DNA Binding Characteristics and Protective Effects of Yellow Pigment from Freshly Cut Yam (Dioscorea opposita)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
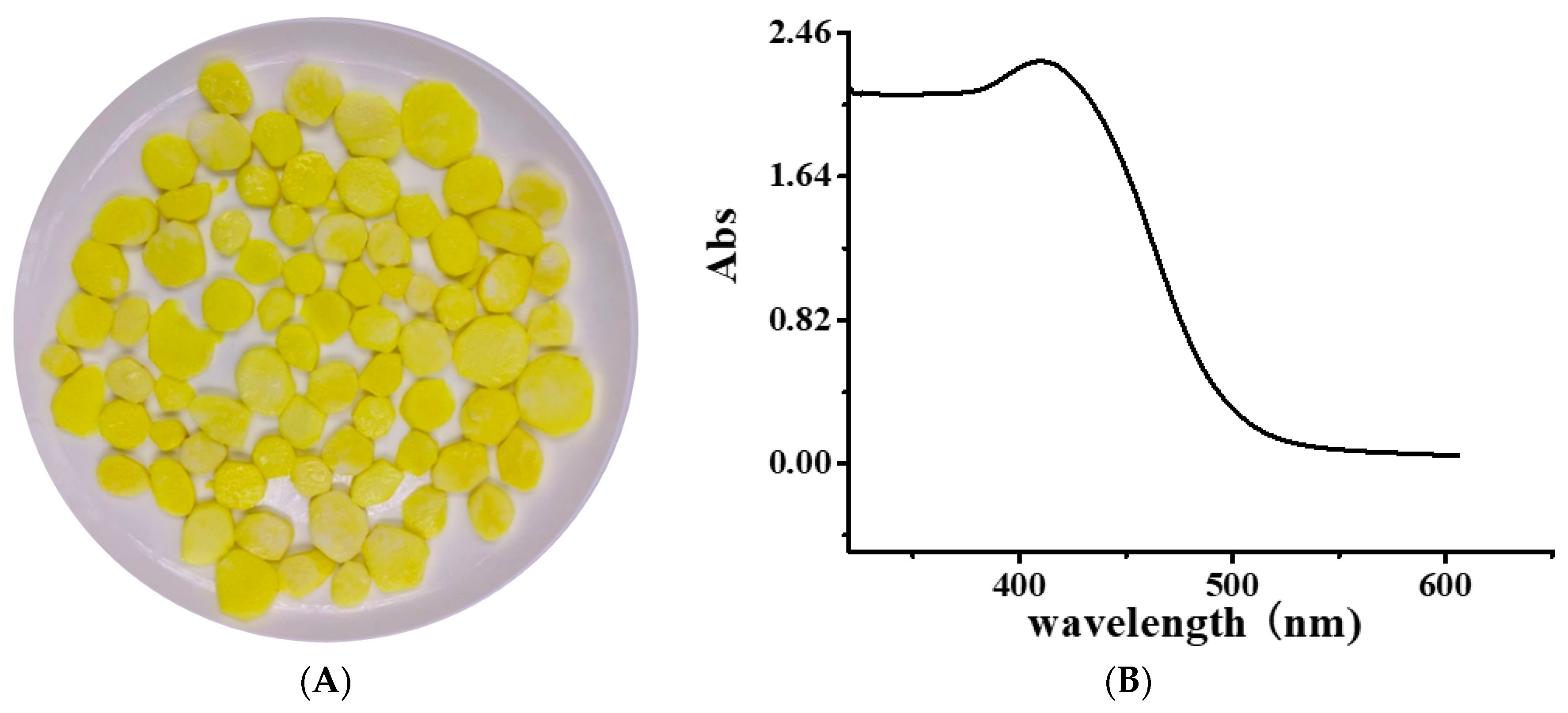
2.1. YP Binding to DNA
