A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
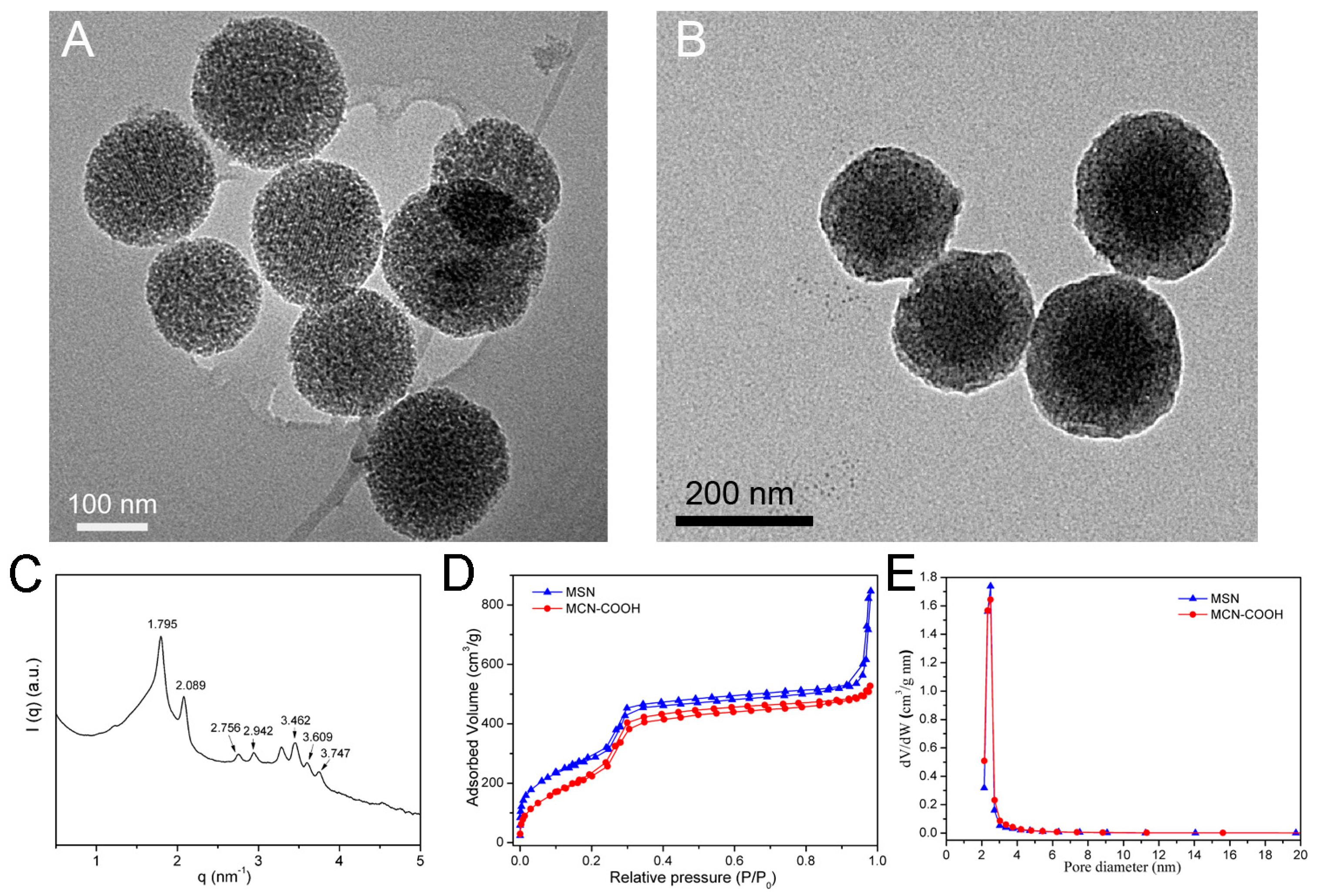
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSN) and Mesoporous Carbon Nanoparticles (MCN)–COOH
2.2. Drug Loading by Different Loading Methods
2.2.1. Drug Loading by the Solvent Adsorption Method
2.2.2. Drug Loading by the Solvent Evaporation Method
2.3. Solid State Characterization by X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Drug Dissolution Tests
2.5. In Vitro Cell Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.6. Gastrointestinal Mucosa Irritation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Preparation of MSN
3.3. Preparation of MCN and MCN–COOH
3.4. Drug Loading by Different Methods
3.4.1. Drug Loading by the Solvent Adsorption Method
3.4.2. Drug Loading by the Solvent Evaporation Method
3.4.3. Evaluation of Loading Efficiency
3.5. Dissolution Testing
3.6. Characterization
3.7. Cellular Toxicity
3.8. Gastrointestinal Mucosa Irritation Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yun, Y.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, K. Nanoparticles for oral delivery: Targeted nanoparticles with peptidic ligands for oral protein delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.; Abraham, T.E. Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: Alginate and chitosan—A review. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choonara, B.F.; Choonara, Y.E.; Kumar, P.; Bijukumar, D.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. A review of advanced oral drug delivery technologies facilitating the protection and absorption of protein and peptide molecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs-Barrable, K.; Lee, S.D.; Wasan, E.K.; Thornton, S.J.; Wasan, K.M. Enhancing drug absorption using lipids: A case study presenting the development and pharmacological evaluation of a novel lipid-based oral amphotericin B formulation for the treatment of systemic fungal infections. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, G.D. Extensive Diminution of Particle Size and Amorphization of a Crystalline Drug Attained by Eminent Technology of Solid Dispersion: A Comparative Study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 1770–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.F.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, T.Y.; Cheng, G.; Wang, S.L. Template-directed hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite as a drug delivery system for the poorly water-soluble drug carvedilol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 10126–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.; Shimpi, S.; Paradkar, A. Preparation and evaluation of glibenclamide-polyglycolized glycerides solid dispersions with silicon dioxide by spray drying technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Sha, Z.; Di, D.; Han, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Mechanism study on pH-responsive cyclodextrin capped mesoporous silica: Effect of different stalk densities and the type of cyclodextrin. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 165704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Hu, D.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Gao, D.; Gong, P.; Gao, G.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y. Smart human serum albumin-indocyanine green nanoparticles generated by programmed assembly for dual-modal imaging-guided cancer synergistic phototherapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 12310–12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuner, C.; Dressman, J. Improving drug solubility for oral delivery using solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Barnes, J.C.; Bosoy, A.; Stoddart, J.F.; Zink, J.