A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
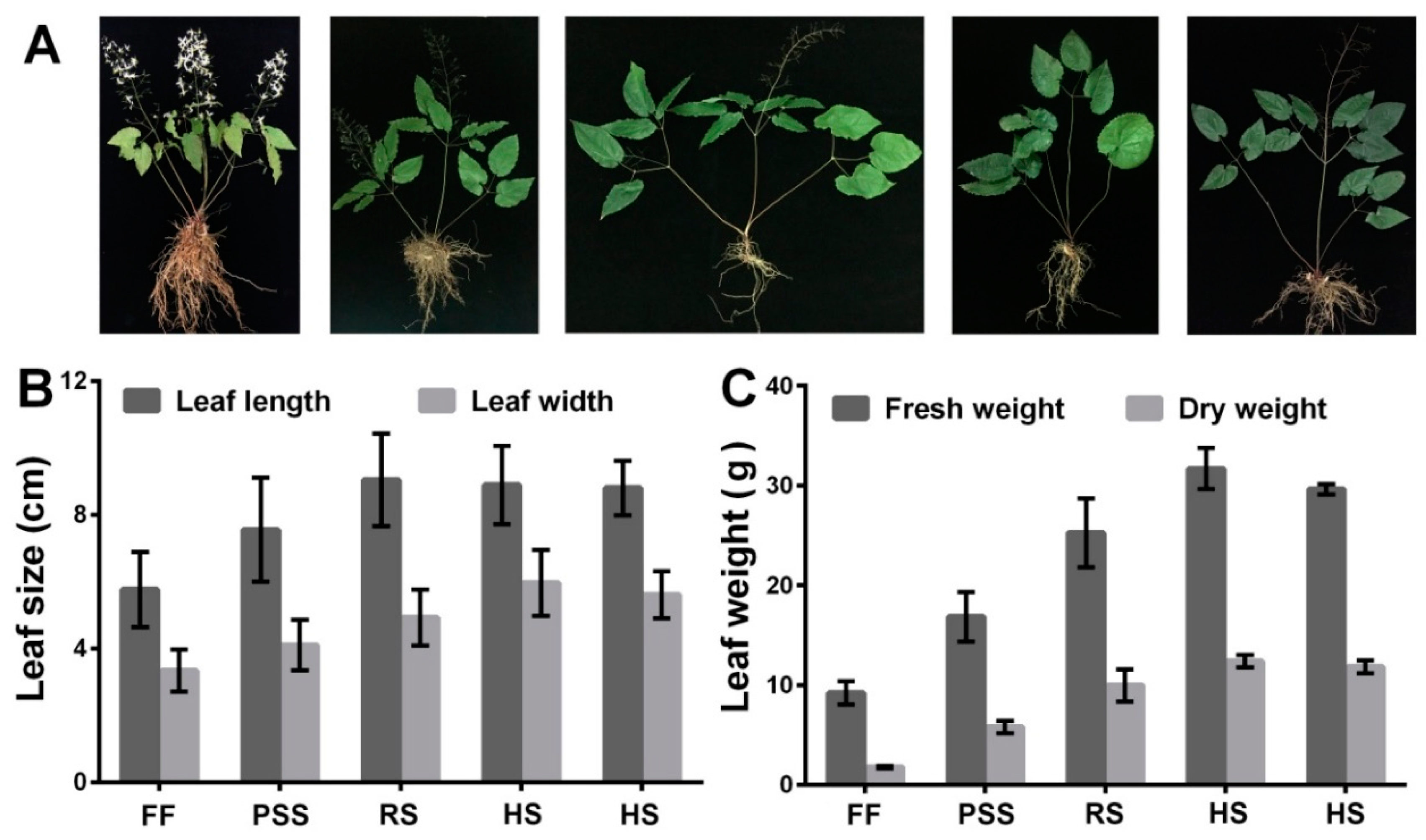
2.1. E. Pubescens Growth in the Shaded Field
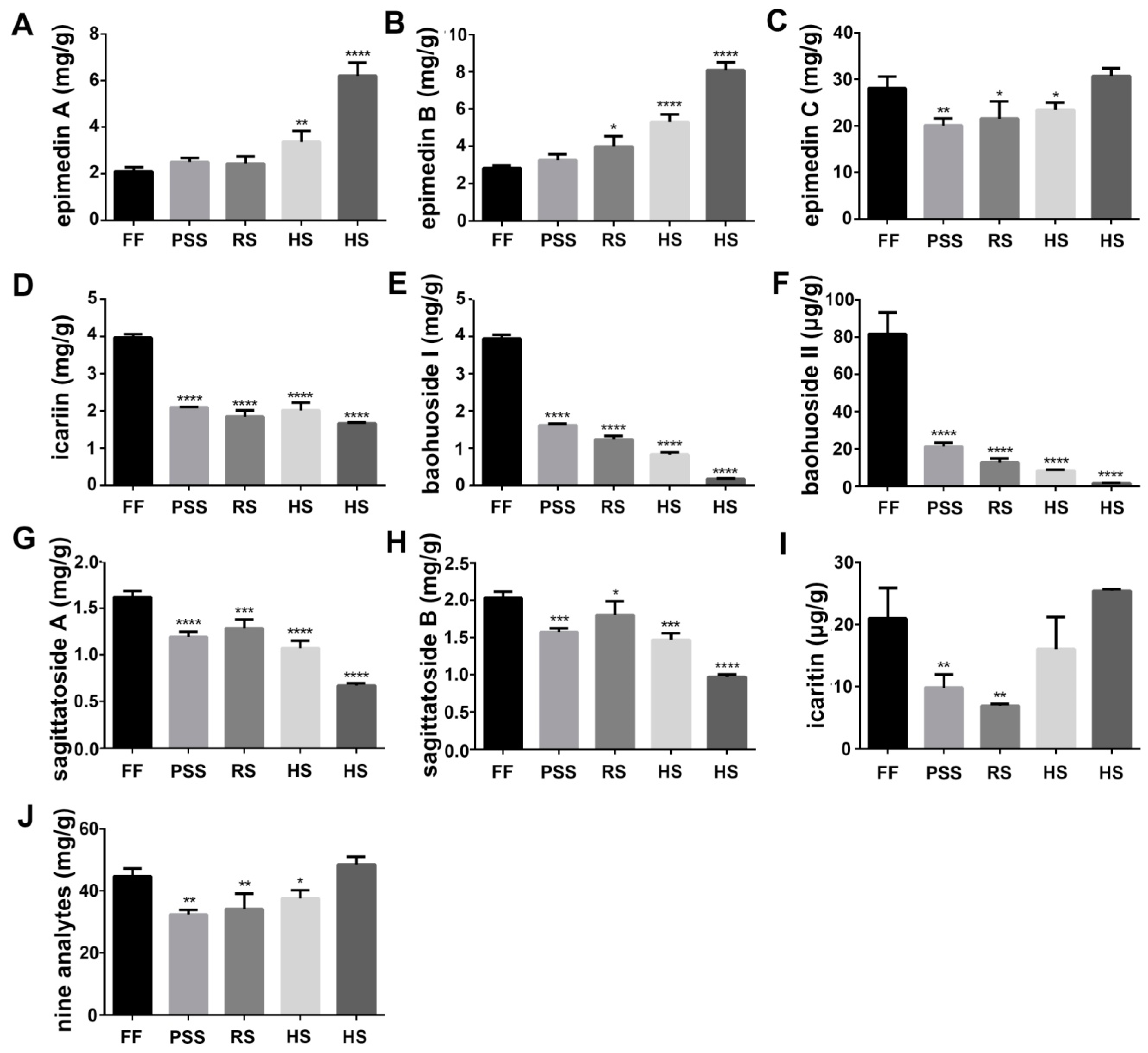
2.2. Flavonoid Content Fluctuated with E. Pubescens Leaf Growth and Development
2.3. Widely-Targeted Metabolomics Analyis of E. Pubescens Leaves at Various Developmental Stages
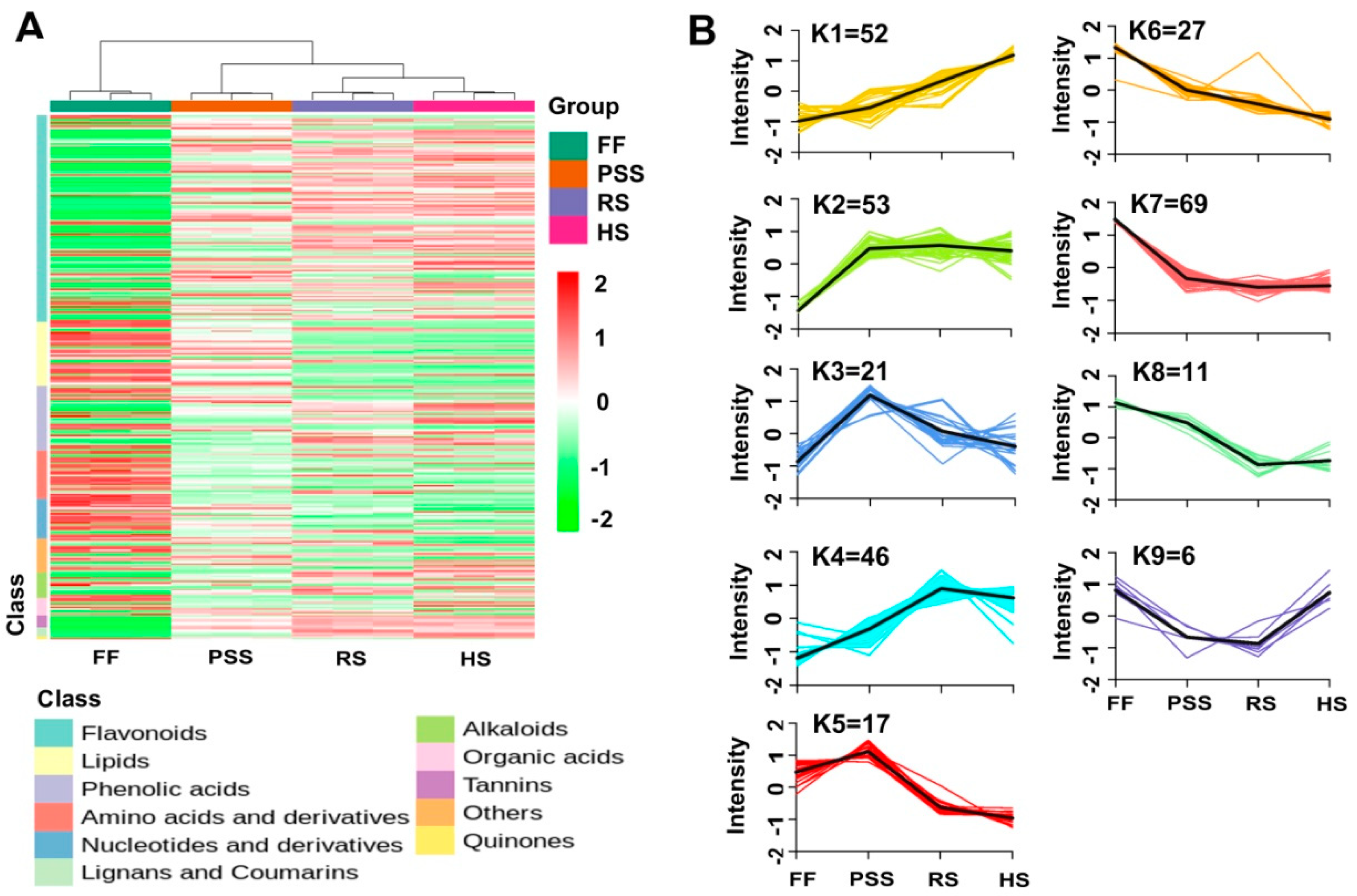
2.3.1. Overview of E. Pubescens Foliar Metabolome
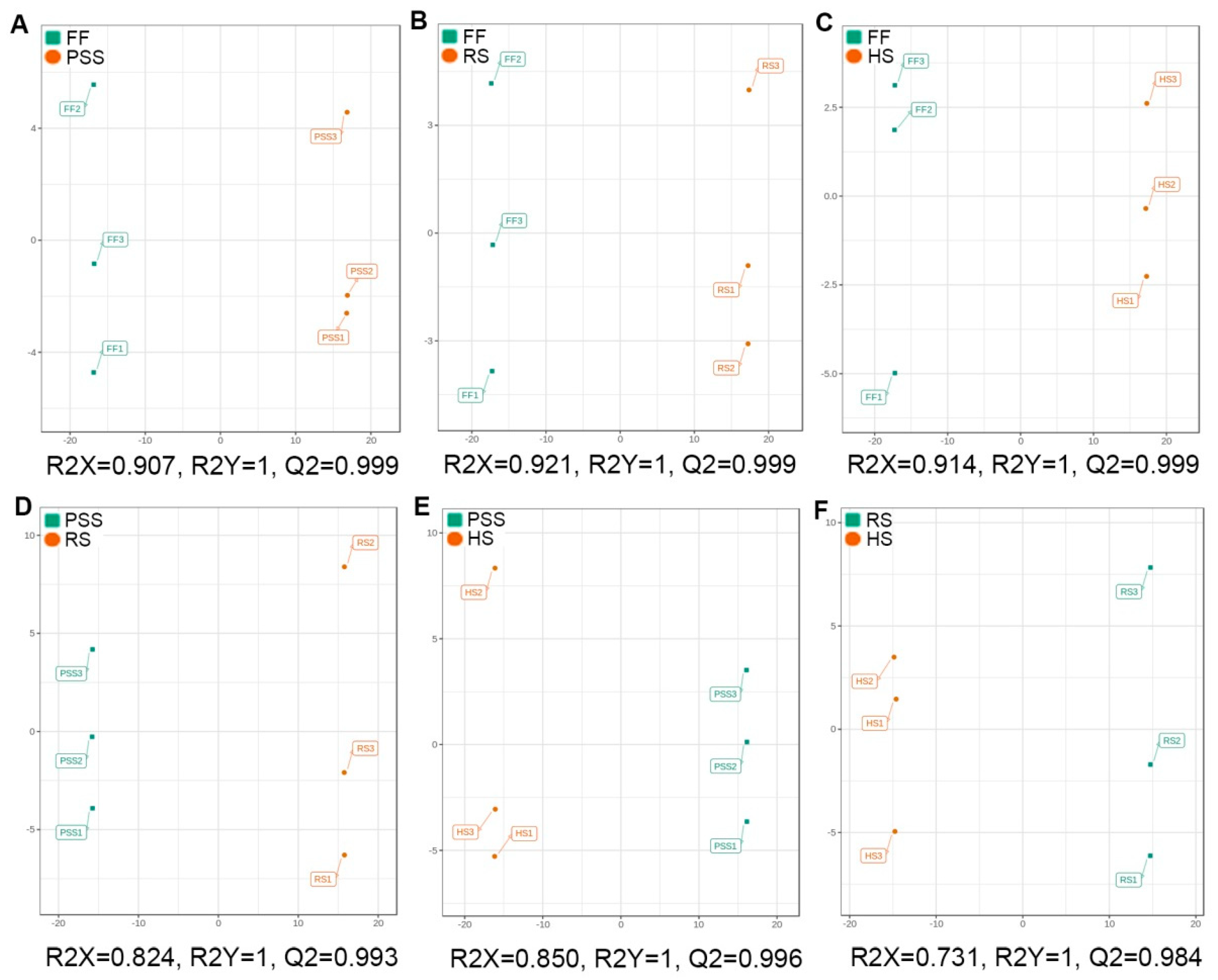
2.3.2. Multivariate Analysis of E. Pubescens Foliar Metabolomes at Various Developmental Stages
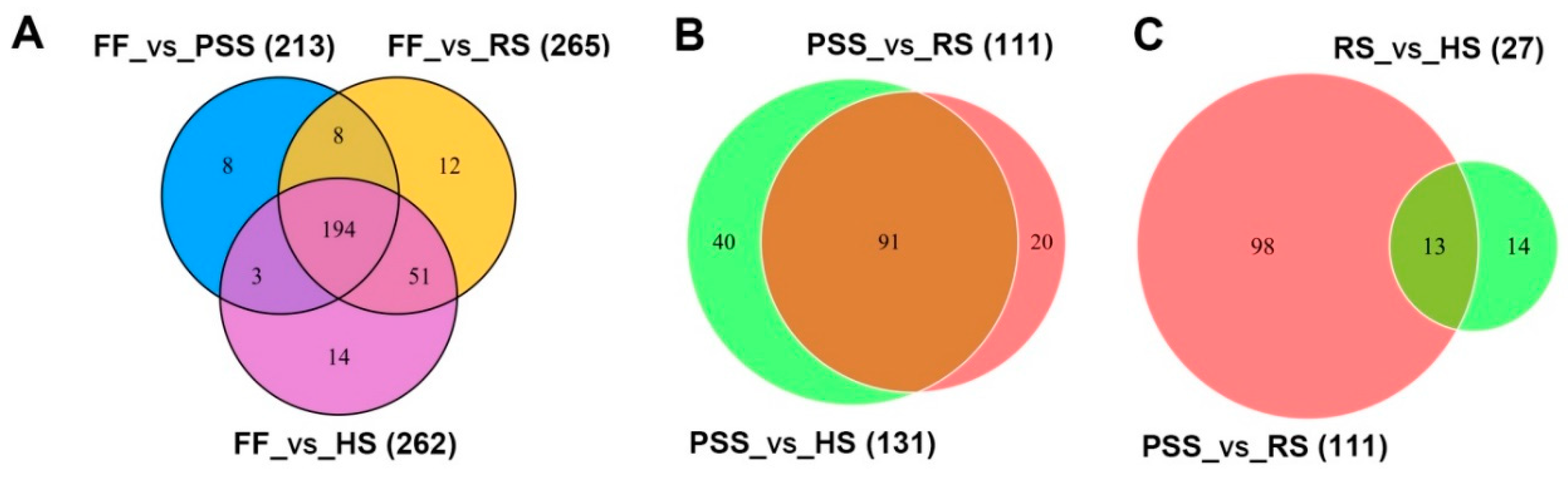
2.3.3. Differential Metabolite Profiling of E. Pubescens Leaves during the Leaf Growth and Development.
2.3.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Growth and Sampling
4.3. LC-MS/MS Quantitative Analysis of Icariin Analogues
4.3.1. Preparation of Quantitative Analysis Samples and Standard Solutions
4.3.2. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.3.3. Method Validation
4.4. Widely-Targeted Metabolomic Analysis of E. Pubescens Leaves
4.4.1. Leaf Metabolite Extraction
4.4.2. UPLC- ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS Analysis of E. Pubescens Leaf Metabolomes
4.4.3. Data Processing, Metabolite Identification and Quantitation and Multivariate Statistical Analysis
4.4.4. KEGG Pathway Analysis of the Identified Metabolites
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, H.; He, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, D.; Jia, Z. The genus Epimedium: An ethnopharmacological and phytochemical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 519–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Song, J.; Jia, X.