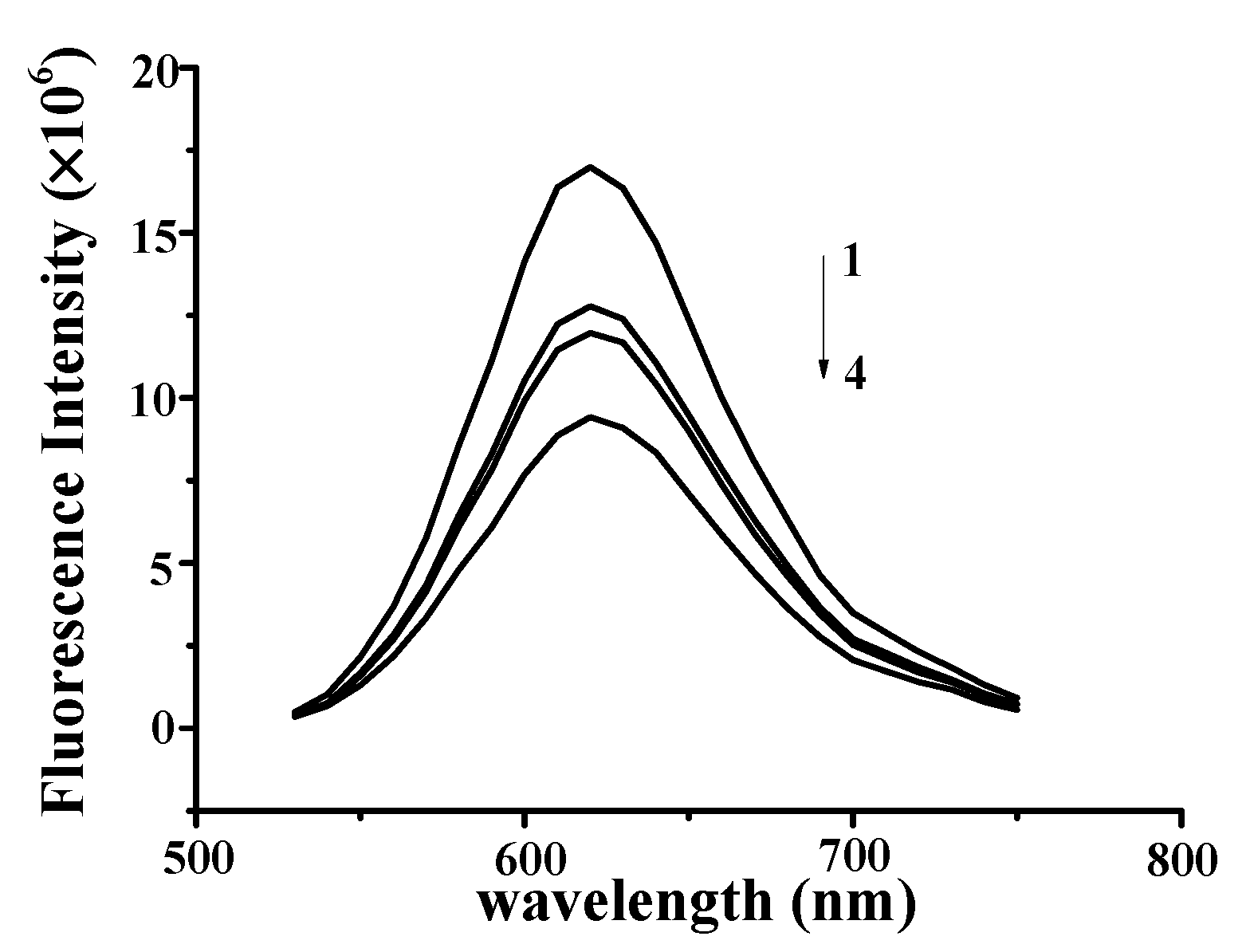
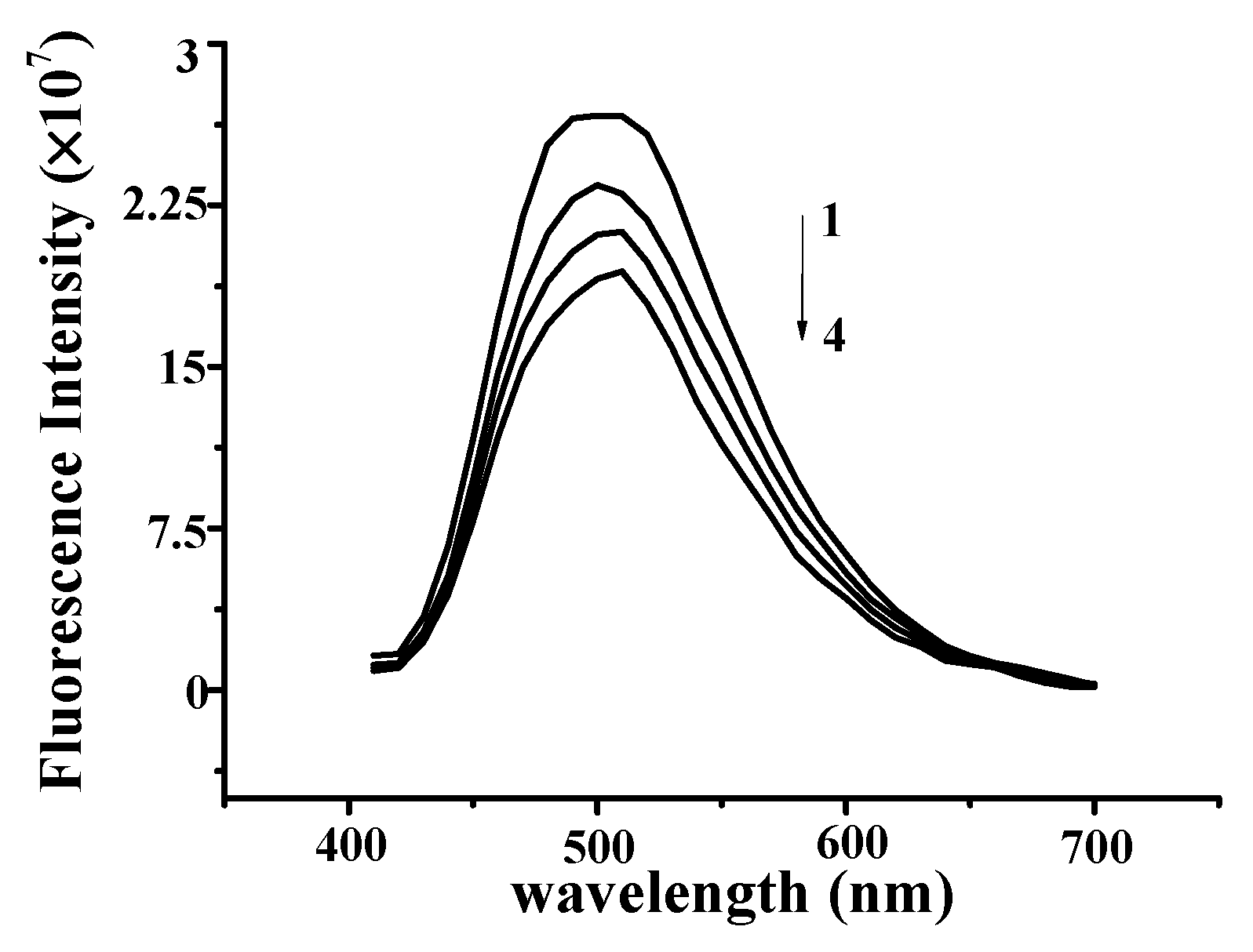
2.2. Binding Mode of DNA–YP
2.3. Binding of YP to DNA in the Presence of Competing Ions
2.4. DNA Viscosity
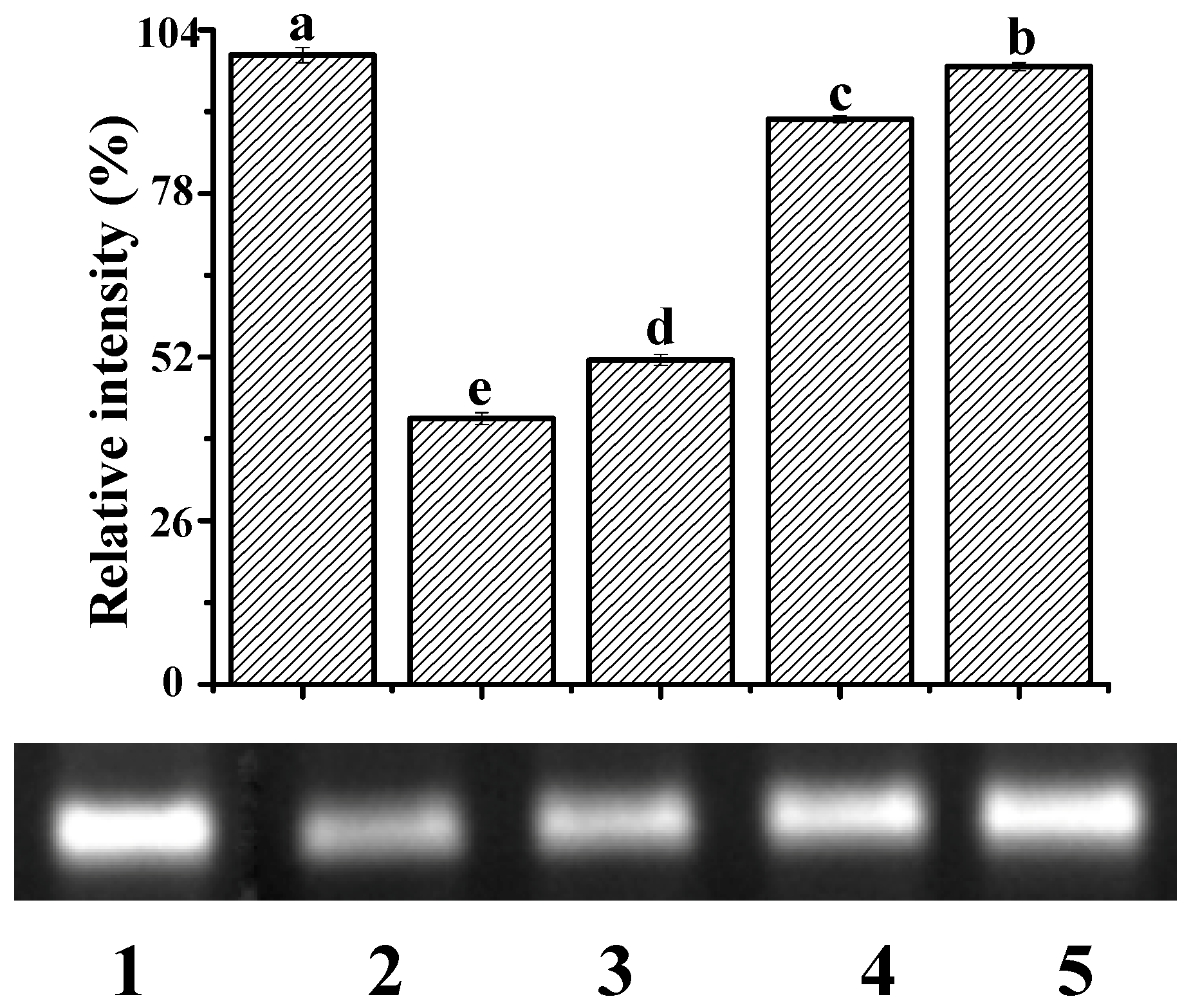