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2590–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.F.; Liu, J.; Zhu, W.Q.; Sun, C.S.; Di, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, S.L. Dual-stimuli responsive hyaluronic acid-conjugated mesoporous silica for targeted delivery to CD44-overexpressing cancer cells. Acta Biomater. 2015, 23, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, C.A.; Lee, B.Y.; Clemens, D.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. Facile Strategy Enabling Both High Loading and High Release Amounts of the Water-Insoluble Drug Clofazimine Using Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31870–31881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Kim, H.Y.; Oh, J.Y.; Thomas, A.P.; Choi, E.S.; Jeena, M.T.; Joo, S.H.; Ryu, J.H. Noncovalent Surface Locking of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Exceptionally High Hydrophobic Drug Loading and Enhanced Colloidal Stability. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2701–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.; Lei, W.; Cui, Y.; Jiao, J.; Mao, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. Size effect on oral absorption in polymer-functionalized mesoporous carbon nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 511, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mourabit, S.; Guillot, M.; Toquer, G.; Cambedouzou, J.; Goettmann, F.; Grandjean, A. Stability of mesoporous silica under acidic conditions. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10916–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Wan, L.; Hou, Z.; Wang, T.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Mesoporous carbon as a novel drug carrier of fenofibrate for enhancement of the dissolution and oral bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Han, N.; Li, X.; Geng, H.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S. Mesoporous carbon nanomaterials in drug delivery and biomedical application. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Wan, L.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Poly dimethyl diallyl ammonium coated CMK-5 for sustained oral drug release. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 461, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, H.B.; Thomas, N.; Rao, S.; Prestidge, C.A. Supersaturated silica-lipid hybrids (super-SLH): An improved solid-state lipid-based oral drug delivery system with enhanced drug loading. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 125, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Y.; Sun, L.; Bai, L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Ordered nanoporous silica as carriers for improved delivery of water insoluble drugs: A comparative study between three dimensional and two dimensional macroporous silica. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4015–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.J.; Slipper, I.; Walunj, A.; Jain, A.; Favretto, M.E.; Kallinteri, P.; Douroumis, D. Inclusion of poorly soluble drugs in highly ordered mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.; Awadallah, A.; Sunoqrot, S.; Tarawneh, O.; Nazzal, S.; AlBaraghthi, T.; Al Sayyad, J.; Abbas, A. pH-Dependent Solubility and Dissolution Behavior of Carvedilol--Case Example of a Weakly Basic BCS Class II Drug. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.H.