-B. Phytochemistry and Ethnopharmacology of Epimedium L. Species. Chin. Herb. Med. 2015, 7, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.H.; Lv, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, G.Q. Analysis of the essential oil from two varieties of epimediums by GC-MS. J. Pharm, Pract. 2011, 29, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Fernie, A.R.; Trethewey, R.N.; Krotzky, A.J.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling: From diagnostics to systems biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2004, 5, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.J. Analysis on chemical constituents of Epimedii Folium by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. Traditional and Herbal Drugs 2017, 48, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ji, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, F.; Yu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X. Metabolic profiling of tobacco leaves at different growth stages or different stalk positions by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 116, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Yuk, H.J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Nho, C.W.; Lee, N.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.-R. Evaluation of phytochemicals in Agastache rugosa (Fisch. & C.A.Mey.) Kuntze at different growth stages by UPLC-QTof-MS. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Nadi, R.; Golein, B.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Arbona, V. Developmental Stage- and Genotype-Dependent Regulation of Specialized Metabolite Accumulation in Fruit Tissues of Different Citrus Varieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Jeong, J.; Alves, A.C.; Han, S.-T.; In, G.; Kim, E.-H.; Jeong, W.-S.; Hong, Y.-S. Metabolomic understanding of intrinsic physiology in Panax ginseng during whole growing seasons. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X. Recent developments in qualitative and quantitative analysis of phytochemical constituents and their metabolites using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 72, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Abozeid, A.; Zu, Y.-G.; Tang, Z.-H. The integration of GC–MS and LC–MS to assay the metabolomics profiling in Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius reveals a tissue- and species-specific connectivity of primary metabolites and ginsenosides accumulation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 135, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zou, Q.; Guo, Q.; Yang, F.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W. Widely Targeted Metabolomics Analysis Reveals the Effect of Flooding Stress on the Synthesis of Flavonoids in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Molecules 2019, 24, 3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, M.; Shi, K.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, R.; Shi, Q. Dynamic Changes in Metabolite Accumulation and the Transcriptome during Leaf Growth and Development in Eucommia ulmoides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; McLean, J.A. Untargeted Metabolomics Strategies-Challenges and Emerging Directions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.D.; Souza, A.L.; Gerszten, R.E.; Clish, C.B. Targeted metabolomics. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Boil. 2012, 98, Unit30.2-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A Novel Integrated Method for Large-Scale Detection, Identification, and Quantification of Widely Targeted Metabolites: Application in the Study of Rice Metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yin, Y. Development and Evaluation of a Parallel Reaction Monitoring Strategy for Large-Scale Targeted Metabolomics Quantification. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4478–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yin, Y. Strategies for large-scale targeted metabolomics quantification by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2016, 141, 6362–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Lian, C.J.; Ma, S.C. Investigation of fingerprint and assay of flavonoid glycosides in Epmedii Folium. Drug Stand. Chin. 2018, 19, 359–375. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Wang, K.P.; Guo, T.W.; Zhang, D.W.; Dong, Q.S.; Zhang, C.W.; Zhang, G.H. Correlation analysis on content of active component in Epimedium brevicornum Maxi and soil nutrients in Gansu province. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2015, 26, 2027–2028. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Guo, B. Effects of Light Intensity on the Growth, Photosynthetic Characteristics, and Flavonoid Content of Epimedium pseudowushanense B.L.Guo. Molecules 2016, 21, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.F.; Liang, W.N. Content determination of icariine in Epimedium pubescens and study on its optimum harvest seasons. China Pharm. 2019, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, J.P.; An, X.H. Content determination of epimedin c and icariin in Epimedium from different harvest seasons by HPLC. China Pharm. 2019, 28, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, W.F.; Huang, M. Research on flavonoids in leave of Epimedium myrianthum and Epimedium acuminatum in Guizhou for different growth phase. Guizhou Sci. 2008, 26, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.F.; Dong, C.M.; Su, X.H.; Du, Z.H. Research on suitable harvest period of Epimedium sagittatum. Mod. Chin. Med. 2018, 20, 999–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.F.; Huang, W.H.; Peng, Y.D.; Guo, B.L. The influence of growth time on flavonoid constituents of Epimedium koreanum Nakai. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 32, 2438–2440. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.G.; Sun, W.J.; Zhou, J.Y.; Zhu, C.D.; Xu, D.B. Determination of 2 flavonoids in Epimedium wushanense in different growing seasons by HPLC. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2006, 17, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Abozeid, A.; Zu, Y.-G.; Zhang, X.-N.; Tang, Z.-H. GC-MS Metabolomic Analysis to Reveal the Metabolites and Biological Pathways Involved in the Developmental Stages and Tissue Response of Panax ginseng. Molecules 2017, 22, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zeng, S.; Xiao, G.; Wei, G.; Liao, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, W.