2.5. Protection Against ·OH-Induced DNA Damage
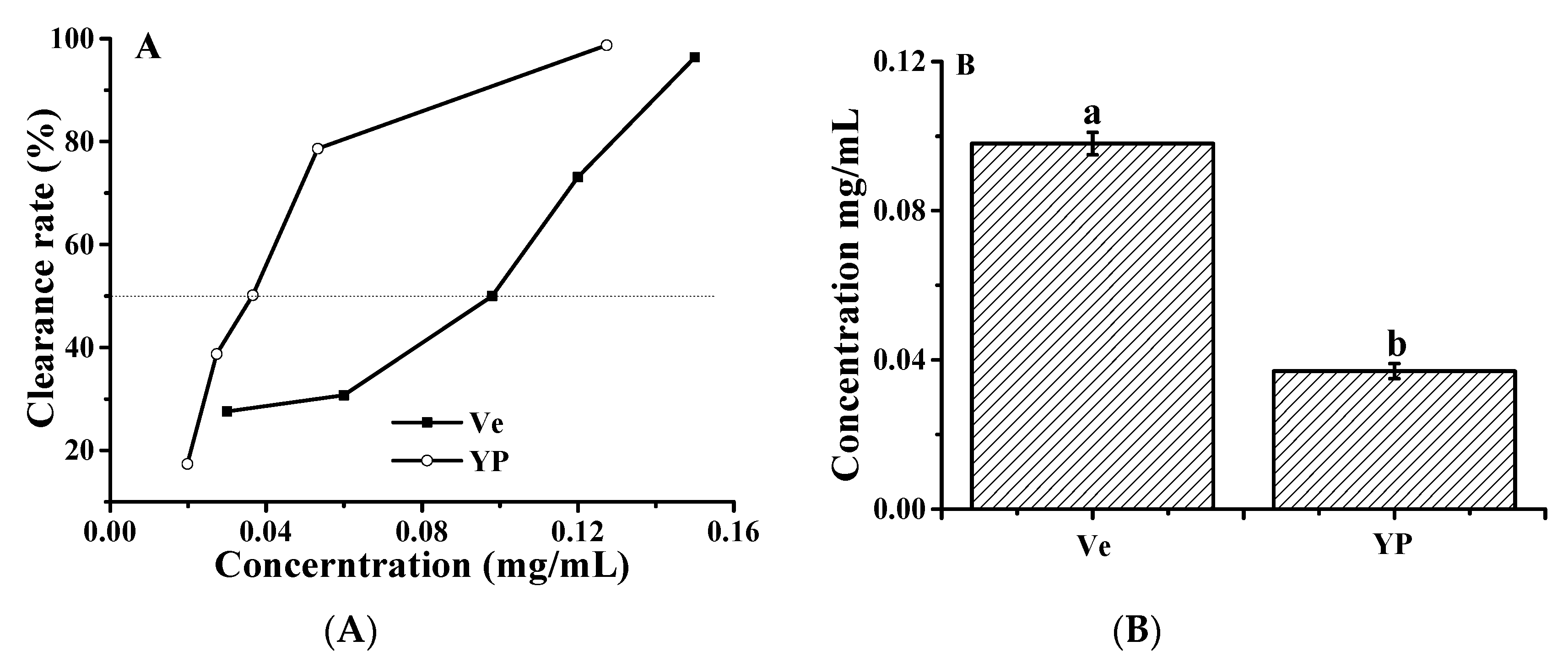
2.6. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Instruments
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation of YP Extract
4.2.2. UV−Vis Spectroscopy
4.2.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
4.2.4. Cationic Quenching by NaCl
4.2.5. Viscosity Measurements
4.2.6. Protective Effect against DNA Damage
4.2.7. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
5. Conclusions
6. Highlight
- —
- The interaction of yam yellow pigment with calf thymus DNA was investigated.
- —
- DNA bound yellow pigment through intercalative binding.
