecid in situ and in vitro. Environ. Toxicol. Phar. 2010, 29, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.R.; Yin, T.J.; Teng, Y.; Wu, B.J.; You, M.; Jiang, Z.H.; Hu, M. Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability of 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 through Improved Understanding of Its Absorption and Efflux Mechanisms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.H.; Qiu, W.; Liu, H.; Jiang, X.H.; Wang, L. Enhancement of oral bioavailability and immune response of Ginsenoside Rh2 by co-administration with piperine. Chin. J. Nat. Medicines 2018, 16, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmed, S.M.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Bahadur, S.; Harwansh, R.K.; Kar, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Duraipandiyan, V. CYP450 mediated inhibition potential of Swertia chirata: An herb from Indian traditional medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 178, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhong, D.F. In Vitro Studies on the Oxidative Metabolism of 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 in Human, Monkey, Dog, Rat, and Mouse Liver Microsomes, and Human Liver S9. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Huang, M.; Chen, G.; Yang, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Cell-based assays in combination with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight tandem mass spectrometry for screening bioactive capilliposide C metabolites generated by rat intestinal microflora. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 119, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Di, L.Q.; Wang, J.; Shan, J.J.; Liu, S.J.; Ju, W.Z.; Cai, B.C. Intestinal absorption of forsythoside A in in situ single-pass intestinal perfusion and in vitro Caco-2 cell models. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Wu, Y.; Feng, D.; Qian, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Gu, M. In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl. Molecules 2019, 24, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071227
Zhang X, Cheng X, Wu Y, Feng D, Qian Y, Chen L, Yang B, Gu M. In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl. Molecules. 2019; 24(7):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071227
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Xiao Cheng, Yali Wu, Di Feng, Yifan Qian, Liping Chen, Bo Yang, and Mancang Gu. 2019. "In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl" Molecules 24, no. 7: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071227
APA StyleZhang, X., Cheng, X., Wu, Y., Feng, D., Qian, Y., Chen, L., Yang, B., & Gu, M. (2019). In Vitro and In Situ Characterization of the Intestinal Absorption of Capilliposide B and Capilliposide C from Lysimachia capillipes Hemsl. Molecules, 24(7), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071227