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Cheng, B.; Hu, F.Q.; You, J.; Du, Y.Z.; Yuan, H. Transport Mechanisms of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles across Caco-2 Cell Monolayers and their Related Cytotoxicology. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5929–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Yadava, P.; Heikkinen, A.T.; Parrott, N.; Railkar, A. Applications of a 7-day Caco-2 cell model in drug discovery and development. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 56, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-W.; Chung, P.-W.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Facile synthesis of monodisperse spherical MCM-48 mesoporous silica nanoparticles with controlled particle size. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5093–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Guo, B.; Binder, A.J.; Chen, J.; Veith, G.M.; Dai, S. Controlled synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanostructures via a “silica-assisted” strategy. Nano Lett. 2012, 13, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Webley, P.A.; Zhao, D. Comprehensive study of pore evolution, mesostructural stability, and simultaneous surface functionalization of ordered mesoporous carbon (FDU-15) by wet oxidation as a promising adsorbent. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10277–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C.; Song, A.; Sun, C.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S. Folate-polyethyleneimine functionalized mesoporous carbon nanoparticles for enhancing oral bioavailability of paclitaxel. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 484, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Che, E.; Zhang, L.; Han, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Development of novel mesoporous nanomatrix-supported lipid bilayers for oral sustained delivery of the water-insoluble drug, lovastatin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds silica and carbon are available from the authors. |








| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | VP a (cm3/g) | Pd (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSN | 1042 | 0.854 | 2.6 |
| MCN–COOH | 923 | 0.857 | 2.6 |
| Sample | Mass of Carrier (mg) | Mass of CAR (mg) | Sample Name after CAR Loading | Drug Loading (%) | Theoretical LE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSN | 100 | 100 | MSN/CAR–1 | 39.5±3.0 | 50.0 |
| 150 | 100 | MSN/CAR–1.5 | 34.0±2.8 | 40.0 | |
| 200 | 100 | MSN/CAR–2 | 28.2±2.3 | 33.3 | |
| MCN–COOH | 100 | 100 | MCN–COOH/CAR–1 | 42.9±2.7 | 50.0 |
| 150 | 100 | MCN–COOH/CAR–1.5 | 35.3±3.0 | 40.0 | |
| 200 | 100 | MCN–COOH/CAR–2 | 27.2±0.9 | 33.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Huang, H.; Dong, Y.; Sui, X.; Jian, B.; Zhu, W. A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol. Molecules 2019, 24, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091770
Han C, Huang H, Dong Y, Sui X, Jian B, Zhu W. A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol. Molecules. 2019; 24(9):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091770
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Cuiyan, Haitao Huang, Yan Dong, Xiaoyu Sui, Baiyu Jian, and Wenquan Zhu. 2019. "A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol" Molecules 24, no. 9: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091770
APA StyleHan, C., Huang, H., Dong, Y., Sui, X., Jian, B., & Zhu, W. (2019). A Comparative Study of the Use of Mesoporous Carbon and Mesoporous Silica as Drug Carriers for Oral Delivery of the Water-Insoluble Drug Carvedilol. Molecules, 24(9), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091770