- —
- Yam yellow pigment protected DNA from damage by hydroxyl radicals.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Łodyga-Chruścińska, E.; Kowalska-Baron, A.; Błazińska, P.; Pilo, M.; Zucca, A.; Korolevich, V.M.; Cheshchevik, V.T. Position impact of hydroxy groups on spectral, acid–base profiles and DNA interactions of several monohydroxy flavanones. Molecules 2019, 24, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limmongkon, A.; Pankam, J.; Somboon, T.; Wongshaya, P.; Nopprang, P. Evaluation of the DNA damage protective activity of the germinated peanut (Arachis hypogaea) in relation to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 101, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jin, S.F.; Li, H.-C.; Sun, X.-Y.; Yan, S.-Q.; Deng, S.-J.; Zhao, P. The Bio-safety concerns of three domestic temporary hair dye molecules: Fuchsin Basic, Victoria Blue B and Basic Red 2. Molecules 2019, 24, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bravo-Anaya, L.; Roux, D.; Soltero Martínez, J.; Carvajal Ramos, F.; Pignon, F.; Mannix, O.; Rinaudo, M. Role of electrostatic interactions on supramolecular organization in calf-thymus DNA Solutions under Flow. Polymers 2018, 10, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Righini, S.; Rodriguez, E.J.; Berosich, C.; Grotewold, E.; Casati, P.; Ferreyra, M.L.F. Apigenin produced by maize flavone synthase I and II protects plants against UV-B-induced damage. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, X. A new function of Chinese bayberry extract: Protection against oxidative DNA damage. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybastler, O.; Dawbaa, S.; Demir, C. Investigation of antioxidant ability of grape seeds extract to prevent oxidatively induced DNA damage by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1072, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; La Fauci, L.; Acquaviva, R.; Campisi, A.; Raciti, G.; Scifo, C.; Renis, M.; Galvano, G.; Vanella, A.; Galvano, F. Ochratoxin A-induced DNA damage in human fibroblast: Protective effect of cyanidin 3-O-β-d-glucoside. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Dan, W.; Yue, M.; Yan, Z.; Xiaoyan, Z. Yellow pigment formation, pigment composition, and quality of fresh-cut yam (Dioscorea opposita) slices. RSC Adv. 2019. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Jangir, D.K.; Mehrotra, R. Spectroscopic studies of the effects of anticancer drug mitoxantrone interaction with calf-thymus DNA. J. Food Sci. 2013, 120, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Husain, M.A.; Ishqi, H.M.; Tabish, M. Interaction of coumarin with calf thymus DNA: Deciphering the mode of binding by in vitro studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 73, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirajuddin, M.; Ali, S.; Badshah, A. Drug-DNA interactions and their study by UV-Visible, fluorescence spectroscopies and cyclic voltametry. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2013, 124C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Jaisankar, P.; Suresh Kumar, G. Synthesis of novel 9-O-N-aryl/aryl-alkyl amino carbonyl methyl substituted berberine analogs and evaluation of DNA binding aspects. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012, 20, 2498–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenkuytu, E.; Yıldırım, T.; Ölçer, Z.; Uludağ, Y.; Yenilmez Çiftçi, G. DNA interaction analysis of fluorenylidene double bridged cyclotriphosphazene derivatives. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 477, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Fu, P. Spectroscopic studies on the interaction between carbaryl and calf thymus DNA with the use of ethidium bromide as a fluorescence probe. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2012, 108, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, M.; Markowski, M. Color characteristics of carrots: Effect of drying and rehydration. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotta, E.; Prosposito, P.; Pizzoferrato, R. Positive curvature in Stern-Volmer plot described by a generalized model for static quenching. J. Lumines 2019, 206, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-F.; Zhou, B.; Hou, H.-N.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, G.-Y. Studies on the interaction between Oxaprozin-E and bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 39, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Lu, Z. Membrane disruption and DNA binding of Fusarium graminearum cell induced by C16-Fengycin A produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Food Control. 2019, 102, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Guo, J.; Zhao, N.; Wang, J. Study of interaction between kaempferol–Eu3+ complex and DNA with the use of the Neutral Red dye as a fluorescence probe. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2010, 144, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heli, H.; Bathaie, S.Z.; Mousavi, M. Electrochemical investigation of neutral red binding to DNA at the surface. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongnian, N. Synchronous fluorescence and UV-vis spectrometric study of the competitive interaction of chlorpromazine hydrochloride and Neutral Red with DNA using chemometrics approaches. Talanta 2005, 65, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Beigoli, S.; Saberi, M.R.; Chamani, J. Probing the binding of lomefloxacin to a calf thymus DNA-histone H1 complex by multi-spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Du, S.; Kokot, S. Interaction between quercetin-copper (II) complex and DNA with the use of the Neutral Red dye fluorophor probe. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 584, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Xiong, C.; Gong, D. Intercalation binding of food antioxidant butylated hydroxyanisole to calf thymus DNA. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2014, 141, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, F.; Salehzadeh, S.; Golbedaghi, R.; Hosseinpour Moghadam, N.; Sharifinia, S.; Khazalpour, S.; Baghaeifar, Z. DNA binding and molecular docking studies of a new Cu(II) complex of isoxsuprine drug. Polyhedron 2019, 162, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.Y.; Xiang, Y.L.; Wu, Y.M.; Xie, F.Y. Study of interaction of a fluorescent probe with DNA. J. Lumines 2009, 129, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashanian, S.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N. In vitro studies on calf thymus DNA interaction and 2-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol food additive. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 230, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Probing the binding of insecticide permethrin to calf thymus DNA by spectroscopic techniques merging with chemometrics method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2638–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, V.G.; Nair, B.U. Nucleobase oxidation of DNA by (Terpyridyl)chromium(III) derivatives. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2004, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Pan, J.; Zhang, G.; Gong, D. Interaction of isoeugenol with calf thymus DNA and its protective effect on DNA oxidative damage. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 282, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, L.-H.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, D. Binding Characteristics of Sodium Saccharin with calf thymus DNA in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Mai, W.; Wang, L.; Weijuan, H. A hydroxyl-scavenging assay based on DNA damage in vitro. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 438, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Cai, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X. Binding characteristics and protective capacity of cyanidin-3-glucoside and its aglycon to calf thymus DNA. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, H889–H893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Mir, H.; Kapur, N.; Gales, D.; Carriere, P.P. Quercetin inhibits prostate cancer by attenuating cell survival and inhibiting anti-apoptotic pathways. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 16, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibtissam, T.; Matkarimov, B.; Tchénio, T.; Zharkov, D.; Saparbaev, M. Aberrant base excision repair pathway of oxidatively damaged DNA: Implications for degenerative diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, S.; Bordbar, A.-K.; Tangestaninejad, S.; Yadollahi, B.; Amiri, R.; Zarkesh-Esfahani, S.-H.; Habibi, P. In vitro antitumor activity of free and nano-encapsulated Na5[PMo10V2O40]·nH2O and its binding properties with ctDNA by using combined spectroscopic methods. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 152, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, A.; Pazin, W.; Ito, A.; Kuzmin, V.; Borissevitch, I. Acridine orange interaction with DNA: Effect of ionic strength. Biochim. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J. Groove binding interaction between daphnetin and calf thymus DNA. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, F.; Lin, J.; Han, L.; Hong, Y.; Lu, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, D. Flos chrysanthemi indici protects against hydroxyl-induced damages to DNA and MSCs via antioxidant mechanism. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei-Kalar, Z. In vitro binding interaction of atorvastatin with calf thymus DNA: Multispectroscopic, gel electrophoresis and molecular docking studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018, 161, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Abraham, T.E. Studies on the antioxidant activities of cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) bark extracts, through various in vitro models. Food Chem. 2006, 94, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. DNA Binding Characteristics and Protective Effects of Yellow Pigment from Freshly Cut Yam (Dioscorea opposita). Molecules 2020, 25, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010175
Zhao L, Zhao X, Ma Y, Zhang Y, Wang D. DNA Binding Characteristics and Protective Effects of Yellow Pigment from Freshly Cut Yam (Dioscorea opposita). Molecules. 2020; 25(1):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010175
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Lei, Xiaoyan Zhao, Yue Ma, Yan Zhang, and Dan Wang. 2020. "DNA Binding Characteristics and Protective Effects of Yellow Pigment from Freshly Cut Yam (Dioscorea opposita)" Molecules 25, no. 1: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010175
APA StyleZhao, L., Zhao, X., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wang, D. (2020). DNA Binding Characteristics and Protective Effects of Yellow Pigment from Freshly Cut Yam (Dioscorea opposita). Molecules, 25(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010175