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y. Elucidating the biosynthetic and regulatory mechanisms of flavonoid-derived bioactive components in Epimedium sagittatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y. Functional Characterization of a Novel R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor Modulating the Flavonoid Biosynthetic Pathway from Epimedium sagittatum. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compared Stages | PSS vs. FF | RS vs. FF | HS vs. FF | RS vs. PSS | HS vs. PSS | HS vs. RS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound class | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | Up | Down | |
| Flavonoids (119/138) | 84 | 18 | 88 | 22 | 85 | 22 | 26 | 21 | 30 | 22 | 6 | 2 | |
| Lipids (37/52) | 6 | 15 | 5 | 29 | 5 | 27 | 2 | 20 | 2 | 21 | 0 | 2 | |
| Phenolic acids (37/48) | 16 | 10 | 20 | 12 | 19 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 11 | 8 | 3 | 2 | |
| Amino acids and its derivatives (28/46) | 2 | 14 | 7 | 20 | 5 | 19 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 3 | |
| Nucleotide and its derivatives (23/26) | 3 | 8 | 3 | 12 | 4 | 15 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 2 | |
| Organic acids (10/23) | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | |
| Alkaloids (15/21) | 6 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |
| Tannins (7/7) | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Lignans and coumarins (5/6) | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Quinones (2/2) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Other metabolites (19/34) | 4 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 1 | |
| Significant differentials | 136 | 77 | 154 | 111 | 149 | 113 | 52 | 59 | 62 | 69 | 13 | 14 | |
| All Significant differentials (302) | 213 | 265 | 262 | 111 | 131 | 27 | |||||||
| Analyte | Time (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | DP (v) | CE (v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| epimedin A | 1.26 | 883.4 | 675.3 | −92 | −30 |
| epimedin B | 1.32 | 853.5 | 645.3 | −100 | −27 |
| epimedin C | 1.37 | 867.4 | 659.3 | −110 | −24.9 |
| icariin | 1.57 | 721.4 | 513.3 | −120 | −23 |
| baohuoside I | 4.79 | 513.3 | 366.1 | −120 | −36 |
| baohuoside II | 3.37 | 499.3 | 352.2 | −190 | −37.5 |
| sagittatoside A | 4.01 | 675.4 | 366.2 | −180 | −45 |
| sagittatoside B | 4.26 | 645.3 | 366.2 | −130 | −44 |
| icaritin | 7.45 | 367.3 | 352.2 | −170 | −29.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Z.; Liao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, R.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X. A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules 2020, 25, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010137
Qin Z, Liao D, Chen Y, Zhang C, An R, Zeng Q, Li X. A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules. 2020; 25(1):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010137
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Zhenxian, Dengqun Liao, Yalan Chen, Chenyang Zhang, Ruipeng An, Qing Zeng, and Xian’en Li. 2020. "A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages" Molecules 25, no. 1: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010137
APA StyleQin, Z., Liao, D., Chen, Y., Zhang, C., An, R., Zeng, Q., & Li, X. (2020). A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules, 25(1), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010137






